Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cloud Computing
Uploaded by
imtishal_ali3263Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cloud Computing
Uploaded by
imtishal_ali3263Copyright:
Available Formats
Cloud computing is a technology that uses the internet and central remote servers to
maintain data and applications. Cloud computing allows consumers and businesses to use
applications without installation and access their personal files at any computer with
internet access. This technology allows for much more efficient computing by
centralizing storage, memory, processing and bandwidth.
A simple example of cloud computing is Yahoo email or Gmail etc. You dont need a
software or a server to use them. All a consumer would need is just an internet
connection and you can start sending emails. The server and email management software
is all on the cloud ( internet) and is totally managed by the cloud service provider Yahoo ,
Google etc. The consumer gets to use the software alone and enjoy the benefits. The
analogy is , 'If you only need milk , would you buy a cow ?' All the users or consumers
need is to get the benefits of using the software or hardware of the computer like sending
emails etc. Just to get this benefit (milk) why should a consumer buy a (cow) software
/hardware ?
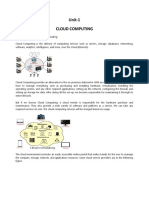
Cloud computing is broken down into three segments: "applications," "platforms," and
"infrastructure." Each segment serves a different purpose and offers different products for
businesses and individuals around the world. In June 2009, a study conducted by
VersionOne found that 41% of senior IT professionals actually don't know what cloud
computing is and two-thirds of senior finance professionals are confused by the concept,
[1]
highlighting the young nature of the technology. In Sept 2009, an Aberdeen Group
study found that disciplined companies achieved on average an 18% reduction in their IT
budget from cloud computing and a 16% reduction in data center power costs.[2]
Cloud Computing Segments
Applications: It's all On Demand
So far the applications segment of cloud computing is the only segment that has proven
useful as a business model.The Cloud Wars: $100 Billion at Stake, Published by Merrill
Lynch, May 7, 2008</ref> By running business applications over the internet from
centralized servers rather than from on-site servers, companys can cut some serious
costs. Furthermore, while avoiding maintenance costs, licensing costs and the costs of
the hardware required to run servers on-site, companies are able to run applications
much more efficiently from a computing standpoint.
On Demand software services come in a few different varieties which vary in their
pricing scheme and how the software is delivered to the end users. In the past, the end-
user would generally purchase a servers and is accessed by the end user over the internet.
While this is the most common platform for On Demand software services, there are also
some slightly different offerings which can be described as a hybrid of these two
platforms. For instance, a program through which the end user pays a license fee, but then
accesses the software over the internet from centralized servers is considered a hybrid
service.
• Who is Offering On Demand Software? - The companies below are already
established in the On-Demand software or SaaS business. These companies
charge their customers a subscription fee and in return host software on central
servers that are accessed by the end user via the internet.
o Salesforce.com (CRM)
o Google (GOOG)
o NetSuite (N)
o Cordys
o Taleo (TLEO)
o Concur Technologies (CNQR)
• Who is Offering Traditional Software? - The following companies have
established themselves as traditional software providers. These companies sell
licenses to their users, who then run the software from on premise servers.
o SAP AG (SAP)
o Oracle (ORCL)
o Blackbaud (BLKB)
o Lawson Software (LWSN)
o Blackboard (BBBB)
Platforms:
Many of the companies that started out providing On Demand application services have
developed platform services as well. The platform segment of cloud computing refers to
products that are used to deploy internet. NetSuite, Amazon, Google, and Microsoft have
also developed platforms that allow users to access applications from centralized servers.
