Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CLOUD COMPUTING A PAPER PRESENTATION ON CLOUD COMPUTING
Uploaded by
Gonella NagamallikaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
CLOUD COMPUTING A PAPER PRESENTATION ON CLOUD COMPUTING
Uploaded by
Gonella NagamallikaCopyright:
Available Formats
A PAPER PRESENTATION
ON
CLOUD COMPUTING
AUTHORS:
Y.S.CHANDANA
Email:chandanabharadwajasa@gmail.com
V.S.B.L.LALITHA
Email: lalithavempati4@gmail.com
II YEAR ECE
SAGI RAMALRISHNAM RAJU ENGINEERING COLLEGE
BHIMAVARAM
West Godavari District
ABSTRACT:-Cloud computing is the use and software maintenance and support to the
of computing resources (hardware and cloud provider. This enables the business to
software) that are delivered as a service over reallocate IT operations costs away from
hardware/software spending and personnel
a network (typically the Internet). The name
expenses, towards meeting other IT goals. In
comes from the use of a cloud-shaped
addition, with applications hosted centrally,
symbol as an abstraction for the complex updates can be released without the need for
infrastructure it contains in system diagrams. users to install new software. One drawback
Cloud computing entrusts remote services of SaaS is that the users' data are stored on
with a user's data, software and the cloud providers server. As a result,
computation. there could be unauthorized access to the
data.
There are many types of public cloud
End users access cloud-
computing:
based applications through a web browser or
a light-weight desktop or mobile app while
Infrastructure as a service (IaaS)
the business software and user's data are
Platform as a service (PaaS)
stored on servers at a remote location.
Software as a service (SaaS) Proponents claim that cloud computing
Network as a service (NaaS) allows enterprises to get their applications
Storage as a service (STaaS) up and running faster, with improved
Security as a service (SECaaS) manageability and less maintenance, and
Data as a service (DaaS) enables IT to more rapidly adjust resources
Desktop as a service (DaaS - see above) to meet fluctuating and unpredictable
Database as a service (DBaaS) business demand.
Test environment as a service (TEaaS) Cloud computing relies on sharing of
API as a service (APIaaS) resources to achieve coherence
Backend as a service (BaaS) and economies of scale similar to
Integrated development environment as a utility (like the electricity grid) over a
a service (IDEaaS) network. At the foundation of cloud
Integration platform as a service computing is the broader concept
(IPaaS), see Cloud-based integration of converged infrastructure and shared
services.
In the business model using software as a
service, users are provided access to Characteristics
application software and databases. The
Cloud computing exhibits the following key
cloud providers manage the infrastructure
characteristics:
and platforms on which the applications run.
SaaS is sometimes referred to as on-
Agility improves with users' ability to
demand software and is usually priced on a
re-provision technological infrastructure
pay-per-use basis. SaaS providers generally
resources.
price applications using a subscription fee.
Application programming
Proponents claim that the SaaS allows a interface (API) accessibility to software
business the potential to reduce IT that enables machines to interact with
operational costs by outsourcing hardware cloud software in the same way the user
interface facilitates interaction between Peak-load capacity increases (users
humans and computers. Cloud
need not engineer for highest
computing systems typically use REST-
based APIs. possible load-levels)
Cost is claimed to be reduced and in a Utilisation and
public cloud delivery model capital efficiency improvements for
expenditure is converted to operational
systems that are often only 1020%
expenditure. This is purported to
lower barriers to entry, as infrastructure utilised.
is typically provided by a third-party and Reliability is improved if multiple
does not need to be purchased for one- redundant sites are used, which makes
time or infrequent intensive computing well-designed cloud computing suitable
tasks. Pricing on a utility computing for business continuity and disaster
basis is fine-grained with usage-based recovery.
options and fewer IT skills are required Scalability and elasticity via dynamic
for implementation (in-house). The e- ("on-demand") provisioning of resources
FISCAL project's state of the art on a fine-grained, self-service basis near
repository contains several articles real-time, without users having to
looking into cost aspects in more detail, engineer for peak loads.
most of them concluding that costs Performance is monitored, and
savings depend on the type of activities consistent and loosely coupled
supported and the type of infrastructure architectures are constructed using web
available in-house. services as the system interface.
