Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Negligence Analysis
Uploaded by
Brat WurstCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Negligence Analysis
Uploaded by
Brat WurstCopyright:
Available Formats
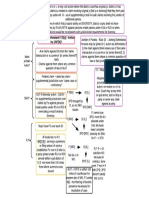
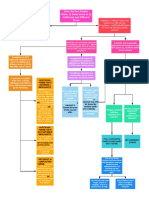
Standard narrowed for physically disabled, children (not mentally disabled!).
In
1. Zone of Danger
emergency situations, act as a reasonable person in that emergency.
2. Relationships
NEGLIGENCE 3. Public Policy
Professional standard of care: professional must exercise the requisite degree
4. Misfeasance
ANALYSIS Is a duty owed? of learning, skills, and ability of that calling with reasonable and ordinary care.
Generally, not to expose Custom: not a duty in itself, but evidence of a reasonable common practice can
foreseeable victims to an show a reasonable person would've followed it
What is the unreasonable risk of harm - to
act as a reasonable person Statute: can impose a duty to comply in cases where safety statute, P in class of
duty? would. people protected by statute, suffered harm statute designed to prevent
Duty
Invitee (business purposes): duty to keep premises reasonably safe and inspect for latent defects
Licensee (Social Guest): no duty to act to keep premises safe, just warn of hidden dangers known to host and refrain from
Affirmative/Heightened hurting licensee
Duties Trespasser:generally no duty until you discover them or have reason to except them (diff. for children)
Landlord to Tenant: generally, no duty, six exceptions (no duty to social guests either)
NO DUTY OWED Rescue: no duty to rescue, but if you voluntarily undertake a rescue, you assume a duty to proceed in a
WHEN: pure non-negligent manner
economic harm or
emotional distress
If you caused the harm or what caused the harm is under your control, duty
without physical
Special Relationships: to render assistance
symptoms (unless
bystander) Duty to warn a third party if you know of a specific danger to that specfic
plaintiff
B < PL: likelihood that conduct will cause harm + gravity of harm outweigh Common carriers to passengers, innkeepers to guests, public utilities,
the burden, so a reasonable person would have taken precautions business/possessor of land with premises open to public, employer to
employees who are in imminent danger or injured and helpless
Social utility: does the social utility of the conduct outweigh the harm?
Special relationship can arise between parties if one party has control ability
Social utility argument can fail if harm is very severe.
over person/area and other doesn't and therefore, D should've taken
measures to protect P (sex abuse case)
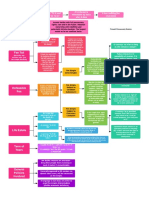
Custom can be indication of how a reasonable person would act. If they
Breach deviated from established custom, P can argue evidence of unreasonable
person. If D complied, maybe the whole industry is wrong and the custom
is unreasonable.
Circumstantial evidence (such as constructive notice) and Rep Ipsa Loquitor can be used to show
breach.
Violation of a safety statute or regulation can establish breach if P was in class statute designed to
D can argue that's not necessarily true, exact
protect and harm was of kind designed to prevent. cause of harm was undetermined, could have
been due to other D. P can argue that had
they done X, the harm wouldn't have occurred
either way.
But for Test: but for your negligent act, my harm wouldn't have occurred.
Cause in Fact Types:
1. Joint & Several Liability (multiple sufficient causes)
Substantial Factor Test for Concurrent Causes
2. Market Share Liability (fungible products)
3. Multiple actions caused uncertainty
D will argue superseding or intervening cause was
Foreseeability: it was foreseeable that your act would cause harm, so the exact
not foreseeable, so he didn't cause the harm
Proximate manner in which that harm occurs is irrelevant
Cause Direct, Natural, Immediate: harm was a direct, natural, immediate result of your
D will argue harm is too remote, too attenuated in
actions
time and space (work retrospectively, find break in
chain)
Superseding Criminal Act often cuts off
liability unless risk is what made D neg.
1. Unlimited liability would destroy civilization
2. Insurance available?
Public Policy
3. Avoid "ruinous liability" when damages are that great
4. However, is there a public policy reason to hold liable?
To person or property
1. In zone of danger Example: P's act was a failure to exercise reasonable care,
Harm Purely emotional
2. Related to victim by blood or
marriage
and his negligence is the superseding cause.
distress if physical
3. Distress was severe and
manifestation
beyond what a reasonable
emotional response would be Example: When P did X, he P can argue if no other
Bystander Test for voluntarily and knowingly options = not voluntary;
emotional distress from assumed the risk of doing so. he didn't know of risk.
