Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter Two Literature Review
Uploaded by
ifiok0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views4 pagesaaa
Original Title
Chapter Twoddd
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentaaa
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views4 pagesChapter Two Literature Review
Uploaded by
ifiokaaa
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
CHAPTER TWO
LITERATURE REVIEW
2.0 History of Biodiesel
2.1 Biodiesel
2.1.1 Quality and Standards
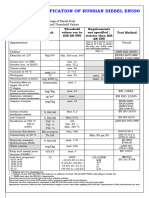
Table 1 presents a list of the most important biodiesel quality standards in the world
Country/Area Specifications Title
EU EN 14214 EN 14214 Automotive fuels -
Fatty acid methyl esters
(FAME) for diesel engines -
Requirements and test
methods
U.S. ASTM D 6751 ASTM D6751 - 11a Standard
Specification for Biodiesel
Fuel Blend Stock (B100) for
Middle Distillate Fuels
Table 1. Biodiesel standards
Property Test method Limits unit
min max
Ester content EN 14103 96.5 - % (m/m)
Density at 15C EN ISO 3675 860 900 kg/m3
Viscosity at 40C EN ISO 3104, ISO 3105 3.5 5.0 mm2/s
Flash point EN ISO 3679 120 - oC
Sulfur content EN ISO 20846 - 10.0 mg/kg
Earth alkali metals (Ca + EN 14538 - 5.0 mg/kg
Mg)
Cetane number EN ISO 5165 51 - -
Acid value EN 14104 - 0.5 mg KOH/g
Iodine value - 120 g I/100 g
Methanol content - 0.20 % (m/m)
Total glycerine EN 14105 - 0.25 % (m/m)
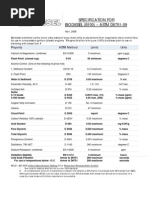
Table 3. European biodiesel standard (EN 14214)
Property Test method Limits unit
min max
Density at 15C EN ISO 3675 860 900 kg/m3
Kinematic Viscosity, at 40 D 445 1.9 6.0 mm2/s
C
Flash point D93 130 - oC
Earth alkali metals (Ca + EN 14538 - 5.0 ppm (g/g)
Mg)
Cetane number D 613 47 - -
Acid value D 664 - 0.05 mg KOH/g
Iodine value - 120 g I/100 g
Methanol content EN 14110 - 0.20 % (m/m)
Total glycerine D 6584 - 0.25 % (m/m)
Table 4. Biodiesel standard ASTM D6751 (United States)
2.1.2 Properties
2.1.3 Advantages and Disadvantages
2.2 Feedstock for Biodiesel Production
2.2.1 Characteristics of Feedstock
2.2.2 Palm Kernel Oil as a Feedstock
2.2.3 Methods to Convert Feedstock to Biodiesel
2.3 Transesterification
2.3.1 Selection of Alcohol for Transesterification
2.3.2 Acid versus Base Catalyzed Process
2.3.3 Homogenous versus Heterogeneous Catalyzed process
2.3.4 CaO Catalyzed process
2.4 Stages in biodiesel production
2.5 Parametric Effects on Alkali-catalyzed Transesterification Process
2.3.2.3 Effect of the catalyst type and concentration
2.3.2.4 Effect of the reaction temperature
You might also like
- Biodiesel Quality, Standards and PropertiesDocument27 pagesBiodiesel Quality, Standards and PropertiesNestor Armando Marin SolanoNo ratings yet
- Quality Standards For BiofuelsDocument28 pagesQuality Standards For BiofuelsSeph PasagNo ratings yet
- Biodiesel, Analytical Aspects: Florence LACOSTE, Lionel LAGARDERE Institut Des Corps Gras, Rue Monge, Pessac (France)Document9 pagesBiodiesel, Analytical Aspects: Florence LACOSTE, Lionel LAGARDERE Institut Des Corps Gras, Rue Monge, Pessac (France)BijayNo ratings yet
- Biodiesel Puri Fication and Upgrading Technologies: Hbateni@iastate - EduDocument44 pagesBiodiesel Puri Fication and Upgrading Technologies: Hbateni@iastate - EduRyan FebrinoNo ratings yet
- II StandardsDocument96 pagesII StandardsSami Onur VuralNo ratings yet
