Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Corporate Tax II Outline
Uploaded by
proveitwasmeCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Corporate Tax II Outline
Uploaded by
proveitwasmeCopyright:
Available Formats
Corporate Tax II Weisbach 2009
I.
Taxable Acquisitions
A. Asset Purchases
1.
2 levels of tax asset sale + liquidation
a. Forward Merger T mergers into Acq sub
i. Rev. Ruling 69-6: where Acq sub is formed for purpose of merger & T s/hs get cash, transitory existence of
Acq sub is disregarded and transaction is treated as an asset sale
2.
Intangibles, 197: permits amortization of intangible assets over 15 year period
3.
Purchase Price Allocation, Regs. 1.338-6: (see slide 5)
B. Stock Purchases
1.
1 level of tax, carryover basis
a. Reverse Merger Acq sub mergers into T
2.
Historical Treatment Kimbell-Diamond: step trans makes stock purchase + liquidation = asset purchase; eventually
repealed by statute
3.
Current Treatment of Stock Purchases, 338 if corp makes Qualified Stock Purchase it may elect to qualify for
either asset or stock purchase treatment
a. Qualified Stock Purchase (QSP), Requirements and Consequences
i. P must make taxable purchase of 80% of value and vote of T w/in 12 month period
ii. Election must be made no later than 9.5 months from QSP
iii. In QSP, Old T treated as selling assets to New T and liquidating into P one day after stock purchase and
outside of any consolidated returns
b. 338(h)(10): If S & T eligible to file consolidated return, then P & S may make joint election to treat stock
purchase as an asset sale
c. 336(e): if corp owns 80% of vote/value of sub & owner sells, exchanges or distributes stock (Qualified Stock
Disposition, QSD), election may be made to treat the disposition as a disposition of assets w/ no gain/loss
recognized with respect to stock
d. Rev Ruling 90-95: where P created transitory acquisition sub to acquire T in reverse subsidiary cash merger;
i. Situation 1: creation of acquisition sub is disregarded, and merger is treated as QSP
ii. Situation 2: subsequent liquidation of T is given independent significance and does not result in QSP being
recast as asset purchase; step trans turned off and trans treated as stock purchase + liquidation
a.
Rationale: Congress intended to completely repeal Kimbell-Diamond by enacting 338, thus 338
election principles control
4.
Sale/Redemption: where subsidiary borrows and distributes cash to s/h after a merger, distribution is treated as a
redemption to be analyzed under 302
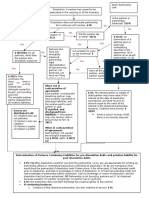
II. Corporate Reorganizations
A. Reorganization Checklist
1.
Determine the type of reorg and check requirements
2.
If stock/assets has been transferred check -2(k)
3.
Make sure entities involved are parties to the reorganization under -2(f)
B. Statutory Forms
1.
A Reorganizations, 368(a)(1)(A)
a. Requirements
i. Merger or consolidation
a.
Rev. Rul 2000-5: where T transfers only half of assets to P and continues to exist, or where T transfers
half of assets to each of two purchasers, such transfers are not mergers b/c merger contemplates T
ceasing to exist and divisive mergers only dealt with in 355
ii. Continuity of interest (COI)
iii. Continuity of business Enterprise (COBE)
b. (a)(2)(C) may make one drop to a subsidiary
c. Disregarded Entities
i. Regs. 1.368-2(b)(1)(ii): assets/liabilities of transferors combining unit become assets/liabilities of transferee
combined unit and transferor combining unit ceases to exist
2.
B Reorganizations, 368(a)(1)(B)
a. Requirements
i. Exchange of T stock solely for voting stock of acquiring (no boot allowed)
a.
Creeping B: may consummate creeping B so long as exchanges are solely for stock; possibly up to 16
years required to make cash purchases old and cold
b.
Contingent Consideration: P may agree to issue future stock under certain circumstances; contingent
consideration/poison pill does not qualify as boot
c.
Rev. Ruling 98-10: B reorg + debenture exchange does not violate B reorg rules if substantially all
holders of debentures are non-stockholders and principal of new debentures is same as old debentures
ii. Immediately after acquisition acquiring has control of target (no need to transfer control)
a.
Rev. Ruling 67-274: B reorg + liquidation of T or acq is a C reorg b/c no control immediately after is
liquidation; no QSP b/c it is a stock for stock exchange, thus step trans applies
b.
