Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Linear Motion Guide
Uploaded by
Puven JrOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Linear Motion Guide
Uploaded by
Puven JrCopyright:
Available Formats
DEFINE LINEAR
MOTION
UNIFORM & NON-
UNIFORM MOTION
DESCRIBE DISTANCE,
DISPLACEMENT,SPEED,
VELOCITY,AVERAGE
SPEED & VELOCITY,
ACCELERATION AND
DECELERATION
PROBLEM SOLVING
OF LINEAR MOTION
-USING FORMULA
-USING GRAPH
JMSK || Jabatan Matematik, Sains & Komputer Page 19
DBS 1012: ENGINEERING SCIENCE
LINEAR NON- LINEAR
MOTION MOTION
DEFINITION DEFINITION
A car moves at a A car moves at a bent
straight road road
EXAMPLE EXAMPLE
JMSK || Jabatan Matematik, Sains & Komputer Page 20
DBS 1012: ENGINEERING SCIENCE
EXERCISE
V (m/s)
DEFINE LINEAR MOTION b)
1. Define Linear motion
.
.................................
t (s)
..
2. Define Non-Linear motion
.
5. Classify each of the following
.................................
situation is linear motion or non-
linear motion.
3. State THREE (3) examples of linear
a) A passenger on a moving
motion and non-linear motion each.
escalator
Linear Motion:
..
..
b) Luqman running a 100m race
..
Non-Linear Motion:
..
c) The earth orbiting the sun
..
..
d) A lorry is travelling along a
4. Determine whether the graph is
straight road at 15m/s
linear motion or non-linear motion
graph
a)
V (m/s) e) Wandy and her family
enjoying a roller coaster ride
...
f) Sufi enjoy playing a swing at
t (s) playground
...
..
JMSK || Jabatan Matematik, Sains & Komputer Page 21
DBS 1012: ENGINEERING SCIENCE
DIFFERENCE
UNIFORM NON-UNIFORM
MOTION MOTION
DEFINITION DEFINITION
Situation Situation
Graph Graph
EXAMPLE EXAMPLE
Time in Time in
0 5 10 15 20 0 5 10 15 20
Seconds Seconds
Distance Distance
covered in 0 10 20 30 40 covered in 0 2 15 27 48
metres metres
The car travels in equal The car travels in equal times
distances and in equal intervals but not in equal intervals of
of time distance
JMSK || Jabatan Matematik, Sains & Komputer Page 22
DBS 1012: ENGINEERING SCIENCE
EXERCISE
UNIFORM AND NON-MOTION
1. Define Uniform motion
b) d (m)
.
.................................
2. Define Non-Uniform motion
. t (s)
.................................
..
3. State TWO (2) examples of uniform d (m)
c)
motion and non-uniform motion each.
Uniform Motion:
.
..
. t (s)
..
..
Non-Uniform Motion:
. d (m)
d)
..
.
..
4. Determine whether the graph is t (s)
uniform motion or non-uniform
..
motion graph
a) d (m)
e)
V (m/s)
t (s)
t (s)
..
..
JMSK || Jabatan Matematik, Sains & Komputer Page 23
DBS 1012: ENGINEERING SCIENCE
DIFFERENCE
DISTANCE DISPLACEMENT
DEFINITION DEFINITION
DIAGRAM DIAGRAM
M
FORMULA FORMULA
QUANTITY QUANTITY
SIMILARITY
UNIT
JMSK || Jabatan Matematik, Sains & Komputer Page 24
DBS 1012: ENGINEERING SCIENCE
EXERCISE
DISTANCE AND DISPLACEMENT EXAMPLE
1. Give the definition of the followings: A C
B
5m 20m
a) Distance
Ali moves from point A to C through point
. B. Then, he turn back to point B and
................................. return back to point C. Determine:
a) The distance of the journey
b) The displacement of the journey
b) Displacement
Solution:
.
a) distance AC CB BC
.................................
(5 20) 20 20
65m
2. State THREE (3) differences
b) displacement AC CB BC
between distance and displacement. (5 20) 20 20
25m
DISTANCE DISPLACEMENT
1.
