Professional Documents
Culture Documents
PSE610S Lab 2 2017
Uploaded by
TimoOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
PSE610S Lab 2 2017
Uploaded by
TimoCopyright:
Available Formats
BACHELOR OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING
PSE610S: Power Systems Engineering 316 Laboratory 2
Students Full Name: ------------------------------------------- Students No: -------------------------------
Bench No: ------------------------------ Date: ---------------------------
SIMULATION OF POLYPHASE ELECTRICAL QUANTITIES AND PHASE SEQUENCE.
OBJECTIVES
1. To model and simulate a 3-phase source in PSpice.
2. To detect and show phase rotation using PSpice and by measurement.
3. To investigate the relationship between voltage and current in 3-phase balanced loads through
simulation and measurements.
4. To investigate the relationship between voltage and current in 3-phase unbalanced loads
through simulation and measurements.
EQUIPMENTS:
A 3-Phase AC/DC Variable 380/220V
An RLC Panel
Multimeters
Laboratory connecting leads
MARKS OBTAINED:
Marks % weight
Part 1 27.5 35
Part 2 27.5 35
Part 3 15 10
Report 16 20
TOTAL MARKS 86 100
PSE610S LAB 2 2017 Isaiah & Reza Page 1
BACKGROUND THEORY
The most commonly used polyphase system in electric power applications is a 3-phase supply. This
consists of 3 separate power carrying circuits, whose voltages and currents are displaced
symmetrically in time. A 3-phase source consists of 3 phase voltages with a phase displacement of
1200 between them.
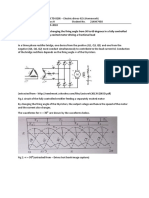
Part 1: SIMULATION OF A Y CONNECTED 3-PHASE SYSTEM
Procedures:
1. Create in PSpice or OrCad Capture a 380V, Y-connected, 3-phase power supply with phase
sequence R-Y-B.
2. On each phase connect variable inductors of 160mH each.
3. Corresponding to each phase, connect a resistor (100) in series with the inductor to form an
R-L load. Use the series combinations for the star (Y)) configuration of the load.
4. Set the power supply to give an amplitude value of 220V AC per phase and construct the
network as shown in Figure 1. NB: The power supply should be connected in star.
5. Set the simulation to time-domain (transient) analysis, with run-to-stop time of 8cycles. The
simulation should start recording data after 4cycles of the input supply voltage for each
simulation run.
6. By use of voltage probes, run the simulation to show the relationship between the phase
voltages.
7. By taking one phase as the reference run the simulation to show the relationship between the
phase voltage and the line voltage (line-line voltage).
8. Run the simulation to show the relationship between the phase current and line current for
each type of load. Run the simulation to get the phase voltages and phase currents of the Y-
connected load. Explain the phase relationships between the voltages and currents. Is the load
balanced? Support your answer with a detailed calculation and analysis.
PSE610S LAB 2 2017 Isaiah & Reza Page 2
Part 2: SIMULATION OF A -CONNECTED 3-PHASE SYSTEM
9. Repeat Steps 1 to 8 for a -connected load.
Part 3a: Simulation of the Phase Detector Circuit
10. Using a balanced Y-connected load, remove the elements on the Yellow phase of the load
and replace it with a variable capacitor whose value is such that its reactance is equal to the
impedance of the other remaining two phases.
11. Run the simulation to get the phase voltages and phase currents of the Y-connected load.
Explain the phase relationships between the voltages and currents. Is the load balanced?
Support your answer with a detailed explanation.
12. By considering that the other two remaining phases (Red and Blue) have indicator
lamps in series with each impedance, deduce which lamp will be brighter than the other. The
phase whose lamp is brighter is leading the other phase.
Figure 1
PSE610S LAB 2 2017 Isaiah & Reza Page 3
Part 3b Experimental/Practical validation of the Phase Detector Circuit
1. Connect the Phase Sequence Detector Circuit as in your simulation using components
available from the Power Engineering Laboratory. Use 60W bulbs as your indicator lamps in
the Red and Blue phases and a capacitor in the Yellow phase.
2. Observe the phase sequence as shown by indicator lamps.
3. Is the phase sequence deduced from the simulation results the same as the one shown by the
practical experiment? If there is a difference, give an explanation for the difference between
the simulation results and the practical experimental results.