Device and location Security could improve due to
independence enable users to access centralization of data, increased
systems using a web browser regardless security-focused resources, etc., but
of their location or what device they are concerns can persist about loss of
using (e.g., PC, mobile phone). As control over certain sensitive data, and
infrastructure is off-site (typically the lack of security for stored
provided by a third-party) and accessed kernels. Security is often as good as or
via the Internet, users can connect from better than other traditional systems, in
anywhere. part because providers are able to devote
Virtualization technology allows resources to solving security issues that
servers and storage devices to be shared many customers cannot
and utilization be increased. afford. However, the complexity of
Applications can be easily migrated security is greatly increased when data is
from one physical server to another. distributed over a wider area or greater
Multitenancy enables sharing of number of devices and in multi-tenant
resources and costs across a large pool systems that are being shared by
of users thus allowing for: unrelated users. In addition, user access
to security audit logs may be difficult or
Centralization of infrastructure in
impossible. Private cloud installations
locations with lower costs (such as are in part motivated by users' desire to
real estate, electricity, etc.) retain control over the infrastructure and
avoid losing control of information Measured service. Cloud systems
security. automatically control and optimize resource
Maintenance of cloud computing use by leveraging a metering capability at
applications is easier, because they do some level of abstraction appropriate to the
not need to be installed on each user's type of service (e.g., storage, processing,
computer and can be accessed from bandwidth, and active user accounts).
different places. Resource usage can be monitored,
controlled, and reported, providing
The National Institute of Standards and
transparency for both the provider and
Technology's definition of cloud computing
consumer of the utilized service.
identifies "five essential characteristics":
National Institute of Standards and
On-demand self-service. A consumer can Technology
unilaterally provision computing
capabilities, such as server time and network
storage, as needed automatically without Service models
requiring human interaction with each
Cloud computing providers offer their
service provider.
services according to three fundamental
Broad network access. Capabilities are models: infrastructure as a service (IaaS),
platform as a service (PaaS), and software as
available over the network and accessed
a service (SaaS) where IaaS is the most
through standard mechanisms that promote basic and each higher model abstracts from
use by heterogeneous thin or thick client the details of the lower models. In 2012
platforms (e.g., mobile phones, tablets, network as a service (NaaS) and
communication as a service (CaaS) were
laptops, and workstations).
officially included by ITU (International
Resource pooling. The providers computing Telecommunication Union) as part of the
resources are pooled to serve multiple basic cloud computing models, recognized
service categories of a telecommunication-
consumers using a multi-tenant model, with centric cloud ecosystem.
different physical and virtual resources
dynamically assigned and reassigned
according to consumer demand. ...
Rapid elasticity. Capabilities can be
elastically provisioned and released, in some
cases automatically, to scale rapidly outward
and inward commensurate with demand. To
the consumer, the capabilities available for
provisioning often appear to be unlimited
and can be appropriated in any quantity at
any time.
application software on the cloud
infrastructure. In this model, the cloud user
patches and maintains the operating systems
and the application software. Cloud
providers typically bill IaaS services on a
utility computing basis: cost reflects the
amount of resources allocated and
consumed.
Examples of IaaS providers include Amazon
CloudFormation, Amazon EC2, Windows
Azure Virtual Machines,DynDNS, Google
Compute Engine, HP
Cloud, iland, Joyent, Oracle Infrastructure as
a Service, Rackspace Cloud,ReadySpace
Cloud
Services, SAVVIS, Terremark and NaviSite.
Infrastructure as a service (IaaS) Platform as a service (PaaS)
In the most basic cloud-service model, In the PaaS model, cloud providers deliver
providers of IaaS offer computers - physical a computing platform typically including
or (more often) virtual machines - and other operating system, programming language
resources. (A hypervisor, such execution environment, database, and web
as Xen or KVM, runs the virtual machines server. Application developers can develop
as guests. Pools of hypervisors within the and run their software solutions on a cloud
cloud operational support-system can platform without the cost and complexity of
support large numbers of virtual machines buying and managing the underlying
and the ability to scale services up and down hardware and software layers. With some
according to customers' varying PaaS offers, the underlying computer and
requirements.) IaaS clouds often offer storage resources scale automatically to
additional resources such as images in a match application demand such that cloud
virtual-machine image-library, raw (block) user does not have to allocate resources
and file-based storage, firewalls, load manually.
