Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Steam Power Plant
Uploaded by
Cherry Obias0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
27 views2 pagessteam power plant
Original Title
steam power plant
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentsteam power plant
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
27 views2 pagesSteam Power Plant
Uploaded by
Cherry Obiassteam power plant
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
Thermal power plants help almost half of the world's power demand
They use water as the working fluid
Today's thermal power plants are capable to run under great efficiency by conforming to precise
environmental standards
In this video we will see how a coal-based thermal power plant achieves this in a detailed step-by-
step manner
By turning the shaft of this generator we will be able to generate electricity
The generator derives motion from a steam turbine the heart of the power plant
In order to turn steam turbine, you have to supply a high pressure and high temperature steam at
the inlet of the turbine
As the turbine absorbs energy from the high-energy fluid its pressure and temperature drop
toward the outlet
You can take a closer look at the uniquely shaped steam turbine rotor blades
High capacity power plant often use different stages of steam turbines such as high pressure
turbine
Intermediate pressure turbine and low pressure turbine
So now we have met our objective, we have produced electricity from the generator
If we can bring the low pressure and low temperature steam back to their original states
Which were of a much higher pressure and temperature we can repeat the process
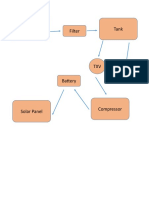
The first step is to raise the pressure
You can use a compressor for this purpose
But compressing steam is a highly energy intensive process and such a power plant will not be
efficient at all
The easy way is to convert the steam into liquid and boost the pressure
For this purpose we'll introduce condenser heat exchangers
Which sit beneath the low pressure turbine
In the condenser a stream of cold water flows through the tubes
The steam rejects heat to this liquid stream and became condensed
Now we can use the pump to increase the pressure of this feed water
Typically multi-stages centrifugal pumping is used for this purpose
That way the pressure will revert to its original state
The next task is to bring the temperature back to its original value
For this purpose heat is added to the exit of the pump with the help of a boiler
High capacity power plants generally use a type of boiler called a "water tube boiler"
Pulverized coal is then burnt inside boiler
The incoming water initially passes through any economizer session
Here the water will capture energy from the flue gas
The water flow straight down-comer
And then through water walls, where transforms into steam
The pure steam is separated at a steam drum
Now the working fluid is back to its original state
High pressure and high temperature
This steam can be fed back into the steam turbine
And the cycle can be repeated over and over again for continuous power production
But a power plant working on this basic Rankine cycle will have a very low efficiency and a low
capacity
We can increase the performance of the power plant considerably with the help of a few simple
techniques
In case of super heating even after the liquid has been converted into steam even more heat is
added
And with that the steam becomes super-heated
The higher the temperature of the steam the more efficient the cycle
Just remember the Carnots theorem of maximum thermal efficiency possible
But the steam turbine material will not withstand temperatures of more than 600 degrees Celsius
So super heating is limited to the threshold
The temperature of the steam decreases as it flows along the rows of the blade
Consequently a great way to increase the
Efficiency of the power plant is to add more heat after the first turbine stage
This is known as reheating and it will
Increase the temperature of the steam
Again leading to a high power output and greater efficiency
The low pressure side of the power plan are prone to suck the atmospheric air