- Biodiesel Standards & PropertiesDocument6 pagesBiodiesel Standards & PropertiesMarta Lopez BerralNo ratings yet
- SF-43 Standard DieselDocument2 pagesSF-43 Standard DieselClaudiu PanaNo ratings yet
- 03 Blending PowerpointDocument70 pages03 Blending PowerpointNinhHoàngHải100% (4)
- Biodiesel Standards ComparisonDocument10 pagesBiodiesel Standards ComparisonAlfonso MartínezNo ratings yet
- Bio Diesel b20, En590-Biodiesel b5 SpecsDocument1 pageBio Diesel b20, En590-Biodiesel b5 Specsmohammed wajid100% (1)
- Euro 5 Diesel: Use: As Fuel For Diesel EnginesDocument2 pagesEuro 5 Diesel: Use: As Fuel For Diesel EnginesMahmoud NasrNo ratings yet
- UNIT II-CharacterizationDocument12 pagesUNIT II-CharacterizationSampanna AwareNo ratings yet
- Test Specifications For Biodiesel FuelDocument6 pagesTest Specifications For Biodiesel FuelYariela CedeñoNo ratings yet
- TDS GrilloDocument5 pagesTDS GrillomaxNo ratings yet
- Extracted Pages From A001064 - 12EDocument4 pagesExtracted Pages From A001064 - 12EAwais8888No ratings yet
- Biodeisel Using FuelProDocument4 pagesBiodeisel Using FuelProSylab InstrumentsNo ratings yet
- Bio Diesel b20, En590 b5 SpecificationsDocument1 pageBio Diesel b20, En590 b5 Specificationsmohammed wajidNo ratings yet
- 2862Document7 pages2862Yuvaraj RajNo ratings yet
- Crown Oil HVODocument1 pageCrown Oil HVOLuca CarazzoloNo ratings yet
- Biodiesel Spec SheetDocument3 pagesBiodiesel Spec SheetMohamed HalemNo ratings yet
- ASTM MethodsDocument9 pagesASTM MethodsLe Nguyen Phuc ThienNo ratings yet
- EN590 10ppm SPECIFICATIONS PEGASUS OILDocument1 pageEN590 10ppm SPECIFICATIONS PEGASUS OILSephiwe Mafilika100% (1)
- En 590Document1 pageEn 590anil divveNo ratings yet
- Biodiesel Emissions Champions Meeting InsightsDocument27 pagesBiodiesel Emissions Champions Meeting InsightsPablo Luis Pérez PostigoNo ratings yet
- AlchemyDocument5 pagesAlchemySylab InstrumentsNo ratings yet
- Base Oil Mixtures For Engine Oil: November 2005Document2 pagesBase Oil Mixtures For Engine Oil: November 2005Mohamed SalemNo ratings yet
- Category and Sub-Category of Certified Reference Material Test, Analysis, Measurement Method Measurement TechniqueDocument7 pagesCategory and Sub-Category of Certified Reference Material Test, Analysis, Measurement Method Measurement TechniqueJacekNo ratings yet
- ..... Biodiesel Production SystemDocument22 pages..... Biodiesel Production SystemmohamedNo ratings yet
- 4 Dissolved Gas AnalysisDocument55 pages4 Dissolved Gas AnalysisHoang Thanh VanNo ratings yet
- Ti-ExR04_PDSDocument2 pagesTi-ExR04_PDSBorja AzkargortaNo ratings yet
- MEG Product Certificate of AnalysisDocument1 pageMEG Product Certificate of AnalysisMahamNo ratings yet
- TDS Pennol 15W40 Ci-4 EngDocument1 pageTDS Pennol 15W40 Ci-4 EngDieudonné PounmbokNo ratings yet
- Appnote Icpoes 0013 enDocument8 pagesAppnote Icpoes 0013 enejvelazcorNo ratings yet
- Jet A-1 fuel standard specificationDocument3 pagesJet A-1 fuel standard specificationbj100% (1)
- Power Oil Data SheetDocument1 pagePower Oil Data SheetSreeram PanigrahiNo ratings yet
- Presentasi Oil Refinery Process Rev0Document36 pagesPresentasi Oil Refinery Process Rev0menner100% (1)
- Standard Specification July 9 2015Document10 pagesStandard Specification July 9 2015Ade Nur FauzanNo ratings yet
