Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ab Domino Perineal
Uploaded by
Ahmed RamiCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ab Domino Perineal
Uploaded by
Ahmed RamiCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 25 Anorectal Surgeries 989
got high mortality of 10-20%. Restoration of the continuity is done only is done by anastomosing the colon to the dentate line or below it.
after 3-6 months for benign conditions (Figs 25-17A to C). Ultralow and coloanal types need laparoscopy for dissection and
4. Pelvic evisceration (Brunschwig’s operation): It is removal of stapler for anastomosis. Low anterior resection (LAR) is commonly
rectum with the tumour, all the lymph nodes, urinary bladder, fat, advocated either by open or through laparoscopy.
fascia, uterus, vagina, with colostomy and urinary diversion. It is
Preoperative evaluation and preparations are same—colonoscopy
neither favourable nor popular.
and biopsy; CEA; CT abdomen and pelvis to check nodal status and
5. Palliative colostomy is done in advanced unresectable growth
secondaries in liver; MRI pelvis to identify local infiltration; EUS is also
which presents with intestinal obstruction.
very useful. Bowel preparation is done as similar for colonic diseases
(please read in previous Chapter 24).
ANTERIOR RESECTION/ABDOMINAL
RADICAL RESTORATIVE OPERATION/ Technique
ANTERIOR PROCTOSIGMOIDECTOMY Position
(OPEN METHOD)
Patient is kept in modified lithotomy position with steep head down
It is called as anterior resection as dissection is done from above in front at 40°. Surgeon stands on left side. One assistant stands on right side;
through laparotomy. It is done in rectal carcinoma wherein tumour another in between legs of the patient.
is above, 6–14 cm from the anal verge; i.e. middle and upper thirds of
the rectum. Anterior resection is done as sphincter saving procedure
Incision
otherwise patient might have undergone abdominoperineal resection
with a permanent end colostomy. Lengthy midline incision is placed; abdominal cavity is explored for
Presently anterior resection of the rectum has widened definition secondaries; self retaining retractor is placed.
than the earlier one due to availability of the modern laparoscopic set
up. Anterior resection may be high (anastomosis above the peritoneal Sigmoid Dissection
reflection); low (anastomosis below the peritoneal reflection; ultra
low (anastomosis within 2 cm of the dentate line with sphincter Small bowel is pushed upwards and kept away from the pelvis. Distal
preservation). Coloanal anastomosis as sphincter saving procedure sigmoid may be occluded using a tape. Sigmoid colon is retracted
medially. Peritoneum on the left lateral paracolic gutter is exposed;
held between two haemostats and incised using scissor. Adhesions
in this lower pat are common which are released carefully. Peritoneal
incision on the lateral paracolic gutter is extended towards the
splenic flexure. Left ureter, left gonadals are identified. Left ureter
is dissected carefully and plastic loop is passed around it. Ureter is
dissected carefully downwards using scissor and bipolar cautery
down into the pelvis. Left hypogastric nerve in front of the internal
iliac artery is identified and safeguarded. Sigmoid colon is retracted
medially; incision is made on the right side of the sigmoid mesocolon.
A Dissection is done from bifurcation of the aorta downwards into the
pelvis. Right ureter is also identified as it crosses the bifurcation of the
common iliac artery in front of it. Right hypogastric nerve is identified
now. Incision is made on the rectovesical or rectouterine pouch to
mobilise the rectum from front. This also can be done at later period
during rectal mobilisation.
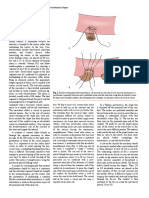
Vascular Ligation
Colon is mobilised and held upwards and left with traction. Gonadal
B vein is separated. Inferior mesenteric artery originating from the front
of the aorta is identified; fat and lymphatics (lymphovascular bundle)
are swept towards the specimen colorectum; inferior mesenteric artery
is divided 1.5 cm from its origin; it is also ligated and divided after it
gives off left colic branch to maintain the adequate blood supply in the
eventual anastomotic site which is essential. Preaortic sympathetic
nerve should be retained.