Rev. Ruling 55-440: preferred stock called but not presented by exchange date is disregarded for
purposes of control under 368(c)
b. (a)(2)(C) may make one drop to a subsidiary
3.
C Reorganizations, 368(a)(1)(C)
a. Requirements
i. Exchange sub all T assets/liabilities solely for voting stock of acquiring, may include unlimited assumption
of liabilities
a.
Rev. Ruling 57-518: substantially all assets is 90% gross, 70% net
b.
Rev. Ruling 88-48: where T has two lines of business, sells one line of business to unrelated parties,
then transfers proceeds + other lines of business to P in exchange for P stock, sub all requirement is
met
c.
Creeping C: preexisting stock of T owned by P does not count as boot in a C reorg (must be old and
cold)
ii. Boot relaxation: 20% boot allowed, but if boot used must count liabilities towards boot
iii. Target liquidates
b. (a)(2)(C) may make one drop to a subsidiary
4.
Triangular Reorganizations
a. Triangular A by (a)(2)(D) forward triangular merger
i. Requirements
a.
All regular A requirements met (merger, COI, COBE)
b.
Exchange must be completely in parent stock (no S stock used in trans)
c.
Acquire sub all target assets
ii. Drop to subsidiary via (a)(2)(C)
a.
Rev. Ruling 2001-24: forward triangular merger w/ subsequent drop of acquiring into another wholly
owned subsidiary of P qualifies as a valid reorg via (a)(2)(C) & -2(k)/-2(f)
b. Triangular A by (a)(2)(E) reverse triangular merger
i. Requirements
a.
All regular A requirements met (merger, COI, COBE)
b.
Exchange must be completely in parent stock (no S stock used in trans)
c.
T must hold sub all assets
i. Rev. Ruling 2001-25: sale of 50% of assets to unrelated party after reorg is valid if P holds
proceeds
d.
T s/hs must surrender control in exchange (no creeping (a)(2)(E)s)
ii. Drop to subsidiary via (a)(2)(C)
c. Triangular C w/ solely parent stock
d. Triangular B w/ solely parent stock
C. Continuity of Interest,
1.
Generally, Regs. 1.368-1(e): proprietary interest in T must be preserved to get COI in a reorg
a. Proprietary interest is preserved if
i. It is exchanged for proprietary interest in P
ii. It is exchanged by acquirer for direct interest in T
iii. It otherwise continues as proprietary interest in T
b. Measured by consideration received in merger, not stake in new company
c. Amount
i. 50% or greater is always granted
ii. Regs allow as low as 40%
iii. Southwest Natural Gas: statutory merger w/ 16% stock consideration does not qualify as tax free reorg b/c
not sufficient COI
d. Dispositions of stock to unrelated parties b/f or after the reorg to persons unrelated to P or T are disregarded for
COI purposes
i. Related party: 50% or greater ownership
ii. Redemptions by P pursuant to plan of reorg count as cash/property consideration
a.
Rev. Ruling 99-58: regular stock repurchase plan which causes P to buy back T stock on the open
market after reorg will not affect COI if not purposefully directed at T s/hs
2.
Rev. Ruling 66-224: COI not measured w/ respect to individual s/h, instead look to s/h as a group (i.e., 50% stock to
half of s/h and 50% cash to other half is identical to each s/h receiving 50% stock and 50% cash for COI purposes)
3.
Kass: where P purchased 80% of T stock, then T merged into P w/ P exchanging minority s/h T stock for P stock,
COI for minority s/h measured from point b/f the initial purchase, and thus 20% s/hs did not qualify for A reorg
treatment b/c they failed COI
4.
Seagrams: where P purchases stock from old s/h, P steps into shoes of old s/h for purposes of COI
5.
Regs 1.338-3(d): stock purchased in QSP immediately becomes old and cold
D. Continuity of Business Enterprise
1.
Generally, Regs 1.368-1(d): P must either
a. Continue significant line of Ts historic business, or
b. Use a significant portion of Ts historic business assets in a business
i. Significant is at least 1/3 of business/assets
ii. Historic must at least be longer than 2 years
2.
Bentsen: no need to carry on identical business of T to qualify for CBOE
3.
