Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cpa Review School of The Philippines 3
Uploaded by
Jhopel Casagnap EmanOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cpa Review School of The Philippines 3
Uploaded by
Jhopel Casagnap EmanCopyright:
Available Formats
1
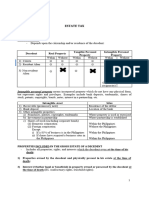
ESTATE TAXATION
Atty. C. Llamado
GROSS ESTATE
- Depends upon the citizenship and/or residence of the decedent:
Tangible Personal Intangible Personal
XDecedent Real Property
Property Property
Within Without Within Without Within Without
1) Citizen
2) Resident Alien
3) Non-resident
Alien
(if there is
reciprocity)
Intangible personal property means incorporeal property which do not have any physical form,
but represent right and privileges. Example includes bank deposits, Trademarks, share of stock,
patents, copyright, bonds, notes, interest in a partnership, etc.
Intangible Asset Situs
1) Receivable (promissory note) Residence of the debtor
2) Bank deposit Location of the bank
3) Other intangible properties:
a) Franchises, patents, copyright, trademark Where property is used or exercised
b) Investment in partnership Where partnership is establish
c) Share of stock (including corporate bond)
(1) Domestic corporation Within the Philippines
(2) Foreign corporation Without the Philippines
Except:
i) if > 85% of the business is in the Philippines Within the Philippines
ii) if shares have acquired a business situs in the
Philippines Within the Philippines
PROPERTIES INCLUDED IN THE GROSS ESTATE F A DECEDENT
- Includes all properties, right, and interests which the decedent owns at the time of his
death;
1) Property owned by the decedent and physically present in his estate at the time of death;
2) Interest (whether legal of beneficial) in property owned or possessed by the decedent at the time
of death (Ex. Usufructuary rights);
3) Taxable Transfer made during lifetime, but are in the nature of testamentary dispositions (mortis
causa in substance). The decedent remains in control of the property, and the transfer is transfer
is intended to take effect at or after his death.
a) Transfer in Contemplation of Death
- Transfer is implled by the thought of death
You might also like
- Module 2 Estate TaxDocument14 pagesModule 2 Estate TaxClarissa Atillano FababairNo ratings yet
- Estate TaxDocument10 pagesEstate Taxlamborghini aventadorNo ratings yet
- CPAR Estate Tax (Batch 89) HandoutDocument18 pagesCPAR Estate Tax (Batch 89) HandoutlllllNo ratings yet
- CPAR Estate-TaxationDocument18 pagesCPAR Estate-Taxationwendygilbuela2022No ratings yet
- Material 11 Estate TaxDocument20 pagesMaterial 11 Estate Taxnodnel salonNo ratings yet
- Estate Tax NotesDocument11 pagesEstate Tax NotesClaire Araneta AlcozeroNo ratings yet
- 2-Gross EstateDocument12 pages2-Gross EstateJim Kyrone GenobisaNo ratings yet
- Modes of Acquiring Ownership & Estate TaxesDocument11 pagesModes of Acquiring Ownership & Estate TaxesMarko JerichoNo ratings yet
- Estate Taxation BasicsDocument11 pagesEstate Taxation BasicsPrincess EngresoNo ratings yet
- Tax-2-Recits Estate Tax Donors TaxDocument5 pagesTax-2-Recits Estate Tax Donors TaxEmmanuel MabolocNo ratings yet
- Estate Tax and Some Exempt TransfersDocument3 pagesEstate Tax and Some Exempt TransfersfcnrrsNo ratings yet
- Estate Tax - Is The Tax On The Right To Transmit Property at Death and On Certain Transfers Which Are Made by Law The Equivalent ofDocument4 pagesEstate Tax - Is The Tax On The Right To Transmit Property at Death and On Certain Transfers Which Are Made by Law The Equivalent ofAlliah SomidoNo ratings yet
- Taxation Law II Green NotesDocument126 pagesTaxation Law II Green NotesNewCovenantChurchNo ratings yet
- CH07 Gross EstateDocument9 pagesCH07 Gross EstateRenelyn FiloteoNo ratings yet
