Professional Documents
Culture Documents
BTS Components
Uploaded by
SHIWANGI GARGCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
BTS Components
Uploaded by
SHIWANGI GARGCopyright:
Available Formats
Experiment-12
Aim: - To study GSM architecture and BTS components.
Theory: -
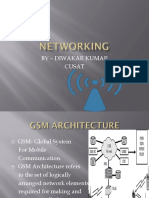
Global System for Mobile (GSM) is a second generation cellular system
standard that was developed to solve the fragmentation problems of the first cellular systems
in Europe. The GSM system architecture consists of three major interconnected subsystems.
The subsystems are the Base Station Subsystem (BSS), Network and Switching Subsystem
(NSS), and the Operation Support Subsystem (OSS).
Mobile device is connected to BTS (Antenna).
Base Station: It is a fixed station that consists of transmitters and receivers mounted
on tall Towers strategically placed at different locations.
BTS is connected to the Switching system called BSC.
BSC is connected to the main switching system called MSC.
MSC contains its own VLR (VLR: is a temporary database which stores the
information of the visitors under its coverage area. VLR stands for Visitor Location
register. When you roam in a different place VLR stores your user information.).
MSC's are connected to GMSC which is connected to HLR. (HLR stands for Home
location register; it is the main database where the documents or information of user is
stored. All the documents that you give during purchase of a SIM card are stored in this
HLR. VLR takes your information from HLR when you roam in other state or region).
BTS Components:
1. Base Band Unit (BBU): - A unit that processes baseband in telecomm systems. A
typical wireless telecom station consists of the baseband processing unit and the RF
processing unit (remote radio unit - RRU). The baseband unit is placed in the
equipment room and connected with RRU via optical fiber. The BBU is responsible
for communication through the physical interface. A BBU has the following
characteristics: modular design, small size, low power consumption and can be easily
deployed.
Modules of BBU
I. Universal Power and Environment Interface Unit (UPEU): -
It supports the -48V/+24V DC Power input, supplies power to the boards,
modules and fan in the BBU and provides access to multiple environment
monitoring signals.
II. Universal Environment Interface Unit (UEIU): - It supports multiple
environment monitoring signals and eight Boolean alarm signals and two RS485
environment monitoring signals.
2. Double Radio Filter Unit (DRFU): - It performs modulation and demodulation
between base band signals and RF signals, processes data, and combines and divides
signals. It consists of high speed interface unit, signal processing unit, power
amplifier and dual duplexer.
3. Direct Current Distribution Unit (DCDU): - It is the DC distribution unit or device.
It serves for distributing the DC power needed for different power needed devices like
RRU, EMUB, BBU and many more. DCDU-12B of Huawei consists of two input
terminal blocks and 10 different ports for output. Each port or certain port is assign
for its maximum output fuse current.
4. GSM Transmission and Management Unit (GTMU): - It controls and manages the
entire BTS. It provides interface related to the reference clock, power supply, OM and
external alarm collection. It supports fault management, configuration management,
performance management and security management. It provides port for terminal
maintenance and clock input for testing.
