Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Fluid Mechanics
Uploaded by
kennypenny0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
334 views3 pagesbest pdf
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentbest pdf
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
334 views3 pagesFluid Mechanics
Uploaded by
kennypennybest pdf
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
69
FLUID MECHANICS
Course Code: 13CE1107 L T P C
4 0 0 3
Course Educational Objectives:
✤ To introduce the concepts of fluid mechanics (along with application)
and fluid flow measurements.
✤ To familiarize the students with fluid statics and fluid dynamics.
Course Outcomes:
✤ Students will demonstrate the ability to apply the boundary layer
theory in aircraft structures.
✤ Students will be capable of understanding the behaviour in their static
and dynamic conditions of a fluid along with simple applications.
UNIT-I (10 Lectures)
INTRODUCTION :
Dimensions and units – Physical properties of fluids, density, specific
weight, specific volume, specific gravity, viscosity, surface tension, vapour
pressure and their influences on fluid motion- fluid continuum- pressure
at a point, Pascal’s law, Hydrostatic law - atmospheric, gauge and
vaccum pressure- measurement of pressure, Pressure gauges, Manometers:
Differential and Micro Manometers.
HYDROSTATIC FORCES:
Hydrostatic forces on submerged plane (Horizontal, Vertical, inclined)
and curved surfaces – Center of pressure, Derivations and problems.
UNIT-II (14 Lectures)
FLUID KINEMATICS:
Description of fluid flow, velocity, acceleration – convective, local and
total, Stream line, path line and streak lines and stream tube. Classification
of flows: Steady, unsteady, uniform, non-uniform, laminar, turbulent,
rotational and irrotational flows – Equation of continuity- one, two, three
G V P College of Engineering (Autonomous) 2013
70
dimensional flows – stream and velocity potential functions, flownet analysis.
UNIT-III (15 Lectures)
FLUID DYNAMICS:
Surface and body forces, Lagrangean and Eularian approaches – Concepts
of fluid system and control volume – control volume approach for fluid
flow problems – Euler’s and Bernoulli’s equations for flow for 2-D flow,
Momentum equation and its application – forces on pipe bend.
MEASUREMENT OF FLOW:
Pitot tube, Venturi meter and Orifice meter – classification of orifices and
mouth pieces–flow over rectangular, triangular and trapezoidal notches–
Broad crested weirs.
UNIT-IV (15 Lectures)
VISCOUS FLOW:
Reynolds experiment – Classification of Laminar & Turbulent flows. Flow
between two parallel plates, Flow through long pipes.
CLOSED CONDUIT FLOW:
Laws of Fluid friction – Darcy-Weisbach equation, Minor losses – pipes
in series – pipes in parallel – Total energy line and hydraulic gradient line,
variation of friction factor with Reynolds number – Moody’s Chart.
UNIT-V (10 Lectures)
BOUNDARY LAYER (BL) THEORY:
Concepts, Prandtl’s contribution, Characteristics of boundary layer along
a thin flat plate, laminar and turbulent Boundary layers (no derivations),
BL in transition, separation of BL, control of BL separation, flow around
submerged objects-Drag and Lift- Magnus effect.
TEXT BOOKS:
1. V.L.Streeter, E. Benjamin Wiley and W. Bedford, “Fluid
Mechanics”, 9th Edition, McGraw-Hill Companies, 1997.
2. P.N Modi and S.M. Seth, “Hydraulics and Fluid Mechanics
Including Hydraulic Machines”, 14th Edition, Standard Book
House, 2002.
G V P College of Engineering (Autonomous) 2013
71
3. K.L. Kumar, “Fluid Mechanics”, 6th Edition, Eurasia Publishing
House, 1995.
REFERENCES:
1. Frank.M. White, “Fluid Mechanics”, 14th Edition, Tata
McGraw hill Pvt. Ltd, 2002.
2. A.K. Mohanty, “Fluid Mechanics”, 14th Edition, Prentice Hall
of India Pvt. Ltd., New Delhi, 2002.
3. J.F. Douglas, J.M. Gasirock and J.A. Swaffield, “Fluid
Mechanics”, 14th Edition, Pearson Education Publishers, 2002.