In July 2008, HP, Yahoo! (YHOO), and Intel (INTC) announced a joint cloud
computing research project called the Cloud Computing Test Bed. The companies are
jointly designing and producing the internet based testing utilizing HP hardware and Intel
processors.[3]
• Active platforms - The following companies are some that have developed
platforms that allow end users to access applications from centralized servers
using the internet. Next to each company is the name of their platform.
o Google (GOOG) - Apps Engine
o Amazon.com (AMZN) - EC2
o Microsoft (MSFT) - Windows Live
o SAVVIS (SVVS) - Symphony VPDC
o Terremark Worldwide (TMRK) - The Enterprise Cloud
o Salesforce.com (CRM) - Force.com
o NetSuite (N) - Suiteflex
o Rackspace Cloud - cloudservers, cloudsites, cloudfiles
o Metrisoft - Metrisoft SaaS Platform
o [1] - SUN Oracle direct link
o Cordys Process Factory - The Enterprise Cloud Platform
Infrastructure:
The final segment in cloud computing, known as the infrastructure, is very much the
backbone of the entire concept. Infrastructure vendors environments (such as Google
gears) that allow users to build applications. Cloud storage, such as Amazon's S3, is also
considered to be part of the infrastructure segment.
• Major Infrastructure Vendors - Below are companies that provide
infrastructure services:
o Google (GOOG) - Managed hosting, development environment
o International Business Machines (IBM) - Managed hosting
o SAVVIS (SVVS) - Managed hosting & cloud computing
o Terremark Worldwide (TMRK) - Managed hosting
o Amazon.com (AMZN) - Cloud storage
o Rackspace Hosting (RAX) - Managed hosting & cloud computing
What does a Shift Towards Cloud Computing Mean?
So who is affected by a paradigm shift in the computing industry? The shift would affect
companies in a few different sub-industries including software companies, internet
service providers and hardware manufacturers. Companies in each of these industries will
face significant change if cloud computing is to be the next step for the industry. While it
is relatively easy to see how the main software and internet companies will be affected by
such a shift, how companies in the internet and hardware sectors will be affected is
slightly more difficult.
Who Gains?
• Consulting/Software/Hardware and Services companies that could gain from
a shift towards cloud computing include:
o IBM
• Software Producers that could gain from a shift towards cloud computing
include:
o NetSuite (N)
o Salesforce.com (CRM)
o Taleo (TLEO)
o RightNow Technologies (RNOW)
o Concur Technologies (CNQR)
o Omniture (OMTR)
o Hyperic
o Quest Software (QSFT)
o Walt Disney Company (DIS)
• Internet-based companies that could gain from a shift towards cloud
computing include:
o Amazon.com (AMZN)
o Yahoo! (YHOO)
o Microsoft (MSFT)
o Google (GOOG)
o Cisco Systems (CSCO)
• Consulting companies that could gain from a shift towards cloud computing
include:
o Cloud Technology Partners
o SAVVIS (SVVS)
Who Loses Out?
• Traditional software producers that could have some catching up to do if
cloud computing ultimately wins out include:
o Oracle (ORCL)
o SAP AG (SAP)
o Blackbaud (BLKB)
o Lawson Software (LWSN)
You might also like
- 6 Cloud ComputingDocument51 pages6 Cloud ComputingWafa BenzaouiNo ratings yet
- Cloud computing: Moving IT out of the officeFrom EverandCloud computing: Moving IT out of the officeBCS, The Chartered Institute for ITNo ratings yet
- Moving Your Business to the Cloud (A Guide for Business People Shifting to eCommerce)From EverandMoving Your Business to the Cloud (A Guide for Business People Shifting to eCommerce)No ratings yet
- Cloud computing paper on SaaS, PaaS and IaaS modelsDocument8 pagesCloud computing paper on SaaS, PaaS and IaaS modelsSwapnil NarnawareNo ratings yet
