Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Bradycardia Causes and Treatments
Uploaded by
della fergina0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
27 views3 pagesMEDS
Original Title
ACLS H & T new
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentMEDS
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
27 views3 pagesBradycardia Causes and Treatments
Uploaded by
della ferginaMEDS
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
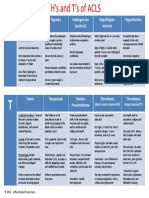
The H’s and T’s of Bradycardia
Potential Cause How to Identify Treatments
Rapid heart rate and narrow QRS on ECG;
Hypovolemia Infusion of normal saline or Ringer’s lactate
other symptoms of low volume
Airway management and effective
Hypoxia Slow heart rate
oxygenation
Hydrogen Ion Excess Hyperventilation; consider sodium
Low amplitude QRS on the ECG
(Acidosis) bicarbonate bolus
Hypoglycemia Bedside glucose testing IV bolus of dextrose
Flat T waves and appearance of a U wave
Hypokalemia IV Magnesium infusion
on the ECG
Consider calcium chloride, sodium
Peaked T waves and wide QRS complex on
Hyperkalemia bicarbonate, and an insulin and glucose
the ECG
protocol
Typically preceded by exposure to a cold
Hypothermia Gradual rewarming
environment
Slow heart rate and narrow QRS
Tension Pneumothorax Thoracostomy or needle decompression
complexes on the ECG; difficulty breathing
Rapid heart rate and narrow QRS
Tamponade – Cardiac Pericardiocentesis
complexes on the ECG
Typically will be seen as a prolonged QT
Toxins interval on the ECG; may see neurological Based on the specific toxin
symptoms
Thrombosis (pulmonary Rapid heart rate with narrow QRS Surgical embolectomy or administration of
embolus) complexes on the ECG fibrinolytics
Thrombosis (myocardial ECG will be abnormal based on the
Dependent on extent and age of MI
infarction) location of the infarction
Cardioversion Rules
QRS narrow and regular 50-100 Joules
QRS narrow and irregular 120-200 Joules
QRS wide and regular 100 Joules
QRS wide and irregular Turn off the synchronized mode and defibrillate immediately
Stable patients with tachycardia with a palpable pulse can be treated with more conservative measures first.
Attempt vagal maneuvers
If unsuccessful, administer adenosine 6 mg IV bolus followed by a rapid normal saline flush
If unsuccessful, administer adenosine 12 mg IV bolus followed by a rapid normal saline flush
Beta-blockers and calcium channel blockers may be considered for narrow QRS tachycardia (QRS <0.12 sec)
For stable, wide QRS complex tachycardia (QRS ≥0.12 sec)
Strongly consider expert consultation
Consider procainamide 20-50 mg/min IV, OR
Amiodarone 150 mg IV over 10 minutes, OR
Sotalol 100 mg (1.5 mg/kg) over 5 minutes
You might also like
- Standard Treatment GuidelinesDocument431 pagesStandard Treatment Guidelinesadnan khanNo ratings yet
- ECG Mastery Improving Your ECG Interpretation SkillsDocument23 pagesECG Mastery Improving Your ECG Interpretation SkillsHitesh Deora100% (2)
- Study Notes PediatricsDocument86 pagesStudy Notes PediatricsMedShare100% (19)
- IM Shelf - AmbossDocument61 pagesIM Shelf - AmbossHaadi AliNo ratings yet
- Maternal Midterm Reviewer Common ProblemsDocument58 pagesMaternal Midterm Reviewer Common ProblemsEya BaldostamonNo ratings yet
- Ecg Interpretation New TemplateDocument88 pagesEcg Interpretation New TemplateJonathan NgNo ratings yet
- Cardiac ArrhythmiasDocument60 pagesCardiac ArrhythmiasMelissa Monique Peart-YatesNo ratings yet
- Arrhythmias: Sing Khien Tiong Gpst1Document34 pagesArrhythmias: Sing Khien Tiong Gpst1preethi preethaNo ratings yet