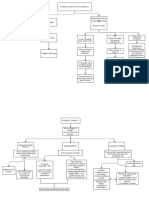
Comparative Negligence
witnessing
Assumption of Risk Immune from intentional torts, discretionary acts, libel/slander
Plaintiff's Conduct Employees can be sued for 1) negligent/wrongful acts 2) within scope
of employment 3) not discretionary
Parental Immunity for neg.
supervision
Affirmative Not immune for MINISTERIAL ACTS - operational level, no
judgment/choice made
Defenses Charities (mostly abolished)
Immunity for discretionary acts, legislative and judicial decision making,
Federal Gov. NOT IMMUNE FOR MINISTERIAL ACTS
State agencies: usually immune, unless private function - sometimes
No duty to protect a specific individual unless relationship develops; not
Immunities State Gov. immune for propriety or private functions
Municipalities Judges, president, governor, legislators have ABSOLUTE immunity for actions on the job
Public Officials Prosecutors, officers, lower level officials have QUALIFIED immunity - can be lost if
reasonable person would know actions are violating a statutory or constitutional right
You might also like
- Business Organizations: Outlines and Case Summaries: Law School Survival Guides, #10From EverandBusiness Organizations: Outlines and Case Summaries: Law School Survival Guides, #10No ratings yet
- Standard for disabled and children narrowed in emergenciesDocument1 pageStandard for disabled and children narrowed in emergenciesFernanda Rodriguez Torres100% (13)
- Intentional Torts OutlineDocument6 pagesIntentional Torts OutlineAmandaNo ratings yet
- Torts ChecklistDocument2 pagesTorts ChecklistnegrilledNo ratings yet
- Torts Skeleton OutlineDocument1 pageTorts Skeleton OutlineFeel_The_HeatNo ratings yet
- ContractsDocument1 pageContractsBrat Wurst100% (2)
- SMJDocument1 pageSMJBrat WurstNo ratings yet
- Commerce ClauseDocument1 pageCommerce ClauseBrat WurstNo ratings yet
- P JoiningDocument1 pageP JoiningBrat WurstNo ratings yet
- Future Estates Flow ChartDocument1 pageFuture Estates Flow ChartKelsey100% (4)
- Property Present EstatesDocument1 pageProperty Present EstatesBrat Wurst100% (1)
- P ReclusionDocument1 pageP ReclusionBrat WurstNo ratings yet
- Future InterestsDocument1 pageFuture InterestsBrat WurstNo ratings yet
- Torts Negligence ChecklistDocument1 pageTorts Negligence ChecklistLindsey Blackwell100% (2)
- DCCDocument1 pageDCCBrat WurstNo ratings yet
- Strict Liability - Torts - FlowchartDocument3 pagesStrict Liability - Torts - Flowchartfranco-44467% (3)
- Impleader DiagramDocument1 pageImpleader DiagramBrat WurstNo ratings yet
- Civ Pro PrewritesDocument18 pagesCiv Pro PrewritesACDC100% (5)
- Answering A Con Law QuestionDocument1 pageAnswering A Con Law QuestionBrat WurstNo ratings yet
- Takings FlowchartDocument1 pageTakings FlowchartAmandaNo ratings yet
- Civ Pro OutlineDocument52 pagesCiv Pro OutlineMoshe Shemtov 'student'100% (4)
- Contracts Essay Chart - FaiqDocument4 pagesContracts Essay Chart - FaiqRahimah Faiq100% (6)
- Removal FlowchartDocument1 pageRemoval FlowchartAmandaNo ratings yet
- 1L - Criminal - OUTLINEDocument18 pages1L - Criminal - OUTLINEtanner boydNo ratings yet
- Joinder of Claims Under FRCP 18 and 13Document1 pageJoinder of Claims Under FRCP 18 and 13Ronnie Barcena Jr.No ratings yet
- Property Flowchart 1Document1 pageProperty Flowchart 1Sam TheEsquire Ryan100% (3)
- Executive Powers - Page 1Document1 pageExecutive Powers - Page 1Brat WurstNo ratings yet
- Civil Procedure Freer 7th ed: Personal JurisdictionDocument39 pagesCivil Procedure Freer 7th ed: Personal JurisdictionACDCNo ratings yet
- TORTS EXAM TITLEDocument5 pagesTORTS EXAM TITLEjennwyse8208No ratings yet
- Joinder-Big Picture: R J I R Diver TyDocument1 pageJoinder-Big Picture: R J I R Diver Tysafkdjafgh leeeNo ratings yet
- Civ Pro Freer OutlineDocument12 pagesCiv Pro Freer OutlineDanielle D'Ambrosio100% (7)
- Commerce Clause Cases ExplainedDocument1 pageCommerce Clause Cases ExplainedkillerokapiNo ratings yet
- Personal Jurisdiction RequirementsDocument3 pagesPersonal Jurisdiction RequirementsLauren Walker100% (2)
