Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pressure Buildup Analysis Techniques For Oil Wells ....................................................................... 153
Uploaded by
سحر سلامتیانOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Pressure Buildup Analysis Techniques For Oil Wells ....................................................................... 153
Uploaded by
سحر سلامتیانCopyright:
Available Formats
Contents ix
4.4 Late Transient Analysis Bounded (Developed)
Reservoirs .............................................................. 111
4.5 Semi-steady-state Analysis Reservoir Limit
Test ........................................................................ 115
4.6 Two-rate Flow Test Analysis ................................. 121
4.7 Variable-rate Flow Tests ....................................... 129
4.8 Multi-rate Flow Test Analysis ................................ 137
4.9 Drawdown Rate Normalization Methods .............. 146
4.10 Summary ............................................................... 150
References ......................................................................... 151
Additional Reading ............................................................. 151
5. Pressure Buildup Analysis Techniques for Oil
Wells ....................................................................... 153
5.1 Introduction ............................................................ 153
5.2 Ideal Pressure Buildup Test .................................. 153
5.3 Actual Buildup Tests Infinite Reservoir .............. 156
5.4 Pressure Buildup Test Analysis in Infinite-acting
Reservoir ............................................................... 157
5.5 Pressure Buildup Testing Methods for Finite
(Bounded) Reservoir ............................................. 176
5.6 Multiphase Buildup Test Analysis ......................... 194
5.7 Afterflow Analysis Using Russels Technique ....... 199
5.8 Pressure Buildup Tests Preceded by Two
Different Flow Rates .............................................. 201
5.9 Variable-rate Pressure Buildup Analysis ............... 206
5.10 Multi-phase, Multi-rate Buildup Analysis ............... 210
5.11 Rate Normalization Techniques and Procedures
(Pressure Buildup Data) ........................................ 214
5.12 Summary ............................................................... 231
References and Additional Reading .................................. 232
This page has been reformatted by Knovel to provide easier navigation.
x Contents
6. Original and Average Reservoir Pressure
Estimation Methods .............................................. 234
6.1 Introduction ............................................................ 234
6.2 Original Reservoir Pressure in Infinite
Reservoirs .............................................................. 234
6.3 Estimating Average and Initial Reservoir
Pressure ................................................................ 235
6.4 Estimating Constant Pressure at Aquifer in
Water-drive Reservoirs .......................................... 244
6.5 Summary ............................................................... 252
References and Additional Reading .................................. 252
7. Well Testing Methods for Naturally Fractured
Reservoirs .............................................................. 254
7.1 Introduction ............................................................ 254
7.2 Identification of Natural Fractures ......................... 254
7.3 Characteristics of Naturally Fractured
Reservoirs .............................................................. 255
7.4 Typical Pressure Drawdown Behavior Curve
Shapes ................................................................... 255
7.5 Pressure Buildup Behavior Characteristics .......... 256
7.6 Well Test Interpretation Methods, Uses, and
Limitations .............................................................. 257
7.7 Buildup Analysis Techniques for Tight Reservoir
Matrix ..................................................................... 270
7.8 Interpretation of Interference Tests in Matrix and
Fractured Reservoirs ............................................. 275
7.9 Horizontal Well Pressure Behavior Curve
Shapes ................................................................... 278
7.10 Horizontal Well Production Forecasting Dual-
porosity Reservoir .................................................. 284
This page has been reformatted by Knovel to provide easier navigation.