- History Taking: DR Anwar H. SiddiquiDocument26 pagesHistory Taking: DR Anwar H. SiddiquiAssad mustafNo ratings yet
- Heart Dysrhythmias Cheat Sheet ExplainedDocument5 pagesHeart Dysrhythmias Cheat Sheet ExplainedpcmundotNo ratings yet
- Pharmacotherapy of Cardiac ArrhythmiasDocument68 pagesPharmacotherapy of Cardiac ArrhythmiasABREHAM BUKULONo ratings yet
- Heart BlockDocument26 pagesHeart BlockMihir Patel86% (7)
- EKG Interpretation Basics Guide: Electrocardiogram Heart Rate Determination, Arrhythmia, Cardiac Dysrhythmia, Heart Block Causes, Symptoms, Identification and Medical Treatment Nursing HandbookFrom EverandEKG Interpretation Basics Guide: Electrocardiogram Heart Rate Determination, Arrhythmia, Cardiac Dysrhythmia, Heart Block Causes, Symptoms, Identification and Medical Treatment Nursing HandbookNo ratings yet
- H's and T's of ACLSDocument1 pageH's and T's of ACLSgabbyneng100% (1)
- CPG Management of Diabetic FootDocument64 pagesCPG Management of Diabetic Footapalaginih100% (2)
- Drugs used to treat cardiac arrhythmiasDocument74 pagesDrugs used to treat cardiac arrhythmiasGunel Sadiqova100% (1)
- Nurse Monitoring Client's Lipid Infusion StatusDocument9 pagesNurse Monitoring Client's Lipid Infusion StatusPatricia Vardon OdonkorNo ratings yet
- ECG Presentation 2020Document131 pagesECG Presentation 2020Kiskeya KafeNo ratings yet
- Cardiac ArrhythmiasDocument11 pagesCardiac ArrhythmiasChino Paolo SamsonNo ratings yet
- Arrhythmias: BY Zarish FazilDocument64 pagesArrhythmias: BY Zarish FazilZarish Amanat100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug StudyAika CortesNo ratings yet
- Arrhythmia: Dian Pratiwi Cardiology Department Chasan Boesoerie HospitalDocument73 pagesArrhythmia: Dian Pratiwi Cardiology Department Chasan Boesoerie HospitalummuabNo ratings yet
- Retinitis Pigmentosa and Diabetic Retinopathy QuestionsDocument10 pagesRetinitis Pigmentosa and Diabetic Retinopathy QuestionsYUAN LINo ratings yet
- ACLS Bradycardia Algorithm GuideDocument1 pageACLS Bradycardia Algorithm GuideTracy PopeNo ratings yet
- Aritmia Maligna - Abraham PDFDocument21 pagesAritmia Maligna - Abraham PDFDavid Ithu AgkhuNo ratings yet
- ECG Intro With Ref To QT Interval FinalDocument59 pagesECG Intro With Ref To QT Interval FinalGeorge VergheseNo ratings yet
- ArrhythmiasDocument47 pagesArrhythmiasJaismi AntonyNo ratings yet
- Life Threatening ArrhytmiaDocument41 pagesLife Threatening ArrhytmiaJanetty TjandraNo ratings yet
- AclsDocument29 pagesAclsTharakanzzNo ratings yet
- Electrocardiogram Interpretation and Nursing InterDocument4 pagesElectrocardiogram Interpretation and Nursing InterJulia Rae Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- Diagnosing TachyarrhythmiasDocument7 pagesDiagnosing TachyarrhythmiasSandeep m rNo ratings yet
- Disturbances in AcidDocument11 pagesDisturbances in AcidShannen Alija M. LaoNo ratings yet
- Ecg 8Document14 pagesEcg 8api-3757039100% (1)
- ACLS For TachycardiaDocument31 pagesACLS For TachycardiaTausif HaqueNo ratings yet
- Cardiothoracic VascularDocument44 pagesCardiothoracic VascularApoorva ShandilyaNo ratings yet
- EKG Arrhythmia Identification and Treatment GuideDocument28 pagesEKG Arrhythmia Identification and Treatment GuideJason LinNo ratings yet
- ARITMIADocument47 pagesARITMIASarah JR Nur AzizahNo ratings yet
- Management of Cardiac Arrhythmias in Advanced Cardiac Life Support (ACLSDocument34 pagesManagement of Cardiac Arrhythmias in Advanced Cardiac Life Support (ACLSrhezzaagxxNo ratings yet
