Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Communicable Disease Lectures 2
Uploaded by
Sheana TmplCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Communicable Disease Lectures 2
Uploaded by
Sheana TmplCopyright:
Available Formats
COMMUNICABLE DISEASE (additional LECTURES)
By: DR. CLEMENT JOHN FERDINAND M. NAVARRETE
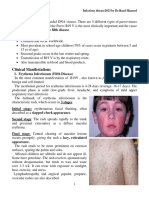
MEASLES
o
The pathognomonic sign of measles is Kopliks spot which
can be seen by inspecting the buccal mucosa.
o
It is an airborne disease
German measles.
o
To prevent congenital rubella, women in the first
trimester of pregnancy in the barangay should avoid
crowded places, such as markets and movie houses.
o
Masks, gowns and gloves should be used by the nurse in
taking care of the client.
Hemophilus influenza
o
The microorganism which causes the most prevalent form
of meningitis among children 2-3 years of age.
Possible mode of transmission for influenza are through
o
direct contact e.g. droplet, indirect e.g. by articles
Contaminatedwith discharges of nose and throat of infected
person or it can also be transmitted AIRBORNE
o
Methods of Prevention and Control for influenza include
3 measures:
o
1.) Education of the public as to sanitary Hazard
from spitting, sneezing and coughing. 2.) Avoid use of
common towels, glasses and eating utensils. 3.) Active
Immunization with Influenza Vaccine
Acute poliomyelitis
>Is spread through the fecal
oral route and contact with throat secretions Classical sign
POKERS SIGN
> Diagnostic exam PANDYS TEST
Diphtheria
>is through direct and
indirect contact with respiratory secretions.
MALARIA
o
Human beings are the major reservoir of malaria
o
ZOOPROPHYLAXIS is done by putting animals like cattle or dogs close to
o
windows or doorways just before nightfall. The
Anopheles mosquito takes his blood meal from the animal and goes
back to its breeding place, thereby preventing
infection of humans
o
Mosquito-borne diseases are prevented mostly with the
use of mosquito control measures like:
Use of chemically treated mosquito nets
Seeding of breeding places with larva-eating fish
STREAM
SEEDINGis done by putting tilapia fry in streams or
other bodies of water identified as breeding places o
f the Anopheles mosquito
Destruction of breeding places of the mosquito
vector
Chicken pox
o
To prevent an outbreak in the community, quarantine
may be imposed by health authorities.
o
Chicken pox is usually more severe in adults than in
children. Complications, such as pneumonia, are higher in
incidence in adults
CHOLERA
o
Patients chief complaint is severe diarrhea and the
passage of rice water stools
Rubeola
o
Signs and symptoms includes:
Small blue-white spots with a red base
may appear in the mouth.
The rush usually begins behind the ears
and spreads downward toward the feet
The communicable period ranges from 10
days before the onset of symptoms to 15
days after the rash appears.
o
Protective precaution is required
Giardiasis
> Giardiasis is characterized by fat malabsorption
and, therefore, steatorrhea.
ROSEOLA INFANTUM
o
The disease is transmitted through the respiratory tract,
so the child should be isolated from the other children as
much as possible.
infectious parotitis (mumps)
>may be serious in young adult males
>Epididymitis and orchitis are possible complications of
mumps. In post adolescent males, bilateral inflammation of the
testes and epididymis may cause sterility
o
The length of time required for respiratory precautions
are indicated during the period of communicability.
PERTUSSIS
o
HEALTH TEACHINGS MAY INCLUDE
We need to maintain respiratory
precautions and a quiet environment for at
least 2 weeks.
Coughing spells may be trigged by dust or
smoke.
we need to encourage our child to drink
fluids.
Viral conjunctivitis
>is transmitted by direct or indirect contact with discharges
from infected eyes.