Even with sophisticated ceiling arrangements
The dissolved gases in the feed water will spoil the boiler material over time
To remove these dissolved gases and open ,feed water heater is introduced
Hot steam from the turbine is mixed into the feed water
Steam bubbles so generated will absorb the dissolved gases
The mixing also preheats the feed water which helps improve the efficiency of the power plant to
an even greater extent
All these techniques make the modern power plant work under an efficiency range of forty to forty-
five percent
Now we'll take a look at how heat addition
And heat rejection are executed in an actual power plant
The cold liquid is supplied at the condenser with the help of a cooling tower
The heated up water from the condenser are rid is sprayed in the cooling tower which induces a
natural air draft and the sprayed water loses heat
This is how a colder liquid is always provided at the condenser inlet
At a heat addition side the burning coal produces many pollutants
We cannot release these pollutants directly into the atmosphere
So before transferring them to a stack the exhaust gases cleaned in an electro static
precipitator
The ESP uses plates with high voltage static electricity to absorb the pollutant particles
We hope that we've given you new insights into the inner workings of thermal power plants
You might also like
- ThermodynamicsDocument29 pagesThermodynamicsCherry ObiasNo ratings yet
- SchemDocument1 pageSchemCherry ObiasNo ratings yet
- New ShitsssDocument5 pagesNew ShitsssCherry ObiasNo ratings yet
- Efficiency Testing of Air Conditioning SystemDocument14 pagesEfficiency Testing of Air Conditioning SystemCherry Obias100% (1)
- Probability and Statistics: Presented By: Cruzena, Lone Christiansen F. Ramos, Mhariell CDocument55 pagesProbability and Statistics: Presented By: Cruzena, Lone Christiansen F. Ramos, Mhariell CCherry ObiasNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration ComputationDocument1 pageRefrigeration ComputationCherry ObiasNo ratings yet
- Types Of: Presented By: Arlvin C. Armada Florentino R. Babao Elpidio BelilaDocument20 pagesTypes Of: Presented By: Arlvin C. Armada Florentino R. Babao Elpidio BelilaCherry ObiasNo ratings yet
- Activity No. 8: DryersDocument19 pagesActivity No. 8: DryersCherry ObiasNo ratings yet
- GROUP 3 Questions Solved Problems in Gas Turbine and Geothermal Power PlantDocument62 pagesGROUP 3 Questions Solved Problems in Gas Turbine and Geothermal Power PlantCherry Obias0% (1)
- 50 Terms About Diesel Power Plant: Manuel S. Enverga Univesity Foundation College of EngineeringDocument5 pages50 Terms About Diesel Power Plant: Manuel S. Enverga Univesity Foundation College of EngineeringCherry ObiasNo ratings yet
- BiogasDocument14 pagesBiogasCherry ObiasNo ratings yet
- Nuclear TermsDocument14 pagesNuclear TermsCherry ObiasNo ratings yet
- Ignacio, Fernand Lui B. Generoso, John Michael IDocument18 pagesIgnacio, Fernand Lui B. Generoso, John Michael IAnonymous aWxiNE7w100% (1)
- MINI ICE PLANT EFFICIENCYDocument40 pagesMINI ICE PLANT EFFICIENCYCherry Obias100% (1)
- ReferencesDocument2 pagesReferencesCherry ObiasNo ratings yet
- Civil Service Exam Complete Reviewer Philippines 2017Document46 pagesCivil Service Exam Complete Reviewer Philippines 2017JJ Torres84% (434)
- Harmonically Excitation VibrationDocument17 pagesHarmonically Excitation VibrationCherry ObiasNo ratings yet
- Drying Process Ppt. AmenDocument18 pagesDrying Process Ppt. AmenCherry ObiasNo ratings yet
- Nuclear TermsDocument14 pagesNuclear TermsCherry ObiasNo ratings yet
- Ind. Processes FinalDocument41 pagesInd. Processes FinalCherry ObiasNo ratings yet
- Design ConsiderationsDocument18 pagesDesign ConsiderationsCherry ObiasNo ratings yet
- Methods and Equipment for Separating SolidsDocument19 pagesMethods and Equipment for Separating SolidsCherry ObiasNo ratings yet
- Project Study Critic Paper FormDocument2 pagesProject Study Critic Paper FormCherry ObiasNo ratings yet
- ETEEAP (Transfromer)Document13 pagesETEEAP (Transfromer)Cherry ObiasNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration System: Group 3Document12 pagesRefrigeration System: Group 3Cherry ObiasNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Engineering LawDocument20 pagesMechanical Engineering Lawnepaulo100% (1)