Presacral Dissection
C Sigmoid is retracted upwards and towards left to identify a tissue band
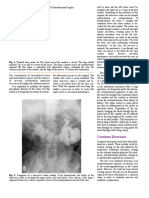
Figs 25-17A to C: Surgeries for carcinoma rectum (A) A-P resection, between posterior aspect of the rectum. It should be divided using
(B) Anterior resection, (C) Hartmann’s resection. cautery as it contains branches of the middle sacral artery. Loose
You might also like
- Abdominoperineal ResectionDocument17 pagesAbdominoperineal ResectionOhana S.No ratings yet
- Left Lateral Liver SegmentectomyDocument7 pagesLeft Lateral Liver SegmentectomyTeja Laksana NukanaNo ratings yet
- Visceral RenalDocument120 pagesVisceral RenalShivik PatelNo ratings yet
- Surgical Management Ca Colon 1Document81 pagesSurgical Management Ca Colon 1Shweta Achuthan KuttyNo ratings yet
- ChanDocument2 pagesChankenny stefanusNo ratings yet
- Miles Operation - Abdominoperineal Excision - Rectal CADocument5 pagesMiles Operation - Abdominoperineal Excision - Rectal CASpencer DempseyNo ratings yet
- Anatomy - B. Rabischong - GRDocument20 pagesAnatomy - B. Rabischong - GRAnonymous UHnQSkxLBDNo ratings yet
- Total Abdominal HysterectomyDocument19 pagesTotal Abdominal HysterectomyMeidina Rachma Amanda100% (1)
- Total Pelvic ExenterationDocument13 pagesTotal Pelvic ExenterationRirin Wahyuni100% (1)
- Lap NephrectomyDocument13 pagesLap NephrectomynadalNo ratings yet
- COLON ANATOMY AND SURGERYDocument37 pagesCOLON ANATOMY AND SURGERYDjan Kurvie ValencerinaNo ratings yet
- SOFT TISSUE EXPLORATORY CELIOTOMY PROCEDUREDocument8 pagesSOFT TISSUE EXPLORATORY CELIOTOMY PROCEDURECASANDRA ELIABETH PONCE VAZQUEZNo ratings yet
- Abdominal Vascular TraumaDocument7 pagesAbdominal Vascular TraumaKolea HanganuNo ratings yet
- ANATOMY AND EXAMINATION OF THE RECTUM AND ANAL CANALDocument129 pagesANATOMY AND EXAMINATION OF THE RECTUM AND ANAL CANALRadhika SethuNo ratings yet
- M6T4 - Máster en Actualización en Cirugía General y Del Aparato Digestivo - PDF - ENGDocument11 pagesM6T4 - Máster en Actualización en Cirugía General y Del Aparato Digestivo - PDF - ENGAbigail MirandaNo ratings yet
- Colonic Interposition For Benign DiseaseDocument18 pagesColonic Interposition For Benign DiseaseOhana S.No ratings yet
- Operative Procedures Guide: Venous Cut Down to VasectomyDocument10 pagesOperative Procedures Guide: Venous Cut Down to VasectomyLubeeha HaselNo ratings yet
- Aorto IliacDocument56 pagesAorto IliacShivik PatelNo ratings yet
- Sample Type: Obstetrics / Gynecology Sample NameDocument1 pageSample Type: Obstetrics / Gynecology Sample NamemmmooolllNo ratings yet
- Common ostomy surgeries and urinary diversionsDocument4 pagesCommon ostomy surgeries and urinary diversionsMohamed SalamaNo ratings yet
- PeritonioDocument5 pagesPeritonioSandro PinhoNo ratings yet
- Sleeve Gastrectomy 1Document3 pagesSleeve Gastrectomy 1alaaNo ratings yet
- Transhiatal EsophagectomyDocument12 pagesTranshiatal EsophagectomyprofarmahNo ratings yet