Amoebiasis and bacillary dysentery
o
characterized by the presence of blood and/or mucus in the stools
SCHISTOSOMIASIS
o
Etiologic agent is Schistosoma JAPONICUM
Common in certain regions in the
Philippines which affects the small intestineand the liver. Liver dam
age is a consequence of fibrotic reactions to schistosoma eggs
in the live.The ova of the parasite get out of the human body together
with feces. Cutting the cycle at this stage is the mosteffective way of
preventing the spread of the disease to susceptible hosts.
o
Praziquantel (Biltricide) is the Drug of choice for all species of Sc
histosoma parasite
o
Snails of species Oncomelia Quadrasi is the most common intermed
iate host for Schistosomiasis
o
Classical sign katayama fever
FILIRIASIS
o
Causative agents are
Wuchereria bancrofti
Bruga malai
B. timori
Hepatitis A
o
Hepatitis A is transmitted through the fecal oral route
Hepatitis B
>Hepatitis B is transmitted through infected body secretions
like blood and semen.
Tetanus
o
Classical sign lock-jaw
Leptospirosis
>is transmitted through contact with the skin or mucou
s
membrane with water or moist soil contaminated
with urine of infected animals, like rats
Leprosy (hansens disease)
o
is a chronic skin and peripheral nerve disease caused by
Mycobacterium leprae
o
the mode of transmission of this disease are sexual
contact and droplet infection.
o
BCG can be administered to prevent the occurrence of
the Hansens disease
o
The following are early signs and symptoms of leprosy:
contractures
o
The following are late signs and symptoms of leprosy :
Muscle weakness or paralysis of extremities
o
The lesion of leprosy
is characterized by a change in skin color (either
reddish or whitish) and sensation, sweating and hair growth
over the lesion. Inability to close the eyelids (lagophthalmos)
and sinking of the nosebridge are late symptoms.
A multibacillary leprosy case is one who has a
positive slit skin smear and at least 5 skin lesio
ns.
o
Classical sign of LEPROSY are: Madarosis,
Lagopthalmos, Chronic ulcer
SCABIES
o
There would be presence of a multiple straight or wavy,
threadlike line beneath the skin upon assessment
and the nurse should institute wearing gown and gloves
when visiting and assessing a patient suspected with
scabies.
AIDS
o
WESTERN BLOT definitive test for AIDS which can
supplement ELIZA test which can give you a false or
negative result.
o
The most frequent causes of death among
clients with AIDS are opportunistic diseases:
Respiratory candidiasis
Infectious mononucleosis
Cytomegalovirus disease
Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia characterized by tonsillopharyngitis
o
o
Contact tracing - BEST method that may be undertaken
by the public health nurse to determine possible
Antiretroviral agents, such as AZT, are used in the
management of AIDS sources of sexually transmitted
infections. Expected actions of this drugs are the
following:
They prolong the life of the client with
AIDS.
They reduce the risk of opportunistic
infections
There is no known treatment for AIDS - They shorten the period
of communicability of the disease.
-
Cytomegalovirus disease
o
is an acute viral disease characterized by fever, sore thro
at and lymphadenopathy
Herpes zoster (shingles)
o
Woods light examination is the definitive test for
shingles
o
Type of lesion - Clustered skin vesicles
pulmonary tuberculosis
o
caused by mycobacterium tuberculi.
A client is considered a PTB suspect when he has
o
cough for 2 weeks or more, plus one or more of the
following signs:
fever for 1 month or more; chest pain lasting for 2 week
s or more not attributed to other conditions; progressive
,unexplained weight loss; night sweats; and hemoptys
is.Directly Observed Treatment Short Course is socalled because a treatment partner, preferably a health
Workeraccessible to the client, monitors the clients
compliance to the treatment
o
proper technique for obtaining a sputum specimen
o
tuberculin skin test which has an area of induration
measuring 10mm or more in diameter indicates a
positive reaction and can indicate exposure to TB
o
BCG (BACILLUS CALMETE GUERIN) - This contains
live attenuated bacterial vaccine. Also considered as the
most stable vaccine.