- Cloud ComputingDocument3 pagesCloud Computinganon_183226207No ratings yet
- Cloud ComputingDocument5 pagesCloud ComputingchsaipavankumarNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing Enables Business Opportunities and Cost SavingsDocument8 pagesCloud Computing Enables Business Opportunities and Cost SavingsMilan JoshiNo ratings yet
- How Cloud Computing WorksDocument6 pagesHow Cloud Computing WorkspankajganotraNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Cloud ComputingDocument10 pagesIntroduction to Cloud ComputingDeepeshZaveriNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing OverviewDocument30 pagesCloud Computing OverviewGaurang BasarkarNo ratings yet
- Digital Technologies – an Overview of Concepts, Tools and Techniques Associated with itFrom EverandDigital Technologies – an Overview of Concepts, Tools and Techniques Associated with itNo ratings yet
- Name:-Subhash Ramaswamy Roll No. 10 (New Sies) Topic: - Cloud Computing & Web ServicesDocument12 pagesName:-Subhash Ramaswamy Roll No. 10 (New Sies) Topic: - Cloud Computing & Web ServicessubashNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing Made Simple: Navigating the Cloud: A Practical Guide to Cloud ComputingFrom EverandCloud Computing Made Simple: Navigating the Cloud: A Practical Guide to Cloud ComputingNo ratings yet
- Cloud ComputingDocument7 pagesCloud ComputingHanan BinsalehNo ratings yet
- Cloud ComputingDocument5 pagesCloud ComputinghimanshuNo ratings yet
- Industry Analysis On Cloud ServicesDocument12 pagesIndustry Analysis On Cloud ServicesBaken D DhungyelNo ratings yet
- Trends in Recent Cloud Computing TechnologiesDocument22 pagesTrends in Recent Cloud Computing TechnologiesRajesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Cloud Cpting by GoogleDocument8 pagesCloud Cpting by GoogleBnaren NarenNo ratings yet
- Cloud ComputingDocument8 pagesCloud ComputinghinaNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be Asked: Second EditionFrom EverandCloud Computing Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be Asked: Second EditionNo ratings yet
- Understanding Cloud ComputingDocument14 pagesUnderstanding Cloud ComputingPawanNo ratings yet
- Loud Computing: Download Now: Speech-to-Text Services: AWS vs. Microsoft vs. GoogleDocument26 pagesLoud Computing: Download Now: Speech-to-Text Services: AWS vs. Microsoft vs. GoogleVincent MoralesNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing What The Enterprise Needs To Know About Cloud ComputingDocument22 pagesCloud Computing What The Enterprise Needs To Know About Cloud ComputingLoegas AristoNo ratings yet
- World Cloud Computing MarketDocument21 pagesWorld Cloud Computing MarketleosashNo ratings yet
- Cloud ComputingDocument36 pagesCloud Computingsubhayanmanna1234No ratings yet
- What is Cloud ComputingDocument4 pagesWhat is Cloud ComputingwalabuNo ratings yet
- Cloud Enabling The EnterpriseDocument14 pagesCloud Enabling The EnterprisemoyalynneNo ratings yet
- The Implication, Opportunity and Risk of Cloud Computing in A Shoe Manufacturing CompanyDocument10 pagesThe Implication, Opportunity and Risk of Cloud Computing in A Shoe Manufacturing CompanyAchara larryNo ratings yet
- Everything you need to know about cloud computingDocument14 pagesEverything you need to know about cloud computingamphoen2528100% (3)
- Task 1 Cloud ComputingDocument7 pagesTask 1 Cloud ComputinghasanhayatNo ratings yet
- Unit1 1Document30 pagesUnit1 1HimajanaiduNo ratings yet
- References: Cloud Computing Deployment ModelsDocument2 pagesReferences: Cloud Computing Deployment ModelsSneha SinghNo ratings yet