balancers, IP addresses, virtual local area
networks (VLANs), and software Examples of PaaS include: AWS Elastic
bundles. IaaS-cloud providers supply these Beanstalk, Cloud
resources on-demand from their large pools Foundry, Heroku, Force.com, EngineYard,
installed in data centers (or on hardware Mendix, Google App Engine, Windows
installed in customer premises). Forwide- Azure Compute and OrangeScape.
area connectivity, customers can use either
the Internet or carrier clouds (dedicated
virtual private networks).
To deploy their applications, cloud users
install operating-system images and their
Software as a service (SaaS) considering network and computing
In the SaaS model, cloud providers install resources as a unified whole.
and operate application software in the cloud Traditional NaaS services include flexible
and cloud users access the software from and extended VPN, and bandwidth on
cloud clients. The cloud users do not demand. NaaS concept materialization also
manage the cloud infrastructure and includes the provision of a virtual network
platform on which the application is service by the owners of the network
running. This eliminates the need to install infrastructure to a third party (VNP VNO).
and run the application on the cloud user's
own computers simplifying maintenance and
support. What makes a cloud application Cloud clients
different from other applications is its
scalability. This can be achieved by cloning Users access cloud computing using
tasks onto multiple virtual machines at run- networked client devices, such as desktop
time to meet the changing work demand. computers, laptops, tablets and smartphones.
Load balancers distribute the work over the Some of these devices - cloud clients - rely
set of virtual machines. This process is on cloud computing for all or a majority of
transparent to the cloud user who sees only a their applications so as to be essentially
single access point. To accommodate a large useless without it. Examples are thin
number of cloud users, cloud applications clients and the browser-based Chromebook.
can be multitenant, that is, any machine Many cloud applications do not require
serves more than one cloud user specific software on the client and instead
organization. It is common to refer to special use a web browser to interact with the cloud
types of cloud based application software application.
with a similar naming convention: desktop With Ajax and HTML5 these Web user
as a service, business process as a interfaces can achieve a similar or even
service, test environment as a service, better look and feel as native applications.
communication as a service. Some cloud applications, however, support
specific client software dedicated to these
The pricing model for SaaS applications is applications (e.g., virtual desktop clients and
typically a monthly or yearly flat fee per most email clients). Some legacy
user, so price is scalable and adjustable if applications (line of business applications
users are added or removed at any point. that until now have been prevalent in thin
Examples of SaaS include: Google client Windows computing) are delivered
Apps, Microsoft Office 365, Onlive, GT via a screen-sharing technology.
Nexus, Marketo, and TradeCard.
Network as a service (NaaS)
A category of cloud services where the
capability provided to the cloud service user
is to use network/transport connectivity
services and/or inter-cloud network
connectivity services. NaaS involves the
optimization of resource allocations by
Deployment models By utilizing "hybrid cloud" architecture,
companies and individuals are able to obtain
degrees of fault tolerance combined with
locally immediate usability without
dependency on internet connectivity. Hybrid
cloud architecture requires both on-premises
resources and off-site (remote) server-based
cloud infrastructure.
Hybrid clouds lack the flexibility, security
and certainty of in-house
Cloud computing types applications. Hybrid cloud provides the
Public cloud flexibility of in house applications with the
fault tolerance and scalability of cloud based
Public cloud applications, storage, and other
services.
resources are made available to the general
public by a service provider. These services
are free or offered on a pay-per-use model. Private cloud
Generally, public cloud service providers
Private cloud is cloud infrastructure
like Amazon AWS, Microsoft and Google
operated solely for a single organization,
own and operate the infrastructure and offer
whether managed internally or by a third-
access only via Internet (direct connectivity
party and hosted internally or
is not offered).
externally. Undertaking a private cloud
project requires a significant level and
Community cloud degree of engagement to virtualize the
business environment, and it will require the
Community cloud shares infrastructure
organization to reevaluate decisions about
between several organizations from a
existing resources. When it is done right, it
specific community with common concerns
can have a positive impact on a business, but
(security, compliance, jurisdiction, etc.),
every one of the steps in the project raises
whether managed internally or by a third-
security issues that must be addressed in
party and hosted internally or externally.
order to avoid serious vulnerabilities.