- 18 Apr 20 AFRICAN FLAMINGO (9802322) IFO 380 (RMG 380) : Report Date Vessel Fuel GradeDocument4 pages18 Apr 20 AFRICAN FLAMINGO (9802322) IFO 380 (RMG 380) : Report Date Vessel Fuel GradeNguyễn Hữu DũngNo ratings yet
- Liquefied Petroleum Gas - LPG: Composition: A Liquefied Propane-Butane Mixture Quality: Use: ShippingDocument1 pageLiquefied Petroleum Gas - LPG: Composition: A Liquefied Propane-Butane Mixture Quality: Use: ShippingKhai SpringNo ratings yet
- Maersk Olie Og Gas AS Esplanaden 50 DK-1263 Copenhagen K. Denmark Attn. Mr. L. AnderssonDocument21 pagesMaersk Olie Og Gas AS Esplanaden 50 DK-1263 Copenhagen K. Denmark Attn. Mr. L. AnderssonFatih FıratNo ratings yet
- 2 Specification Russian EN590Document1 page2 Specification Russian EN590Sephiwe MafilikaNo ratings yet
- Accredited Laboratory Scope of Testing for Saudi Aramco Total Refining and Petrochemical Company LabDocument6 pagesAccredited Laboratory Scope of Testing for Saudi Aramco Total Refining and Petrochemical Company LabSarbast KhoshnawNo ratings yet
- Determination of Total Organic Halides, Total Non-Methane Hydrocarbons, and Formaldehyde in Hydrogen Fuel by Gas Chromatography/Mass SpectrometryDocument8 pagesDetermination of Total Organic Halides, Total Non-Methane Hydrocarbons, and Formaldehyde in Hydrogen Fuel by Gas Chromatography/Mass SpectrometryasmaNo ratings yet
- Standard Spec FAME-EBTKE+PETDocument1 pageStandard Spec FAME-EBTKE+PETMuhamad Firmansyah Hermana PutraNo ratings yet
- Reolube Turbofluid 46Xc Fire-Resistant EHC Fluid: Data SheetDocument5 pagesReolube Turbofluid 46Xc Fire-Resistant EHC Fluid: Data SheetJicheng PiaoNo ratings yet
- ASTM-D95-13e1Document3 pagesASTM-D95-13e1EdwinNo ratings yet
- TDS StaSo Transformer Oil I Englisch 01-2013Document2 pagesTDS StaSo Transformer Oil I Englisch 01-2013Sreeram PanigrahiNo ratings yet
- Quality Control of Products in Petroleum RefiningDocument29 pagesQuality Control of Products in Petroleum RefiningAdrian RodriguezNo ratings yet
- FORZA 15W40 CK4 SN CONVENCIONAL App T50sa1Document4 pagesFORZA 15W40 CK4 SN CONVENCIONAL App T50sa1Herberth Joel Winter GarciaNo ratings yet
- Your local gas generation partner: Detailed hydrocarbon analysis in under 75 minutesDocument4 pagesYour local gas generation partner: Detailed hydrocarbon analysis in under 75 minutesAllif FathurrahmanNo ratings yet
- Petroleum Chemistry Labs PDFDocument54 pagesPetroleum Chemistry Labs PDFHassan AnwerNo ratings yet
- IMPCA Ref Spec 01 July 2021Document16 pagesIMPCA Ref Spec 01 July 2021Wayne GajadharNo ratings yet
- E - Norma Astm 6751 - 12 BiodieselDocument10 pagesE - Norma Astm 6751 - 12 BiodieselSamirNarvaezNo ratings yet
- Specification For BIODIESEL (B100) - ASTM D6751-09: Property ASTM Method Limits UnitsDocument1 pageSpecification For BIODIESEL (B100) - ASTM D6751-09: Property ASTM Method Limits UnitsIzzul HazimNo ratings yet
- Hydrogen Production TechnologiesFrom EverandHydrogen Production TechnologiesMehmet SankirNo ratings yet
- Biomass as a Sustainable Energy Source for the Future: Fundamentals of Conversion ProcessesFrom EverandBiomass as a Sustainable Energy Source for the Future: Fundamentals of Conversion ProcessesNo ratings yet
- Multiphase Reactor Engineering for Clean and Low-Carbon Energy ApplicationsFrom EverandMultiphase Reactor Engineering for Clean and Low-Carbon Energy ApplicationsYi ChengNo ratings yet