A B C D
5m 12m 3m
Auni drive from A to C and return
back to B. Then, she returns back to
D. Determine:
a) The distance of the journey
b) The displacement of the journey
JMSK || Jabatan Matematik, Sains & Komputer Page 25
DBS 1012: ENGINEERING SCIENCE
2. 4.
North ? East
10m
East 5m
South 15m 13m
A bird is flying 10m to the south and
then turns to the east about 15m
distance. Calculate:
A butterfly is flying to north about 5m
a) distance along the journey
and turn to east. If the displacement
b) displacement along the journey.
is 13m, how long the butterfly flying
from north to east.
3. 5. A girl leaves a History classroom
and walks 10m north to a drinking
fountain. Then she turns and walks
30m south to an Art classroom.
What is the total displacement and
direction from the History classroom
An object moves from point A through B, to the Art classroom?
C, D, E and stops at point F.
a) Find the displacement from A to F.
b) Find the distance from point A to D.
JMSK || Jabatan Matematik, Sains & Komputer Page 26
DBS 1012: ENGINEERING SCIENCE
DIFFERENCE
SPEED VELOCITY
DEFINITION DEFINITION
FORMULA FORMULA
QUANTITY QUANTITY
SIMILARITY
UNIT
JMSK || Jabatan Matematik, Sains & Komputer Page 27
DBS 1012: ENGINEERING SCIENCE
EXERCISE EXAMPLE
SPEED AND VELOCITY
A B C
1. Give the definition of the followings: 3m 10m
a) Speed Nini drive from point A to C through point
. B. Then, he turn back to point B and
return back to point C. If the total journey
................................. takes 3.5minutes,determine:
a) The speed of the car
b) Velocity b) The velocity of the car
.
Solution:
.................................
a) distance AC CB BC
(3 10) 10 10
2. State THREE (3) differences
33m
between speed and velocity.
dis tan ce
speed
time
SPEED VELOCITY 33
3.5 60
0.16m / s
b) displacement AC CB BC
(3 10) 10 10
13m
displacemn et
velocity
time
13
3.5 60
0.06m / s
JMSK || Jabatan Matematik, Sains & Komputer Page 28
DBS 1012: ENGINEERING SCIENCE
1. 2. A bird is flying from west to east
for 0.02km in 5minutes. It then
A B C D
4m 10m 2m turn to south for 0.04km in 14
Shira is driving from A to C and minutes. Calculate:
return back to B. Then, she returns a) The speed of the bird flying
back to D. Determine: from starting point to end
a) The speed of the car point
b) The velocity of the car b) The velocity of the bird flying
from starting point to end
(Given time taken is 20s) point if the time taken is 15
minutes
JMSK || Jabatan Matematik, Sains & Komputer Page 29
DBS 1012: ENGINEERING SCIENCE
3. 14km 5.
O P
A B C
5m 25m
5km
A lorry travel from point A to point
R Q C. The driver took 3 hours to
2km
Diagram above shows the path travel from point A to B and 4
travelled by Zara from O to R. If hours from point B to C. Find:
the journey take 20minutes, a) The velocity from A to B
calculate: b) The velocity from B to C
a) The speed of Zara in km/h
b) The velocity of Zara in km/h
6. Mira is driving a car with a
velocity of 120km/h. If she is
driving along a 35km journey,
calculate the time taken for the
whole journey in second.
4. Ravi runs for 100m in 1.2minutes.
How fast he run?
JMSK || Jabatan Matematik, Sains & Komputer Page 30
DBS 1012: ENGINEERING SCIENCE
DIFFERENCE
AVERAGE SPEED AVERAGE VELOCITY
DEFINITION DEFINITION
FORMULA FORMULA
QUANTITY QUANTITY
SIMILARITY
UNIT
JMSK || Jabatan Matematik, Sains & Komputer Page 31
DBS 1012: ENGINEERING SCIENCE
EXERCISE EXAMPLE
AVERAGE SPEED AND AVERAGE
VELOCITY B 12km C
1. Give the definition of the followings: 8km
a) Average Speed A D
.