Rev. Ruling 81-25: CBOE does not require the acq corp to maintain its own line of business or assets during the
reorg
4.
Qualified Group, Regs. 1.368-1(d)(4)(i), (ii): P treated as holding all businesses and assets of al the members of the
qualified group
a. Qualified Group: P owns directly stock meeting reqs of 368(c) in at least one corp, and stock meeting the reqs
of 368(c) in each of the corps is owned by one or more of the other corps
i. Direct subsidiary
ii. Subsidiary of a subsidiary
iii. Diamond pattern
iv. Partnership if P owns of significant interest or P has active and substantial management role
v. NOT parent
vi. NOT sister corp
E. Regulatory Modifications to Reorganization Requirements
1.
Grohman & Bashford Doctrine: dropping assets into subsidiary or using parent stock to acquire T violate reorg
requirements (has since been mitigated by regs, but still good law)
2.
Asset/Stock Transfers, Regs. 1.368-2(k): transfer of assets/stock after a reorg in accordance w/ this rule will not
blow up an otherwise good reorg
Assets of acquired, acquiring + no liquidation
Distributions
Stock w/in qualified group + not all of acquired
Assets of acquired, acquiring
Other Transfers
No Termination
Stock of acquired, acquiring w/in qualified group
3.
Party to the Reorganization, Regs. 1.368-2(f)
Acquired w/in -2(k)
Stock or assets
PRS w/in COBE
Stock of acquiring w/in -2(k)
F.
Step Transaction Doctrine in Reorganizations
King Enterprises: where P exchanged 51% P stock and 49% cash/notes for T, then pursuant to a plan T merged into
P in an upstream merger, the step trans doctrine operates to qualify the entire transaction as a valid A reorg
2.
Rev. Ruling 2001-26: where P exchanges P voting stock for 51% of T stock, then S merges into T w/ T surviving and
T s/hs getting P stock + cash, such a transaction is a valid (a)(2)(E) reorg b/c step trans makes it so that 100% control
is transferred from T s/hs to P in the plan of reorganization
3.
Rev. Ruling 2001-46: where P transfers 70% stock and 30% cash to T s/hs so as to qualify independently as a QSP
with S merging into T and T surviving, and the transaction is followed by a merger of T into P, the transaction will
be treated as a single merger by T into P qualifying as an A reorg QSP will be disregarded
4.
Rev. Ruling 2008-25: where T is leveraged, and P transfers 90% stock and 10% cash to T s/h and S merges into T w/
T surviving, followed by a liquidation of Ts assets into P, transaction is a fully taxable QSP (which turns off step
trans) followed by an A reorg
G. Consequences to a Reorganization
1.
1.
2.
3.
4.
To Target Shareholders
a. Recognition of Gain/Loss
i. 354(a)(1): no gain/loss if stock/securities exchanged solely for stock/securities of a party to the reorg
ii. 354(a)(2): principal amount of securities received cannot exceed principal amount of securities
surrendered (see 356(d))
iii. 356(a)(1): gain recognized to the extent of boot
iv. 356(a)(2): if gain recognized, it is considered dividend if it has the effect of dividend
a.
Clark: where sole s/h of T receives stock + boot in connection w/ merger, exchange must be analyzed
under 302 to determine whether it qualifies for dividend treatment
v. 356(c): no loss recognized in a reorg
vi. 356(d): if principal amount of securities increased, the FMV of increase is taxed as boot
b. Basis
i. 358: basis is carryover increased by gain, decreased by boot
To Target
a. On Exchange
i. 361(a): no gain/loss recognized if T exchanges property solely for P stock/securities
ii. If boot, then no gain/loss recognized on exchange if boot is distributed
b. On Distribution
i. No gain/loss recognized on distribution of qualified property (refers to stock, securities, etc) to
creditors/shareholders
ii. Gain recognized on any property distributed that is not qualified property
c. Basis
i. 358: P stock gets carryover basis + gain - boot
ii. 358(f): boot given FMV basis on exchange
To Acquiring
a. Recognition of Gain
i. 1032: no gain/loss recognized on receipt of money/property in exchange for stock
b. Basis
i. 362(b): basis is carryover increased by gain, decreased by boot
a.