- Total Abdominal Hysterectomy TechniqueDocument9 pagesTotal Abdominal Hysterectomy TechniqueVikram DevNo ratings yet
- Procedural ReportDocument14 pagesProcedural ReportiamcharraeNo ratings yet
- Thoracic Vasculature: A. Thoracic Anatomy: IDocument87 pagesThoracic Vasculature: A. Thoracic Anatomy: IShivik PatelNo ratings yet
- Total Vaginal HysterectomyDocument7 pagesTotal Vaginal HysterectomyDR RISKA WAHYUNo ratings yet
- Rardin, Craig A.: Laparoscopic Low Anterior ResectionDocument2 pagesRardin, Craig A.: Laparoscopic Low Anterior ResectionTad SchmittNo ratings yet
- 2014-06-03-Anterior Abdominal Wall Slides PDFDocument18 pages2014-06-03-Anterior Abdominal Wall Slides PDFGrigore PopaNo ratings yet
- Caecocolic Intussusceptions in Horses: Clinical CommentaryDocument3 pagesCaecocolic Intussusceptions in Horses: Clinical CommentaryKiimBerly RcNo ratings yet
- DR (Major) Parthasarathy S Junior Resident, MS Orthopaedics Stanley Medical College, ChennaiDocument49 pagesDR (Major) Parthasarathy S Junior Resident, MS Orthopaedics Stanley Medical College, ChennaiKapil JagtapNo ratings yet
- Laparoscopic Flank Hernia RepairDocument10 pagesLaparoscopic Flank Hernia Repairmarquete72100% (3)
- Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy Dissection StepsDocument7 pagesLaparoscopic Cholecystectomy Dissection StepsTeja Laksana NukanaNo ratings yet
- Bilateral Direct HerniaDocument7 pagesBilateral Direct HerniaTeja Laksana NukanaNo ratings yet
- Iatrogenci BDIDocument90 pagesIatrogenci BDIUsmle GuyNo ratings yet
- Page 2089Document1 pagePage 2089cesaliapNo ratings yet
- CT scan confirms benign mesenteric cystDocument3 pagesCT scan confirms benign mesenteric cystmichelleNo ratings yet
- Abdominal Wall: Um-Hani'S Qbank Um-Hani'S QbankDocument5 pagesAbdominal Wall: Um-Hani'S Qbank Um-Hani'S QbankmedisharedNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Kidney and UreterDocument6 pagesAnatomy of The Kidney and UreterMario Ivan De la Cruz LaraNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Histology of the Large IntestineDocument7 pagesAnatomy and Histology of the Large IntestineredderdatNo ratings yet
- Surgical Anatomy Large IntestineDocument3 pagesSurgical Anatomy Large IntestineWildor Herrera GuevaraNo ratings yet
- APPENDECTOMYDocument12 pagesAPPENDECTOMYayouNo ratings yet
- Part VIII: Nongastrointestinal Transabdominal Surgery TechniquesDocument1 pagePart VIII: Nongastrointestinal Transabdominal Surgery TechniquescesaliapNo ratings yet
- Surgical Position Supino DecubbitusDocument4 pagesSurgical Position Supino DecubbitusMariana AmayaNo ratings yet
- Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy Technique and ComplicationsDocument13 pagesLaparoscopic Cholecystectomy Technique and ComplicationsNobalekunNo ratings yet
- 0.7 Surgery Trans PDFDocument29 pages0.7 Surgery Trans PDFJoy ManzanoNo ratings yet
- 4 Low AnteriorDocument8 pages4 Low AnteriorZikry SitaniaNo ratings yet
- TLHRSDocument2 pagesTLHRSxyzahoNo ratings yet