................................. An object moves from A to D through B
and C as shown above in 35 minutes
and 40 seconds. Find:
b) Average Velocity
. a) The average speed of the object
................................. in m/s
b) The average velocity of the object
2. State THREE (3) differences in m/s
between average speed and Solution:
Time = (35 x 60) + 40
average velocity.
= 2140s
AVERAGE AVERAGE
a) Distance = AB + BC + CD
SPEED VELOCITY
= 8 + 12 + 8
= 28km 28000m
total distance
Average speed
total time
28000
2140
13.08m / s
b) Displacement = AD to the east
= 12km 12000m
total displacement
Average velocity
total time
12000
2140
5.61m / s
JMSK || Jabatan Matematik, Sains & Komputer Page 32
DBS 1012: ENGINEERING SCIENCE
1. 2.
R S T 5m
14m 3m
East
A helicopter moves along a line from South 12m
point R to S to T and then back to S A bird is flying 5m to the south and
again as shown above in half an then turns to the east about 12m
hour. Calculate: distance. If the time taken along the
a) The average speed of the journey is 3.2 minutes, calculate:
helicopter in km/h a) The average speed along the
b) The average velocity of the journey in m/s
helicopter in km/h b) The average velocity along the
journey in m/s
JMSK || Jabatan Matematik, Sains & Komputer Page 33
DBS 1012: ENGINEERING SCIENCE
3. 4. Fifi is driving from point X to point Y
21.5km
Klang in 4minutes. She takes 2minutes to
7.5km
rest at point Y and continues to point
Z about 5minutes. If the distance
Kuala
Lumpur
between point X to Y is 5m, and
point Y to Z is 7m, determine:
A car is travelling from Klang to a) The average speed from point X
Kuala Lumpur along a curve path to Z
as shown above. If it takes b) The average velocity from point X
30minutes travelling along a curve to Z
path and 12minutes travelling using
shortcut, calculate:
a) The average speed from Klang
to Kuala Lumpur
b) The average velocity from Klang
to Kuala Lumpur
JMSK || Jabatan Matematik, Sains & Komputer Page 34
DBS 1012: ENGINEERING SCIENCE
DIFFERENCE
ACCELERATION DECELERATION
DEFINITION DEFINITION
GRAPH GRAPH
VALUE VALUE
UNIT
SIMILARITY
QUANTITY
FORMULA
JMSK || Jabatan Matematik, Sains & Komputer Page 35
DBS 1012: ENGINEERING SCIENCE
EXERCISE EXAMPLE
ACCELERATION AND
DECELERATION
u = 65m/s
1. Give the definition of the followings:
a) Acceleration
v = 120m/s
.
1. A lorry moving with a constant
.................................
velocity of 65m/s increases its
velocity to 120m/s in 0.5minutes.
b) Deceleration
What is the acceleration of the lorry?
.
Solution:
.................................
Time,t = 0.5 x 60
2. State THREE (3) differences = 30s
between acceleration and vu
Accelerati on,a
deceleration. t
120 65
30
ACCELERATION DECELERATION 1.83ms 2
2. A lorry moving with a constant
velocity of 45m/s and finally stop
about 6minutes later. What is the
deceleration of the lorry?
Solution:
Time,t = 6 x 60
= 360s
vu
Accelerati on,a
t
0 45
360
0.13ms 2
JMSK || Jabatan Matematik, Sains & Komputer Page 36
DBS 1012: ENGINEERING SCIENCE
1. A van is starting to move from rest 4. Afiq is winning a 100m challenge
and accelerate to a velocity of tournament with a new record of
35m/s in 24s. What is the 8.5m/s2. If he starts to run and
acceleration of the van? accelerate to a velocity of 110m/s,
how long he takes to the finishing
line?
2. Didi is driving at velocity of 65m/s 5. A cyclist riding at a velocity of 34m/s
and slow down his car when the was applied a brakes with a uniform
traffic light turned red. If he takes 7s deceleration and stopped in 10s.
undergoing uniform deceleration Calculate his deceleration.
until it stop, determine the
acceleration of the car.