- Untitled 1Document2 pagesUntitled 1sasa_sagNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing For Education A New Dawn 2010 International Journal of Information ManagementDocument8 pagesCloud Computing For Education A New Dawn 2010 International Journal of Information ManagementKhizer SikanderNo ratings yet
- What Cloud Computing Really Means: by Eric Knorr, Galen GrumanDocument3 pagesWhat Cloud Computing Really Means: by Eric Knorr, Galen GrumanDarvin AnanthanNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing Pros and ConsDocument7 pagesCloud Computing Pros and ConsKarla Isael AscNo ratings yet
- IIIT Allahabad: Software Testing & Quality Assurance Cloud ComputingDocument9 pagesIIIT Allahabad: Software Testing & Quality Assurance Cloud ComputingRohit PandeyNo ratings yet
- Edge Computing and Data Replication With InfluxDBDocument11 pagesEdge Computing and Data Replication With InfluxDBNicole CortesNo ratings yet
- Cloud CompDocument5 pagesCloud CompGgn KhuranaNo ratings yet
- CASE 1 Planning For Rise of Cloud Computing at MicrosoftDocument3 pagesCASE 1 Planning For Rise of Cloud Computing at MicrosoftVarunKeshariNo ratings yet
- Cloud ComputingDocument24 pagesCloud ComputingRohit Kumar RanjanNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing - ppt11Document33 pagesCloud Computing - ppt11Abhishek Kumar Anand100% (1)
- Unit I - Understanding Cloud ComputingDocument15 pagesUnit I - Understanding Cloud ComputingHarsh Verdhan RajNo ratings yet
- Understanding Cloud Computing FundamentalsDocument14 pagesUnderstanding Cloud Computing FundamentalsKarthik Sara MNo ratings yet
- What Is Cloud ComputingDocument4 pagesWhat Is Cloud ComputinghasanhayatNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing Challenges & OpportunitiesDocument3 pagesCloud Computing Challenges & OpportunitiesdeepeshuklaNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing: Prepared By: Shekhar AvasaralaDocument17 pagesCloud Computing: Prepared By: Shekhar Avasaralashekhar_a2kNo ratings yet
- 3 Kings of Cloud ComputingDocument5 pages3 Kings of Cloud ComputingSoumya Narayana MukkalaNo ratings yet
- sW9iMeqmQRmvYjHqpjEZvA Modern Computing TrendsDocument9 pagessW9iMeqmQRmvYjHqpjEZvA Modern Computing TrendsДанила ВильховийNo ratings yet
- Cloud ComputingDocument3 pagesCloud ComputinggupthasterNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing Definitions and Solutions: FromDocument6 pagesCloud Computing Definitions and Solutions: FromRajesh SaxenaNo ratings yet
- C-Loud Computing: An IntroductionDocument30 pagesC-Loud Computing: An IntroductionDeepak RohillaNo ratings yet
- Mobile Cloud Computing: Issues, Challenges and ImplicationsDocument4 pagesMobile Cloud Computing: Issues, Challenges and ImplicationsAurangzaib BhattiNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing: (Business Needs)Document38 pagesCloud Computing: (Business Needs)starvamsi123No ratings yet
- Hite Aper ON Loud Omputing: W P C CDocument11 pagesHite Aper ON Loud Omputing: W P C CChaitanya DevNo ratings yet
- If The Marks Obtained by A Student in Five Different Subjects Are Input Through The KeyboardDocument4 pagesIf The Marks Obtained by A Student in Five Different Subjects Are Input Through The Keyboardimtishal_ali3263No ratings yet
- Exception TutorialDocument7 pagesException Tutorialimtishal_ali3263No ratings yet
- Higher Algebra - Hall & KnightDocument593 pagesHigher Algebra - Hall & KnightRam Gollamudi100% (2)
- FouziaDocument4 pagesFouziaimtishal_ali3263No ratings yet
- Remote DebuggerDocument10 pagesRemote Debuggerimtishal_ali3263No ratings yet
- Remote Debugger by Aamir AnsariDocument3 pagesRemote Debugger by Aamir Ansariimtishal_ali3263No ratings yet