Contents xi
7.11 Summary ............................................................... 285
References and Additional Reading .................................. 285
8. Fundamentals of Type Curve Matching
Methods for Oil Wells ............................................ 287
8.1 Introduction ............................................................ 287
8.2 Application to Conventional Tests ......................... 287
8.3 Fracture Type Curve Matching Techniques .......... 313
8.4 Type Curves Horizontal Fractured Oil Wells ...... 329
8.5 Summary ............................................................... 337
References and Additional Reading .................................. 338
9. Flow Regime Identification and Analysis Using
Special Methods .................................................... 339
9.1 Introduction ............................................................ 339
9.2 Fracture Linear Flow Period .................................. 339
9.3 Bilinear Flow .......................................................... 341
9.4 Formation Linear Flow ........................................... 345
9.5 Pseudo-radial Flow ................................................ 346
9.6 Type Curve Matching Methods ............................. 346
9.7 Summary ............................................................... 356
References ......................................................................... 357
Additional Reading ............................................................. 357
10. Application of Pressure Derivative in Oil Well
Test Analysis ......................................................... 359
10.1 Introduction ............................................................ 359
10.2 Pressure Derivative Applications in Well Test
Analysis .................................................................. 359
10.3 Pressure Derivative Analysis Methods ................. 359
10.4 Fractured Reservoir Systems ................................ 365
This page has been reformatted by Knovel to provide easier navigation.
xii Contents
10.5 Pressure Derivative Trends for Other Common
Flow Regimes ........................................................ 370
10.6 Summary ............................................................... 371
References ......................................................................... 371
Additional Reading ............................................................. 371
11. Massive Hydraulic-fractured Oil Well Behavior
Analysis .................................................................. 372
11.1 Introduction ............................................................ 372
11.2 Methods of Evaluating MHF Oil Wells .................. 372
11.3 Analyzing Infinite Flow Capacity Fractures ........... 372
11.4 Analyzing Finite Flow Capacity Fractures ............. 373
11.5 Estimating Formation Characteristics of Finite
Conductivity Fractures ........................................... 378
11.6 Pretreatment Testing of Hydraulically Fractured
Candidate .............................................................. 384
11.7 Summary ............................................................... 385
References ......................................................................... 386
Additional Reading ............................................................. 386
12. Drill-stem Testing Methods .................................. 387
12.1 Introduction ............................................................ 387
12.2 DST Equipment and Operational Procedures ...... 388
12.3 Recommended Flow and Shut-in Time for Drill-
stem Tests ............................................................. 389
12.4 Troubleshooting DST Pressure Charts ................. 390
12.5 Checking Validity and Consistency of Reporting
DST Data ............................................................... 391
12.6 Estimation of Average Flow Rate .......................... 392
12.7 DST Analysis Methods, Uses, and Limitations ..... 396
12.8 Wireline Formation Test Data Evaluation ............. 414
This page has been reformatted by Knovel to provide easier navigation.
Contents xiii
12.9 Summary ............................................................... 427
References and Additional Reading .................................. 427
13. Interference and Pulse Test Analysis Methods .... 429
13.1 Introduction ............................................................ 429
13.2 Interference Test Analysis Techniques ................. 429
13.3 Analysis of Pulse Test Pressure Response .......... 434
13.4 Vertical Pulse Test Design and Analysis
Methods ................................................................. 445
13.5 Design and Analysis of Unequal Pulses ............... 448
13.6 Summary ............................................................... 462
References ......................................................................... 462
Additional Reading ............................................................. 462
14. Injection Well Transient Testing and Analysis ... 463
14.1 Introduction ............................................................ 463
14.2 Injectivity Test Analysis Methods .......................... 463
14.3 Pressure Fall-off Test Analysis Methods .............. 475
14.4 Two-rate Injectivity Test Analysis .......................... 492
14.5 Step-rate Injectivity Testing Technique ................. 496
14.6 Summary ............................................................... 502
References ......................................................................... 502
Additional Reading ............................................................. 503
15. Well Testing Methods in Multilayered Oil
Reservoir Systems ................................................ 504
15.1 Introduction ............................................................ 504
15.2 Identification of Layered Oil Reservoir Systems ... 504
15.3 Analyzing Pressure Behavior in Multilayered
Systems ................................................................. 505
This page has been reformatted by Knovel to provide easier navigation.