3. A car is undergoing uniform 6. A car starts from rest with a constant
deceleration about 35km/h in acceleration of 9.8m/s2. What is its
8minutes until it stop. Calculate the velocity after 7seconds later?
initial velocity of the car in m/s.
JMSK || Jabatan Matematik, Sains & Komputer Page 37
DBS 1012: ENGINEERING SCIENCE
USING
FORMULA
Smart Facts
When an object falls to earth freely (without any
other forces involved) the acceleration is
called acceleration due to gravity. It is often given
the symbol g or a.
JMSK || Jabatan Matematik, Sains & Komputer Page 38
DBS 1012: ENGINEERING SCIENCE
EXERCISE 1. A cheetah can accelerate from rest
PROBLEM SOLVING BY USING to 33m/s in 5.8s. Assuming constant
FORMULA acceleration, how far has the
cheetah run in this time?
LETS TRY!!! Fill in the blank:
Quantity Symbol Unit
ms-2
u
Time
m
Final velocity
Gravity
EXAMPLE 2. An object is starting from rest moves
with uniform acceleration of 4.2m/s2
A cat is running from a velocity of
for 6s. Find:
32m/s and accelerate to 7m/s2. What is
a) It velocity
the final velocity of cat after 10s?
b) It displacement
Solution:
u = 32m/s
a = 7m/s2
t = 10s
v=?
From the formula of linear motion;
vu
a
t
v 32
7
10
v 102m / s
JMSK || Jabatan Matematik, Sains & Komputer Page 39
DBS 1012: ENGINEERING SCIENCE
3. A rocket is moving with a constant EXAMPLE (Free Fall)
velocity of 2030m/s and accelerates
A coin is thrown upward until it reaches
uniformly at 12.3m/s2. Determine the a maximum height. If the initial velocity
velocity after 4 minutes. is 5.4m/s, determine:
a) The maximum height of the coin
b) The time taken
Solution:
u = 5.4m/s
v = 0m/s (reach maximum height)
a = -9.81m/s2
a) From the formula of linear motion;
v 2 u 2 2as
0 2 5.4 2 2(9.81)( s)
s 1.49m
4. A lorry is moving with a velocity of b) From the formula of linear motion;
15km/h and accelerates uniformly. 1 vu
s(u v)t a
After 1.2 minutes, the velocity 2 t
1 OR 0 5.4
increases to 55km/h. Calculate the 1.49 (5.4 0)t 9.81
2 t
total distance in that 1.2 minutes. t 0.55s t 0.55s
1. A ball is thrown straight upward from
the ground with initial velocity 76m/s.
How high does the ball rise?
JMSK || Jabatan Matematik, Sains & Komputer Page 40
DBS 1012: ENGINEERING SCIENCE
2. A ball at rest is thrown downward 4. A stone is started to drop into a deep
from a tree. If the final velocity when well and is heard to hit the water
it reach the ground is 12m/s, 0.11minutes after being dropped.
calculate: Determine the depth of the well.
a) the high of the tree
b) the time taken
3. A kangaroo is capable of jumping to 5. A feather is started to drop on the
a height of 165cm. Determine the moon from a height of 1.40 meters.
takeoff speed of the kangaroo. The acceleration of gravity on the
moon is 1.67 m/s2. Determine the
time for the feather to fall to the
surface of the moon.
JMSK || Jabatan Matematik, Sains & Komputer Page 41
DBS 1012: ENGINEERING SCIENCE
USING
GRAPH
VELOCITY TIME GRAPH
Smart Facts
Distance or displacement is
equal to area under the graph
JMSK || Jabatan Matematik, Sains & Komputer Page 42
DBS 1012: ENGINEERING SCIENCE
EXERCISE EXAMPLE
PROBLEM SOLVING BY USING
GRAPH
LETS TRY!!! Classify each of the
followings:
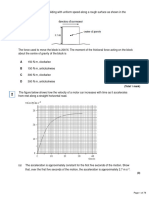
GRAPH DESCRIPTION From the graph above, calculate:
a) The acceleration
b) The deceleration
c) The total distance
Solution:
a) vu
a
t
12 6
10
0.6m. / s 2
b) vu
a
t
0 12
Sketch a graph based 9
LETS TRY!!!