o
A client with a positive Mantoux test result will be sent f
or a chest x- ray to determine if there is a primary or
secondary infection
Community-acquired pneumonia
o
Streptococcus pneumonia most common etiologic
agent of acute CAP
o
Classical features of pneumococcal pneumonia includes:
Abrupt onset accompanied by a single
rigor
G.I. symptoms
Pleuritic chest pain
Pneumonia
o
is also one of the most common nosocomial infections
accompanied by fever, chills, night sweats and chest pain
o
Caused by - Streptococcus pneumonia
You might also like
- Fungal & Bacterial Infections in HIV PatientsDocument32 pagesFungal & Bacterial Infections in HIV PatientsAndrew SagalovNo ratings yet
- Sexual Self: Presented By: Group 1Document26 pagesSexual Self: Presented By: Group 1Vanessa Joyce Isleta100% (3)
- Poppers BookDocument66 pagesPoppers Bookbadboy6.868510No ratings yet
- Atlas of Male Genital DisordersDocument182 pagesAtlas of Male Genital DisorderssjulurisNo ratings yet
- First Aid Reference Guide V4.1 PublicDocument340 pagesFirst Aid Reference Guide V4.1 PublicChristine St. John100% (3)
- Questionnaire (HTMLE)Document16 pagesQuestionnaire (HTMLE)Angelo Mercede100% (1)
- ANP Heart Anatomy & PhysiologyDocument3 pagesANP Heart Anatomy & PhysiologySheana Tmpl100% (1)
- Disha Publication Chapter With Exercises BiologyDocument32 pagesDisha Publication Chapter With Exercises BiologyAnuj TripathiNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Tuberculosis (PTB)Document6 pagesPulmonary Tuberculosis (PTB)carls burg a. resurreccion100% (2)
- Choledocholithias PathophysiologyDocument2 pagesCholedocholithias PathophysiologySheana Tmpl100% (2)
- Choledocholithias PathophysiologyDocument2 pagesCholedocholithias PathophysiologySheana Tmpl100% (2)
- Immunology and SerologyDocument225 pagesImmunology and SerologyialegnaNo ratings yet
- The Facts About AidsDocument5 pagesThe Facts About AidsTAMBAKI EDMONDNo ratings yet
- Communicable DiseasesDocument101 pagesCommunicable DiseasesKira100% (4)
- 911 Pigeon Disease & Treatment Protocols!From Everand911 Pigeon Disease & Treatment Protocols!Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Communicable DiseasesDocument161 pagesCommunicable DiseasesNader Smadi95% (20)
- Malawi National Urban ProfileDocument52 pagesMalawi National Urban ProfileUnited Nations Human Settlements Programme (UN-HABITAT)No ratings yet
- By-Dr. Samarjeet Kaur JR-II BRD Med. College GKPDocument17 pagesBy-Dr. Samarjeet Kaur JR-II BRD Med. College GKPSamarjeet Kaur100% (1)
- DR As TuberculosisDocument59 pagesDR As TuberculosisAchhar SinghNo ratings yet
- Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDS)Document24 pagesSexually Transmitted Diseases (STDS)Bimby Ali LimpaoNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Coronary Artery Disease and Myocardial InfarctionDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of Coronary Artery Disease and Myocardial InfarctionSheana TmplNo ratings yet
- MS 1 PERIOPERATIVE NURSING ROLES AND RESPONSIBILITIESDocument41 pagesMS 1 PERIOPERATIVE NURSING ROLES AND RESPONSIBILITIESSheana TmplNo ratings yet
- NAME: Zodinpuia: Field Work SummaryDocument16 pagesNAME: Zodinpuia: Field Work SummaryLalmuanpuii sailoNo ratings yet
- Community Health Nursing Practice Questions With RationalesDocument15 pagesCommunity Health Nursing Practice Questions With RationalesFelice Lamzon Labrador100% (2)