xiv Contents
15.4 Concept of Reservoir Layer Fracture
Conductivity ........................................................... 509
15.5 Pressure Production Performance Response
Equations ............................................................... 510
15.6 Investigating Degree of Communication and
Type of Crossflow .................................................. 512
15.7 Pressure Buildup Characteristics in Layered
Reservoir Systems ................................................ 512
15.8 Pressure Analysis Methods for Oil Wells
Producing Commingled Zones .............................. 514
15.9 Factors Affecting Multilayered Reservoir
Performance .......................................................... 520
15.10 Economic Aspects of Interlayer Crossflow ............ 521
15.11 Summary ............................................................... 521
References and Additional Reading .................................. 521
16. Pressure Analysis Methods in Heterogeneous
Oil Reservoir Systems .......................................... 523
16.1 Introduction ............................................................ 523
16.2 Effect of Pressure on Rock Properties .................. 523
16.3 Major Causes of Heterogeneities .......................... 524
16.4 Pressure Responses near No Flow Boundaries ... 524
16.5 Effect of Hydraulic Diffusivity on Reservoir
Behavior ................................................................. 534
16.6 Simple Procedures and Guidelines to Estimate
Reservoir Heterogeneity Properties ...................... 536
16.7 General Approach to Estimate Fracture Trends
or Heterogeneity .................................................... 536
16.8 Determination of Reservoir Parameters and
Fracture Orientations ............................................. 536
This page has been reformatted by Knovel to provide easier navigation.
Contents xv
16.9 Defining Reservoir Heterogeneity by Multiple-
well Tests ............................................................... 539
16.10 Method for Calculating Fracture Orientation ......... 555
16.11 Estimating Two-dimensional Permeability with
Vertical Interference Testing ................................. 556
16.12 Application of Pulse Tests to Describe Reservoir
Heterogeneity ........................................................ 561
16.13 Validity of Various Models and Steps Used to
Obtain Reservoir Description ................................ 573
16.14 Summary ............................................................... 574
References and Additional Reading .................................. 574
Appendices
Appendix A: Conversion Factors between Unit Systems ........ 577
Appendix B: Correlation Tables and Dimensionless
Functions .............................................................. 585
References and Additional Reading ................ 594
Appendix C: Pressure Drop through Vertical, Inclined, and
Horizontal Oil Wells .............................................. 595
C.1 Hagedorn and Brown Method ................. 596
C.2 Beggs and Brill Method ........................... 602
References and Additional Reading ................ 606
Appendix D: Oil and Water PVT Properties and Correlation
Equations ............................................................. 607
D.1 Oil PVT Properties and Correlations ....... 608
D.2 Solution Gas-oil Ratio ............................. 612
D.3 Oil Formation Volume Factor .................. 613
D.4 Total Formation Volume Factor ............... 616
D.5 Oil Density .............................................. 616
D.6 Oil Viscosity ............................................ 618
D.7 Oil Compressibility .................................. 622
This page has been reformatted by Knovel to provide easier navigation.
xvi Contents
D.8 Reservoir Rock Properties ...................... 623
D.9 Reservoir PVT Water Properties ............. 624
References and Additional Reading ................ 639
Nomenclature ................................................................ 640
Bibliography .................................................................. 645
Index ............................................................................... 661
This page has been reformatted by Knovel to provide easier navigation.
Chapter 1
Introduction
1.1 Role of Oil Well Tests and Information
in Petroleum Industry
Oil well test analysis is a branch of reservoir engineering. Information
obtained from flow and pressure transient tests about in situ reservoir condi-
tions are important to determining the productive capacity of a reservoir.
Pressure transient analysis also yields estimates of the average reservoir
pressure. The reservoir engineer must have sufficient information about the
condition and characteristics of reservoir/well to adequately analyze reservoir
performance and to forecast future production under various modes of opera-
tion. The production engineer must know the condition of production and
injection wells to persuade the best possible performance from the reservoir.
Pressures are the most valuable and useful data in reservoir engineering.