1.33m. / s 2
on the information given.
c) Total distance:
A car moves at a constant velocity of
=
10m/s about 5s. It then accelerates his
car to a velocity of 25m/s in 8s. Finally,
he slows down the car and stop after 7s
later.
JMSK || Jabatan Matematik, Sains & Komputer Page 43
DBS 1012: ENGINEERING SCIENCE
1. 2. The diagram below shows the v-t
graph for a car.
v(ms-1)
X Y
25
Z
t(s)
O 4 18 22
From the graph above, calculate: a) What is the cars acceleration
in each of the time intervals
a) The acceleration OX, XY, and YZ?
b) The deceleration b) Calculate the distance when
c) The total distance the car moves at constant
velocity.
c) What is the total distance for
the whole journey?
JMSK || Jabatan Matematik, Sains & Komputer Page 44
DBS 1012: ENGINEERING SCIENCE
3. Diagram shows the v-t graph of a 4. Diagram shows the v-t graph of a
railway coach. Calculate: railway coach from A to D.
v(ms-1)
v(ms-1) 40 A
30 30 D
20
20
10 B C
10 t(s)
10
t(s) 7s
5 10 20 26 32 Calculate:
a) the total acceleration a) The acceleration of the coach.
b) the total distance when the
b) The distance travelled when the
coach moves at constant
coach is decelerating.
velocity
c) The total time taken for the whole
c) the total distance for the whole
AD journey if the total distance is
journey
1000 m.
JMSK || Jabatan Matematik, Sains & Komputer Page 45
DBS 1012: ENGINEERING SCIENCE
5. 6. The v-t graph of a particle moving
along straight line as shown.
5
Calculate the distance and
displacement travelled.
v(ms-1)
Given the acceleration at first 7s is 20
8.6m/s2, calculate:
t(s)
a) The maximum velocity can be 0
4 6 8 12
reach
-20
b) The total distance
7. The v-t graph in figure below shows
a particle starting from rest and
travelling east.
v(ms-1)
20
0 t(s)
8 18 22
-10
a) How long does the particle travel
towards the east?
b) How long does the particle travel
towards the west?
JMSK || Jabatan Matematik, Sains & Komputer Page 46
DBS 1012: ENGINEERING SCIENCE
8. Diagram shows a v-t graph. 9. A car is traveling from rest to a
Calculate: velocity of 22ms-1 about 8s. It then
moves at constant velocity along
V(m/s)
10s and start to slow down until it
x
stops 4s later.
16
a) Sketch the v-t graph.
8
b) Calculate the deceleration of
the car before it stops.
t(s)
5 y 12 18 c) Find the total distance of the
car
a) The value of x if the total
deceleration is -6.5ms-2.
b) The value of y if the distance
when the car moves at constant
velocity is 40m
c) The total distance traveled
JMSK || Jabatan Matematik, Sains & Komputer Page 47
DBS 1012: ENGINEERING SCIENCE
10. A lorry is travelling at constant 11. A car starting from rest accelerated
velocity of 20 ms-1 about 7s. The uniformly to 50 m/s over a period of
lorry then accelerates to a velocity 10 seconds. The car then
of 35 ms-1 about 10s and slows maintained the velocity for 20
down until it stops 9s later. seconds. The velocity is then
a) Sketch the v-t graph. reduced uniformly to 30 m/s in 10
b) Calculate the acceleration of seconds and finally brought to rest
the lorry after another further 10 seconds.
c) Find the total distance travelled. a) Sketch the v-t graph.
b) Calculate the acceleration for
the first 10 seconds.
c) Find the total distance travelled
by the car.