- Community Health Nursing Practice Questions With RationalesDocument15 pagesCommunity Health Nursing Practice Questions With RationalesFelice Lamzon Labrador100% (2)
- Leprosy Written ReportDocument7 pagesLeprosy Written Reportnicah05No ratings yet
- Communicable Disease Lectures 2Document10 pagesCommunicable Disease Lectures 2NadeshikoNo ratings yet
- A. Infectious ProcessDocument22 pagesA. Infectious ProcessKyla Malapit GarvidaNo ratings yet
- DiphtheriaDocument10 pagesDiphtheriakudzaimuregidubeNo ratings yet
- Meningococalmeningitis: Presented by Class 6 B Community Medicine DepartmentDocument41 pagesMeningococalmeningitis: Presented by Class 6 B Community Medicine DepartmentMohamed AhmedNo ratings yet
- 2 - SyphilisDocument24 pages2 - SyphilisCaila LimNo ratings yet
- Name: Carlo M. Yao Bachelor of Science in NursingDocument33 pagesName: Carlo M. Yao Bachelor of Science in Nursingcarlo24_briggsNo ratings yet
- Disease-WPS OfficeDocument4 pagesDisease-WPS OfficeSHUBHANG SHARMANo ratings yet
- Lerelyn Case Reading4Document53 pagesLerelyn Case Reading4Ma Lerelyn DatinguinooNo ratings yet
- CHN - Communicable DiseaseDocument117 pagesCHN - Communicable DiseaseGetom NgukirNo ratings yet
- East Africa University Bosaso, Puntland Somalia Faculty of Medicine Communicable Disease MR Buruj Ali SaladDocument42 pagesEast Africa University Bosaso, Puntland Somalia Faculty of Medicine Communicable Disease MR Buruj Ali SaladShaimaa AbdulkadirNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Bacterial Diseases of Ruminants 2020Document30 pagesChapter 5 Bacterial Diseases of Ruminants 2020JAD IMADNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Infections ....Document195 pagesRespiratory Infections ....Poorny PurushothNo ratings yet
- Chickenpox & ChlamydialDocument5 pagesChickenpox & ChlamydialEliezah RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Viral InfectionsDocument110 pagesViral InfectionsMark Anthony CorpuzNo ratings yet
- 14-Diphtheria - Pertussis - and Brucellosis 44-45Document40 pages14-Diphtheria - Pertussis - and Brucellosis 44-45Manar AlhakamiNo ratings yet
- Microbial ResearchDocument12 pagesMicrobial Researchharshit kumarNo ratings yet
- InfectiousDocument4 pagesInfectiouszainabd1964No ratings yet
- Small Pox (CHN)Document13 pagesSmall Pox (CHN)Getom NgukirNo ratings yet
- Diphtheria Pertussis TetanusDocument43 pagesDiphtheria Pertussis Tetanuspnalinl108No ratings yet
- Typhoid and Dengue PPT by Shefali RanaDocument47 pagesTyphoid and Dengue PPT by Shefali RanariyaNo ratings yet
- Childhood Sicknesses1111Document17 pagesChildhood Sicknesses1111abdulrahmanbelewa96No ratings yet
- Gusti Izza - English Medical ArticleDocument6 pagesGusti Izza - English Medical Articlenuna_idaNo ratings yet
- MICROORGANISMS AND DISEASESDocument14 pagesMICROORGANISMS AND DISEASESDima MasadehNo ratings yet
- Trachoma Assignment On CHNDocument6 pagesTrachoma Assignment On CHNSovon SamantaNo ratings yet
- ROUNDWORM, WHIPWORM, HOOKWORM AND PINWORM: CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS, DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENTDocument6 pagesROUNDWORM, WHIPWORM, HOOKWORM AND PINWORM: CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS, DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENTKrystal Jane SalinasNo ratings yet
- Chickenpox: 2008/9 Schools Wikipedia Selection Health and MedicineDocument5 pagesChickenpox: 2008/9 Schools Wikipedia Selection Health and MedicinenvijaykanthNo ratings yet