- Constitutional Law - Essay OpenersDocument4 pagesConstitutional Law - Essay OpenersMissPardis100% (5)
- Contracts 1 - Quick Issue Spotting GuideDocument8 pagesContracts 1 - Quick Issue Spotting GuideVirginia Crowson100% (1)
- 1L Torts OutlineDocument12 pages1L Torts Outlineac70119No ratings yet
- Torts Attack OutlineDocument2 pagesTorts Attack Outlinemarthabin100% (33)
- Erie Doctrine FlowchartDocument1 pageErie Doctrine FlowchartElizabeth Andonova100% (2)
- PJ FlowchartDocument3 pagesPJ FlowchartCarley GraceNo ratings yet
- Restrictions On Land UseDocument1 pageRestrictions On Land UseBrat Wurst100% (1)
- Powers & Limitations of The Judiciary Step 1: Can/will The Supreme Court Hear The Case?Document1 pagePowers & Limitations of The Judiciary Step 1: Can/will The Supreme Court Hear The Case?Brat WurstNo ratings yet
- Civ. Pro (Flow Charts)Document2 pagesCiv. Pro (Flow Charts)William Little100% (1)
- Supplemental Jurisdiction FlowchartDocument1 pageSupplemental Jurisdiction FlowchartAmandaNo ratings yet
- CONTRACTS SHORT OUTLINE - HendersonDocument20 pagesCONTRACTS SHORT OUTLINE - HendersonSio Mo0% (1)
- Personal Jurisdiction Framework for Asserting Court AuthorityDocument2 pagesPersonal Jurisdiction Framework for Asserting Court AuthorityAlodieEfamba100% (5)
- Personal JurisdictionDocument1 pagePersonal JurisdictionKelly GrillsNo ratings yet
- Civil Procedure Rule ProofsDocument18 pagesCivil Procedure Rule Proofsang3lwings100% (2)
- Torts - Attack Sheet - Schechter - 2010Document7 pagesTorts - Attack Sheet - Schechter - 2010kellan schmelzNo ratings yet
- Ucc 2-207Document1 pageUcc 2-207Brat WurstNo ratings yet
- Torts Flowchart Outline BennettDocument6 pagesTorts Flowchart Outline BennettDewey Bennett100% (18)
- Present and Future Estates ExplainedDocument4 pagesPresent and Future Estates ExplainedTripp Rush100% (2)
- Civ Pro Flow ChartDocument8 pagesCiv Pro Flow Chartnhjefferson100% (2)
- Civ Pro Rule StatementsDocument15 pagesCiv Pro Rule StatementsMoshe Shemtov 'student'No ratings yet
- Steel Seizure FrameworkDocument1 pageSteel Seizure FrameworkBrat WurstNo ratings yet
- Torts Attack Sheet 1Document1 pageTorts Attack Sheet 1Micah Carper100% (1)
- Exam Answer Outline-TortsDocument3 pagesExam Answer Outline-TortsAhmad A. Hussein100% (1)
- Assault & Battery ElementsDocument12 pagesAssault & Battery Elementsferrante4100% (4)
- Torts Negligence OutlineDocument21 pagesTorts Negligence OutlineAmandaNo ratings yet
- To The States, Are Reserved To The States Respectively, or To The People."Document1 pageTo The States, Are Reserved To The States Respectively, or To The People."Brat WurstNo ratings yet
- Allocation of Foreign Policy PowerDocument1 pageAllocation of Foreign Policy PowerBrat WurstNo ratings yet
- Restrictions On Land UseDocument1 pageRestrictions On Land UseBrat Wurst100% (1)
- Steel Seizure FrameworkDocument1 pageSteel Seizure FrameworkBrat WurstNo ratings yet
- Property Present EstatesDocument1 pageProperty Present EstatesBrat Wurst100% (1)
- Civil War Enforcement PowersDocument1 pageCivil War Enforcement PowersBrat WurstNo ratings yet
- SSI Under 11thDocument1 pageSSI Under 11thBrat Wurst100% (1)
- Executive Powers - Page 1Document1 pageExecutive Powers - Page 1Brat WurstNo ratings yet
- Answering A Con Law QuestionDocument1 pageAnswering A Con Law QuestionBrat WurstNo ratings yet
- Basic Commerce Clause FrameworkDocument1 pageBasic Commerce Clause FrameworkBrat WurstNo ratings yet
- Class Action - Rule 23 To Be Certified, Must Meet 23A Requirements & Fit Into A 23B - Not Class Action Until Court Certifies It As SuchDocument1 pageClass Action - Rule 23 To Be Certified, Must Meet 23A Requirements & Fit Into A 23B - Not Class Action Until Court Certifies It As SuchBrat Wurst100% (1)
- Con Law Master ChartDocument1 pageCon Law Master ChartBrat Wurst100% (1)
- Commerce ClauseDocument1 pageCommerce ClauseBrat WurstNo ratings yet
- Joinder DiagramsDocument1 pageJoinder DiagramsBrat Wurst100% (2)
- Ucc 2-207Document1 pageUcc 2-207Brat WurstNo ratings yet