JMSK || Jabatan Matematik, Sains & Komputer Page 48
You might also like
- Modelling of Mechanical Systems: Structural ElementsFrom EverandModelling of Mechanical Systems: Structural ElementsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Physics Module Forces & MotionDocument87 pagesPhysics Module Forces & Motionnickphysics4927100% (1)
- Year 9 Forces TestDocument17 pagesYear 9 Forces Testaysha kamar halabiNo ratings yet
- Int Diff QsDocument20 pagesInt Diff QsarihantbuchchaNo ratings yet
- 2013 Mid Term Exam Term 3 Phy F0RM3 Mid2013Document15 pages2013 Mid Term Exam Term 3 Phy F0RM3 Mid2013Grey IzackNo ratings yet
- Billabong High School Physics Practice SheetDocument10 pagesBillabong High School Physics Practice SheetvarshatarateNo ratings yet
- Velocity Time GraphsDocument9 pagesVelocity Time GraphsChristineGarcesCondrillonNo ratings yet
- Measuring Coefficient of Static FrictionDocument12 pagesMeasuring Coefficient of Static Frictionsareena lawNo ratings yet
- mechanics practice questionsDocument79 pagesmechanics practice questionsryan sNo ratings yet
- Waves 1Document4 pagesWaves 1api-377518221No ratings yet
- Physics Unit 1 Questions 1Document13 pagesPhysics Unit 1 Questions 1panda bearNo ratings yet
- End of Term RevisionDocument127 pagesEnd of Term RevisionEsa FarhanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To SU (2) LQGDocument67 pagesIntroduction To SU (2) LQGpablomorosNo ratings yet
- Form 3 21. Linear Motion qDocument23 pagesForm 3 21. Linear Motion qjohnn1.jrugunaNo ratings yet
- Motion Along A Straight Line QPDocument8 pagesMotion Along A Straight Line QPadmaNo ratings yet
- Momentum 1 QPDocument18 pagesMomentum 1 QPtechnical videosNo ratings yet
- Mid - Exammination 2020Document9 pagesMid - Exammination 2020Siciid Jaamac DalmarNo ratings yet
- Physics principles and motion graph analysisDocument6 pagesPhysics principles and motion graph analysisRadia Khandaker ProvaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Motion Exam Question PackDocument49 pagesChapter 9 Motion Exam Question PackMariel AbadecioNo ratings yet
- Forces Revision Questions 1. Resistive Force.: Island School 1Document13 pagesForces Revision Questions 1. Resistive Force.: Island School 1Deepal PrasankaNo ratings yet
- Motion Along A Straight Line QPDocument8 pagesMotion Along A Straight Line QPSelina LINo ratings yet
- Dokumen - Pub Cambridge Senior Mathematics Mathematical Methods Vce Units 1 Amp 2 2nbsped 9781009110457 1009110454Document862 pagesDokumen - Pub Cambridge Senior Mathematics Mathematical Methods Vce Units 1 Amp 2 2nbsped 9781009110457 1009110454Willam100% (1)
- I. Section A Using The Following Words Complete The Sentences. (10 Marks)Document10 pagesI. Section A Using The Following Words Complete The Sentences. (10 Marks)DhanBahadurNo ratings yet
- PHY F3 PP2 ASSIGN Assignments - Form 3 - PhysicsDocument10 pagesPHY F3 PP2 ASSIGN Assignments - Form 3 - Physicsvkimemia5No ratings yet
- Physic PDFDocument4 pagesPhysic PDFNo PainNo ratings yet
- Form 2 Physics End of Term ExamDocument12 pagesForm 2 Physics End of Term ExamBenjamin mwanikiNo ratings yet
- End of Term 2 Exam MohamedDocument21 pagesEnd of Term 2 Exam MohamedDr. Mohamed AlhosaniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Force and Motion STUDENTS MODULEDocument44 pagesChapter 2 Force and Motion STUDENTS MODULEMohd Khairul Anuar100% (4)
- Waves in Geosciences 2023Document302 pagesWaves in Geosciences 2023frederic.bouchetteNo ratings yet
- Single Diffractiobn2009Document5 pagesSingle Diffractiobn2009Alex HeinNo ratings yet