4. A.K.Jain, “Fluid Mechanics Including Hydraulic Machines”,
8th Edition, Khanna Publishers, New Delhi, 2003.
pqr
G V P College of Engineering (Autonomous) 2013
You might also like
- Gears DifferentialDocument13 pagesGears Differentialpulkitymcaust_112907100% (1)
- Aliran TransienDocument7 pagesAliran Transienmdalimunthe_3No ratings yet
- 372 Quiz2 SolutionsDocument6 pages372 Quiz2 SolutionsDaniel Thomas EngleNo ratings yet
- MachineDocument32 pagesMachineArnabDasNo ratings yet
- Overviews of StaticsDocument70 pagesOverviews of StaticsJacous WcyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Evaporator ExercisesDocument1 pageChapter 9 Evaporator ExercisesAndrew PantaleonNo ratings yet
- I.C.E Assig.Document3 pagesI.C.E Assig.sherifkazem20100% (1)
- Chapter 12 OneSlideDocument143 pagesChapter 12 OneSlideSupper CoolNo ratings yet
- NRRS 2055first Revision 2069 DoLIDAR Reduced For WebDocument37 pagesNRRS 2055first Revision 2069 DoLIDAR Reduced For WebRazn Nhemaphuki100% (1)
- Engineering-Curves 1Document17 pagesEngineering-Curves 1api-327264533No ratings yet
- VL2018195002092 Da02Document3 pagesVL2018195002092 Da02ANKUR50% (2)
- V-Notch Weir Dimensional AnalysisDocument18 pagesV-Notch Weir Dimensional AnalysisDenys Ilyushenko100% (2)
- DR Raudhah Ahmadi KNS1633 Engineering Mechanics Civil Engineering, UNIMASDocument32 pagesDR Raudhah Ahmadi KNS1633 Engineering Mechanics Civil Engineering, UNIMASAriff JasniNo ratings yet
- CH 02Document32 pagesCH 02TahaNo ratings yet
- Orifice Mouthpiece ManualDocument5 pagesOrifice Mouthpiece ManualgpradiptaNo ratings yet
- Non-Uniform Flow Specific Energy DiagramsDocument16 pagesNon-Uniform Flow Specific Energy DiagramsLuqma IllieanaNo ratings yet
- Numerical Methods and Computer ProgrammingDocument19 pagesNumerical Methods and Computer ProgrammingSabby OnindoNo ratings yet
- Cmo 28 s2007 Annex III - Course SpecificationsDocument63 pagesCmo 28 s2007 Annex III - Course SpecificationsRonald CordobaNo ratings yet
- 03-Hydrostatics Hydrokinematics HydrodynamicsDocument30 pages03-Hydrostatics Hydrokinematics HydrodynamicsSarmad KhanNo ratings yet
- Docslide - Us - Gate MFG Latest PDFDocument210 pagesDocslide - Us - Gate MFG Latest PDFAnonymous Zx7EG1PaNo ratings yet
- Applications Hamilton PrincipleDocument12 pagesApplications Hamilton PrincipleSeparatorNo ratings yet
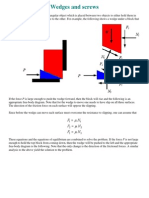
- Wedges and ScrewsDocument4 pagesWedges and ScrewsK-Jay Eduku ArmahNo ratings yet
- Static and Dynamic Analysis of Suspension SystemDocument6 pagesStatic and Dynamic Analysis of Suspension SystemTrbvmNo ratings yet
- Relative MotionDocument3 pagesRelative Motionkaushik247No ratings yet
- PSC Automobile Question PaperDocument12 pagesPSC Automobile Question PaperArun KNo ratings yet
- Hibbeler, Mechanics of Materials-Stress Transformation 2Document69 pagesHibbeler, Mechanics of Materials-Stress Transformation 2poom2007No ratings yet
- Scheme – E Sample Question Paper for Fluid Mechanics & MachineryDocument4 pagesScheme – E Sample Question Paper for Fluid Mechanics & MachineryaadhanNo ratings yet
- Characteristics Curves of Pelton WheelDocument4 pagesCharacteristics Curves of Pelton WheelbhucoolsNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Sheet 2Document1 pageTutorial Sheet 2Supriya YadavNo ratings yet
- Experiment NoDocument9 pagesExperiment NoAli RazaNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics and Hydraulic Machines CourseDocument3 pagesFluid Mechanics and Hydraulic Machines CourseAbdul Rauf Noohani100% (1)