P recognizes gain/loss on all transfers of boot
Triangular Reorganizations
a. Triangular C and (a)(2)(D) Forward Triangular Merger
i. Regs. 1.358-6(c)(1)(i): Ps basis in stock adjusted as if P acquired the T assets in the reorg and dropped
them into S as a 351
b. Reverse Triangular
i. Regs. 1.358-6(c)(2)(i): Ps basis determined as if transaction were a forward triangular merger
c. Triangular B
i. Regs. 1.358-6(c)(3):
d. Consequences to S
i. Regs. 1.1032-2(b): S does not recognize gain where P stock issued to S in a triangular reorg pursuant to
plan of reorg
You might also like
- Corp Tax I OutlineDocument6 pagesCorp Tax I OutlineproveitwasmeNo ratings yet
- Estate and Gift Tax OutlineDocument24 pagesEstate and Gift Tax Outlineastepps1No ratings yet
- Final Exam Outline Full Ver1263165054Document22 pagesFinal Exam Outline Full Ver1263165054LawNerdNYCNo ratings yet
- Advanced Corporate Tax OutlineDocument15 pagesAdvanced Corporate Tax OutlineCfurlan02100% (1)
- Federal Income Tax Computation and DefinitionsDocument42 pagesFederal Income Tax Computation and Definitionsabmo33No ratings yet
- Closely Held Business Org and Agency DutiesDocument85 pagesClosely Held Business Org and Agency DutiesnabarrowNo ratings yet
- US Taxation - Outline: I. Types of Tax Rate StructuresDocument12 pagesUS Taxation - Outline: I. Types of Tax Rate Structuresvarghese2007No ratings yet
- Spring 2012 EGT OutlineDocument63 pagesSpring 2012 EGT OutlineJessica Rae FarrisNo ratings yet
- Corporations Outline Partnoy PalmiterDocument20 pagesCorporations Outline Partnoy PalmiterMatt ToothacreNo ratings yet
- Agency and Partnership GuideDocument3 pagesAgency and Partnership GuidetoddmbakerNo ratings yet
- Outline Taxation of PartnershipsDocument22 pagesOutline Taxation of PartnershipsHardeep ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Attack Short SheetDocument18 pagesAttack Short SheetjesNo ratings yet
- Dividing Partnership Income and Formation OperationsDocument74 pagesDividing Partnership Income and Formation Operationssunildmirchandani100% (1)
- CORPORATIONS AND AGENCY RELATIONSHIPSDocument131 pagesCORPORATIONS AND AGENCY RELATIONSHIPSIvy Ziedrich100% (1)
- Taxation of Business Entities Spring 2020 OutlineDocument26 pagesTaxation of Business Entities Spring 2020 OutlineMichael Langer100% (1)
- Wills and Estates Cheat Sheet: by ViaDocument4 pagesWills and Estates Cheat Sheet: by ViaMartin LaiNo ratings yet
- Partnership & LLP Davidian TaxDocument47 pagesPartnership & LLP Davidian TaxbornkellerNo ratings yet
- Federal Income Tax (Wells)Document30 pagesFederal Income Tax (Wells)Bear100% (2)
- Federal Income Tax Section 1(c) and Gross Income ExplainedDocument7 pagesFederal Income Tax Section 1(c) and Gross Income ExplainedVanessa Joyce MongeNo ratings yet
- Income Tax OutlineDocument52 pagesIncome Tax OutlineAina Niaz100% (1)
- Corporations OutlineDocument4 pagesCorporations OutlineKeith DyerNo ratings yet
- UPA DissolutionDocument1 pageUPA DissolutionNiraj ThakkerNo ratings yet
- HW Questions Income TaxDocument34 pagesHW Questions Income TaxAina Niaz100% (1)
- Professor Jose Gabilondo Federal Income Tax Florida International University College of LawDocument89 pagesProfessor Jose Gabilondo Federal Income Tax Florida International University College of Lawjfeyg100% (1)
- Fedincometaxoutline 19Document17 pagesFedincometaxoutline 19ashajimerNo ratings yet
- Federal Taxation of Gross Income and DeductionsDocument28 pagesFederal Taxation of Gross Income and DeductionsAstha AdhikaryNo ratings yet
- Corporations Bar OutlineDocument4 pagesCorporations Bar OutlineJohn RisvoldNo ratings yet
- BusOrgTemplates 1 2Document48 pagesBusOrgTemplates 1 2Sam Hughes100% (1)
- Int TaxDocument24 pagesInt TaxDane4545No ratings yet
- Harvard Law Agency Course Over CorporationsDocument61 pagesHarvard Law Agency Course Over CorporationsChaim SchwarzNo ratings yet