- Pediculosis: Pubis (Pubic Louse)Document4 pagesPediculosis: Pubis (Pubic Louse)christian quiaoitNo ratings yet
- Common DiseasesDocument7 pagesCommon DiseasesAlter BadonNo ratings yet
- Diphtheria HandoutsDocument8 pagesDiphtheria HandoutsRachelle Mae DimayugaNo ratings yet
- W9 Measles German Measles Influenza Chicken Pox Covid19Document16 pagesW9 Measles German Measles Influenza Chicken Pox Covid19Jamie De LunaNo ratings yet
- Deadly Bubonic PlagueDocument12 pagesDeadly Bubonic PlagueMendoza AnnetteNo ratings yet
- GFDFDFDocument7 pagesGFDFDFRm98No ratings yet
- MeaslesDocument4 pagesMeaslespauline erika buenaventuraNo ratings yet
- Viral Infections of the Oral CavityDocument44 pagesViral Infections of the Oral CavityAMIT GUPTANo ratings yet
- Veterinary Presentation on Zoonotic Diseases in DogsDocument36 pagesVeterinary Presentation on Zoonotic Diseases in DogsCATHERINE CHONG FUI YEENo ratings yet
- Ulcerations of The Oral Cavity Infection Causing Oral UlcerationDocument17 pagesUlcerations of The Oral Cavity Infection Causing Oral UlcerationSebastian QuinteroNo ratings yet
- Chickenpox 1Document7 pagesChickenpox 1Nica Joy CandelarioNo ratings yet
- ImpetigoDocument66 pagesImpetigozbestgurlNo ratings yet
- Mycotic Diseases and PeriodontiumDocument43 pagesMycotic Diseases and PeriodontiumAhmed Tawfig GamalNo ratings yet
- 420 052 Guideline DiphtheriaDocument12 pages420 052 Guideline DiphtheriaLeo RinaldiNo ratings yet
- DENGUE CONTROL PROGRAM: Prevention, Symptoms, TreatmentDocument23 pagesDENGUE CONTROL PROGRAM: Prevention, Symptoms, TreatmentERMIAS, ZENDY I.No ratings yet
- Cdnursing PPT 2021Document37 pagesCdnursing PPT 2021yuuki konnoNo ratings yet
- Case Discussion ImpetigoDocument3 pagesCase Discussion ImpetigolouisNo ratings yet
- Common Fungal InfectionsDocument23 pagesCommon Fungal Infections180045No ratings yet
- PlagueDocument33 pagesPlaguesurajaarya11No ratings yet
- Nur 218 Peds Exam 1 Study Guide Role of The Pediatric NurseDocument9 pagesNur 218 Peds Exam 1 Study Guide Role of The Pediatric NurseNurseme13No ratings yet
- Bacillary DysenteryDocument8 pagesBacillary DysenteryRijane Tabonoc OmlangNo ratings yet
- Diphtheria Pertussis TetanusDocument43 pagesDiphtheria Pertussis TetanusPURVI BARIANo ratings yet
- Contagious Ecthyma: Orf, Contagious Pustular Dermatitis, Sore Mouth, Scabby MouthDocument27 pagesContagious Ecthyma: Orf, Contagious Pustular Dermatitis, Sore Mouth, Scabby MouthMohammedNo ratings yet
- Causative Agent:: M. Tuberculosis Has An Unusual, Waxy Coating On The Cell Surface (Primarily Mycolic Acid)Document4 pagesCausative Agent:: M. Tuberculosis Has An Unusual, Waxy Coating On The Cell Surface (Primarily Mycolic Acid)Ervin BatangosoNo ratings yet
- NML 4an3b DiscussionDocument17 pagesNML 4an3b DiscussionSheana TmplNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Action Indication Contraindication Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument1 pageDrug Name Action Indication Contraindication Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesSheana TmplNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Action Indication Contraindication Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument1 pageDrug Name Action Indication Contraindication Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesSheana TmplNo ratings yet
- Pareto ChartDocument1 pagePareto ChartSheana TmplNo ratings yet
- Nursing TheoriesDocument2 pagesNursing TheoriesSheana TmplNo ratings yet