Lab Report Instructions
1. Please use a word processor to typeset your report.
2. Your report should include at least the following sections:
Objectives
Simulation results
Analysis
Conclusion
NB: Make the cover page of this manual the cover page of your report.
PSE610S LAB 2 2017 Isaiah & Reza Page 4
You might also like
- Assignment 1 QuestionsDocument1 pageAssignment 1 QuestionsTimoNo ratings yet
- 2 SlideDocument1 page2 SlideTimoNo ratings yet
- CV Template - Personal and Academic DetailsDocument2 pagesCV Template - Personal and Academic DetailsTimoNo ratings yet
- ETD 820S HomeworkDocument3 pagesETD 820S HomeworkTimoNo ratings yet
- Speed Control of DC Motor: Lecture-11Document5 pagesSpeed Control of DC Motor: Lecture-11TimoNo ratings yet
- EMC510S - Elect. Mcs 216 - Test 2 - MemoDocument7 pagesEMC510S - Elect. Mcs 216 - Test 2 - MemoTimoNo ratings yet
- FINAL Yearbook 2017 Part 4 Computing and InformaticsDocument55 pagesFINAL Yearbook 2017 Part 4 Computing and InformaticsTimoNo ratings yet
- Etd820s-Homework CH 5&6Document2 pagesEtd820s-Homework CH 5&6TimoNo ratings yet
- Economic AspectsDocument16 pagesEconomic AspectsTimoNo ratings yet
- System ProtectionDocument35 pagesSystem ProtectionTimoNo ratings yet
- Homework 4 SolutionDocument3 pagesHomework 4 SolutionTimoNo ratings yet
- 11ee701 - Solid State Drives: Unit - I - Electric Drives Unit - I - SyllabusDocument2 pages11ee701 - Solid State Drives: Unit - I - Electric Drives Unit - I - SyllabusTimoNo ratings yet
- Java - Encapsulation: ExampleDocument2 pagesJava - Encapsulation: ExampleTimoNo ratings yet
- Lecture-9: Load Equalization and Two Mark QuestionsDocument6 pagesLecture-9: Load Equalization and Two Mark QuestionsTimoNo ratings yet
- Electric drive lecture notesDocument24 pagesElectric drive lecture notesShashank SinghNo ratings yet
- Reasons for Load Equalization in Electric DrivesDocument1 pageReasons for Load Equalization in Electric DrivesTimoNo ratings yet
- Unit-2 DC Drives: DC Motors and Their PerformanceDocument19 pagesUnit-2 DC Drives: DC Motors and Their PerformanceTimoNo ratings yet
- Etd820s Lab 3 2018Document3 pagesEtd820s Lab 3 2018TimoNo ratings yet
- CH Egg SolutionsDocument34 pagesCH Egg SolutionsTimoNo ratings yet
- Etd820s Lab 1 2018Document4 pagesEtd820s Lab 1 2018TimoNo ratings yet
- Etd820s Lab 3 2018Document3 pagesEtd820s Lab 3 2018TimoNo ratings yet
- Open Loop Speed Regulation of a Three Phase Induction MotorDocument4 pagesOpen Loop Speed Regulation of a Three Phase Induction MotorTimoNo ratings yet
- AC Drives PDFDocument105 pagesAC Drives PDFTimoNo ratings yet
- Ice BPDocument24 pagesIce BPTimoNo ratings yet
- AC Drives PDFDocument105 pagesAC Drives PDFTimoNo ratings yet
- Etd820s Lab 1 2018Document4 pagesEtd820s Lab 1 2018TimoNo ratings yet
- Atm711s Lab 1Document4 pagesAtm711s Lab 1TimoNo ratings yet
- 4 ICN Slides Addressing 2016Document135 pages4 ICN Slides Addressing 2016TimoNo ratings yet
- Open Loop Speed Regulation of a Three Phase Induction MotorDocument4 pagesOpen Loop Speed Regulation of a Three Phase Induction MotorTimoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Computer Networking ICN511S: Loini Iiyambo Department of Computer ScienceDocument30 pagesIntroduction To Computer Networking ICN511S: Loini Iiyambo Department of Computer ScienceTimoNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5783)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (72)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Coe Sem 5 End Sem 2008Document10 pagesCoe Sem 5 End Sem 2008ashwaniNo ratings yet