- Business OrganizationsDocument71 pagesBusiness Organizationsjdadas100% (2)
- Determining Formation of Partnership: or Agree To Form A PartnershipDocument74 pagesDetermining Formation of Partnership: or Agree To Form A PartnershipAlana Hans-CohenNo ratings yet
- Business Organizations OutlineDocument71 pagesBusiness Organizations Outlineesquire2014fl100% (3)
- Business Associations Outline - Klein, 3rd EdDocument75 pagesBusiness Associations Outline - Klein, 3rd Edjanklewich100% (2)
- Federal Income Taxation OutlineDocument87 pagesFederal Income Taxation OutlineSaul100% (1)
- Sec Reg Attack 2021 - NEWDocument28 pagesSec Reg Attack 2021 - NEWmattytangNo ratings yet
- Business Associations OutlineDocument30 pagesBusiness Associations OutlineClaudia GalanNo ratings yet
- Community Property Final Outline - ADDocument62 pagesCommunity Property Final Outline - ADAlexandra DelatorreNo ratings yet
- I. Who Is An Agent?: Gorton v. Doty (1937)Document109 pagesI. Who Is An Agent?: Gorton v. Doty (1937)Erick VelizNo ratings yet
- Community Property OutlineDocument27 pagesCommunity Property OutlineDevon Pollard100% (2)
- International Tax Residency RulesDocument58 pagesInternational Tax Residency RulesMa FajardoNo ratings yet
- Corporations - Loewenstein - Spring 2007 - Alexande - Grade 97Document45 pagesCorporations - Loewenstein - Spring 2007 - Alexande - Grade 97a thaynNo ratings yet
- Corporations OutlineDocument35 pagesCorporations OutlineSteve AdamsonNo ratings yet
- Tax Answers - Chapter 3Document4 pagesTax Answers - Chapter 3Jonathan VelaNo ratings yet
- Checklist PRDocument8 pagesChecklist PRDouglas GromackNo ratings yet
- Income Tax OutlineDocument44 pagesIncome Tax OutlineMatt PriceNo ratings yet
- Tax 08 Gina OutlineDocument159 pagesTax 08 Gina OutlineCameron SnowdenNo ratings yet
- Tax Answers - Chapter 2Document5 pagesTax Answers - Chapter 2Jonathan Vela0% (1)
- MBCADocument172 pagesMBCAlissettm08No ratings yet
- Agency and Partnership BasicsDocument27 pagesAgency and Partnership BasicsRory FarrellNo ratings yet
- 2016 Secured Transactions Outline 2Document17 pages2016 Secured Transactions Outline 2jackojidemasiadoNo ratings yet
- Agency and Partnerships Condensed OutlineDocument4 pagesAgency and Partnerships Condensed OutlineJerome MaNo ratings yet
- 15 Tax On S CorpDocument90 pages15 Tax On S CorpWahyudiNo ratings yet
- Corporate Tax Outline OverviewDocument44 pagesCorporate Tax Outline Overviewproveitwasme75% (4)
- Chart of Entity ComparisonDocument4 pagesChart of Entity ComparisonDee BeldNo ratings yet
- Agency Relationships & LiabilityDocument75 pagesAgency Relationships & LiabilityjryanandersonNo ratings yet
- Attack Corp OutlineDocument81 pagesAttack Corp OutlineJennesa WilsonNo ratings yet
- Mini OutlineDocument10 pagesMini OutlineadamNo ratings yet
- Ebook Corporate Partnership Estate and Gift Taxation 6Th Edition Pratt Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument29 pagesEbook Corporate Partnership Estate and Gift Taxation 6Th Edition Pratt Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFselenatanloj0xa100% (10)
- Corporate Partnership Estate and Gift Taxation 6th Edition Pratt Solutions ManualDocument21 pagesCorporate Partnership Estate and Gift Taxation 6th Edition Pratt Solutions Manualtaylorhughesrfnaebgxyk100% (21)
- Employment Law Outline Explains Key ConceptsDocument112 pagesEmployment Law Outline Explains Key ConceptsproveitwasmeNo ratings yet
- Employment Law Outline TitleDocument42 pagesEmployment Law Outline TitleproveitwasmeNo ratings yet
- Employment Law I DrummondsdocDocument38 pagesEmployment Law I DrummondsdocproveitwasmeNo ratings yet
- Estate Tax - Love - Spring 2005Document28 pagesEstate Tax - Love - Spring 2005proveitwasmeNo ratings yet