- Gross EstateDocument63 pagesGross EstateMark Angelo SibayanNo ratings yet
- Estate TaxDocument4 pagesEstate TaxLovely Jane Raut CabiltoNo ratings yet
- Module 4 Estate Taxation 2Document4 pagesModule 4 Estate Taxation 2Melanie SamsonaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Gross Estate PDFDocument6 pagesChapter 2 - Gross Estate PDFVanessa Castor GasparNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Gross EstateDocument4 pagesChapter 2 Gross EstateMary Anne KazuyaNo ratings yet
- Business Tax MODULEDocument32 pagesBusiness Tax MODULEDanica GeneralaNo ratings yet
- Estate TaxDocument6 pagesEstate TaxElla CastilloNo ratings yet
- SPECIAL PROCEEDINGS | Judge Cinco EH 403Document2 pagesSPECIAL PROCEEDINGS | Judge Cinco EH 403Chezka Bianca TorresNo ratings yet
- Tax 2 Reviewer: A. Transfer TaxesDocument11 pagesTax 2 Reviewer: A. Transfer TaxesIsay YasonNo ratings yet
- Excel Professional Services, Inc.: Management Firm of Professional Review and Training Center (PRTC)Document21 pagesExcel Professional Services, Inc.: Management Firm of Professional Review and Training Center (PRTC)Mae Angiela TansecoNo ratings yet
- 01/31/23 - First Discussion: Transfer Tax and Types of DecedentDocument2 pages01/31/23 - First Discussion: Transfer Tax and Types of Decedentalexandra.gutierrez.cNo ratings yet
- Tax2 - L02 - Notes (Business Tax)Document12 pagesTax2 - L02 - Notes (Business Tax)Savage KongNo ratings yet
- Gross Estate: Maria Princess G. Bacungan December 7, 2009Document5 pagesGross Estate: Maria Princess G. Bacungan December 7, 2009CessBacunganNo ratings yet
- TAX Tax Law 2Document158 pagesTAX Tax Law 2iamtikalonNo ratings yet
- Tax2 L02 NotesDocument14 pagesTax2 L02 NotesSavage KongNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Succession and Transfer TaxesDocument17 pagesChapter 1 Succession and Transfer TaxesChristian James Umali BrionesNo ratings yet
- Business Tax Chapter 2 ReviewerDocument4 pagesBusiness Tax Chapter 2 ReviewerMurien LimNo ratings yet
- Tax 2 T Lecture TranscriptDocument26 pagesTax 2 T Lecture TranscriptEphraimEnriquez100% (1)
- Property LawDocument117 pagesProperty LawAhmed NazeedNo ratings yet
- Handout 07 - Donor's TaxDocument6 pagesHandout 07 - Donor's TaxJelyn RuazolNo ratings yet
- Law On Property: Lawyers in The MakingDocument8 pagesLaw On Property: Lawyers in The MakingpasmoNo ratings yet
- Tax Lectures TranscribeDocument29 pagesTax Lectures TranscribeNeri DelfinNo ratings yet
- PPLAWDocument15 pagesPPLAWSomesh9652 Somesh9652No ratings yet
- Review Notes For Taxation 2: Sequuntur Personam and Situs of Taxation)Document41 pagesReview Notes For Taxation 2: Sequuntur Personam and Situs of Taxation)JImlan Sahipa IsmaelNo ratings yet
- Estate Tax BasicsDocument18 pagesEstate Tax BasicsIan De DiosNo ratings yet
- Estate Tax ReviewDocument47 pagesEstate Tax ReviewhowaanNo ratings yet
- Ch07 Gross EstateDocument8 pagesCh07 Gross EstateRenelyn FiloteoNo ratings yet
- Property: Concept/Qualities Classifications Importance of ClassificationDocument19 pagesProperty: Concept/Qualities Classifications Importance of ClassificationZen DanielNo ratings yet
- Bar Prep - Outline - Civ Pro - ShortDocument16 pagesBar Prep - Outline - Civ Pro - ShortAnonymous Cbr8Vr2SX100% (4)
- Estate & Donors TaxationDocument7 pagesEstate & Donors TaxationDaphnie BoloNo ratings yet
- Property: Concept/Qualities Classifications Importance of ClassificationDocument20 pagesProperty: Concept/Qualities Classifications Importance of ClassificationMJNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Transfer and Business Tax and Basic Concept of Succession and Will (Philippines)Document16 pagesIntroduction To Transfer and Business Tax and Basic Concept of Succession and Will (Philippines)Randy Delumen100% (1)