- Elective II ReviewerDocument4 pagesElective II ReviewerSheana TmplNo ratings yet
- Performance Improvement ToolsDocument5 pagesPerformance Improvement ToolsSheana TmplNo ratings yet
- Pareto ChartDocument1 pagePareto ChartSheana TmplNo ratings yet
- DSA worksheet guides quality improvement cyclesDocument7 pagesDSA worksheet guides quality improvement cyclesSheana TmplNo ratings yet
- GYNECOLOGICALNURSINGDocument4 pagesGYNECOLOGICALNURSINGSheana TmplNo ratings yet
- ManualDocument9 pagesManualSheana TmplNo ratings yet
- Common Surgical Procedure1Document4 pagesCommon Surgical Procedure1Sheana TmplNo ratings yet
- Elective IIDocument13 pagesElective IISheana TmplNo ratings yet
- DSA worksheet guides quality improvement cyclesDocument7 pagesDSA worksheet guides quality improvement cyclesSheana TmplNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument3 pagesNCPSheana TmplNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic CellDocument2 pagesProkaryotic CellSheana TmplNo ratings yet
- ObjectivesDocument2 pagesObjectivesSheana TmplNo ratings yet
- Review Eeee ErDocument8 pagesReview Eeee ErSheana TmplNo ratings yet
- Group QuestionsDocument7 pagesGroup QuestionsSheana TmplNo ratings yet
- Nursing HistoryDocument2 pagesNursing HistorySheana TmplNo ratings yet
- Walang LamanDocument1 pageWalang LamanSheana TmplNo ratings yet
- First ENCD Youth RallyDocument1 pageFirst ENCD Youth RallySheana TmplNo ratings yet
- 16.MDR-XDR TBDocument18 pages16.MDR-XDR TBLinna SriwaningsiNo ratings yet
- Reducing Teen PregnancyDocument10 pagesReducing Teen PregnancyANo ratings yet
- Case Study Questions HIVDocument2 pagesCase Study Questions HIVJill Arciaga0% (5)
- Legal and Ethical Issues in Blood Transfusion IndianJAnaesth585558-6660548 - 183005Document7 pagesLegal and Ethical Issues in Blood Transfusion IndianJAnaesth585558-6660548 - 183005Lakshmanan KrishnamurtiNo ratings yet
- HIV AIDS Gender Inequality and Cultural Perceptions and Behaviour of SexualityDocument171 pagesHIV AIDS Gender Inequality and Cultural Perceptions and Behaviour of SexualityYousuf AliNo ratings yet
- How HIV and AIDS are spreadDocument4 pagesHow HIV and AIDS are spreadlianghoo94No ratings yet
- Bali 2011Document4 pagesBali 2011ashkisaragiNo ratings yet
- Fever rash guideDocument33 pagesFever rash guideVarun B RenukappaNo ratings yet
- Tuberculous Lymphadenitis: History PathogenesisDocument6 pagesTuberculous Lymphadenitis: History PathogenesisMochamad BilalNo ratings yet
- AidsDocument30 pagesAidsapi-3797941No ratings yet
- Pidato Bahasa InggrisDocument12 pagesPidato Bahasa InggrisAlltopAmriya100% (1)
- Bloodborne Pathogens TrainingDocument102 pagesBloodborne Pathogens Trainingapi-311432115No ratings yet
- GileadSciences 10K 20160224Document131 pagesGileadSciences 10K 20160224terminairNo ratings yet
- Neurological Complications of HIV - Zelalem TemesgenDocument46 pagesNeurological Complications of HIV - Zelalem Temesgeniqbal dwi cahyoNo ratings yet
- OSH Standards Amended 1989 LatestDocument360 pagesOSH Standards Amended 1989 LatestChristian D. AllanaNo ratings yet
- Susruthasamhitha Part 1 PDFDocument22 pagesSusruthasamhitha Part 1 PDFDr Suvarna NalapatNo ratings yet
- Cowan 1999Document20 pagesCowan 1999Fadli_14No ratings yet
- Ipcr NDPDocument1 pageIpcr NDPGABIETA MeshachNo ratings yet
- National Mediclaim Policy: BrochureDocument3 pagesNational Mediclaim Policy: Brochureshukla8No ratings yet