- Internal expanding shoe brake torque calculationDocument7 pagesInternal expanding shoe brake torque calculationKathireswaran PNo ratings yet
- Module 5 PDFDocument15 pagesModule 5 PDFMani chandanNo ratings yet
- Surveying I Syllabus and Lesson PlanDocument124 pagesSurveying I Syllabus and Lesson Planဒုကၡ သစၥာNo ratings yet
- Practice Exam2 - SolutionsDocument10 pagesPractice Exam2 - SolutionsRyan KellyNo ratings yet
- Eme Question BankDocument13 pagesEme Question Bankapi-315791751No ratings yet
- Tom-I Question Bank UpdatedDocument174 pagesTom-I Question Bank Updatedkiran_wakchaureNo ratings yet
- KDM 6Document54 pagesKDM 6KarthikeyanRamanujamNo ratings yet
- Dhanalakshmi College of Engineering: (DR - VPR Nagar, Manimangalam, Tambaram) Chennai - 601 301Document18 pagesDhanalakshmi College of Engineering: (DR - VPR Nagar, Manimangalam, Tambaram) Chennai - 601 301Sridiwakaran Parameswaran100% (1)
- Flaw Detection of Materials and ComponentsDocument11 pagesFlaw Detection of Materials and ComponentsSathish Kumar100% (2)
- Stresses and Strains (Part 1)Document44 pagesStresses and Strains (Part 1)AMIE Study Circle, RoorkeeNo ratings yet
- 3 - Kinetics of Particle - Work & EnergyDocument33 pages3 - Kinetics of Particle - Work & EnergyIndroNo ratings yet
- Ce8E - Mechanics of Fluids Ay2018-2019Document5 pagesCe8E - Mechanics of Fluids Ay2018-2019Lyka Jane PesiganNo ratings yet
- CH 14Document13 pagesCH 14mssaber77No ratings yet
- What Is The Difference Between The Classical and The Statistical Approaches To ThermodynamicsDocument1 pageWhat Is The Difference Between The Classical and The Statistical Approaches To ThermodynamicsVikram Kumar100% (1)
- Mohr's Circle Method ExplainedDocument22 pagesMohr's Circle Method ExplainedSurjit Kumar GandhiNo ratings yet
- Final Exam CEE 211: Fluid Mechanics Total Marks: 60 Time: 2.0 HoursDocument2 pagesFinal Exam CEE 211: Fluid Mechanics Total Marks: 60 Time: 2.0 HoursAvijit SahaNo ratings yet
- Theory of Machines and Mechanisms: Solutions Manual To AccompanyDocument10 pagesTheory of Machines and Mechanisms: Solutions Manual To Accompany이원석No ratings yet
- Differential Transformation Method for Mechanical Engineering ProblemsFrom EverandDifferential Transformation Method for Mechanical Engineering ProblemsNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics and Hydraulic Machine PDFDocument3 pagesFluid Mechanics and Hydraulic Machine PDFChaudhary Rahul SinghNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics Course OverviewDocument2 pagesFluid Mechanics Course Overviewnandan144No ratings yet
- Fluid MechanicsDocument2 pagesFluid MechanicsJosiah AdesolaNo ratings yet
- ME 203 Mechanics of FluidsDocument3 pagesME 203 Mechanics of FluidsSherwinNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics SyllabusDocument2 pagesFluid Mechanics Syllabusshailendra_236No ratings yet
- 4me3 Fluid MechanicsDocument4 pages4me3 Fluid MechanicsGautam GunjanNo ratings yet
- CE203 Fluid Mechanics I PDFDocument3 pagesCE203 Fluid Mechanics I PDFBalagopal VNo ratings yet
- Ce8302 FM PresentationDocument102 pagesCe8302 FM PresentationRON SAMUEL 401935100% (1)
- Ce8302 Fluid Mechanics CivilDocument2 pagesCe8302 Fluid Mechanics CivilersnkrishnanNo ratings yet
- ME301 Fluid Mechanics I Syllabus (2022)Document2 pagesME301 Fluid Mechanics I Syllabus (2022)luciatricasarbesuNo ratings yet
- CV 303 Hydraulic Engineering - I: Course ContentsDocument2 pagesCV 303 Hydraulic Engineering - I: Course ContentsSushant WaghmareNo ratings yet
- Biogeochemical CycleDocument22 pagesBiogeochemical CyclekennypennyNo ratings yet