You might also like
- Base Transceiver StationDocument2 pagesBase Transceiver StationArslan Ali100% (1)
- RNT Lte Dim v2.3.6Document305 pagesRNT Lte Dim v2.3.6蘇菲和尚No ratings yet
- LTE Network Planning and Optimizing PDFDocument165 pagesLTE Network Planning and Optimizing PDFlisamharleyNo ratings yet
- Telecom AssignmentDocument5 pagesTelecom Assignmentikra khanNo ratings yet
- HUAWEI BTS3900 Hardware StructureDocument26 pagesHUAWEI BTS3900 Hardware Structurejisjthomas100% (1)
- HUAWEI DBS3900 Dual-Mode Base Station Hardware Structure and PincipleDocument75 pagesHUAWEI DBS3900 Dual-Mode Base Station Hardware Structure and PincipleJordan Tuazon Unidad100% (1)
- BTS3900 GSM Site Maintenance Guide - (V300R008&R009 - 02)Document55 pagesBTS3900 GSM Site Maintenance Guide - (V300R008&R009 - 02)engrvinzz100% (1)
- Fitsum Mergia-2Document5 pagesFitsum Mergia-2mickyalemuNo ratings yet
- 8 - Huawei Hardware and Site Solution For NB-IoTDocument33 pages8 - Huawei Hardware and Site Solution For NB-IoTHuy LieuNo ratings yet
- Local Maintenance TerminalDocument2 pagesLocal Maintenance TerminalPankaj Jaswal100% (1)
- Plan and Optimize Backhaul Networks with Atoll MicrowaveDocument4 pagesPlan and Optimize Backhaul Networks with Atoll MicrowaveRhegindNo ratings yet
- Channel Selective Repeaters Manual, Rev B-1 (GSM+UMTS)Document370 pagesChannel Selective Repeaters Manual, Rev B-1 (GSM+UMTS)Дима ВерхотуровNo ratings yet
- GSM PDFDocument16 pagesGSM PDFAbby WestNo ratings yet
- LTE Network Planning by Alemnew, Tigabu and MulukenDocument29 pagesLTE Network Planning by Alemnew, Tigabu and MulukenAmare Kassaw100% (2)
- Co-BCCH Cell: About This ChapterDocument30 pagesCo-BCCH Cell: About This ChapterPrasoon SinghNo ratings yet
- Huawei GSM Dbs3900 Hardware Structure-20080807-Issue4.0Document50 pagesHuawei GSM Dbs3900 Hardware Structure-20080807-Issue4.0Mohammed Amine HalbabaNo ratings yet
- Quick Guide To DC-HSDPADocument5 pagesQuick Guide To DC-HSDPATrung HieuNo ratings yet
- SJ-20130509142153-001-ZXSDR R8863 (HV1.0) Product Description - 573602Document35 pagesSJ-20130509142153-001-ZXSDR R8863 (HV1.0) Product Description - 573602Nouvric Int100% (1)
- Scope of Work Responsibility MatrixDocument33 pagesScope of Work Responsibility Matrixelectrico servicesNo ratings yet
- Metricell General PresentationDocument39 pagesMetricell General PresentationkarimbandariNo ratings yet
- Timing Advance in GSM ExplainedDocument2 pagesTiming Advance in GSM ExplainedShakil AhmedNo ratings yet
- Actix Troubleshooting and Optimizing UMTS Network PDFDocument124 pagesActix Troubleshooting and Optimizing UMTS Network PDFccmm-1No ratings yet
- Huawei 3900 BtsDocument4 pagesHuawei 3900 Btsdepeople_arsenal7569No ratings yet
- Mobile TelecommunicationDocument79 pagesMobile Telecommunicationteguia donatienNo ratings yet
- 3G Interfaces RNC DimensioningDocument70 pages3G Interfaces RNC Dimensioningcreativemurugan100% (1)
- GUIDELINE TO EXTEND CAPACITY IN 3G NOKIA UpdateDocument32 pagesGUIDELINE TO EXTEND CAPACITY IN 3G NOKIA UpdatesermmysNo ratings yet
- Radio Base Station Site Setup GuideDocument44 pagesRadio Base Station Site Setup GuideAung Thein Oo100% (1)
- TE 484: Network PlanningDocument65 pagesTE 484: Network PlanningopareaduboahenNo ratings yet
- MU-MIMO in LTEDocument13 pagesMU-MIMO in LTECM_123No ratings yet