- Pre Op GEJ TumorDocument24 pagesPre Op GEJ TumorShankar LamichhaneNo ratings yet
- Open Gastrectomy - Radical: 1. Abdominal Cavity ApproachDocument12 pagesOpen Gastrectomy - Radical: 1. Abdominal Cavity ApproachTeja Laksana NukanaNo ratings yet
- Extracted Pages From Schwartz's EDITEDDocument5 pagesExtracted Pages From Schwartz's EDITEDMuhammed lotfiNo ratings yet
- Total Abdominal Hysterectomy With Bilateral Salpingo Oophorectomy.Document3 pagesTotal Abdominal Hysterectomy With Bilateral Salpingo Oophorectomy.Daywalker PedragozaNo ratings yet
- Schwartz UrologyDocument10 pagesSchwartz UrologyRem Alfelor100% (1)
- CHOLECYSTECTOMYDocument6 pagesCHOLECYSTECTOMYJagannath DasNo ratings yet
- Maniobras QuirurgicasDocument6 pagesManiobras Quirurgicasyesmaster15100% (3)
- Large Intestine PIMSR-Dr - Gosai 2022Document40 pagesLarge Intestine PIMSR-Dr - Gosai 2022Dr.B.B.GosaiNo ratings yet
- The Pancreas: Dr. Ali Kadhim Alhaider Consultant SurgeonDocument16 pagesThe Pancreas: Dr. Ali Kadhim Alhaider Consultant Surgeonhussain AltaherNo ratings yet
- Laparotomy & Laparocopy: Natalie Beatrice Horasia - 01073170054Document23 pagesLaparotomy & Laparocopy: Natalie Beatrice Horasia - 01073170054BOONo ratings yet
- Nongastrointestinal Transabdominal Surgery TechniquesDocument1 pageNongastrointestinal Transabdominal Surgery TechniquescesaliapNo ratings yet
- A Manual of the Operations of Surgery: For the Use of Senior Students, House Surgeons, and Junior PractitionersFrom EverandA Manual of the Operations of Surgery: For the Use of Senior Students, House Surgeons, and Junior PractitionersNo ratings yet
- AcneDocument20 pagesAcneAhmed RamiNo ratings yet
- NUGGETS INTERNAL MEDICINE FOR USMLE STEP-2Document75 pagesNUGGETS INTERNAL MEDICINE FOR USMLE STEP-2hippocamperNo ratings yet
- Sarw GTDocument1 pageSarw GTAhmed RamiNo ratings yet
- Tiki Taka CK SurgeryDocument50 pagesTiki Taka CK SurgeryEmad MerganNo ratings yet
- KD 2 Ahqkg N0 LP KHSVGN GDocument1 pageKD 2 Ahqkg N0 LP KHSVGN GAhmed RamiNo ratings yet
- Dermatology MnemonicDocument16 pagesDermatology MnemonicAhmed RamiNo ratings yet
- Making SenseDocument9 pagesMaking SenseAhmed RamiNo ratings yet
- Calibration and maintenance of blood pressure devicesDocument1 pageCalibration and maintenance of blood pressure devicesAhmed RamiNo ratings yet
- luJVYQb-jW1ImJJ YjWxDocument1 pageluJVYQb-jW1ImJJ YjWxAhmed RamiNo ratings yet
- GIDocument42 pagesGIAhmed RamiNo ratings yet
- Presented By: Bhagyashree KaleDocument58 pagesPresented By: Bhagyashree KaleSupriya JajnurkarNo ratings yet
- RPH Finals Quiz BeeDocument29 pagesRPH Finals Quiz BeeJoshua Liann EscalanteNo ratings yet
- NeurobiologyDocument2 pagesNeurobiologyjulianaNo ratings yet
- Schools Division of Roxas CityDocument4 pagesSchools Division of Roxas CityHuge Propalde EstolanoNo ratings yet
- Efektivitas Penggunaan Komposit Polimer Yang Diperkuat Serat Untuk Perbaikan Pipa Baja Bawah AirDocument15 pagesEfektivitas Penggunaan Komposit Polimer Yang Diperkuat Serat Untuk Perbaikan Pipa Baja Bawah Air31Hanif ArdhioNo ratings yet