- Torts Outline for Evans on Causes of Action, Negligence, and DefensesDocument70 pagesTorts Outline for Evans on Causes of Action, Negligence, and DefensesBear100% (1)
- Child Abuse in Tanzania (2015)Document26 pagesChild Abuse in Tanzania (2015)Childreach International100% (1)
- Rojek Advance Solutions Employee HandbookDocument32 pagesRojek Advance Solutions Employee HandbookJämes ScarlétteNo ratings yet
- Gallione (2017) Screening Tools For Identification of Elder Abuse, A Systematic Review (Artículo)Document47 pagesGallione (2017) Screening Tools For Identification of Elder Abuse, A Systematic Review (Artículo)Lorena RodríguezNo ratings yet
- Working With Persecutory AltersDocument14 pagesWorking With Persecutory AltersTiberiu100% (1)
- Cri 317 Ulo C SimDocument46 pagesCri 317 Ulo C SimopxNo ratings yet
- Partner Exploitation and ViolenceDocument210 pagesPartner Exploitation and Violencepaul machariaNo ratings yet
- Bullying Behavior Study of Ma-a National HS StudentsDocument29 pagesBullying Behavior Study of Ma-a National HS StudentsDevilz GamingNo ratings yet
- SUDAN Darfur ComissionDocument176 pagesSUDAN Darfur ComissionBUSHRA_KHARIFNo ratings yet
- Boarding SchoolDocument24 pagesBoarding Schooledwardoplunkett100% (1)
- Effectiveness of Child Protection Policy in School As Perceived by Grade 12 StudentsDocument39 pagesEffectiveness of Child Protection Policy in School As Perceived by Grade 12 StudentsJed Garcia100% (1)
- Jigl Revision Notes Cs Ankush BansalDocument10 pagesJigl Revision Notes Cs Ankush BansalPratiksha pariiNo ratings yet
- Rights of The ChildDocument11 pagesRights of The ChildacaylarveronicayahooNo ratings yet
- Signs of Child Abuse ChecklistDocument2 pagesSigns of Child Abuse ChecklistEcaterina IacobNo ratings yet
- Study Material Law of TortsDocument145 pagesStudy Material Law of TortsApoorvnujs88% (17)
- Defining Violence Against Women: Information Sheet Activity 1Document6 pagesDefining Violence Against Women: Information Sheet Activity 1Clémence CourdvtNo ratings yet
- RoughdraftDocument5 pagesRoughdraftapi-305336351No ratings yet
- NCPCR's Role in Implementing India's Right to Education ActDocument31 pagesNCPCR's Role in Implementing India's Right to Education ActSrinjoy BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- Protection of Women From Domestic Violence Act 2005Document3 pagesProtection of Women From Domestic Violence Act 2005Anshika SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Manuscript For HarassmentDocument12 pagesManuscript For HarassmentJocelyn Mae CabreraNo ratings yet
- Kearney Ch13Document12 pagesKearney Ch13Savio RebelloNo ratings yet
- United States Court of Appeals, Third CircuitDocument7 pagesUnited States Court of Appeals, Third CircuitScribd Government DocsNo ratings yet
- Dr. Graham Spanier: and Training in Higher EducationDocument35 pagesDr. Graham Spanier: and Training in Higher EducationJudith Reisman, Ph.D.No ratings yet
- The State of The World's Children 2017: Children in A Digital WorldDocument215 pagesThe State of The World's Children 2017: Children in A Digital WorldUNICEFNo ratings yet
- Ranjith Keerikkattil False and Defamatory InformationDocument2 pagesRanjith Keerikkattil False and Defamatory InformationDC MPDNo ratings yet
- Gender and Culture in Psychology: Study Guide For Module No. - 3Document9 pagesGender and Culture in Psychology: Study Guide For Module No. - 3Lysander GarciaNo ratings yet
- Clinical and Social Factors Associated With Violent Behavior in Persons With Schizophrenia Spectrum DisordersDocument6 pagesClinical and Social Factors Associated With Violent Behavior in Persons With Schizophrenia Spectrum DisordersIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Ropes Gray Full ReportDocument252 pagesRopes Gray Full ReportWXYZ-TV Channel 7 DetroitNo ratings yet
- Paedophilia Website List - Joseph RobertsDocument28 pagesPaedophilia Website List - Joseph RobertsX-Files145420% (5)
- War of DrugsDocument18 pagesWar of DrugsGleyn LusayaNo ratings yet