Professional Documents
Culture Documents
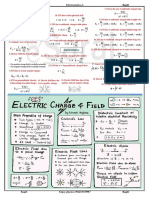
F.5 Physics - Electrostatics Electric Charges
Uploaded by
tony hoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
F.5 Physics - Electrostatics Electric Charges
Uploaded by
tony hoCopyright:
Available Formats
F.
5 Physics – Electrostatics
Electric charges
1. There are two kinds of charges, namely __________________
positive and __________________
negative
charges.
2. Like charges _________________ each other, unlike charges ________________ each other.
repel attract
3. A __________________ atom has equal numbers of protons and electrons.
neutral
4. When a neutral object loses electrons, it becomes __________________ charged. When it
gains electrons, it becomes __________________ charged.positively
5. The amount of charge in an isolated system is __________________.
negatively
conserved
6. Electric charges are measured in __________________ (C).
coulombs
7. Charges can flow easily in __________________.
conductors
8. Charges cannot move in __________________ but stay at where they are placed.
insulators
9. __________________ objects can attract both neutral and oppositely charged objects.
Charged
Exercise 1
A student rubs a balloon with a dry cloth. Then the balloon can be attracted to a board.
Explain the phenomenon briefly.
(What happens when a balloon is rubbed? (How does the balloon affect the charge distribution of the board when the
balloon is put close to the board? (What electric forces will be caused?)
The balloon becomes charged after being rubbed by a dry cloth. When it is
brought close to the board, the charge distribution of the board is distorted.
Charges of a sign opposite to that on the balloon are induced on the side of the
board facing the balloon and this results in attraction. At the same time, charges of
a sign the same as the balloon are induced on the side of the board far away from
F.5 Physics
the balloon and this results in repulsion. – Electrostatics
Since – p. 1is greater than
the attraction
repulsion, the balloon can be attracted to the board.
Charging and discharging methods
1. Conductors and insulators can be charged by __________________.
rubbing
10. Conductors can also be charged by __________________ or by
__________________________. sharing
11. Instruments
inductionlike
andEHT supply and Van de Graaff generator can be used to charge objects.
earthing
Exercise 2
A and B are two identical, insulated metal spheres. After rubbed by a cloth, A carries a charge of QA
= +4 1010 C. B is then brought in contact with the cloth. Assume that B shares half of the charge
on the cloth.
(a) What is the charge on B?
2 10−10 C
(b) A is then brought in contact with B.
(i) What is the amount of charge on A and B after they touch each other? Explain briefly.
Each of A and B carries +1 × 10−10 C of charge after they touch each other.
It is because A and B are identical, they will have the same share of charge
when they touch each other. As they initially have +2 10−10 C of charge in
total, each of them has a share of +1 × 10−10 C of charge when they are brought
in contact.
(ii) What charged particle(s) move(s) between A and B? What is the amount of charge
transferred?
Electrons flow from B to A.
amount of charge transferred = 3 10−10 C
(c) What would happen if the spheres are not insulated?
If the spheres are not insulated, the charges on them would flow to the
earth easily.
F.5 Physics – Electrostatics – p. 2
Hazards and applications of electrostatics
1. Sparks
___________________ may be produced when a huge amount of charge are built up
on an object.
2. Sparks can be dangerous in places where ___________________
inflammable substances are present.
3. Attractive electric force can be a help or a nuisance in everyday life.
12. ___________________ materials are used to prevent the build-up of charges on
objects.Anti-static
Applications of ___________________
electrostatics include photocopying, laser printing, electrostatic
precipitators and electrostatic spraying
Exercise 3
Electrostatic charges can be applied to separate minerals. The following diagram shows a simple
machine that can separate conducting and non-conducting minerals. Minerals first fall from a funnel
onto a positively charged rotor. The minerals then pass beneath a negatively charged electrode.
funnel negatively charged
electrode
to ground positively
charged rotor
non-conducting mineral conducting mineral
When
(a) What non-conducting
happens minerals minerals
when non-conducting fall on the rotor,
fall negative
on the charge
rotor? Why areisthey
induced on minerals
attracted to the
rotor?
on the side facing the rotor and positive charge is induced on minerals on the side far
from the rotor. Since negative induced charge is closer to rotor, the attraction between
the minerals and rotor is stronger than repulsion. The net attraction between the rotor
and the induced charge on the minerals keep minerals attracted to rotor.