Directly or indirectly, they enter into all phases of reservoir engineering
calculations. Therefore accurate determination of reservoir parameters is
very important. In general, oil well test analysis is conducted to meet the
following objectives:
To evaluate well condition and reservoir characterization;
To obtain reservoir parameters for reservoir description;
To determine whether all the drilled length of oil well is also a pro-
ducing zone;
To estimate skin factor or drilling- and completion-related damage to an
oil well. Based upon the magnitude of the damage, a decision regarding
well stimulation can be made.
1.2 History of Oil Well Testing and Uses
of Oil Well Tests
Two monographs1'3 and numerous additional oil well test analysis
technical papers have been published. Those papers have extended the
scope of oil well test analysis, publicized many new problems, provided
solutions for previously unsolved problems, and changed the approach to
some phases of oil well test analysis. Thus, it is appropriate to provide an
updated handbook dealing with advances in oil well test analysis in a
manner that presents an up-to-date treatment of the state of the art. This
book presents popular pressure transient test analysis techniques and
estimates of the range of applicability. More than 100 actual field exam-
ples illustrate most analysis techniques. Figure 1-1 shows uses of well
tests.
1.3 Oil Well Test Data Acquisition, Analysis,
and Management
Throughout the life of an oil well, from exploration to abandonment, a
sufficient amount of well test data are collected to describe well condition
and behavior. It should be emphasized that the multidisciplinary profes-
sionals need to work as an integrated team to develop and implement the
well test data management program.
Efficient Oil Well Test Analysis Programs
Initial bottom-hole pressure measurements should be made, preferably at
each well and at selected "Key Oil Wells" periodically. Key oil wells repre-
sent 25% of the total wells2. Reference 2 has also found that it is beneficial to
measure pressure in all wells at least every 2-3 years to aid in calibrating
reservoir models. It is essential to establish the specification of what and how
much well test data need to be gathered, and the procedure and frequency to
be followed. A logical, methodical, and sequential well test data acquisition
and analysis program is shown in Figure 1-2.
1.4 Selecting Oil Wells for Optimum
Stimulation Treatment
The key to determining whether or not a well is a good candidate for
stimulation treatment is diagnosing the well to find the cause for its low
productivity. Buildup, drawdown, or drill-stem tests, core analyses offset well
data, and other information can be used to accomplish this. After diagnosis,
the optimum well stimulation treatment, either small or massive hydraulic
You might also like
- Reed Multivariable CalculusDocument499 pagesReed Multivariable CalculusMrDubsterNo ratings yet
- Reservoir Organic Geochemistry: Processes and ApplicationsDocument3 pagesReservoir Organic Geochemistry: Processes and ApplicationsMiguel Angel Vidal Arango100% (1)
- Expro Meters Technology Introduction - Indonesia.01Document29 pagesExpro Meters Technology Introduction - Indonesia.01Dedi MaryonoNo ratings yet
- Python BookDocument445 pagesPython BookShreyas Kolhe100% (3)