- 3D Finite-Difference Time-Domain Modeling of Acoustic Wave Propagation Based On Domain DecompostionDocument32 pages3D Finite-Difference Time-Domain Modeling of Acoustic Wave Propagation Based On Domain DecompostionÇetin EekşiNo ratings yet
- Physics Pp2 ExamDocument13 pagesPhysics Pp2 ExambrinalodhiamboexecutiveNo ratings yet
- Physics P2 - SL FIrst Mid Term 2021 With MSDocument18 pagesPhysics P2 - SL FIrst Mid Term 2021 With MSAlvin YadavNo ratings yet
- Momentum 1 QPDocument16 pagesMomentum 1 QPKEVIN MARIONo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Force and Motion STUDENTS MODULEDocument44 pagesChapter 2 Force and Motion STUDENTS MODULEMuaz GannuNo ratings yet
- Structured Essay - (Part A) : Measurement InstrumentDocument6 pagesStructured Essay - (Part A) : Measurement InstrumentUnicorn WallermanNo ratings yet
- S.3 Term One Examinations 2023 PhysicsDocument11 pagesS.3 Term One Examinations 2023 PhysicsOwani Jimmy100% (1)
- 1foundation Forces and Their Effects Self Study QuestionsDocument44 pages1foundation Forces and Their Effects Self Study QuestionsGame HubNo ratings yet
- 9A Chapter 1 Exam Questions: Q1. A Car Travels Along A Very Busy RoadDocument7 pages9A Chapter 1 Exam Questions: Q1. A Car Travels Along A Very Busy RoadLynn El MasriNo ratings yet
- (2020) (Ardhuin F.) (Waves in Geosciences)Document278 pages(2020) (Ardhuin F.) (Waves in Geosciences)Jenny Lee PennyNo ratings yet
- Linear AlgebraDocument36 pagesLinear AlgebraLuis Alvarado AvalosNo ratings yet
- 9 Velocity Time GraphsDocument7 pages9 Velocity Time GraphskheyNo ratings yet
- CP2 Revision MatDocument1 pageCP2 Revision MatJaskirat MannNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Force and Motion STUDENTS MODULEDocument44 pagesChapter 2 Force and Motion STUDENTS MODULEAfiqah RoshidiNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes On Fluids May 2013 PDFDocument156 pagesLecture Notes On Fluids May 2013 PDFAniket BabutaNo ratings yet
- Chapter Thirty-Three Vertical Alignment: Bureau of Design and Environment ManualDocument88 pagesChapter Thirty-Three Vertical Alignment: Bureau of Design and Environment ManualSantosh RaiNo ratings yet
- Internship ReportDocument49 pagesInternship ReportŞevki SağlamNo ratings yet
- TUTORIAL 5.3 Reflection of WavesDocument3 pagesTUTORIAL 5.3 Reflection of WavesnurularissaNo ratings yet
- Acceleration 1 QPDocument13 pagesAcceleration 1 QPdeepheat_008No ratings yet
- CVNG1013 Exam Questions 2016 2017Document4 pagesCVNG1013 Exam Questions 2016 2017Lee RNo ratings yet
- Forces & Braking 3 QPDocument15 pagesForces & Braking 3 QPdeepheat_008No ratings yet
- Space-Time Processing for MIMO CommunicationsFrom EverandSpace-Time Processing for MIMO CommunicationsAlex GershmanNo ratings yet
- Disturbance rejection control for bipedal robot walkersFrom EverandDisturbance rejection control for bipedal robot walkersNo ratings yet
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2From EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Elliptic Partial Differential Equations and Quasiconformal Mappings in the Plane (PMS-48)From EverandElliptic Partial Differential Equations and Quasiconformal Mappings in the Plane (PMS-48)No ratings yet
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 3From EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 3Rating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Markov Processes and Applications: Algorithms, Networks, Genome and FinanceFrom EverandMarkov Processes and Applications: Algorithms, Networks, Genome and FinanceNo ratings yet
- 11.3b SoundDocument3 pages11.3b SoundWeteachNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Eight - Plane Motion of Rigid Bodies - Impulse Momentum MethodsDocument9 pagesTutorial Eight - Plane Motion of Rigid Bodies - Impulse Momentum MethodsShubham SharmaNo ratings yet