When conducting minerals fall on the rotor, they share a positive charge
(b) What happens when conducting minerals fall on the rotor? Why do conducting minerals fall
from
off thethe
from rotor. This results in repulsion between conducting minerals and
rotor?
the rotor. When conducting minerals pass beneath the electrode, since their
charges are opposite to that of the electrode, they are attracted towards it
and hence fall off from the rotor.
F.5 Physics – Electrostatics – p. 3
F.5 Physics – Electrostatics – p. 4
You might also like
- Sph4u Solutions (Unit 3)Document101 pagesSph4u Solutions (Unit 3)Voormila Nithiananda100% (1)
- Physics for Kids : Electricity and Magnetism - Physics 7th Grade | Children's Physics BooksFrom EverandPhysics for Kids : Electricity and Magnetism - Physics 7th Grade | Children's Physics BooksRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Phy CHP 1 NotesDocument33 pagesPhy CHP 1 Notesayaan ahmedNo ratings yet
- Children's Encyclopedia Electronics & Communications: The World of KnowledgeFrom EverandChildren's Encyclopedia Electronics & Communications: The World of KnowledgeNo ratings yet
- General-Physics-2 Q3 M1 Electric-ChargeDocument8 pagesGeneral-Physics-2 Q3 M1 Electric-ChargeArian Avner De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- 1.9 Electrostatics (I)Document13 pages1.9 Electrostatics (I)Ferdnard WanjalaNo ratings yet
- Electric ChargeDocument7 pagesElectric Chargeokguserfucker idontgiveashitNo ratings yet
- Negative Mass and Negative Refractive Index in Atom Nuclei - Nuclear Wave Equation - Gravitational and Inertial Control: Part 2: Gravitational and Inertial Control, #2From EverandNegative Mass and Negative Refractive Index in Atom Nuclei - Nuclear Wave Equation - Gravitational and Inertial Control: Part 2: Gravitational and Inertial Control, #2No ratings yet
- EGM Fields - ClassconnectDocument118 pagesEGM Fields - Classconnectzia.mudassir2No ratings yet
- Electric Charges and Fields:Chapter 1Document33 pagesElectric Charges and Fields:Chapter 1Maryam MehekNo ratings yet
- Question Paper Static ElectricityDocument3 pagesQuestion Paper Static ElectricityproodootNo ratings yet
- Static Electricity Class 8Document21 pagesStatic Electricity Class 8proodoot50% (2)
- Static NotesDocument9 pagesStatic NotesWang QiyuNo ratings yet
- Electricity UnitDocument33 pagesElectricity UnitReluktantNo ratings yet
- RM 1 - ElectrostaticsDocument4 pagesRM 1 - Electrostaticsibdeveterbo.nhcsNo ratings yet
- ELECTRICITY NotesDocument62 pagesELECTRICITY Notesmallikammu12No ratings yet
- EM2 ElectrostaticsDocument5 pagesEM2 ElectrostaticsNathan TvascorNo ratings yet
- EM1 ElectrostaticsDocument5 pagesEM1 ElectrostaticspencymosothwaneNo ratings yet
- f2 Chapter 7 Electricity and MagnetismDocument21 pagesf2 Chapter 7 Electricity and MagnetismLorza TigaBelasNo ratings yet
- Motion Electrostatics Theory PDFDocument52 pagesMotion Electrostatics Theory PDFGaurav AhujaNo ratings yet
- Notes Physics Grade 8 ElectrostaticsDocument8 pagesNotes Physics Grade 8 ElectrostaticsRejo Raghuvaran100% (2)
- Explanation For ElectrostaticsDocument9 pagesExplanation For Electrostaticsanwar9602020No ratings yet
- ElectrostaticsDocument22 pagesElectrostaticsssenyonjotrevor01No ratings yet
- Module 1 - Jee FoundationDocument240 pagesModule 1 - Jee FoundationJESWIN JOSEPH CHETTOORNo ratings yet
- Physics Grade 7 Unit 8Document31 pagesPhysics Grade 7 Unit 8kidanemariam HabtemariamNo ratings yet