- Conceptual Completions and Well Intervention Design ReportDocument138 pagesConceptual Completions and Well Intervention Design ReportIbama Mirilla100% (1)
- Development of Akkas Gas Field in IraqDocument33 pagesDevelopment of Akkas Gas Field in IraqDr. Wisam Al-Shalchi89% (9)
- Intro To Pore Pressure and Fracture GradientsDocument52 pagesIntro To Pore Pressure and Fracture GradientsLok Bahadur Rana100% (9)
- Multivariable CalculusDocument517 pagesMultivariable CalculusVincent Lin100% (4)
- JavaDocument323 pagesJavalala100% (1)
- Dam Foundation Grouting: Revised and Expanded EditionDocument10 pagesDam Foundation Grouting: Revised and Expanded EditionPaulo ZwierzikowskiNo ratings yet
- An Intuitive Introduction To Data Structures HeinoldDocument167 pagesAn Intuitive Introduction To Data Structures HeinoldJohn DripperNo ratings yet
- Sap Hana SQL Script Reference en PDFDocument138 pagesSap Hana SQL Script Reference en PDFBibiana PalacioNo ratings yet
- SHURMAN Multivariable CalculusDocument523 pagesSHURMAN Multivariable Calculusstevi2896No ratings yet
- Multivariable Calculus - J Shurman PDFDocument493 pagesMultivariable Calculus - J Shurman PDFjaviplay100% (2)
- Fine Pore Aeration SystemsDocument328 pagesFine Pore Aeration Systemsguzman_10100% (2)
- 10 Tricks For Doing Math Quickly in Your HeadDocument8 pages10 Tricks For Doing Math Quickly in Your Headسحر سلامتیانNo ratings yet
- WINPROPDocument296 pagesWINPROPEfrain Ramirez Chavez100% (2)
- Fundamentals of C++Document599 pagesFundamentals of C++Rahayu WilujengNo ratings yet
- PtolemyII DigitalV1 02 PDFDocument690 pagesPtolemyII DigitalV1 02 PDFAbdulbaki Aybakan50% (2)
- SEW Eurodrive K Series Gearmotor Catalog PDFDocument744 pagesSEW Eurodrive K Series Gearmotor Catalog PDFLoxodonta EcNo ratings yet
- Platform Interference in Wireless Systems: Models, Measurement, and MitigationFrom EverandPlatform Interference in Wireless Systems: Models, Measurement, and MitigationRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Financial Econometrics 2010-2011Document483 pagesFinancial Econometrics 2010-2011axelkokocur100% (1)
- LabView TutorialDocument288 pagesLabView TutorialotavarezNo ratings yet
- Multivariable CalculusDocument523 pagesMultivariable CalculusRajvardhan SharmaNo ratings yet
- Enthalpy PDFDocument119 pagesEnthalpy PDFEstuardo Javier Gan RodríguezNo ratings yet
- Underwater Tunnel PiercingDocument119 pagesUnderwater Tunnel PiercingChristopher Gallegos100% (1)
- 608e Design Pipe Systems Pumps 05 2012Document56 pages608e Design Pipe Systems Pumps 05 2012Freddy Virgo100% (1)
- Creel M EconometricsDocument479 pagesCreel M EconometricsTobias LuceroNo ratings yet
- Phaset 1Document235 pagesPhaset 1Francisco PerezNo ratings yet
- Applied-Hydrology-Ven-Te-Chow PART1Document32 pagesApplied-Hydrology-Ven-Te-Chow PART1Ikromi Second100% (1)
- UntitledDocument5 pagesUntitledThắng LưuNo ratings yet
- Advanced Petrophysics Manual v1.02 TOCDocument3 pagesAdvanced Petrophysics Manual v1.02 TOCfzi.rqi.2024No ratings yet
- 21F86B19A8DB56E1D38916B44B3369CDocument5 pages21F86B19A8DB56E1D38916B44B3369CAshraf SeragNo ratings yet
- Ix Xi: This Page Has Been Reformatted by Knovel To Provide Easier NavigationDocument3 pagesIx Xi: This Page Has Been Reformatted by Knovel To Provide Easier NavigationGetapo RaminNo ratings yet
- Applied StatisticsDocument361 pagesApplied StatisticsAnish N SharmaNo ratings yet