- Fossil Fuel Emissions Control Technologies: Stationary Heat and Power SystemsFrom EverandFossil Fuel Emissions Control Technologies: Stationary Heat and Power SystemsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Che323 Note Cooling Tower 3Document130 pagesChe323 Note Cooling Tower 3ifiokNo ratings yet
- Living in The Heart by Drunvalo MelchizedekDocument131 pagesLiving in The Heart by Drunvalo MelchizedekJasmina Tomic100% (2)
- Che 323 Note Heat ConductionDocument5 pagesChe 323 Note Heat ConductionifiokNo ratings yet
- Understanding and Developing Emotional Intelligence: Proposition 37Document11 pagesUnderstanding and Developing Emotional Intelligence: Proposition 37Arpita SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Che323 Note Cooling Tower 3Document130 pagesChe323 Note Cooling Tower 3ifiokNo ratings yet
- Life Is What You Make of It - CDRDocument68 pagesLife Is What You Make of It - CDRAdil Latif100% (1)
- Hypothetical Process PathsDocument9 pagesHypothetical Process Pathsifiok100% (1)
- Che323 Lecture 1 HumidificationDocument32 pagesChe323 Lecture 1 HumidificationifiokNo ratings yet
- ZeoliDocument11 pagesZeoliifiokNo ratings yet
- Che323 Lecture 2 Humidification Wet BulbDocument19 pagesChe323 Lecture 2 Humidification Wet Bulbifiok100% (1)
- Napoleon Hill - Pathway To Personal SuccessDocument23 pagesNapoleon Hill - Pathway To Personal SuccessMariana DiaconuNo ratings yet
- Napoleon Hill - Pathway To Personal SuccessDocument23 pagesNapoleon Hill - Pathway To Personal SuccessMariana DiaconuNo ratings yet
- Oil 1Document64 pagesOil 1VeiliLookNo ratings yet
- ChapterDocument3 pagesChapterifiokNo ratings yet
- SysteminfoDocument1 pageSysteminfoifiokNo ratings yet
- ChapterDocument4 pagesChapterifiokNo ratings yet
- Process Design Engineering-ManualDocument43 pagesProcess Design Engineering-ManualDan Costin100% (9)
- Article1380885145 HossainDocument9 pagesArticle1380885145 HossainifiokNo ratings yet
- HW 6 Solutions 2014Document10 pagesHW 6 Solutions 2014ifiokNo ratings yet
- file:///C:/Users/hon/Downloads/Documents/1 s2.0 S0959652618306565 Main PDFDocument2 pagesfile:///C:/Users/hon/Downloads/Documents/1 s2.0 S0959652618306565 Main PDFifiokNo ratings yet
- ChapterDocument3 pagesChapterifiokNo ratings yet
- Che 517 Test 1 20152016Document3 pagesChe 517 Test 1 20152016ifiok100% (1)
- MEK in School SecondDocument13 pagesMEK in School Secondifiok100% (1)
- SolidDocument3 pagesSolidifiokNo ratings yet
- Che520 Tutorial Questions Covenant UniversityDocument3 pagesChe520 Tutorial Questions Covenant UniversityifiokNo ratings yet
- ChE 517-Ind Haz Env Poll Mod IDocument10 pagesChE 517-Ind Haz Env Poll Mod IifiokNo ratings yet
- CHE 516 New CourseDocument64 pagesCHE 516 New Courseifiok0% (1)
- Group 3 Base Oil EditnoDocument13 pagesGroup 3 Base Oil EditnoifiokNo ratings yet
- Transfer FunctionDocument3 pagesTransfer FunctionifiokNo ratings yet
- Fuck The Population........ by IfyDocument11 pagesFuck The Population........ by IfyifiokNo ratings yet
- 5674 12871 1 PBDocument13 pages5674 12871 1 PBAri Fernando PanjaitanNo ratings yet
- Oil Palm Planting Materials: Mohd Din AmiruddinDocument45 pagesOil Palm Planting Materials: Mohd Din AmiruddinFirdaus Huzaide100% (1)
- Harvest Management of Oil Palm (Elaeis Guineensis Jacq..) in Pelantaran Agro Estate, Kota Waringin Timur, Center BorneoDocument8 pagesHarvest Management of Oil Palm (Elaeis Guineensis Jacq..) in Pelantaran Agro Estate, Kota Waringin Timur, Center BorneoNova OktarinaNo ratings yet