- Aritmia LetalDocument49 pagesAritmia LetalfebriyakNo ratings yet
- Problem Based Learning Cardiovascular System: 2nd GroupDocument47 pagesProblem Based Learning Cardiovascular System: 2nd GroupClaudia Narinda R. PNo ratings yet
- Arrhythmias GeneralDocument131 pagesArrhythmias GeneralAnonymous IRl5fn6No ratings yet
- Management of Perioperative ArrhythmiasDocument51 pagesManagement of Perioperative ArrhythmiasAbhishek LonikarNo ratings yet
- ECG Junctional & Ventricular Arrhythmias GuideDocument21 pagesECG Junctional & Ventricular Arrhythmias GuideMorad KananNo ratings yet
- NCM 118 - Lesson 11 (Arrhythmia)Document5 pagesNCM 118 - Lesson 11 (Arrhythmia)Bobby Christian DuronNo ratings yet
- 3 EcgDocument34 pages3 EcgAYSHA ANWARNo ratings yet
- Peri Operative Arryhthmias: Dr. Juzny Alkatiri, SPPD, SPJPDocument102 pagesPeri Operative Arryhthmias: Dr. Juzny Alkatiri, SPPD, SPJPAstari Pratiwi NuhrintamaNo ratings yet
- Ecg Arrhythmia: Dr. Lowry Yunita, SPJP, FihaDocument48 pagesEcg Arrhythmia: Dr. Lowry Yunita, SPJP, FihaMaria JozilynNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis Dan Tatalaksana Awal SVTDocument47 pagesDiagnosis Dan Tatalaksana Awal SVTZuly Vita AulyaNo ratings yet
- TachycardiaDocument7 pagesTachycardiaArvind SahniNo ratings yet
- EKG Rhythm Characteristics and EtiologiesDocument21 pagesEKG Rhythm Characteristics and EtiologiesDanial Hassan ShahNo ratings yet
- Lecture - 2 Advanced Cardiac Life SupportDocument28 pagesLecture - 2 Advanced Cardiac Life SupportJixon GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Cardia Arrhythmias Zuket 3.0Document68 pagesCardia Arrhythmias Zuket 3.0Mohd ZulkhairiNo ratings yet
- ELECTROCARDIOGRAM by Aldrin Jayson AlmadenDocument23 pagesELECTROCARDIOGRAM by Aldrin Jayson AlmadenItsMe AJNo ratings yet
- ECG Arrhythmia Classification GuideDocument6 pagesECG Arrhythmia Classification GuideEzzat SalemNo ratings yet
- ICU Rounds: Recognizing and Treating Ventricular TachycardiaDocument4 pagesICU Rounds: Recognizing and Treating Ventricular TachycardiaDicky SaputraNo ratings yet
- Intepretasi EKG (DR Eka)Document93 pagesIntepretasi EKG (DR Eka)Danil Anugrah JayaNo ratings yet
- Curs Engl S Preexcit Corect Nic MPDocument72 pagesCurs Engl S Preexcit Corect Nic MPErland BordNo ratings yet
- 2 - PPT DR Erika Maharani SPJPDocument42 pages2 - PPT DR Erika Maharani SPJPAmry YusufNo ratings yet
- Entrikel Takikardi (VT) Tanpa NadiDocument3 pagesEntrikel Takikardi (VT) Tanpa NadiraffellaNo ratings yet
- Atrial Fibrillation: Key TreatmentsDocument2 pagesAtrial Fibrillation: Key TreatmentschoobiNo ratings yet
- VT IndoDocument37 pagesVT IndotyaraNo ratings yet
- ArrhythmiasDocument48 pagesArrhythmiasHarshan JeyakumarNo ratings yet
- ABC of Clinical Electrocardiography Broad Complex Tachycardia-Part IDocument4 pagesABC of Clinical Electrocardiography Broad Complex Tachycardia-Part IIgnacio Aguilar ValdiviesoNo ratings yet
- ACLS ReportDocument58 pagesACLS ReportCamille Honeyleith FernandoNo ratings yet
- TACHYARRHYTMIASDocument40 pagesTACHYARRHYTMIASRoy Sandy PermanaNo ratings yet
- Neonatal Cardiac Arrhythmias: Intensive Care Nursery House Staff ManualDocument3 pagesNeonatal Cardiac Arrhythmias: Intensive Care Nursery House Staff ManualAhmed MohammedNo ratings yet
- Intensive Care Nursery House Staff ManualDocument3 pagesIntensive Care Nursery House Staff ManualgalaxytwyNo ratings yet
- Doctor Attendance SheetDocument4 pagesDoctor Attendance Sheetdella ferginaNo ratings yet
- Minimally Invasive Surgery PDFDocument4 pagesMinimally Invasive Surgery PDFdella ferginaNo ratings yet