- VcalcDocument517 pagesVcalcMark Chadrick CruzNo ratings yet
- Bandaranayake, Samangi - Final PHD ThesisDocument274 pagesBandaranayake, Samangi - Final PHD ThesisBerry BéoNo ratings yet
- Full Download Ebook PDF Mind On Statistics Australian New Zealand 2nd PDFDocument41 pagesFull Download Ebook PDF Mind On Statistics Australian New Zealand 2nd PDFheather.philipps242100% (29)
- Chemical Engineering: Fluid MechanicsDocument15 pagesChemical Engineering: Fluid MechanicsPratyush singhNo ratings yet
- Time Series and Its ApplicationsDocument6 pagesTime Series and Its ApplicationsRicardo Loureiro SoaresNo ratings yet
- 1 Basic ConceptsDocument7 pages1 Basic Conceptsanon_824763156No ratings yet
- Experimental Investigation of Tube Rupture Under Boiler Dynamic Operating Conditions (Mossaedyousid Alawwad Id 199656100) Dec 2013Document152 pagesExperimental Investigation of Tube Rupture Under Boiler Dynamic Operating Conditions (Mossaedyousid Alawwad Id 199656100) Dec 2013rajanarsu100% (1)
- Asymptotic Theory of Statistics and Probability: Anirban DasguptaDocument15 pagesAsymptotic Theory of Statistics and Probability: Anirban DasguptaIlham Ait LakhyarNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Definition of Dimensioning and Tolerancing PrinciplesDocument3 pagesMathematical Definition of Dimensioning and Tolerancing Principlessaravana pandianNo ratings yet
- 28642 論文Document173 pages28642 論文javierzmorNo ratings yet
- Annex4 Pacific Bluefin Assmt Report 2014-June1-Final-PostingDocument121 pagesAnnex4 Pacific Bluefin Assmt Report 2014-June1-Final-PostingPhuong Anh LeNo ratings yet
- Multivariable Calculus: Jerry Shurman Reed CollegeDocument499 pagesMultivariable Calculus: Jerry Shurman Reed CollegeLynn Hollenbeck BreindelNo ratings yet
- Eugene de Villiers PHD 2006Document375 pagesEugene de Villiers PHD 2006Arindam SenNo ratings yet
- 105 2Document17 pages105 2Diego TobrNo ratings yet
- Col10241 PDFDocument288 pagesCol10241 PDFMaricela FreireNo ratings yet
- Antonios Vytiniotis Master Thesis 2009 PDFDocument184 pagesAntonios Vytiniotis Master Thesis 2009 PDFAshishBastolaNo ratings yet
- SAP HANA SQL Script Reference en PDFDocument126 pagesSAP HANA SQL Script Reference en PDFrajuasapNo ratings yet
- Progcpp PDFDocument638 pagesProgcpp PDFHaley PachecoNo ratings yet
- Realizability Theory for Continuous Linear SystemsFrom EverandRealizability Theory for Continuous Linear SystemsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Emilio J. Castilla 2007 Dynamic Analysis in Social Sciences PDFDocument403 pagesEmilio J. Castilla 2007 Dynamic Analysis in Social Sciences PDFDoina AlbescuNo ratings yet
- R Applied StatisticsDocument457 pagesR Applied StatisticsFelipe Chacón HoppeNo ratings yet
- Learn R For Applied StatisticsDocument457 pagesLearn R For Applied StatisticsyasortyNo ratings yet
- SQL Script Reference SP09Document130 pagesSQL Script Reference SP09Yakub ShahNo ratings yet
- VII Ix X: This Page Has Been Reformatted by Knovel To Provide Easier NavigationDocument9 pagesVII Ix X: This Page Has Been Reformatted by Knovel To Provide Easier NavigationShawn LearnNo ratings yet
- Ross SheldonDocument2 pagesRoss SheldonJ Madhansharma JeyarajNo ratings yet
- 49E9442272D388D055FAC88F7E7163ADocument6 pages49E9442272D388D055FAC88F7E7163AVitor OliveiraNo ratings yet