The costs are spread over fewer users than a
public cloud (but more than a private cloud), They have attracted criticism because users
so only some of the cost savings potential of "still have to buy, build, and manage them"
cloud computing are realized. and thus do not benefit from less hands-on
management, essentially "[lacking] the
economic model that makes cloud
Hybrid cloud computing such an intriguing concept".
Hybrid cloud is a composition of two or
more clouds (private, community or public)
that remain unique entities but are bound
together, offering the benefits of multiple
deployment models.
Architecture as systems, software, web, performance, inf
ormation, security, platform, risk,
and quality engineering.
References:
www.google.com
www.ask.com
www.wikipedia.org
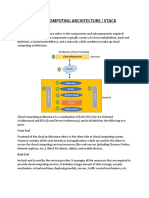
Cloud computing sample architecture
Cloud architecture, the systems
architecture of the software
systems involved in the delivery of cloud
computing, typically involves multiple cloud
components communicating with each other
over a loose coupling mechanism such as a
messaging queue. Elastic provision implies
intelligence in the use of tight or loose
coupling as applied to mechanisms such as
these and others.
The Intercloud
The Intercloud is an interconnected global
"cloud of clouds" and an extension of the
Internet "network of networks" on which it
is based.
Cloud engineering
Cloud engineering is the application
of engineering disciplines to cloud
computing. It brings a systematic approach
to the high-level concerns of
commercialisation, standardisation, and
governance in conceiving, developing,
operating and maintaining cloud computing
systems. It is a multidisciplinary method
encompassing contributions from diverse
areas such
You might also like
- Oracle Applications Messages ManualDocument952 pagesOracle Applications Messages ManualrohitkchaubeNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Cloud ComputingDocument21 pagesPresentation On Cloud ComputingPraveen Kumar PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- Computer-Networks Lecture 2 SlideDocument26 pagesComputer-Networks Lecture 2 SlidekdkdkdNo ratings yet
- Survey On Security Issues in Cloud ComputingDocument20 pagesSurvey On Security Issues in Cloud ComputingRishi KumarNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Cloud ComputingDocument21 pagesIntroduction to Cloud ComputingabiNo ratings yet
- CC DocumentDocument13 pagesCC Documentgopikrishnan1234No ratings yet
- Cloud Computing: An OverviewDocument3 pagesCloud Computing: An OverviewAkash BansalNo ratings yet
- AN Assignment ON "Cloud Computing" "Master of Computer Application" Session 2012-2015Document8 pagesAN Assignment ON "Cloud Computing" "Master of Computer Application" Session 2012-2015ravindersehgalNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing DraftDocument14 pagesCloud Computing Draftakhil829208No ratings yet
- Cloud Computing: Presentation ByDocument20 pagesCloud Computing: Presentation Bymahesh_mallidiNo ratings yet
- 1.IJAEST Vol No 5 Issue No 1 Privacy Issues and Challenges in Cloud Computing 001 006Document6 pages1.IJAEST Vol No 5 Issue No 1 Privacy Issues and Challenges in Cloud Computing 001 006iserpNo ratings yet
- Proxy Re-Encryption Scheme for Encrypted Big Data DeduplicationDocument31 pagesProxy Re-Encryption Scheme for Encrypted Big Data DeduplicationsantoshNo ratings yet
- Compiled Note On Cloud Computing - 2Document44 pagesCompiled Note On Cloud Computing - 2Suresh SinghNo ratings yet
- Overview of Cloud Computing TechnologyDocument3 pagesOverview of Cloud Computing Technologyzubair90No ratings yet