- Cegielski 110 X 2.000 - 1985Document2 pagesCegielski 110 X 2.000 - 1985Cherry ObiasNo ratings yet
- Cooling System Report TodayDocument14 pagesCooling System Report TodayCherry ObiasNo ratings yet
- Feed Pump ReportDocument10 pagesFeed Pump ReportCherry ObiasNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5784)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (72)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Lecture - 3Document28 pagesLecture - 3hassan baradaNo ratings yet
- VSSG/VSG Compressor: For Natural Gas and Process Gas ApplicationsDocument8 pagesVSSG/VSG Compressor: For Natural Gas and Process Gas ApplicationsCarlos Roberto TamarizNo ratings yet
- Formalin Plant Training: Nse Polymer SDN BHDDocument13 pagesFormalin Plant Training: Nse Polymer SDN BHDMario_othman100% (1)
- Centrifugal Compressor P&ID GuideDocument4 pagesCentrifugal Compressor P&ID Guidenaveenbaskaran1989100% (1)
- Vacuum Manhole Test of New Sanitary Sewer ManholesDocument2 pagesVacuum Manhole Test of New Sanitary Sewer ManholesMahmoud GaberNo ratings yet
- Stability of Floating BodiesDocument2 pagesStability of Floating Bodiescielo_cetd3670100% (1)
- Data Sheet BPH 60 250.40 T PDFDocument3 pagesData Sheet BPH 60 250.40 T PDFzajednosexNo ratings yet
- AQT MSV 1 Suavizador Manual UnlockedDocument8 pagesAQT MSV 1 Suavizador Manual UnlockedEdgar CastroNo ratings yet
- Section 12 - Compressed Air System - Group 12Document3 pagesSection 12 - Compressed Air System - Group 12Miodrag HuberNo ratings yet
- Compressor Oils: Compressor Oils Are Fluids Used For Lubrication of Moving Metal Parts of Gas (Air) CompressorsDocument3 pagesCompressor Oils: Compressor Oils Are Fluids Used For Lubrication of Moving Metal Parts of Gas (Air) Compressorsspyros_peiraiasNo ratings yet
- Updated Manual02Document254 pagesUpdated Manual02claytoncash100% (2)
- Cooling System WA600!6!22272Document15 pagesCooling System WA600!6!22272Ventsislav VenevNo ratings yet
- SPIE Oil & Gas Services: Pressure VesselsDocument56 pagesSPIE Oil & Gas Services: Pressure VesselsSadashiw PatilNo ratings yet
- 04 WreDocument6 pages04 WreDipuNo ratings yet
- Explosion Protection: ... ... Clearly ExplainedDocument1 pageExplosion Protection: ... ... Clearly ExplainedfrlNo ratings yet
- Types DistillationDocument81 pagesTypes Distillationhet sevakNo ratings yet
- PIPE Solving 2-5Document28 pagesPIPE Solving 2-5monNo ratings yet
- Saudi Arabian Oil Company: Instrument Specification Sheet - Hydrocarbon Liquid Sampling SystemsDocument1 pageSaudi Arabian Oil Company: Instrument Specification Sheet - Hydrocarbon Liquid Sampling SystemsMuhammad SalmanNo ratings yet
- Graspit Gcse Write OnDocument5 pagesGraspit Gcse Write OnKausar AhmedNo ratings yet
- 01 Installation of Ratio Flow ControllersDocument1 page01 Installation of Ratio Flow ControllersBrandon TrocNo ratings yet
- Air Liquide Presentation (Siddhartha Mukherjee) Rev 0Document48 pagesAir Liquide Presentation (Siddhartha Mukherjee) Rev 0sara25dec689288100% (1)
- gt2006 90105Document16 pagesgt2006 90105tadele10No ratings yet
- Vodonik Stenli MajerDocument17 pagesVodonik Stenli MajerSinišaNo ratings yet
- HVAC Equipment Guide for Heating and Cooling SystemsDocument16 pagesHVAC Equipment Guide for Heating and Cooling SystemsRahul Prajapati100% (1)
- 1st Law of Thermodynamics RK RajputDocument63 pages1st Law of Thermodynamics RK RajputKshitij PatleNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Worksheet 3 - PVTN Problems: P T V N Initial Final EffectDocument3 pagesUnit 2 Worksheet 3 - PVTN Problems: P T V N Initial Final EffectBillyNo ratings yet
- 31.PEAK Depressurization RATEDocument1 page31.PEAK Depressurization RATEDILIP MATALNo ratings yet
- Service Book Manual 191835 - NP 040420 Pedal W20EDocument17 pagesService Book Manual 191835 - NP 040420 Pedal W20ERicardo Bilbao100% (2)
- Interpret phase diagrams and heating cooling curvesDocument3 pagesInterpret phase diagrams and heating cooling curvesAyesha MhallawiNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2Document2 pagesExperiment 2Ir Fik TNo ratings yet