- GetDP Reference ManualDocument152 pagesGetDP Reference ManualositisNo ratings yet
- Smart Nanocarriers Bearing Docetaxel for Improved Chemotherapy CancerFrom EverandSmart Nanocarriers Bearing Docetaxel for Improved Chemotherapy CancerNo ratings yet
- Retention and Selectivity in Liquid Chromatography: Prediction, Standardisation and Phase ComparisonsFrom EverandRetention and Selectivity in Liquid Chromatography: Prediction, Standardisation and Phase ComparisonsNo ratings yet
- It Probably Does Not MatterDocument34 pagesIt Probably Does Not Matterسحر سلامتیانNo ratings yet
- We Have Included ADocument27 pagesWe Have Included Aسحر سلامتیانNo ratings yet
- Practice Exercises: Verbs Meaning Show'Document76 pagesPractice Exercises: Verbs Meaning Show'سحر سلامتیانNo ratings yet
- Testing The Entry TechniqueDocument24 pagesTesting The Entry Techniqueسحر سلامتیانNo ratings yet
- Invert ScaleDocument14 pagesInvert Scaleسحر سلامتیانNo ratings yet
- The WithDocument12 pagesThe Withسحر سلامتیانNo ratings yet
- DifficultiesDocument23 pagesDifficultiesسحر سلامتیانNo ratings yet
- ChaudhriDocument10 pagesChaudhriسحر سلامتیانNo ratings yet
- Evaluating SumsDocument83 pagesEvaluating Sumsسحر سلامتیانNo ratings yet
- 035 BADA 2 6 User ManualDocument92 pages035 BADA 2 6 User Manualسحر سلامتیانNo ratings yet
- 017 BADA 3 5 User ManualDocument103 pages017 BADA 3 5 User Manualسحر سلامتیانNo ratings yet
- 1 Book of SamuelDocument82 pages1 Book of Samueljames52No ratings yet
- Reservoir BedDocument14 pagesReservoir Bedسحر سلامتیانNo ratings yet
- Fact Sheet Enhanced Oil Recovery FinalDocument4 pagesFact Sheet Enhanced Oil Recovery FinalAsyriNo ratings yet
- Bleed Pressure FromDocument19 pagesBleed Pressure Fromسحر سلامتیانNo ratings yet
- How To Ensure H2S Safety On Offshore Rigs - Drilling ContractorDocument10 pagesHow To Ensure H2S Safety On Offshore Rigs - Drilling Contractorسحر سلامتیانNo ratings yet
- Prior To Reservoir Fill-Up-Unit Mobility RatioDocument10 pagesPrior To Reservoir Fill-Up-Unit Mobility Ratioسحر سلامتیانNo ratings yet
- دعای مشلول - متن و ترجمه استاد انصاریان - صوتیDocument5 pagesدعای مشلول - متن و ترجمه استاد انصاریان - صوتیسحر سلامتیانNo ratings yet
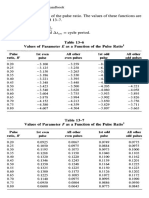
- Table 13-6 Values of Parameter E As A Function of The Pulse RatioDocument10 pagesTable 13-6 Values of Parameter E As A Function of The Pulse Ratioسحر سلامتیانNo ratings yet
- Table 13-6 Values of Parameter E As A Function of The Pulse RatioDocument10 pagesTable 13-6 Values of Parameter E As A Function of The Pulse Ratioسحر سلامتیانNo ratings yet
- End of Straight Line: D Versus (TDocument10 pagesEnd of Straight Line: D Versus (Tسحر سلامتیانNo ratings yet
- Table 13-6 Values of Parameter E As A Function of The Pulse RatioDocument10 pagesTable 13-6 Values of Parameter E As A Function of The Pulse Ratioسحر سلامتیانNo ratings yet
- End of Straight Line: D Versus (TDocument10 pagesEnd of Straight Line: D Versus (Tسحر سلامتیانNo ratings yet
- ChaudhriDocument10 pagesChaudhriسحر سلامتیانNo ratings yet
- Using The Following Equation:: Example 13-1 Analyzing Interference Test Using Type Curve MatchingDocument10 pagesUsing The Following Equation:: Example 13-1 Analyzing Interference Test Using Type Curve Matchingسحر سلامتیانNo ratings yet
- ChaudhriDocument10 pagesChaudhriسحر سلامتیانNo ratings yet
- ChaudhriDocument10 pagesChaudhriسحر سلامتیانNo ratings yet