- CPI 2016 corruption levels by countryDocument1 pageCPI 2016 corruption levels by countryproveitwasmeNo ratings yet
- Chevigny f94Document30 pagesChevigny f94proveitwasmeNo ratings yet
- Environmental Law (Attack Outline) Revesz Fall 20093Document15 pagesEnvironmental Law (Attack Outline) Revesz Fall 20093proveitwasme100% (1)
- Corporate Tax - Brennan - Spring 2007Document35 pagesCorporate Tax - Brennan - Spring 2007proveitwasmeNo ratings yet
- Moore - Trusts and Estates - Fall 07Document39 pagesMoore - Trusts and Estates - Fall 07proveitwasmeNo ratings yet
- Tax Outline Comparing Mike Lee's ApproachDocument60 pagesTax Outline Comparing Mike Lee's ApproachproveitwasmeNo ratings yet
- Case's Estate Tax OutlineDocument51 pagesCase's Estate Tax OutlineproveitwasmeNo ratings yet
- Trusts and Estates OutlineDocument45 pagesTrusts and Estates OutlineproveitwasmeNo ratings yet
- 15gift and Estate Tax - Katzenstein - Fall 2002Document95 pages15gift and Estate Tax - Katzenstein - Fall 2002proveitwasmeNo ratings yet
- Federal Income Tax Yale Zolt Fall2005Document43 pagesFederal Income Tax Yale Zolt Fall2005proveitwasmeNo ratings yet
- Taxation of Business Conduits Taylor Fall2008 1Document105 pagesTaxation of Business Conduits Taylor Fall2008 1proveitwasmeNo ratings yet
- Wills & Trusts GuideDocument67 pagesWills & Trusts Guideproveitwasme100% (1)
- Spring 2015 Robinson Fed in Come TaxDocument40 pagesSpring 2015 Robinson Fed in Come TaxproveitwasmeNo ratings yet
- TrustsEstates Foster Fall07Document50 pagesTrustsEstates Foster Fall07Pakimunda09100% (1)
- TrustsEstates Foster Fall07Document50 pagesTrustsEstates Foster Fall07Pakimunda09100% (1)
- Trusts and Estates - Edmisten - Summer 2003-2-3Document18 pagesTrusts and Estates - Edmisten - Summer 2003-2-3champion_egy325No ratings yet
- Fall 2012 Morley T&EDocument75 pagesFall 2012 Morley T&EproveitwasmeNo ratings yet
- On Line OutlineDocument93 pagesOn Line Outlineheffer07No ratings yet
- Venable s94Document46 pagesVenable s94proveitwasmeNo ratings yet
- Estate Tax - Love - Spring 2005Document28 pagesEstate Tax - Love - Spring 2005proveitwasmeNo ratings yet
- Maxfield f04Document63 pagesMaxfield f04proveitwasmeNo ratings yet
- Taxation of Business Conduits Taylor Fall2008 1Document105 pagesTaxation of Business Conduits Taylor Fall2008 1proveitwasmeNo ratings yet
- Corporate Tax Outline OverviewDocument44 pagesCorporate Tax Outline Overviewproveitwasme75% (4)
- Income Tax I BrowndocDocument9 pagesIncome Tax I BrowndocproveitwasmeNo ratings yet
- Indiareit Domestic Fund IV PresentationDocument28 pagesIndiareit Domestic Fund IV PresentationChetan Mukhija100% (1)
- CA Final SFM Compiler Ver 6.0Document452 pagesCA Final SFM Compiler Ver 6.0Accounts Primesoft100% (1)
- CFO Tax Partner CPA in Houston TX Resume Darryl SiefkasDocument3 pagesCFO Tax Partner CPA in Houston TX Resume Darryl SiefkasDarrylSiefkasNo ratings yet
- Bisiness Plan For Porrige Flour-Dago Network Youth GroupDocument21 pagesBisiness Plan For Porrige Flour-Dago Network Youth GroupUmair BaigNo ratings yet
- Research Report Dabur India LTDDocument10 pagesResearch Report Dabur India LTDDheerajNo ratings yet
- Cw2-Individual-Amended VersionDocument5 pagesCw2-Individual-Amended VersiontswNo ratings yet
- C C 2021 Cfa® E: Ritical Oncepts For The XamDocument6 pagesC C 2021 Cfa® E: Ritical Oncepts For The XamGonzaloNo ratings yet
- Finance Project Mahindra and MahindraDocument34 pagesFinance Project Mahindra and Mahindrarohitraj.iitm3326100% (3)
- Output No. 2 - PAS 1 Instruction: Write Your Answers On Long Bond PapersDocument2 pagesOutput No. 2 - PAS 1 Instruction: Write Your Answers On Long Bond Papersnmdl123No ratings yet
- Thomson Reuters Eikon BrochureDocument5 pagesThomson Reuters Eikon BrochureIvon BacaicoaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 - Efficient Markets and Behavioral Finance MCQsDocument35 pagesChapter 13 - Efficient Markets and Behavioral Finance MCQsym5c2324No ratings yet