- InternaDocument6 pagesInternadella ferginaNo ratings yet
- Elderly Arrhythmia ManagementDocument39 pagesElderly Arrhythmia Managementdella ferginaNo ratings yet
- InternaDocument6 pagesInternadella ferginaNo ratings yet
- WOC - Calcium Crystal Formation and Urinary Tract ObstructionDocument2 pagesWOC - Calcium Crystal Formation and Urinary Tract Obstructionvictor zhefaNo ratings yet
- Hepato-Biliary System and Their DisordersDocument131 pagesHepato-Biliary System and Their DisordersIton BumatayNo ratings yet
- CS1 AntibioticsDocument4 pagesCS1 AntibioticsTaraKyleUyNo ratings yet
- How To Interpret Thyroid Function TestsDocument5 pagesHow To Interpret Thyroid Function TestsnonieshzNo ratings yet
- مدونة كل العرب الطبية Davidson - Mcq - 22 - edition PDFDocument232 pagesمدونة كل العرب الطبية Davidson - Mcq - 22 - edition PDFنورهانعزالدين100% (1)
- High Blood Pressure Medication Classes and Side EffectsDocument12 pagesHigh Blood Pressure Medication Classes and Side EffectsSARFRAZ ALINo ratings yet
- Functional Neurological Disorder - New Subtypes and Shared MechanismsDocument14 pagesFunctional Neurological Disorder - New Subtypes and Shared MechanismsDalal HazelNo ratings yet
- Clinical Management Guidelines For Suspected or Confirmed COVID 19 Infection in Adults Version 4 April 2023 MOH NUGDocument94 pagesClinical Management Guidelines For Suspected or Confirmed COVID 19 Infection in Adults Version 4 April 2023 MOH NUGFrozenboy. 1993No ratings yet
- Neuroprotection Is Possible in The Real LifeDocument3 pagesNeuroprotection Is Possible in The Real Lifeperoxidasa1No ratings yet
- Handbook of Drugs in Intensive Care GuideDocument6 pagesHandbook of Drugs in Intensive Care GuideardriangollerNo ratings yet
- Malabsorption and Elimination DisordersDocument120 pagesMalabsorption and Elimination DisordersBeBs jai SelasorNo ratings yet
- عبد الرحمن خالد الزميلي Assighment Of Dental Surgery /Principle of routine exodontiaDocument20 pagesعبد الرحمن خالد الزميلي Assighment Of Dental Surgery /Principle of routine exodontiaعبد الرحمن خالد الزميليNo ratings yet
- Functions of the Nervous SystemDocument10 pagesFunctions of the Nervous SystemJovi Leo PunoNo ratings yet
- 8 Morphology and InclusionsDocument31 pages8 Morphology and InclusionsLian Marie ViñasNo ratings yet
- Anemia: Kristine Krafts, M.DDocument38 pagesAnemia: Kristine Krafts, M.DNatalieMoralesNo ratings yet
- Ginkgobiloba: Indications, Mechanisms, and SafetyDocument11 pagesGinkgobiloba: Indications, Mechanisms, and SafetyEmirgibraltarNo ratings yet
- Basic Neuroscience CompiledDocument71 pagesBasic Neuroscience CompiledDr.Rathod RanjithNo ratings yet
- Download Case Files Pediatrics 6E Oct 6 2021_126047495X_Mcgraw Hill Eugene C Toy full chapterDocument67 pagesDownload Case Files Pediatrics 6E Oct 6 2021_126047495X_Mcgraw Hill Eugene C Toy full chaptermarion.wade943100% (2)
- Sent On Behalf of Henry Simmons, Chief Executive, Alzheimer Scotland by Email and TwitterDocument3 pagesSent On Behalf of Henry Simmons, Chief Executive, Alzheimer Scotland by Email and Twitterapi-252287910No ratings yet
- American Family Physician - April 15, 2020 - Chronic Diarrhea in Adults - Evaluation and Differential DiagnosisDocument16 pagesAmerican Family Physician - April 15, 2020 - Chronic Diarrhea in Adults - Evaluation and Differential DiagnosismariaNo ratings yet
- Glaucoma 1Document8 pagesGlaucoma 1xoxoNo ratings yet
- Chronic-Cholecystitis-and-Metastatic-Breast-CA FinalDocument3 pagesChronic-Cholecystitis-and-Metastatic-Breast-CA FinalRishi Du AgbugayNo ratings yet