- Central BankingDocument24 pagesCentral Bankingimtishal_ali3263No ratings yet
- Product Data Sheet For CP 680-P and CP 680-M Cast-In Firestop Devices Technical Information ASSET DOC LOC 1540966Document1 pageProduct Data Sheet For CP 680-P and CP 680-M Cast-In Firestop Devices Technical Information ASSET DOC LOC 1540966shama093No ratings yet
- CFO TagsDocument95 pagesCFO Tagssatyagodfather0% (1)
- Chapter 19 - 20 Continuous Change - Transorganizational ChangeDocument12 pagesChapter 19 - 20 Continuous Change - Transorganizational ChangeGreen AvatarNo ratings yet
- Journals OREF Vs ORIF D3rd RadiusDocument9 pagesJournals OREF Vs ORIF D3rd RadiusironNo ratings yet
- PeopleSoft Security TablesDocument8 pagesPeopleSoft Security TablesChhavibhasinNo ratings yet
- Use Visual Control So No Problems Are Hidden.: TPS Principle - 7Document8 pagesUse Visual Control So No Problems Are Hidden.: TPS Principle - 7Oscar PinillosNo ratings yet
- Easa Management System Assessment ToolDocument40 pagesEasa Management System Assessment ToolAdam Tudor-danielNo ratings yet
- Masteringphys 14Document20 pagesMasteringphys 14CarlosGomez0% (3)
- Efaverenz p1Document4 pagesEfaverenz p1Pragat KumarNo ratings yet
- MCQ Ch16solDocument4 pagesMCQ Ch16solandiswahlongwa870No ratings yet
- List of Reactive Chemicals - Guardian Environmental TechnologiesDocument69 pagesList of Reactive Chemicals - Guardian Environmental TechnologiesGuardian Environmental TechnologiesNo ratings yet
- Differential Pulse Code ModulationDocument12 pagesDifferential Pulse Code ModulationNarasimhareddy MmkNo ratings yet
- Reading Comprehension Exercise, May 3rdDocument3 pagesReading Comprehension Exercise, May 3rdPalupi Salwa BerliantiNo ratings yet
- Individual Performance Commitment and Review Form (Ipcrf) : Mfos Kras Objectives Timeline Weight Per KRADocument4 pagesIndividual Performance Commitment and Review Form (Ipcrf) : Mfos Kras Objectives Timeline Weight Per KRAChris21JinkyNo ratings yet
- Typical T Intersection On Rural Local Road With Left Turn LanesDocument1 pageTypical T Intersection On Rural Local Road With Left Turn Lanesahmed.almakawyNo ratings yet
- Pemaknaan School Well-Being Pada Siswa SMP: Indigenous ResearchDocument16 pagesPemaknaan School Well-Being Pada Siswa SMP: Indigenous ResearchAri HendriawanNo ratings yet
- 100 Training Games - Kroehnert, GaryDocument180 pages100 Training Games - Kroehnert, GarywindsorccNo ratings yet
- OS LabDocument130 pagesOS LabSourav BadhanNo ratings yet
- United States Bankruptcy Court Southern District of New YorkDocument21 pagesUnited States Bankruptcy Court Southern District of New YorkChapter 11 DocketsNo ratings yet
- CS709 HandoutsDocument117 pagesCS709 HandoutsalexNo ratings yet
- Strategies For StartupDocument16 pagesStrategies For StartupRoshankumar BalasubramanianNo ratings yet
- Case Study IndieDocument6 pagesCase Study IndieDaniel YohannesNo ratings yet
- Manual WinMASW EngDocument357 pagesManual WinMASW EngRolanditto QuuisppeNo ratings yet
- France Winckler Final Rev 1Document14 pagesFrance Winckler Final Rev 1Luciano Junior100% (1)
- CALCULUS PHYSICS MIDTERMDocument41 pagesCALCULUS PHYSICS MIDTERMMACARIO QTNo ratings yet
- ERIKS Dynamic SealsDocument28 pagesERIKS Dynamic Sealsdd82ddNo ratings yet
- GP Rating GSK Exit ExamDocument108 pagesGP Rating GSK Exit ExamMicle VM100% (4)
- 1st SemDocument3 pages1st SemARUPARNA MAITYNo ratings yet
- DOE Tank Safety Workshop Presentation on Hydrogen Tank TestingDocument36 pagesDOE Tank Safety Workshop Presentation on Hydrogen Tank TestingAlex AbakumovNo ratings yet
- PNBONE_mPassbook_134611_6-4-2024_13-4-2024_0053XXXXXXXX00 (1) (1)Document3 pagesPNBONE_mPassbook_134611_6-4-2024_13-4-2024_0053XXXXXXXX00 (1) (1)imtiyaz726492No ratings yet