- Wave MechanicsDocument77 pagesWave MechanicsAlbasher SahibuddinNo ratings yet
- Engg Mechanics Ques BankDocument68 pagesEngg Mechanics Ques BankUtkalNo ratings yet
- Vector Mechanics For Engineers: Dynamics: Kinematics of ParticlesDocument99 pagesVector Mechanics For Engineers: Dynamics: Kinematics of ParticlesMike Raphy T. VerdonNo ratings yet
- Structural Dynamics Equations of MotionDocument3 pagesStructural Dynamics Equations of Motionarchan_daveNo ratings yet
- JEE Physics DPP Daily Practice ProblemsDocument182 pagesJEE Physics DPP Daily Practice Problemsnishchal SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Final Exam - Thermo Fluids Lab - 2013Document1 pageFinal Exam - Thermo Fluids Lab - 2013Siraj MohammedNo ratings yet
- Ch35F PDFDocument19 pagesCh35F PDFKazaValiShaikNo ratings yet
- Gyroscopic InstrumentsDocument23 pagesGyroscopic Instrumentsvinay100% (1)
- 1947levine - On The Radiation of Sound From An Unflanged Circular PipeDocument24 pages1947levine - On The Radiation of Sound From An Unflanged Circular PipeLudwig Edward Gaillard100% (1)
- Rocket Lab Report: Nate Voth Ames B2 Written For MR Hendricks's Physics Honors ClassDocument12 pagesRocket Lab Report: Nate Voth Ames B2 Written For MR Hendricks's Physics Honors Classapi-285896582No ratings yet
- Back2Basic v1 PDFDocument20 pagesBack2Basic v1 PDFBerry101No ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics: Learner's Module 2 (Module 2A, 2B, 2C & 2D) Bsed Science 1GDocument8 pagesFluid Mechanics: Learner's Module 2 (Module 2A, 2B, 2C & 2D) Bsed Science 1GCarlo Jay BasulNo ratings yet
- Fluids Course SummaryDocument9 pagesFluids Course SummaryTed DiehlNo ratings yet
- By H. L. Wong and J. E. Luco, Member, ASCEDocument14 pagesBy H. L. Wong and J. E. Luco, Member, ASCEPaulo Vinícius MartinsNo ratings yet
- Boundary Layer TheoryDocument2 pagesBoundary Layer TheoryHariz MiorNo ratings yet
- General Wave Properties 1 QPDocument13 pagesGeneral Wave Properties 1 QPMELODY CHENNo ratings yet
- GR 9 ICSE Final Exam Question Paper PhysicsDocument4 pagesGR 9 ICSE Final Exam Question Paper PhysicsanjalimenonNo ratings yet
- 02 Lecture PPT Huff Changes-1Document35 pages02 Lecture PPT Huff Changes-1api-225960274No ratings yet
- Advance Fluid Mechanics Lectures 7-8Document18 pagesAdvance Fluid Mechanics Lectures 7-8Khalid YousafNo ratings yet
- Turbomachinery Aerodynamics Prof. Bhaskar Roy Prof. A M Pradeep Department of Aerospace Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, BombayDocument29 pagesTurbomachinery Aerodynamics Prof. Bhaskar Roy Prof. A M Pradeep Department of Aerospace Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, BombayPradyumna Keshari NahakNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 & 2 - Introduction To Vibrations and Single DOF SystemsDocument86 pagesChapter 1 & 2 - Introduction To Vibrations and Single DOF SystemsMohamad Faiz TonyNo ratings yet
- Control 1n v2Document35 pagesControl 1n v2Leiser HartbeckNo ratings yet
- Frequency Wave Length Chart 2013Document1 pageFrequency Wave Length Chart 2013Robert QuattrociocchiNo ratings yet
- Basics of Turbomachinery BalanceDocument14 pagesBasics of Turbomachinery BalanceSuthan RNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Machines: Introduction to CamsDocument51 pagesMechanics of Machines: Introduction to CamsJustin IanNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics MCQDocument30 pagesEngineering Mechanics MCQjasonmani90100% (1)
- CH 2 Assignment 1Document2 pagesCH 2 Assignment 1Hassan Ali BhuttaNo ratings yet
- Waves in Pipes and StringsDocument28 pagesWaves in Pipes and StringsZhu ZhuNo ratings yet