- Experiment 7Document14 pagesExperiment 7Mizhar GerardoNo ratings yet
- WLS 3710Document2 pagesWLS 3710groovey9040No ratings yet
- El Timer 555 PDFDocument28 pagesEl Timer 555 PDFAnonymous 1LD5bpJ15dNo ratings yet
- Advance Engineering Mathematics: Module 6 Exam ReviewDocument2 pagesAdvance Engineering Mathematics: Module 6 Exam ReviewSanty Enril Belardo Jr.No ratings yet
- Basic Electronics Important Expected MCQ With SolutionDocument11 pagesBasic Electronics Important Expected MCQ With SolutionAbhay ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Hyt Tc-518 Service ManualDocument59 pagesHyt Tc-518 Service Manualyd2oyd100% (1)
- Attach File 1678137068040Document16 pagesAttach File 1678137068040paul omondiNo ratings yet
- Status of ACE-9 SanctionedDocument7 pagesStatus of ACE-9 SanctionedPuneet NirajNo ratings yet
- Max 6954Document39 pagesMax 6954danysan2525No ratings yet
- LG L226WTQ B WFS - e PDFDocument29 pagesLG L226WTQ B WFS - e PDFMihaela CaciumarciucNo ratings yet
- Helm PCB - 8088 ComputerDocument9 pagesHelm PCB - 8088 ComputerGabriela FrederickNo ratings yet
- Design and Simulation of Cmos 2-Bit Half Subtractor Using 32NM, 45NM and 65NM FoundryDocument4 pagesDesign and Simulation of Cmos 2-Bit Half Subtractor Using 32NM, 45NM and 65NM Foundryijsret100% (1)
- MATLAB ReportDocument17 pagesMATLAB ReportRaja ShekarNo ratings yet
- 2.electronics Circuits IIDocument9 pages2.electronics Circuits IImanimangaiNo ratings yet
- Mt8870, DTMF Decoder (Application Notes)Document24 pagesMt8870, DTMF Decoder (Application Notes)anmol9100% (1)
- Lm393 Motor Speed Measuring Sensor Module For ArduinoDocument2 pagesLm393 Motor Speed Measuring Sensor Module For ArduinovivekanandkNo ratings yet
- Measuring Current, Voltage & Power in Series LED CircuitDocument4 pagesMeasuring Current, Voltage & Power in Series LED CircuitFelipe CamargoNo ratings yet
- LG W1943C Chass LM92C PDFDocument23 pagesLG W1943C Chass LM92C PDFDaniel Paguay100% (1)
- Watlow981 982 ManualDocument141 pagesWatlow981 982 ManualIsidro Igigi HernándezNo ratings yet
- DELL - Precision-390 - Setup Guide - En-Us PDFDocument190 pagesDELL - Precision-390 - Setup Guide - En-Us PDFDimitris DimitriouNo ratings yet
- 3780 FFDocument30 pages3780 FFhonokaNo ratings yet
- Thesis-2008-Printed Monopole Antenna For UltraDocument271 pagesThesis-2008-Printed Monopole Antenna For UltraDr-Pritam Singh BakariyaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Tests On Gan Devices: Giorgio SpiazziDocument22 pagesElectrical Tests On Gan Devices: Giorgio SpiazziNguyên NghĩaNo ratings yet
- APEC 2011 Seminar ACDC ACAC Final Inclusive Swiss Rectifier As Sent 010211Document268 pagesAPEC 2011 Seminar ACDC ACAC Final Inclusive Swiss Rectifier As Sent 010211Cristian BandilaNo ratings yet
- 7UT613 63xDocument514 pages7UT613 63xdenisseNo ratings yet
- 8051 Microcontroller GuideDocument78 pages8051 Microcontroller GuideArun JyothiNo ratings yet
- ADC Guide, Part 1: The Ideal ADC: Sachin Gupta and Akshay Phatak, Cypress Semiconductor CorpDocument6 pagesADC Guide, Part 1: The Ideal ADC: Sachin Gupta and Akshay Phatak, Cypress Semiconductor CorpBhai BaiNo ratings yet
- On Mimo Channel ModelingDocument24 pagesOn Mimo Channel Modelingsakanat5152100% (2)
- Questions & Answers On Diode CircuitDocument251 pagesQuestions & Answers On Diode Circuitkibrom atsbha86% (7)