- Nastar Network Optimization User Guide (UMTS) - (V600R009 - 01) (PDF) - enDocument437 pagesNastar Network Optimization User Guide (UMTS) - (V600R009 - 01) (PDF) - enSeby SebykNo ratings yet
- Provisional Acceptance Test PAT Report FDocument5 pagesProvisional Acceptance Test PAT Report Fphantd_hcmNo ratings yet
- Sample CV For - NOCDocument4 pagesSample CV For - NOCAzeemuddin KhajaNo ratings yet
- Aster IntershipDocument59 pagesAster IntershipAster Takele Official100% (1)
- ZTE UMTS NodeB Hardware Installation V.2Document101 pagesZTE UMTS NodeB Hardware Installation V.2eliyadi suwardi100% (1)
- Book On UMTS-An Introduction To UMTS TechnologyDocument3 pagesBook On UMTS-An Introduction To UMTS TechnologyDeepakNathNo ratings yet
- Huawei BSC6000 ProceduresDocument72 pagesHuawei BSC6000 Procedureskanisha2014No ratings yet
- MOD CELLALGOSWITCH LocalCellId=0 TD20 ScriptDocument14 pagesMOD CELLALGOSWITCH LocalCellId=0 TD20 ScriptPetson ChirangaraNo ratings yet
- Procedure For Binning Using XcalDocument13 pagesProcedure For Binning Using XcalHazamir HamzahNo ratings yet
- Mplanet 5-8Document76 pagesMplanet 5-8ColbertNo ratings yet
- 2G-3G Conversion HuaweiDocument19 pages2G-3G Conversion HuaweiemailbasirNo ratings yet
- Configuracion y O&M BTS NokiaDocument43 pagesConfiguracion y O&M BTS Nokiajcardenas55No ratings yet
- HUAWEI NASTAR OPTIMIZATION TOOL OVERVIEWDocument37 pagesHUAWEI NASTAR OPTIMIZATION TOOL OVERVIEWdha721100% (1)
- GSA Spectrum For LTE SnapshotDocument6 pagesGSA Spectrum For LTE SnapshotOrgilbayar PurevkhuuNo ratings yet
- White Paper For CDMA2000 1xEV-DO Rev.B Network Planning V1.3 (20100112)Document42 pagesWhite Paper For CDMA2000 1xEV-DO Rev.B Network Planning V1.3 (20100112)cyclicprefixNo ratings yet
- Cell Broadcast (GBSS13.0 01)Document30 pagesCell Broadcast (GBSS13.0 01)Rami DahhanNo ratings yet
- What Is 3GDocument15 pagesWhat Is 3GShampad AyanNo ratings yet
- GSM and Lte Network ArchitectureDocument12 pagesGSM and Lte Network ArchitectureKarthik Mohan KNo ratings yet
- 3900 & 5900 Series Base Station Maintenance Guide (26) (PDF) - ENDocument1,108 pages3900 & 5900 Series Base Station Maintenance Guide (26) (PDF) - ENEurico BarbosaNo ratings yet
- U-Net Planning ToolDocument39 pagesU-Net Planning Toolruqmus100% (2)
- Introduction To ZXSDR Products (GSM)Document68 pagesIntroduction To ZXSDR Products (GSM)golak9107100% (7)
- Huawei's 3900 Series Multi-Mode Base Stations Offer Future-Oriented Network SolutionDocument4 pagesHuawei's 3900 Series Multi-Mode Base Stations Offer Future-Oriented Network SolutionOgbodo EmmanuelNo ratings yet
- Cross-Layer Resource Allocation in Wireless Communications: Techniques and Models from PHY and MAC Layer InteractionFrom EverandCross-Layer Resource Allocation in Wireless Communications: Techniques and Models from PHY and MAC Layer InteractionNo ratings yet
- VoLTE and ViLTE: Voice and Conversational Video Services over the 4G Mobile NetworkFrom EverandVoLTE and ViLTE: Voice and Conversational Video Services over the 4G Mobile NetworkNo ratings yet
- Making Telecoms Work: From Technical Innovation to Commercial SuccessFrom EverandMaking Telecoms Work: From Technical Innovation to Commercial SuccessNo ratings yet
- Chapter # 1Document51 pagesChapter # 1Chea SovongNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 Basic Cellular SystemDocument14 pagesUnit-1 Basic Cellular SystemBhuvan VarmaNo ratings yet