- PROP TABLES ABANO Complete PDFDocument26 pagesPROP TABLES ABANO Complete PDFLeizl A. VillapandoNo ratings yet
- Property: Concept/Qualities Classifications Importance of ClassificationDocument26 pagesProperty: Concept/Qualities Classifications Importance of ClassificationQueenie BoadoNo ratings yet
- Estate Tax LectureDocument7 pagesEstate Tax LectureVanilyn LaresmaNo ratings yet
- Lecture - Estate TaxationDocument11 pagesLecture - Estate TaxationRaz Jisryl0% (1)
- ET2Document5 pagesET2Mary Joy CabilNo ratings yet
- Review Notes on Estate and Gift TaxationDocument44 pagesReview Notes on Estate and Gift TaxationadsleeNo ratings yet
- Estate Donors Taxation 1Document8 pagesEstate Donors Taxation 1Benjamin dela Cruz Cailao IIINo ratings yet
- Gross Estate - Part 1 (Properties Included in Gross Estate) (Philippines)Document28 pagesGross Estate - Part 1 (Properties Included in Gross Estate) (Philippines)Randy DelumenNo ratings yet
- Gross Estate Decedent's Gross EstateDocument1 pageGross Estate Decedent's Gross EstateHazel Joy DemaganteNo ratings yet
- Estate TaxationDocument8 pagesEstate TaxationUbalda AbuboNo ratings yet
- Estate Tax PDFDocument17 pagesEstate Tax PDFJL Baccol100% (1)
- Estate TaxationDocument8 pagesEstate TaxationVincent Fedrick G. LingaNo ratings yet
- EstateDocument6 pagesEstateMarjorie IsonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document24 pagesChapter 6Jhopel Casagnap EmanNo ratings yet
- SRADocument15 pagesSRAMarsha Lei Manabat Caringal50% (4)
- AirplaneNotes PDFDocument22 pagesAirplaneNotes PDFJhopel Casagnap EmanNo ratings yet
- Opposite Of:: Please Look at The Problems BelowDocument7 pagesOpposite Of:: Please Look at The Problems BelowElle Gio Casibang60% (5)
- Cannon Ball Review Part 4Document20 pagesCannon Ball Review Part 4Jhopel Casagnap Eman100% (1)
- Chapter 5Document18 pagesChapter 5Jhopel Casagnap EmanNo ratings yet
- IntroDocument1 pageIntroJhopel Casagnap EmanNo ratings yet
- AmktgmngtDocument148 pagesAmktgmngtJhopel Casagnap EmanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document18 pagesChapter 5Jhopel Casagnap EmanNo ratings yet
- Auditing Theory 250 QuestionsDocument39 pagesAuditing Theory 250 Questionsxxxxxxxxx75% (4)
- Chapter 4-Completing The Accounting Cycle: True/FalseDocument27 pagesChapter 4-Completing The Accounting Cycle: True/FalseJhopel Casagnap EmanNo ratings yet
- BudgetingDocument23 pagesBudgetingShiela Marquez100% (6)
- Chapter 4-Completing The Accounting Cycle: True/FalseDocument27 pagesChapter 4-Completing The Accounting Cycle: True/FalseJhopel Casagnap EmanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document22 pagesChapter 3Jhopel Casagnap EmanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document24 pagesChapter 1Jhopel Casagnap EmanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document22 pagesChapter 2Jhopel Casagnap EmanNo ratings yet
- #3 Financial Accounting and Reporting Test BankDocument32 pages#3 Financial Accounting and Reporting Test BankPatOcampo100% (5)
- Sales Reviewer PDFDocument25 pagesSales Reviewer PDFShaireen Prisco Rojas100% (2)
- Financial Accounting Theory Test Bank QuestionsDocument11 pagesFinancial Accounting Theory Test Bank QuestionsJimmyChaoNo ratings yet
- Management Come BackDocument68 pagesManagement Come BackJhopel Casagnap EmanNo ratings yet
- Obligations and ContractsDocument27 pagesObligations and ContractsMiGay Tan-Pelaez93% (80)
- Law 1 Obligations and Contracts ReviewDocument14 pagesLaw 1 Obligations and Contracts ReviewChristian Blanza Lleva100% (3)
- Tackling Psa by SGV PDFDocument40 pagesTackling Psa by SGV PDFJhopel Casagnap EmanNo ratings yet
- UN 2016 Expenditure SummaryDocument12 pagesUN 2016 Expenditure SummaryJhopel Casagnap EmanNo ratings yet
- BIR Chart of AccountsDocument152 pagesBIR Chart of AccountsIanBesinaNo ratings yet