- Corporate Finance Comprehensive ExamFINALFEB2021Document4 pagesCorporate Finance Comprehensive ExamFINALFEB2021Sam CleonNo ratings yet
- Jul 2022 Performance ReportDocument3 pagesJul 2022 Performance ReportMyles PiniliNo ratings yet
- Module Week 6 EntrepDocument6 pagesModule Week 6 Entrepゔ違でStrawberry milkNo ratings yet
- Modern Trader January 2018Document86 pagesModern Trader January 2018chocobrownie0% (2)
- Preparing Financial StatementsDocument15 pagesPreparing Financial StatementsAUDITOR97No ratings yet
- BBVA OpenMind Libro El Proximo Paso Vida Exponencial2Document59 pagesBBVA OpenMind Libro El Proximo Paso Vida Exponencial2giovanniNo ratings yet
- The Impact of COVID-19 on Banking Sector PerformanceDocument80 pagesThe Impact of COVID-19 on Banking Sector Performancesanjay carNo ratings yet
- Financial Ratio AnalysisDocument15 pagesFinancial Ratio Analysissnigdha songa100% (1)
- Associate Director-General Invest Hong Kong Jrutherford@investhk - Gov.hkDocument18 pagesAssociate Director-General Invest Hong Kong Jrutherford@investhk - Gov.hkS1626No ratings yet
- 96 Pkli AdDocument1 page96 Pkli AdObaidUrRehmanNo ratings yet
- Macroeconomics GDP ExercisesDocument2 pagesMacroeconomics GDP ExercisesAl Marvin SantosNo ratings yet
- Technology Transfer in IndiaDocument9 pagesTechnology Transfer in IndiaMehak Bhargava100% (1)
- Ch01 11HullFundamentals6thEdDocument233 pagesCh01 11HullFundamentals6thEdKaralyos-Szénási PéterNo ratings yet
- BRICS Business Session ProgrammeDocument15 pagesBRICS Business Session ProgrammeJosé EstevesNo ratings yet
- Problem 1: Take Home Quiz Mid Term Advanced Accounting 2Document3 pagesProblem 1: Take Home Quiz Mid Term Advanced Accounting 2Mohamad Nurreza RachmanNo ratings yet
- Model Question Papers: Class 11Document52 pagesModel Question Papers: Class 11Ronak SudhirNo ratings yet
- Side A - The 1st CraftingCases CasebookDocument37 pagesSide A - The 1st CraftingCases CasebookUy KravNo ratings yet
- Due Diligence Closing ChecklistDocument6 pagesDue Diligence Closing Checklistklg.consultant2366No ratings yet
- The McGraw-Hill 36-Hour Course: Finance for Non-Financial Managers 3/EFrom EverandThe McGraw-Hill 36-Hour Course: Finance for Non-Financial Managers 3/ERating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (6)
- These are the Plunderers: How Private Equity Runs—and Wrecks—AmericaFrom EverandThese are the Plunderers: How Private Equity Runs—and Wrecks—AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (14)
- These Are the Plunderers: How Private Equity Runs—and Wrecks—AmericaFrom EverandThese Are the Plunderers: How Private Equity Runs—and Wrecks—AmericaRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- Angel: How to Invest in Technology Startups-Timeless Advice from an Angel Investor Who Turned $100,000 into $100,000,000From EverandAngel: How to Invest in Technology Startups-Timeless Advice from an Angel Investor Who Turned $100,000 into $100,000,000Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (86)
- Add Then Multiply: How small businesses can think like big businesses and achieve exponential growthFrom EverandAdd Then Multiply: How small businesses can think like big businesses and achieve exponential growthNo ratings yet
- Financial Intelligence: A Manager's Guide to Knowing What the Numbers Really MeanFrom EverandFinancial Intelligence: A Manager's Guide to Knowing What the Numbers Really MeanRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (79)
- Venture Deals, 4th Edition: Be Smarter than Your Lawyer and Venture CapitalistFrom EverandVenture Deals, 4th Edition: Be Smarter than Your Lawyer and Venture CapitalistRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (73)