- By - Diwakar Kumar CusatDocument43 pagesBy - Diwakar Kumar CusatDIWAKAR KUMARNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2. Telephone System InstallationsDocument25 pagesLecture 2. Telephone System InstallationsOpilaStephen100% (1)
- Huawei Performance CounterDocument510 pagesHuawei Performance Counterdavemendrofa100% (3)
- IP-LDK Programming Manual V38Document377 pagesIP-LDK Programming Manual V38Daniel TaradaciucNo ratings yet
- CloudGuard security portfolio offerings for cloud native environmentsDocument4 pagesCloudGuard security portfolio offerings for cloud native environmentsGerman DelgadilloNo ratings yet
- CradlePoint CBA250 DataSheetDocument2 pagesCradlePoint CBA250 DataSheetserena8673No ratings yet
- Session 1 ICS Basics - Q and ADocument5 pagesSession 1 ICS Basics - Q and ARocKetNo ratings yet
- VST 1Document3 pagesVST 1Manoj GuruNo ratings yet
- Alerton - LTBT VLC 660R PDFDocument2 pagesAlerton - LTBT VLC 660R PDFcamaleon86No ratings yet
- RACH and BEAM Management 5G NRDocument28 pagesRACH and BEAM Management 5G NRabhijeetfamt88% (17)
- Aws Scte 35Document4 pagesAws Scte 35RobertNo ratings yet
- BrightSpeed system block diagram manualDocument1 pageBrightSpeed system block diagram manualMario RamosNo ratings yet
- Unit 11 Computer Network Assignment 2 Naim Miah Student NoDocument13 pagesUnit 11 Computer Network Assignment 2 Naim Miah Student Noapi-567992098No ratings yet
- ECE3001 Analog Communication Systems NOV-2017Document3 pagesECE3001 Analog Communication Systems NOV-2017Siva ShankarNo ratings yet
- RF Drive Test Tutorial Demo VersionDocument32 pagesRF Drive Test Tutorial Demo Versionanupamkhanna100% (5)
- Qos Drive Test MethodologyDocument11 pagesQos Drive Test MethodologyArinze OkemefunaNo ratings yet
- Astro XTL 2500Document161 pagesAstro XTL 2500RTFGRENo ratings yet
- Classical Encryption TechniquesDocument63 pagesClassical Encryption TechniquesmanNo ratings yet
- 32pfl5606d PDFDocument67 pages32pfl5606d PDFlgNo ratings yet
- PostgreSQL HAProxy Proxy For HA and Load Balance - Alibaba Cloud CommunityDocument9 pagesPostgreSQL HAProxy Proxy For HA and Load Balance - Alibaba Cloud CommunityAymenNo ratings yet
- Backup Ro NinDocument5 pagesBackup Ro Ninkenjiro08No ratings yet
- Wireless CommunicationDocument104 pagesWireless Communicationwroxtar33% (3)
- Module-I TCP-IP Overview & Ethernet PDFDocument61 pagesModule-I TCP-IP Overview & Ethernet PDFswarnendu dasNo ratings yet
- At A Glance c45 736624Document6 pagesAt A Glance c45 736624ShanehalNo ratings yet
- Configure The Mitel 3300 MCD For Use With Microsoft Exchange 2007Document21 pagesConfigure The Mitel 3300 MCD For Use With Microsoft Exchange 2007Chris McAndrewNo ratings yet
- Tipos de AntenasDocument7 pagesTipos de AntenasDaniel AtiNo ratings yet
- LTE Idle ModeDocument27 pagesLTE Idle ModeOmar AbdelhakNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 - Data Center FacilitiesDocument20 pagesUnit 4 - Data Center FacilitiesMohammedNo ratings yet
- 2.7.3 Packet Tracer Multiarea Ospf Exploration Physical Mode Part 1Document4 pages2.7.3 Packet Tracer Multiarea Ospf Exploration Physical Mode Part 1bongNo ratings yet
- Motorola WiNG 5 WLAN PresentationDocument17 pagesMotorola WiNG 5 WLAN PresentationMotorola Wireless Network SolutionsNo ratings yet
- M00667-03 pdl450 Manual Rev C-Lw-Js - 9-30-05Document42 pagesM00667-03 pdl450 Manual Rev C-Lw-Js - 9-30-05Guilherme Zaramella BetoniNo ratings yet
- Para List For UmtsDocument654 pagesPara List For UmtsSubhi RosdianNo ratings yet