- Presentation 1envi EngineeringDocument2 pagesPresentation 1envi EngineeringkennypennyNo ratings yet
- Presentation 1Document15 pagesPresentation 1kennypennyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Rizal in France and GemanyDocument2 pagesChapter 9 Rizal in France and GemanykennypennyNo ratings yet
- Celeritas - C - Speed of Light 670 Million Miles Per Hour Michael Farday-Electromagnetism 144 Divided by 233 Is Equaal To Theta or Golden Ratio Fibonacci Is An Italian Mathematecian From 13ThDocument1 pageCeleritas - C - Speed of Light 670 Million Miles Per Hour Michael Farday-Electromagnetism 144 Divided by 233 Is Equaal To Theta or Golden Ratio Fibonacci Is An Italian Mathematecian From 13ThkennypennyNo ratings yet
- Presentation 2vnhfgsseerDocument20 pagesPresentation 2vnhfgsseerkennypennyNo ratings yet
- Presentation 1Document15 pagesPresentation 1kennypennyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Rizal in France and GemanyDocument2 pagesChapter 9 Rizal in France and GemanykennypennyNo ratings yet
- Jeremy Dan Fabian: Name Media Purpose TimeDocument2 pagesJeremy Dan Fabian: Name Media Purpose TimekennypennyNo ratings yet
- Media - Log 3.0Document2 pagesMedia - Log 3.0kennypennyNo ratings yet
- Swot AnalysisDocument2 pagesSwot AnalysiskennypennyNo ratings yet
- Jeremy Dan Fabian: Name Media Purpose TimeDocument2 pagesJeremy Dan Fabian: Name Media Purpose TimekennypennyNo ratings yet
- Analysis and Design of Structures Analysis and Design of StructuresDocument6 pagesAnalysis and Design of Structures Analysis and Design of StructureskennypennyNo ratings yet
- 3dsmaxdesign 2010 Using Autocad Files00Document87 pages3dsmaxdesign 2010 Using Autocad Files00Arpan Pansuria100% (1)
- The International System of Units (SI) Converter PDFDocument27 pagesThe International System of Units (SI) Converter PDFMaey AkimNo ratings yet
- Physics PG 169 268 PDFDocument100 pagesPhysics PG 169 268 PDFkennypennyNo ratings yet
- Sample Building Plans2 PDFDocument12 pagesSample Building Plans2 PDFAngel Lisette LaoNo ratings yet
- A and The Maximum Deflection. EI Is ConstantDocument41 pagesA and The Maximum Deflection. EI Is Constantrameshaarya99No ratings yet
- Lec Intro ME362Document20 pagesLec Intro ME362Jom BonhayagNo ratings yet
- Structural Analysis by Example PDFDocument66 pagesStructural Analysis by Example PDFkennypennyNo ratings yet
- Free Structural Engineering Solved Problems EbookDocument6 pagesFree Structural Engineering Solved Problems EbookkennypennyNo ratings yet
- UNIT LOAD METHOD TITLEDocument53 pagesUNIT LOAD METHOD TITLEkennypennyNo ratings yet
- Analysis and Design of Structures Analysis and Design of StructuresDocument6 pagesAnalysis and Design of Structures Analysis and Design of StructureskennypennyNo ratings yet
- 2 - Newton - S Second Law of Motion PDFDocument4 pages2 - Newton - S Second Law of Motion PDFRick PongiNo ratings yet
- Review Fe Exam Structures SaoumaDocument51 pagesReview Fe Exam Structures Saoumagtslty99100% (1)
- Fundamental Problems Solution:: 0 A CrateDocument1 pageFundamental Problems Solution:: 0 A CratekennypennyNo ratings yet
- Solution Manuals of Dynamics by Hibbeler 10th Edition PDFDocument564 pagesSolution Manuals of Dynamics by Hibbeler 10th Edition PDFdavidbeh100% (1)
- Cycle Test Solutions 6 Problems PDFDocument6 pagesCycle Test Solutions 6 Problems PDFkennypennyNo ratings yet
- Conductance: Chapter 5 - Series and Parallel CircuitsDocument7 pagesConductance: Chapter 5 - Series and Parallel CircuitskennypennyNo ratings yet