- Summary of The Black Swan: by Nassim Nicholas Taleb | Includes AnalysisFrom EverandSummary of The Black Swan: by Nassim Nicholas Taleb | Includes AnalysisRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (6)
- Mastering Private Equity: Transformation via Venture Capital, Minority Investments and BuyoutsFrom EverandMastering Private Equity: Transformation via Venture Capital, Minority Investments and BuyoutsNo ratings yet
- Financial Risk Management: A Simple IntroductionFrom EverandFinancial Risk Management: A Simple IntroductionRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (7)
- Value: The Four Cornerstones of Corporate FinanceFrom EverandValue: The Four Cornerstones of Corporate FinanceRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (18)
- Financial Modeling and Valuation: A Practical Guide to Investment Banking and Private EquityFrom EverandFinancial Modeling and Valuation: A Practical Guide to Investment Banking and Private EquityRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- Startup CEO: A Field Guide to Scaling Up Your Business (Techstars)From EverandStartup CEO: A Field Guide to Scaling Up Your Business (Techstars)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- The Masters of Private Equity and Venture Capital: Management Lessons from the Pioneers of Private InvestingFrom EverandThe Masters of Private Equity and Venture Capital: Management Lessons from the Pioneers of Private InvestingRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (17)
- Finance Basics (HBR 20-Minute Manager Series)From EverandFinance Basics (HBR 20-Minute Manager Series)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (32)
- Product-Led Growth: How to Build a Product That Sells ItselfFrom EverandProduct-Led Growth: How to Build a Product That Sells ItselfRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Warren Buffett Book of Investing Wisdom: 350 Quotes from the World's Most Successful InvestorFrom EverandWarren Buffett Book of Investing Wisdom: 350 Quotes from the World's Most Successful InvestorNo ratings yet
- Burn the Boats: Toss Plan B Overboard and Unleash Your Full PotentialFrom EverandBurn the Boats: Toss Plan B Overboard and Unleash Your Full PotentialRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (32)
- Key Performance Indicators: Developing, Implementing, and Using Winning KPIsFrom EverandKey Performance Indicators: Developing, Implementing, and Using Winning KPIsNo ratings yet
- Corporate Strategy: A Handbook for EntrepreneursFrom EverandCorporate Strategy: A Handbook for EntrepreneursRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- LLC or Corporation?: Choose the Right Form for Your BusinessFrom EverandLLC or Corporation?: Choose the Right Form for Your BusinessRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (4)
- The Fundraising Strategy Playbook: An Entrepreneur's Guide To Pitching, Raising Venture Capital, and Financing a StartupFrom EverandThe Fundraising Strategy Playbook: An Entrepreneur's Guide To Pitching, Raising Venture Capital, and Financing a StartupNo ratings yet
- Startup Money Made Easy: The Inc. Guide to Every Financial Question About Starting, Running, and Growing Your BusinessFrom EverandStartup Money Made Easy: The Inc. Guide to Every Financial Question About Starting, Running, and Growing Your BusinessRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (9)
- Value: The Four Cornerstones of Corporate FinanceFrom EverandValue: The Four Cornerstones of Corporate FinanceRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- The Business of Venture Capital: The Art of Raising a Fund, Structuring Investments, Portfolio Management, and Exits, 3rd EditionFrom EverandThe Business of Venture Capital: The Art of Raising a Fund, Structuring Investments, Portfolio Management, and Exits, 3rd EditionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)