- Static ElectricityDocument12 pagesStatic Electricityslm8749No ratings yet
- Electrostatics 1Document52 pagesElectrostatics 1Jogindra nath SahooNo ratings yet
- Electrostatic TheoryDocument25 pagesElectrostatic TheoryChesta MalhotraNo ratings yet
- Static ElectricityDocument9 pagesStatic ElectricityEssraa KhamisNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics1 PDFDocument92 pagesElectrostatics1 PDFPriyanshu Raj100% (1)
- Final RevisionDocument9 pagesFinal Revisionhelomen321No ratings yet
- 1-Electrostatic Forcr Field 2022Document19 pages1-Electrostatic Forcr Field 2022Shamit MNo ratings yet
- 1.9 Electrostatics (I)Document10 pages1.9 Electrostatics (I)Jimmy ReeceNo ratings yet
- Name: - Grade and Section: - Date: - GenderDocument2 pagesName: - Grade and Section: - Date: - Genderfitz zamoraNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 Electric CircuitsDocument54 pagesTopic 2 Electric CircuitsMaan PatelNo ratings yet
- Chap 01 Electric Charges and Field (Notes)Document23 pagesChap 01 Electric Charges and Field (Notes)Uves AhmedNo ratings yet
- AP CH 15-TeacherDocument36 pagesAP CH 15-TeacherOnur YavuzcetinNo ratings yet
- General Physics 2Document20 pagesGeneral Physics 2christine isabel mendozaNo ratings yet
- Static Electricity Formation: Chapter OutlineDocument8 pagesStatic Electricity Formation: Chapter OutlinehemontoNo ratings yet
- Form 2 Science Electricty (Test)Document5 pagesForm 2 Science Electricty (Test)chaiseng yongNo ratings yet
- Unit 7 NotesDocument18 pagesUnit 7 Notesyooh9814No ratings yet
- ElectrostaticsDocument87 pagesElectrostaticsart angelNo ratings yet
- Xii Physics Chapter 1 - Electric Charges Fields Saju HssliveDocument16 pagesXii Physics Chapter 1 - Electric Charges Fields Saju Hssliveapi-3487796590% (1)
- Electrostatics SS1Document6 pagesElectrostatics SS1OlusolaNo ratings yet
- Electric Charges: Protons Are Positively Charged. Electrons Are Negatively ChargedDocument22 pagesElectric Charges: Protons Are Positively Charged. Electrons Are Negatively ChargedZunaira AliNo ratings yet
- Electric Charges: Protons Are Positively Charged. Electrons Are Negatively ChargedDocument20 pagesElectric Charges: Protons Are Positively Charged. Electrons Are Negatively ChargedZeedan MohammedNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics (E)Document128 pagesElectrostatics (E)Krishna RNo ratings yet
- Static Electricity: Law of Electrostatics: Like Charges Repel, Unlike Charges AttractDocument8 pagesStatic Electricity: Law of Electrostatics: Like Charges Repel, Unlike Charges AttractMuzammil KhanNo ratings yet
- Jojo AssignmentDocument2 pagesJojo Assignmentherbert rebloraNo ratings yet
- General Physics 2: Activity 1: Charge It!Document20 pagesGeneral Physics 2: Activity 1: Charge It!Mariles PrudencianoNo ratings yet
- Electric Charges and FieldsDocument16 pagesElectric Charges and FieldsPRACHI GUPTANo ratings yet
- MODULE 1 Electric Charge and Coulombs LawDocument12 pagesMODULE 1 Electric Charge and Coulombs LawVenus CaringalNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in PhysicsDocument3 pagesReviewer in PhysicsBeatrice MararacNo ratings yet
- Q3 - Lesson 1 PDFDocument85 pagesQ3 - Lesson 1 PDFTimothy Francisco100% (1)
- Chapter 1 - Electric Charges and FieldsDocument16 pagesChapter 1 - Electric Charges and FieldsAnil SarohaNo ratings yet
- MessageDocument3 pagesMessageabdulrahmanmohammad242kbsNo ratings yet