- Privacy Preserving Intermediate Datasets in The CloudDocument83 pagesPrivacy Preserving Intermediate Datasets in The CloudSuganya PeriasamyNo ratings yet
- Abstract of Cloud ComputingDocument6 pagesAbstract of Cloud ComputingJanaki JanuNo ratings yet
- Topic 2: Cloud Computing OverviewDocument35 pagesTopic 2: Cloud Computing OverviewMoon 131415No ratings yet
- Cloud Computing, Its Applications and Challenges - A GlimseDocument5 pagesCloud Computing, Its Applications and Challenges - A GlimseAniket SonaleNo ratings yet
- Report Cloud ComputingDocument15 pagesReport Cloud ComputingsaneshsivanNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of Cloud ComputingDocument2 pagesCharacteristics of Cloud ComputingSukhjinder Singh GillNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing: Significances For Enterprise Software Vendors (ESV)Document1 pageCloud Computing: Significances For Enterprise Software Vendors (ESV)Nikunj PatelNo ratings yet
- (IJCST-V5I1P16) :andemariam Mebrahtu, Balu SrinivasuluDocument7 pages(IJCST-V5I1P16) :andemariam Mebrahtu, Balu SrinivasuluEighthSenseGroupNo ratings yet
- Cloud ComputingDocument3 pagesCloud ComputingNandan KumarNo ratings yet
- Sunderdeep Group of Institutions Faculty of Engineering & Technology, GhaziabadDocument16 pagesSunderdeep Group of Institutions Faculty of Engineering & Technology, Ghaziabadamitnand7No ratings yet
- Cloud Computing IcacteaDocument5 pagesCloud Computing IcacteaPankaj KabraNo ratings yet
- Cloud ComputingDocument7 pagesCloud ComputingViệt Dũng Trần NguyễnNo ratings yet
- What Is Cloud Computing?: Secure Auditing and Deduplication of Data in CloudDocument79 pagesWhat Is Cloud Computing?: Secure Auditing and Deduplication of Data in CloudVamsi SakhamuriNo ratings yet
- Problem Definition: Implementing Digital Signature With RSA To The Data On CloudDocument22 pagesProblem Definition: Implementing Digital Signature With RSA To The Data On CloudHamid HaqaniNo ratings yet
- Abstract:: What Is Cloud?Document5 pagesAbstract:: What Is Cloud?narmadha27051991No ratings yet
- Cloud Computing: Submitted By: Divya Khandelwal B.Tech (CSE) 7 Sem 0271352707Document31 pagesCloud Computing: Submitted By: Divya Khandelwal B.Tech (CSE) 7 Sem 0271352707divya25sepNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing: Cloud Computing Is The Delivery of Computing As A Service Rather Than A Product, WherebyDocument15 pagesCloud Computing: Cloud Computing Is The Delivery of Computing As A Service Rather Than A Product, WherebyShashank GuptaNo ratings yet
- Data Security, Privacy, Availability and Integrity in Cloud Computing: Issues and Current SolutionsDocument14 pagesData Security, Privacy, Availability and Integrity in Cloud Computing: Issues and Current Solutionssagar sagNo ratings yet
- Data Security, Privacy, Availability and Integrity in Cloud Computing: Issues and Current SolutionsDocument14 pagesData Security, Privacy, Availability and Integrity in Cloud Computing: Issues and Current Solutionssagar sagNo ratings yet
- UNIT III - Cloud Computing-1Document34 pagesUNIT III - Cloud Computing-1struthika DNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing Unit2Document37 pagesCloud Computing Unit2Bella SNo ratings yet
- Attribute-Based Access Control With Constant-Size Ciphertext in Cloud ComputingDocument14 pagesAttribute-Based Access Control With Constant-Size Ciphertext in Cloud ComputingGateway ManagerNo ratings yet
- Introduction About CloudDocument6 pagesIntroduction About CloudMula RamaniNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing - PrashantDocument6 pagesCloud Computing - PrashantSachin MauryaNo ratings yet
