Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Board Game Notes
Uploaded by
api-2770329070 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
141 views3 pagesOriginal Title
board game notes
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
141 views3 pagesBoard Game Notes
Uploaded by
api-277032907Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
Supporting the Big Bang Theory
The Big Bang was an _____. Explosion
The universe is _____. Expanding
Whats moving? Galaxy Clusters
If we role back time, the universe must have come from a _____. Tiny Dot
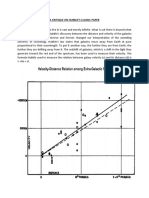
Due to Hubble's Law, are farther away galaxies moving (slower) the (same) or (faster)? Faster
The universe is expending because of the _____of distant galaxies. Redshift
What was the universe in early history? Hot
What did the universe leave behind as it expanded? A "Glow"
How is this "glow" that was left behind after expansion, visible? Through Microwaves
How were the Cosmic Microwaves accurately measured? Orbiting Detectors
What has the temperature of the universe done from the beginning of time, to now? Cooled
_____ were created. Elements
What does the Big Bang theory predict about the elements in the early universe? How much of
each should have been made.
The common alternative to the Big Bang theory is called the ______. Steady State Theory
What is the Steady State Theory about? New matter is being continuously made as the
Universe expands
Production of Elements in the Universe
Nucleosynthesis is the birthing of new _____ _____. Atomic nuclei
The two main kinds of nucleosynthesis are? Big Bang nucleosynthesis and stellar
nucleosynthesis
As the universe expanded, _____ _____ "froze " into neutrons and protons. Quark-gluon
Plasma
When the neutrons and and protons interacted, they caused what kind of reactions? Nuclear
Why did the nuclear reactions stop? It became too cold
After the unstable isotopes and neutrons died away, what was left? (2 or more) Hydrogen,
helium, deuterium and lithium
The elements: hydrogen, helium, deuterium and lithium were made into stars by what
nucleosynthesis? Stellar
Main sequence stars get energy from...? Nuclear reactions in their cores
Non-main sequence stars get energy from...? Nuclear reactions in a shell
Proton-proton chain, triple alpha, s process and CNO cycle all lead to a fusion of _____, _____.
Then, in what star phase are these made? (list at least 4) Hydrogen & helium to produce
oxygen, carbon, nitrogen, and the iron section/Red Giant
When a cosmic ray collides with a nucleus in the Earths atmosphere, it break's into two or more
pieces. What is this process called? Cosmic ray spallation
Cosmic ray spallation produces what elements? (al least 2) lithium, beryllium, and boron
In a core collapse supernova, huge amounts of new nuclei are created in the nuclear reactions
set off by the flood of neutrons. What the main process is this? r process
The "r process" produces what kind of elements? Heavier elements such as copper to uranium.
How are the heavier elements made by the r process? By radioactive decay of unstable
isotopes
The Life Cycle of Stars
Stars are formed in what? Nebulae- Clouds of Dust and Gas
Nuclear reactions from the center of stars offers enough _____ for them to ____ for many
_____. Energy, Shine and Years
What depends on the lifetime of stars? Its Size
Massive stars burn their fuel _____ than smaller stars. Faster
Which star burn longer, Massive or Small Star? Small
How long will massive stars last? Few Hundred Thousand Years
How long will small Star last? Several Billion Years
Why do smaller stars last longer? They Burn Slower
As the star ages, what happens? The hydrogen fuel that powers the nuclear reactions within
stars will begin to run out
As a star enters the final phases of their lifetime, what happens to it physically? It will cool and
change color
Stars will cool, expand and change color to become _____. Red Giants
After Stars become a Red Giant, the path then depends on the _____ of the star. Mass
What is the size of the Sun? So what kind of death will the Sun undergo, What will it become?
Small, peaceful death that sees them pass through a planetary nebula phase to become a white
dwarf
What kind of star will experience an energetic and violent end, which will see their remains
thrown across the cosmos in a gigantic explosion, and what do wee call these massive
explosions? Massive, Supernova
After a "Supernova", what remains? A rapidly spinning neutron star, or possibly even a black
hole
What is the astronomical evidence based on the light spectra of stars
What american astronomer demonstrated that there was more to our universe than our galaxy.