- T, Maximum Time at The: Beginning of Linear FlowDocument10 pagesT, Maximum Time at The: Beginning of Linear Flowسحر سلامتیانNo ratings yet
- XF, Is Based On The Assumption That The Well Was Producing in The InfiniteDocument10 pagesXF, Is Based On The Assumption That The Well Was Producing in The Infiniteسحر سلامتیانNo ratings yet
- Deep Neural Network Application For 4D Seismic Inversion To Changes Inpressure and Saturation Optimizing The Use of Synthetic TrainingDocument22 pagesDeep Neural Network Application For 4D Seismic Inversion To Changes Inpressure and Saturation Optimizing The Use of Synthetic TrainingGuillermo GarzonNo ratings yet
- Omar Al-Saif: Slugging in Large Diameter Pipelines: Field Measurements, Experiments and SimulationDocument405 pagesOmar Al-Saif: Slugging in Large Diameter Pipelines: Field Measurements, Experiments and SimulationDiarista Thoma SaputraNo ratings yet
- SPE 108665 HP/HT Gas-Condensate Well Testing For Shell's Onyx SW ProspectDocument26 pagesSPE 108665 HP/HT Gas-Condensate Well Testing For Shell's Onyx SW ProspectTheNourEldenNo ratings yet
- Image Logging: Maha Ali Haider GY20F18Document26 pagesImage Logging: Maha Ali Haider GY20F18sher afganNo ratings yet
- Schedule Oral PDFDocument1 pageSchedule Oral PDFDewa Made Raditya MNo ratings yet
- Overview of Gas Resources 2018Document31 pagesOverview of Gas Resources 2018Akib ImtihanNo ratings yet
- Ohlins ForkDocument12 pagesOhlins ForkVinicius Luis Lopes100% (1)
- Gas Well Production Optimization Using Dynamic Nodal AnalysisDocument169 pagesGas Well Production Optimization Using Dynamic Nodal AnalysisSimon Chukwuka Ogbuji50% (2)
- Chapter 3 - Well Test Analysis Formulas and CalcuDocument30 pagesChapter 3 - Well Test Analysis Formulas and CalcuCynthia AgredaNo ratings yet
- Baram Delta PDFDocument43 pagesBaram Delta PDFYTF RystadNo ratings yet
- A Nodal Approach For Applying Systems Analysis To The Flowing and Artificial Lift Oil or Gas WellDocument2 pagesA Nodal Approach For Applying Systems Analysis To The Flowing and Artificial Lift Oil or Gas WellKaro MárquezNo ratings yet
- Optimization Drilling Parameters Enhances Horizontal DrilliDocument7 pagesOptimization Drilling Parameters Enhances Horizontal DrilliYuga Agung PratamaNo ratings yet
- Gce Marking Scheme: Geology AS/AdvancedDocument13 pagesGce Marking Scheme: Geology AS/AdvancedEhmedagaNo ratings yet
- Production EngineeringDocument6 pagesProduction EngineeringRAVINNo ratings yet
- For Impes With AsphalteneDocument11 pagesFor Impes With AsphalteneDavid ReyesNo ratings yet
- PETE 323 Syllabus Spring 2018Document4 pagesPETE 323 Syllabus Spring 2018Luke JajouNo ratings yet
- Lufkin Plunger Lift CatalogDocument18 pagesLufkin Plunger Lift CatalogBassem BalghouthiNo ratings yet
- Ryder Scott ReservesDocument8 pagesRyder Scott Reservesdah7542No ratings yet
- Oilfield Basics: For New Starts/traineesDocument49 pagesOilfield Basics: For New Starts/traineesEnJian HuNo ratings yet
- 400 Bad Request 400 Bad Request Nginx/1.2.9Document9 pages400 Bad Request 400 Bad Request Nginx/1.2.9Amar BenAmar0% (1)
- An Experimental Study of AcidizingDocument11 pagesAn Experimental Study of Acidizinggigi17No ratings yet
- JOT Spring 2011 AramcoDocument76 pagesJOT Spring 2011 AramcoHerry Suhartomo100% (1)
- Azadegan VadoodDocument100 pagesAzadegan VadoodadeeyoNo ratings yet