- Sped Holiday (Original Receipt) United Nation (Original Receipt) Foundation Day (Original Receipt)Document3 pagesSped Holiday (Original Receipt) United Nation (Original Receipt) Foundation Day (Original Receipt)Jhopel Casagnap EmanNo ratings yet
- Government Accounting Manual For NGAsDocument27 pagesGovernment Accounting Manual For NGAsIvy Michelle Habagat0% (2)
- The PPSAS and The Revised Chart of Accounts: Tools To Enhance Accountability and Transparency in Financial ReportingDocument98 pagesThe PPSAS and The Revised Chart of Accounts: Tools To Enhance Accountability and Transparency in Financial ReportingJhopel Casagnap EmanNo ratings yet
- Guide to the NEW GOVERNMENT ACCOUNTING SYSTEMDocument6 pagesGuide to the NEW GOVERNMENT ACCOUNTING SYSTEMCarlota Nicolas Villaroman100% (1)
- SIWES Report Example For Civil Engineering StudentDocument46 pagesSIWES Report Example For Civil Engineering Studentolayinkar30No ratings yet
- Military Railway Unit Histories Held at MHIDocument6 pagesMilitary Railway Unit Histories Held at MHINancyNo ratings yet
- Book Two - 2da. EdiciónDocument216 pagesBook Two - 2da. EdiciónJhoselainys PachecoNo ratings yet
- 59 - 1006 - CTP-Final - 20200718 PDFDocument11 pages59 - 1006 - CTP-Final - 20200718 PDFshubh.icai0090No ratings yet
- HW3Document3 pagesHW3Noviyanti Tri Maretta Sagala0% (1)
- CONFLICT ManagementDocument56 pagesCONFLICT ManagementAhmer KhanNo ratings yet
- Mint Delhi 13-12-2022Document18 pagesMint Delhi 13-12-2022Ayush sethNo ratings yet
- Feb 22-Additional CasesDocument27 pagesFeb 22-Additional CasesYodh Jamin OngNo ratings yet
- Chirala, Andhra PradeshDocument7 pagesChirala, Andhra PradeshRam KumarNo ratings yet
- Pike River Case StudyDocument7 pagesPike River Case StudyGale HawthorneNo ratings yet
- Ethical Leadership Karen May P. UrlandaDocument8 pagesEthical Leadership Karen May P. UrlandaKaren May UrlandaNo ratings yet
- Quality Risk ManagementDocument29 pagesQuality Risk ManagementmmmmmNo ratings yet
- FZ16 9B 1KD2 (Patada) PDFDocument62 pagesFZ16 9B 1KD2 (Patada) PDFPanthukalathil Ram100% (1)
- I-Parcel User GuideDocument57 pagesI-Parcel User GuideBrian GrayNo ratings yet
- Literature Review 5Document4 pagesLiterature Review 5api-463653994No ratings yet
- De Thi Thu THPT Quoc Gia Mon Tieng Anh Truong THPT Hai An Hai Phong Nam 2015Document10 pagesDe Thi Thu THPT Quoc Gia Mon Tieng Anh Truong THPT Hai An Hai Phong Nam 2015nguyen ngaNo ratings yet
- Coupled Mode TheoryDocument5 pagesCoupled Mode TheoryRahul RoyNo ratings yet
- ApudDocument53 pagesApudlatifahNo ratings yet
- Characteristics: Wheels Alloy Aluminium Magnesium Heat ConductionDocument4 pagesCharacteristics: Wheels Alloy Aluminium Magnesium Heat ConductionJv CruzeNo ratings yet
- Hilti X-HVB SpecsDocument4 pagesHilti X-HVB SpecsvjekosimNo ratings yet
- SQL-Problems Solutions PDFDocument11 pagesSQL-Problems Solutions PDFManpreet Singh100% (1)
- MMPX 403 Parametr ListDocument30 pagesMMPX 403 Parametr ListOğuz Kağan ÖkdemNo ratings yet
- Checklist PBL 2Document3 pagesChecklist PBL 2Hazrina AwangNo ratings yet
- Hillingdon Health Visiting ServiceDocument12 pagesHillingdon Health Visiting ServiceAnnikaNo ratings yet
- High Frequency Voltage Probe Non-Availability on GeMDocument2 pagesHigh Frequency Voltage Probe Non-Availability on GeMjudeNo ratings yet
- Lecture7 PDFDocument5 pagesLecture7 PDFrashidNo ratings yet
- Continuous torque monitoring improves predictive maintenanceDocument13 pagesContinuous torque monitoring improves predictive maintenancemlouredocasadoNo ratings yet
- Capran+980 CM en PDFDocument1 pageCapran+980 CM en PDFtino taufiqul hafizhNo ratings yet
- Nammo Bulletin 2014Document13 pagesNammo Bulletin 2014Dmitry Karpov0% (1)
- MT R 108 000 0 000000-0 DHHS B eDocument68 pagesMT R 108 000 0 000000-0 DHHS B eRafal WojciechowskiNo ratings yet