- 1 SM PDFDocument7 pages1 SM PDFLilis WenyNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 GSA NOA AcademyDocument14 pagesLecture 3 GSA NOA AcademyFazila umNo ratings yet
- Cassava Starch Bioplastic Water Absorption and Biodegradability CharacteristicsDocument16 pagesCassava Starch Bioplastic Water Absorption and Biodegradability CharacteristicsDEVIA FATAYA MIFTAHUL JANNAHNo ratings yet
- 20 04 How Much Biomass Do Bio Based Plastics Need BM PDFDocument2 pages20 04 How Much Biomass Do Bio Based Plastics Need BM PDFDiana Carolina Meza SepulvedaNo ratings yet
- Microbelift Technology For Anaerobic DigestorDocument15 pagesMicrobelift Technology For Anaerobic Digestordannlee74No ratings yet
- Sustainable BiofuelsDocument2 pagesSustainable BiofuelsEdzwan RedzaNo ratings yet
- Global overview of large biomass energy usersDocument75 pagesGlobal overview of large biomass energy usersmolierosNo ratings yet
- Afes MCQDocument4 pagesAfes MCQPrabhu Govind100% (1)
- Year of The Figh Against Corruption and Impunity"Document9 pagesYear of The Figh Against Corruption and Impunity"Nycoll Andreina Ortiz PardoNo ratings yet
- Esterifikasi Gliserol Menjadi Triasetin Menggunakan Zeolit AlamDocument7 pagesEsterifikasi Gliserol Menjadi Triasetin Menggunakan Zeolit AlamMhimyMiftahulMawaddahNo ratings yet
- 2013 List of China's GasfieldsDocument3 pages2013 List of China's GasfieldsarapublicationNo ratings yet
- Biofuels - Liquid, GaseousDocument41 pagesBiofuels - Liquid, Gaseousshafianik100% (1)
- EN 14214 Biodiesel StandardDocument2 pagesEN 14214 Biodiesel StandardsmsNo ratings yet
- Data Pabrik Kelapa Sawit (Kalbar)Document1 pageData Pabrik Kelapa Sawit (Kalbar)Global Asia BersamaNo ratings yet
- 2017 Summary of Oil Palm Suppliers in the PhilippinesDocument1 page2017 Summary of Oil Palm Suppliers in the PhilippinesShimmer CrossbonesNo ratings yet
- EFFICIENT BIODIESEL PRODUCTIONDocument9 pagesEFFICIENT BIODIESEL PRODUCTIONmuhamad ilhamNo ratings yet
- Progress 3000 - Karta KatalogowaDocument2 pagesProgress 3000 - Karta Katalogowamelanz123No ratings yet
- Transesterifikasi Menggunakan NaOHDocument12 pagesTransesterifikasi Menggunakan NaOHDanar AdityaNo ratings yet
- Biodiesel Potential of Algae SpeciesDocument3 pagesBiodiesel Potential of Algae SpeciesRiskahMappileNo ratings yet
- Peluang Dan Tantangan Di Industri Kelapa SawitDocument25 pagesPeluang Dan Tantangan Di Industri Kelapa SawitikaNo ratings yet
- Fast Pyrolysis of Biomass A Handbook Volume 2 PDFDocument2 pagesFast Pyrolysis of Biomass A Handbook Volume 2 PDFMatthew0% (1)
- Uso Da Espectrofotometria UV-Vis para DiferenciarDocument6 pagesUso Da Espectrofotometria UV-Vis para DiferenciarCarlos Aguilar TorresNo ratings yet
- DAFTAR PUSTAKA PenelitianDocument2 pagesDAFTAR PUSTAKA PenelitianPhen Mien LikNo ratings yet
- Biofuel PresentationDocument37 pagesBiofuel PresentationshahzebNo ratings yet
- KEBUN SAFARI RIAU 2022 July Oil Palm Harvesting Estate Crop Summary - CHECKLISTDocument2 pagesKEBUN SAFARI RIAU 2022 July Oil Palm Harvesting Estate Crop Summary - CHECKLISTFerdiansyah Dwi SastraNo ratings yet
- World Bioufuels MapDocument1 pageWorld Bioufuels MapSugarcaneBlogNo ratings yet
- Bio Refineries in Europe PDFDocument8 pagesBio Refineries in Europe PDFNikhil VermaNo ratings yet