- VAA /RU /DL 34 (100) : Pressure Relief ValvesDocument2 pagesVAA /RU /DL 34 (100) : Pressure Relief ValvesSachin RamadasanNo ratings yet
- Empuje Axial en Bombas VerticalesDocument6 pagesEmpuje Axial en Bombas VerticalesKaler Soto PeraltaNo ratings yet
- Compressible Flow - Water HammerDocument7 pagesCompressible Flow - Water Hammersiroliver39No ratings yet
- 1.3 Basic Hydraulic Symbols and Major ComponentsDocument31 pages1.3 Basic Hydraulic Symbols and Major ComponentsKhaled RabeaNo ratings yet
- Get The Best Performance From Your Cascade Attachment With Hydraulic Valve KitsDocument3 pagesGet The Best Performance From Your Cascade Attachment With Hydraulic Valve KitsVictor ValenciaNo ratings yet
- An Overview of Pump Classification and Performance ParametersDocument58 pagesAn Overview of Pump Classification and Performance Parametersmahadp08No ratings yet
- PD10P FPS PTT Operators ManualDocument2 pagesPD10P FPS PTT Operators ManualesrrdhsreNo ratings yet
- Directional Control Valves ExplainedDocument19 pagesDirectional Control Valves ExplainedMANOJ MNo ratings yet
- Válvulas Solenoíde PARKERDocument70 pagesVálvulas Solenoíde PARKERSamuel AugustoNo ratings yet
- Internal Flow Through Pipes and Ducts PDFDocument30 pagesInternal Flow Through Pipes and Ducts PDFhirenkumar patelNo ratings yet
- Flow Through A Circular TubeDocument8 pagesFlow Through A Circular TubeAnas Iqmal0% (1)
- 00525179001075223667Document1 page00525179001075223667BhaveshNo ratings yet
- SP5A SS StainlessSteelHandOperatedHydraulicPumps SP A&SP A PLSeries PDFDocument3 pagesSP5A SS StainlessSteelHandOperatedHydraulicPumps SP A&SP A PLSeries PDFmadhan rajNo ratings yet
- Accumulator (Pilot) - Test and ChargeDocument7 pagesAccumulator (Pilot) - Test and Chargejohn ayengah100% (1)
- UuuuuuuDocument2 pagesUuuuuuuNandNNo ratings yet
- NASCAR AerodynamicsDocument28 pagesNASCAR Aerodynamicsrajesh_dath100% (2)
- 5 Pipe Loops Versus Compression: 2785 - C005.fm Page 177 Friday, April 1, 2005 3:30 PMDocument24 pages5 Pipe Loops Versus Compression: 2785 - C005.fm Page 177 Friday, April 1, 2005 3:30 PMMMMOH200No ratings yet
- ds65 700 PDFDocument4 pagesds65 700 PDFkumar_chemicalNo ratings yet
- CFM56 Hydraulic Training ManualDocument72 pagesCFM56 Hydraulic Training ManualHeber CastroNo ratings yet
- Industry Guidelines: Solvent Cement Welding of PVC PipeDocument1 pageIndustry Guidelines: Solvent Cement Welding of PVC PipeAnonymous eq5zSUNo ratings yet
- Boiler Mountings and AccessoriesDocument3 pagesBoiler Mountings and AccessoriesAbdul RehmanNo ratings yet
- Technical Specification For Pressure Relief Valves PDFDocument7 pagesTechnical Specification For Pressure Relief Valves PDFat35100% (1)
- Poster Group 7Document1 pagePoster Group 7api-392769552No ratings yet
- CEGP013091: N.B. N.B. N.B. N.B. I Six or or or or or or II III IV VDocument5 pagesCEGP013091: N.B. N.B. N.B. N.B. I Six or or or or or or II III IV VMuhammed YussufNo ratings yet
- Effectiveness of an anti vortex device in a sump modelDocument12 pagesEffectiveness of an anti vortex device in a sump modelVipin JoseNo ratings yet
- Pneumax Omni 36ckDocument48 pagesPneumax Omni 36ckbbaskaranNo ratings yet
- Eeuo Part3 Part3Document2 pagesEeuo Part3 Part3Kelli FloresNo ratings yet
- FLOWMAX CL Variable Range ProportionerDocument4 pagesFLOWMAX CL Variable Range ProportionerAnonymous S9qBDVkyNo ratings yet
- PN15CS1S01Document4 pagesPN15CS1S01joadNo ratings yet
- Glamour Fi Nov 2013 Price ListDocument84 pagesGlamour Fi Nov 2013 Price ListSANTOSH KUMARNo ratings yet