- Virtualizing The Private Cloud For Maximum Resource UtilizationDocument5 pagesVirtualizing The Private Cloud For Maximum Resource UtilizationIjarcet JournalNo ratings yet
- "Cloud Computing": Made By: Aayush Chopra 09itmg1001cseDocument23 pages"Cloud Computing": Made By: Aayush Chopra 09itmg1001cseAbhimanyu NarwalNo ratings yet
- Ijett V21P256Document8 pagesIjett V21P256Bharath KumarNo ratings yet
- Implementation of Cloud Based Query Solver System For Educational Institutes Featuring OntologyDocument7 pagesImplementation of Cloud Based Query Solver System For Educational Institutes Featuring OntologyIjarcet JournalNo ratings yet
- Cloud ComputingDocument3 pagesCloud ComputingAkash RajputNo ratings yet
- Seminar ReportDocument17 pagesSeminar Reportshinchan noharaNo ratings yet
- Seminar ReportDocument17 pagesSeminar Reportshinchan noharaNo ratings yet
- Brief Introduction To Cloud ComputingDocument6 pagesBrief Introduction To Cloud ComputingVASUNo ratings yet
- 186 Cloud Computing From ScetDocument8 pages186 Cloud Computing From Scetomarsaleem3670319No ratings yet
- Seminar ReportDocument17 pagesSeminar ReportJp Sahoo0% (1)
- REsearch Paper PDFDocument7 pagesREsearch Paper PDFDevbrat JhaNo ratings yet
- CSE 423 Lecture 3Document14 pagesCSE 423 Lecture 3Ranjith SKNo ratings yet
- 23 Cloud ComputingDocument7 pages23 Cloud ComputingRamana YellapuNo ratings yet
- EMT 7103 Computer Applications in Engineering Kris KegoDocument28 pagesEMT 7103 Computer Applications in Engineering Kris KegoMugisa PeterNo ratings yet
- A Hybrid BioDocument41 pagesA Hybrid Biomohamed fathimaNo ratings yet
- Big Data and Cloud Computing: Mrs. Premalatha P, Mrs. Marrynal S. EastaffDocument4 pagesBig Data and Cloud Computing: Mrs. Premalatha P, Mrs. Marrynal S. EastafferpublicationNo ratings yet
- Assignment: Q1. What Is Cloud Computing? AnsDocument8 pagesAssignment: Q1. What Is Cloud Computing? Ansvashishttyagi91No ratings yet
- A Technical Seminar Report ON Cloud Computing: D. Sai Krishna. (2220212108)Document19 pagesA Technical Seminar Report ON Cloud Computing: D. Sai Krishna. (2220212108)srgupta99No ratings yet
- Cloud ComputingDocument18 pagesCloud Computingmartin.taruvinga8335No ratings yet
- 14 - 8 - 2018 - 16 - 22 - 55 - 449 - UNIT I (Part A)Document29 pages14 - 8 - 2018 - 16 - 22 - 55 - 449 - UNIT I (Part A)suryanshNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing in A Simple WayDocument19 pagesCloud Computing in A Simple Wayahmed wagihNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing: Cloud Computing Is A Technology That Uses The Internet and Central Remote Servers To Maintain Data andDocument11 pagesCloud Computing: Cloud Computing Is A Technology That Uses The Internet and Central Remote Servers To Maintain Data androhan7801No ratings yet
- Cloud Computing Made Simple: Navigating the Cloud: A Practical Guide to Cloud ComputingFrom EverandCloud Computing Made Simple: Navigating the Cloud: A Practical Guide to Cloud ComputingNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing: Harnessing the Power of the Digital Skies: The IT CollectionFrom EverandCloud Computing: Harnessing the Power of the Digital Skies: The IT CollectionNo ratings yet
- G S T MaterialDocument20 pagesG S T MaterialGonella NagamallikaNo ratings yet
- Chinnu ProjectDocument14 pagesChinnu ProjectGonella NagamallikaNo ratings yet
- Network Devices NotesDocument14 pagesNetwork Devices NotesGonella KameshNo ratings yet
- Cellular NetworksDocument14 pagesCellular NetworksGonella NagamallikaNo ratings yet
- Cellular NetworksDocument14 pagesCellular NetworksGonella NagamallikaNo ratings yet