- QAQC Mechanical EngineerDocument6 pagesQAQC Mechanical EngineerMohammed Anwaar ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Death Certificate: Shaheed Monsur Ali Medical College HospitalDocument3 pagesDeath Certificate: Shaheed Monsur Ali Medical College HospitalBokul80% (5)
- Gregg Perkin QualificationsDocument10 pagesGregg Perkin QualificationsOSDocs2012No ratings yet
- Learning Strand I - EnglishDocument19 pagesLearning Strand I - EnglishMaricel MaapoyNo ratings yet
- Child Development: Resilience & Risk, A Course SyllabusDocument17 pagesChild Development: Resilience & Risk, A Course SyllabusJane GilgunNo ratings yet
- KeirseyDocument28 pagesKeirseyapi-525703700No ratings yet
- 5090 w11 Ms 62Document3 pages5090 w11 Ms 62mstudy123456No ratings yet
- General Biology 1: Quarter 1 - Module - : Title: Cell CycleDocument27 pagesGeneral Biology 1: Quarter 1 - Module - : Title: Cell CycleRea A. Bilan0% (1)
- LakesDocument14 pagesLakesmanwartejam8No ratings yet
- Rock CycleDocument30 pagesRock CycleDenny PrawiraNo ratings yet
- Crude Palm Oil MSDS Provides Safety InformationDocument3 pagesCrude Palm Oil MSDS Provides Safety InformationCarlos MontanoNo ratings yet
- All India Test Series (2023-24)Document22 pagesAll India Test Series (2023-24)Anil KumarNo ratings yet
- PH 611: CO2 Release in RespirationDocument2 pagesPH 611: CO2 Release in RespirationAcuCJamNo ratings yet
- Forming Project ReportDocument9 pagesForming Project ReportMayur ShindeNo ratings yet
- How To Make Waffles - Recipes - Waffle RecipeDocument5 pagesHow To Make Waffles - Recipes - Waffle RecipeJug_HustlerNo ratings yet
- Class 8 Physics 3Document16 pagesClass 8 Physics 3Akhil ChintalapalliNo ratings yet
- A tribute to my mother's handsDocument3 pagesA tribute to my mother's handsAnonymous qAegy6GNo ratings yet
- Therapeutic Interventions in The Treatment of Dissociative DisordersDocument18 pagesTherapeutic Interventions in The Treatment of Dissociative DisordersCarla MesquitaNo ratings yet
- Valve Manual Pocket EditionDocument23 pagesValve Manual Pocket EditionBùi Cảnh Trung100% (1)
- Republic of The Philippines Cordillera Administrative Region Municipality of TanudanDocument1 pageRepublic of The Philippines Cordillera Administrative Region Municipality of Tanudanpablo gayodanNo ratings yet
- PST - Module 2 - Career Stage 2 Breakout Room Discussion Summary Table (g5)Document3 pagesPST - Module 2 - Career Stage 2 Breakout Room Discussion Summary Table (g5)Isidro PalomaresNo ratings yet
- ODI AmE L1 ExtraGrammarWkshtDocument30 pagesODI AmE L1 ExtraGrammarWkshtJuan Carlos FlorezNo ratings yet
- Diseases of The Kidney andDocument12 pagesDiseases of The Kidney andI. C. StraussmanNo ratings yet
- Processing Cacao Pod Husk into Low-Methoxyl PectinDocument9 pagesProcessing Cacao Pod Husk into Low-Methoxyl PectinEmmanuel PlazaNo ratings yet
- QB For HMTDocument11 pagesQB For HMTsmg26thmayNo ratings yet