Who found that there were many separate clumps of stars and that they were far, far far away
from our own galaxy? Edwin Hubble
What color of the light spectrum were galaxies putting off? Red Light
Due to what effect, were these galaxies putting off a certain light? Doppler effect (known as
redshift)
What is Doppler effect (aka redshift)? It indicates that the galaxies around us are in fact
moving away.
After a study of the redshifts of a class of stars called Cepheids, Hubble concluded that the
galaxies and clusters were in fact _____ _____ from each other at _____ _____. Flying Apart
and High Speed
What concluded that the universe was "therefore definitively growing in size"? Hubble's Analysis
In our _____ universe, every galaxy is moving _____ from us with a speed which is in direct
_____ to its distance. Expanding, Away, Proportion
How do we figure out what our sun in made up of, or any star for instance? By measuring
wavelength/frequency of the the light coming from the star.
Spectroscopy is what? Is using light from a far away object to figure out what elements it's made
up of
What do we refer the universe expansion? "metric expansion"
What is the metric expansion? that the galaxies themselves are not expanding, but the clusters
of galaxies into which the matter of the universe has become divided
What is becoming of the galaxies in which the matter of the universe has become divided?
separated and scarcely spread in the universe
..
When we look up at the galaxies, what color are they? Red
http://www.schoolsobservatory.org.uk/astro/stars/lifecycle
http://hubblesite.org/reference_desk/faq/all.php.cat=light
http://www.universetoday.com/51797/nucleosynthesis/
http://www.physicsoftheuniverse.com/topics_bigbang_expanding.html
http://www.schoolsobservatory.org.uk/astro/cosmos/bb_evid
You might also like
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- DG1360 5K6D1FDocument353 pagesDG1360 5K6D1FGovindaSeva100% (1)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Stephen King On Writing Book AnalysisDocument9 pagesStephen King On Writing Book Analysisapi-277032907No ratings yet
- Lesson 1 - Formation of Elements in The Evolution of The UniverseDocument65 pagesLesson 1 - Formation of Elements in The Evolution of The UniverseiMetalloid Gt100% (1)
- Ars WorksheetDocument8 pagesArs WorksheetadamgonoloNo ratings yet
- RasininthesunDocument3 pagesRasininthesunapi-277032907No ratings yet
- Exploring Waves 1 - CompressedDocument12 pagesExploring Waves 1 - Compressedapi-277032907No ratings yet
- PoisoningourselvesslowlyDocument4 pagesPoisoningourselvesslowlyapi-277032907No ratings yet
- Human PathegonsDocument2 pagesHuman Pathegonsapi-277032907No ratings yet
- CopyofconservationofenergylearningmoduleDocument8 pagesCopyofconservationofenergylearningmoduleapi-277032907No ratings yet
- 2nd Amendment PaperDocument8 pages2nd Amendment Paperapi-277032907No ratings yet
- Rules For BoardgameDocument2 pagesRules For Boardgameapi-277032907No ratings yet
- FaithbringselectionpointsDocument2 pagesFaithbringselectionpointsapi-277032907No ratings yet
- SlaveryanddiscriminationDocument3 pagesSlaveryanddiscriminationapi-277032907No ratings yet
- DystopiaDocument40 pagesDystopiaapi-277032907No ratings yet
- Forgotten Killer 2Document5 pagesForgotten Killer 2api-277032907No ratings yet
- The Great DepressionDocument5 pagesThe Great Depressionapi-277032907No ratings yet
- ArchDocument3 pagesArchapi-277032907No ratings yet