- Desktop PC Advantages Over Laptop ComputersDocument1 pageDesktop PC Advantages Over Laptop ComputersGonella NagamallikaNo ratings yet
- Awards SDocument22 pagesAwards SGonella NagamallikaNo ratings yet
- Awards SDocument22 pagesAwards SGonella NagamallikaNo ratings yet
- C ProgramsDocument8 pagesC ProgramsGonella NagamallikaNo ratings yet
- Operation and Maintenance Manual: Sievers 900 Series Total Organic Carbon AnalyzersDocument224 pagesOperation and Maintenance Manual: Sievers 900 Series Total Organic Carbon Analyzersmoh sadliNo ratings yet
- Dali Pro Field Commissioning Guide Classic v2.2.X EN - v2Document87 pagesDali Pro Field Commissioning Guide Classic v2.2.X EN - v2UrfaaNo ratings yet
- Petrel 2010.2.2 Install TutorialDocument17 pagesPetrel 2010.2.2 Install TutorialPaulo Ivo100% (1)
- Chapter 2. Introduction To Data ScienceDocument40 pagesChapter 2. Introduction To Data ScienceMeron EshetuNo ratings yet
- Kendriya Vidyalaya No 1, KalpakkamDocument4 pagesKendriya Vidyalaya No 1, KalpakkamSudersan BalajiNo ratings yet
- SE Modbus Basic Nodes User ManualDocument68 pagesSE Modbus Basic Nodes User ManualAlejandro RoalcabaNo ratings yet
- Datasheet-Cisco FirePOWER 8000 Series AppliancesDocument5 pagesDatasheet-Cisco FirePOWER 8000 Series Appliancesshadab umairNo ratings yet
- AMS Trex Device Communicator: Product Data Sheet Reliability SolutionsDocument9 pagesAMS Trex Device Communicator: Product Data Sheet Reliability SolutionsJUAN CARLOSNo ratings yet
- DLC Lab QP Oct2019Document5 pagesDLC Lab QP Oct2019bnatarajNo ratings yet
- Fddi (Fiber Distributed Data Interface)Document15 pagesFddi (Fiber Distributed Data Interface)ashok_it87No ratings yet
- W M U G NL: Automation How To Make My IT Life EasierDocument34 pagesW M U G NL: Automation How To Make My IT Life EasierHamelNo ratings yet
- Scalable Encryption Algorithm PDFDocument79 pagesScalable Encryption Algorithm PDF9949409548No ratings yet
- GOF Design Patterns OverviewDocument53 pagesGOF Design Patterns OverviewYash PatelNo ratings yet
- Manage Wireless Networks Using Netsh CommandsDocument3 pagesManage Wireless Networks Using Netsh CommandslakbanpoeNo ratings yet
- Installing and Configuring Oracle Fusion Middleware InfrastructureDocument50 pagesInstalling and Configuring Oracle Fusion Middleware InfrastructureHareshNo ratings yet
- Basic C Shell: Change Your Shell To TCSHDocument5 pagesBasic C Shell: Change Your Shell To TCSHDarwinNo ratings yet
- SmarTeam Design Express For CATIA Installation GuideDocument29 pagesSmarTeam Design Express For CATIA Installation GuidelceppetelliNo ratings yet
- Mad VivaDocument6 pagesMad VivaShiv KadiwalaNo ratings yet
- Project Description: 1.1. Current ScenarioDocument57 pagesProject Description: 1.1. Current ScenarioLearning WebsiteNo ratings yet
- Ol Ict Marking Scheme 2018Document10 pagesOl Ict Marking Scheme 2018supun gamageNo ratings yet
- Api RestDocument405 pagesApi RestmuhammadrustamNo ratings yet
- Voting machine using microcontrollerDocument6 pagesVoting machine using microcontrollerAnjani BhargavaNo ratings yet
- Portable-VirtualBox - Download of Portable-VirtualBoxDocument3 pagesPortable-VirtualBox - Download of Portable-VirtualBoxManish DandekarNo ratings yet
- System Programming Notes for 6 Sem BCADocument92 pagesSystem Programming Notes for 6 Sem BCANavaraj Pandey100% (1)
- Python String - UNIT 3Document5 pagesPython String - UNIT 3mishrapriyanshu1975No ratings yet
- Introduction To Computers and Java: Walter Savitch Frank M. CarranoDocument77 pagesIntroduction To Computers and Java: Walter Savitch Frank M. CarranoBrandon KozakNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document15 pagesAssignment 2api-311925791No ratings yet