- Global InterdependanceDocument5 pagesGlobal Interdependanceapi-277032907No ratings yet
- Cold and Korean WarDocument4 pagesCold and Korean Warapi-277032907No ratings yet
- Horses in Forces and MotionDocument18 pagesHorses in Forces and Motionapi-277032907No ratings yet
- DeforesationDocument9 pagesDeforesationapi-277032907No ratings yet
- Climate ChangeDocument3 pagesClimate ChangeFaith BringsNo ratings yet
- War UnitDocument9 pagesWar Unitapi-277032907No ratings yet
- Physics New NotesDocument8 pagesPhysics New NotesDaniel CannywoodNo ratings yet
- Chandrasekhar S. The Mathematical Theory of Black Holes PDFDocument667 pagesChandrasekhar S. The Mathematical Theory of Black Holes PDFBudhaditya Bhattacharjee94% (17)
- Gravitation Short Q.A Class 9Document7 pagesGravitation Short Q.A Class 9Abhinav Chawla 4186No ratings yet
- Branches of AstronomyDocument10 pagesBranches of AstronomyRowela DellavaNo ratings yet
- SW13 ScientificProgramDocument154 pagesSW13 ScientificProgramJim ZhangNo ratings yet
- Physics of Stars Ac Phillips Solutions GongniuoreDocument5 pagesPhysics of Stars Ac Phillips Solutions Gongniuorekrishna0% (1)
- Folio Star and GalaxyDocument33 pagesFolio Star and GalaxyHarry HairiNo ratings yet
- Stellar Nucleosynthesis ExplainedDocument29 pagesStellar Nucleosynthesis ExplainedLoren Marie Lemana AceboNo ratings yet
- 9.2 Space WeatherDocument4 pages9.2 Space WeathersyaNo ratings yet
- Satellite Motion 9 Sputnik SolnDocument4 pagesSatellite Motion 9 Sputnik SolnJoey BryanNo ratings yet
- 1335 EphemDocument1,890 pages1335 EphemakhilNo ratings yet
- Gravity Acceleration of Falling ObjectsDocument39 pagesGravity Acceleration of Falling ObjectsRathi MalarNo ratings yet
- Concept PaperDocument2 pagesConcept Paperivanne arbuesNo ratings yet
- Branches of Physics-ExercisesDocument4 pagesBranches of Physics-ExercisesOnur YavuzcetinNo ratings yet
- The Big Bang Theory TimelineDocument3 pagesThe Big Bang Theory TimelineSamsamNo ratings yet
- Comment On "A Generalized Helmholtz Theorem For Time-Varying Vector Fields," by Artice M. DavisDocument3 pagesComment On "A Generalized Helmholtz Theorem For Time-Varying Vector Fields," by Artice M. Davisfersoto07No ratings yet
- A Study of The Characteristics of The New Planet XDocument73 pagesA Study of The Characteristics of The New Planet XNwigwe Promise ChukwuebukaNo ratings yet
- A Critique On Hubble's Classic PaperDocument4 pagesA Critique On Hubble's Classic PaperJaschaNo ratings yet
- Week 001 Origin of UniverseDocument12 pagesWeek 001 Origin of UniverseAiver VillarNo ratings yet
- Copernican PrincipleDocument7 pagesCopernican Principlemaddy555No ratings yet
- Stars Lifecycle of A Star Stop Motion AnimationDocument1 pageStars Lifecycle of A Star Stop Motion Animationapi-495160390No ratings yet
- Julian Calendar Solar Cycle (Calendar)Document17 pagesJulian Calendar Solar Cycle (Calendar)Ved NarsekarNo ratings yet
- Syllabus 2023-2024pdfDocument28 pagesSyllabus 2023-2024pdfapi-554428889No ratings yet
- Star in A Box Worksheet - BeginningDocument2 pagesStar in A Box Worksheet - BeginningLeanne Cotton0% (1)
- How Stars Are Born: The Stages of Star Formation from Gas Cloud to Nuclear FusionDocument5 pagesHow Stars Are Born: The Stages of Star Formation from Gas Cloud to Nuclear FusionMae Ann GonzalesNo ratings yet
- AST201 Assignment 3Document12 pagesAST201 Assignment 3AnnaaaNo ratings yet
- Mind Mind Bending Bending Physics PhysicsDocument116 pagesMind Mind Bending Bending Physics PhysicsAlejandra Rivera CchNo ratings yet