- 1 Electricity Student Worksheet PackageDocument50 pages1 Electricity Student Worksheet PackageAnita Chan100% (1)
- Notes: Energy and Chemical ReactionsDocument27 pagesNotes: Energy and Chemical Reactionstony hoNo ratings yet
- Physics Projectile Motion 1Document6 pagesPhysics Projectile Motion 1tony hoNo ratings yet
- 1984 Study Guide2Document8 pages1984 Study Guide2Anonymous 5Lm9xU0pENo ratings yet
- As Neutralization Is An Irreversible ReactionDocument1 pageAs Neutralization Is An Irreversible Reactiontony hoNo ratings yet
- Book 2Document59 pagesBook 2tony ho100% (1)
- Chapter 10 Essay - eDocument3 pagesChapter 10 Essay - etony hoNo ratings yet
- GCE Alevel Chem Topic 23 - SampleDocument5 pagesGCE Alevel Chem Topic 23 - Sampletony hoNo ratings yet
- Test 6 Reading PassageDocument2 pagesTest 6 Reading Passagetony hoNo ratings yet
- Physics: 1. Measurements and UnitsDocument43 pagesPhysics: 1. Measurements and UnitsMadhuri Devi100% (1)
- Instructions PDFDocument71 pagesInstructions PDFggeorgelNo ratings yet
- Ibc2003e - Ibc 2003 Seismic Analysis ProgramDocument30 pagesIbc2003e - Ibc 2003 Seismic Analysis Programtham leoNo ratings yet
- AS Unit 1 Revision Note Physics IAL EdexcelDocument9 pagesAS Unit 1 Revision Note Physics IAL EdexcelMahbub Khan100% (1)
- Minimum Learning Competencies: Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia Ministry of EducationDocument13 pagesMinimum Learning Competencies: Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia Ministry of EducationLara CarisaNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Translation SystemsDocument13 pagesMechanical Translation SystemsTrisha SARMIENTONo ratings yet
- Rotational Motion: M V O ADocument1 pageRotational Motion: M V O APornachandraRaoNo ratings yet
- Technological University of The Philippines: Physics For EngineersDocument50 pagesTechnological University of The Philippines: Physics For EngineersChristine Joy VeluzNo ratings yet
- TEST-07 (Impulse and Momentum)Document2 pagesTEST-07 (Impulse and Momentum)abdullah naseerNo ratings yet
- MecDocument2 pagesMecsiddharth yadavNo ratings yet
- 3 KinematicsDocument37 pages3 KinematicsAsif AliNo ratings yet
- Relative Motion Analysis: Acceleration: Today's ObjectivesDocument28 pagesRelative Motion Analysis: Acceleration: Today's ObjectivesNiki BrincatNo ratings yet
- Forces Test PDFDocument3 pagesForces Test PDFmelissaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Quantities 1 MS PDFDocument4 pagesElectrical Quantities 1 MS PDFnssNo ratings yet
- Linear Motion NotesDocument33 pagesLinear Motion NotesPotriyan SivanathanNo ratings yet
- Quiz 3Document2 pagesQuiz 3C G-CNo ratings yet
- Shaheen Public H/S School Mirpur Mathelo CH # 07 Work Power and Energy By: Laghari Zoheb HassanDocument40 pagesShaheen Public H/S School Mirpur Mathelo CH # 07 Work Power and Energy By: Laghari Zoheb HassanLaghari Hassan XohebNo ratings yet
- WME01 01 Que 20201017 3Document4 pagesWME01 01 Que 20201017 3Smile Htar ThetNo ratings yet
- Brilliants KinematicsDocument89 pagesBrilliants KinematicsAbhishekkumar92100% (1)
- Dynamic Model of Robots: Newton-Euler Approach: Robotics 2Document16 pagesDynamic Model of Robots: Newton-Euler Approach: Robotics 2FaRaz AamIrNo ratings yet
- Dynamics Tutorial 7-Kinematiks-Velocity and Acceleration Diagrams-31p PDFDocument31 pagesDynamics Tutorial 7-Kinematiks-Velocity and Acceleration Diagrams-31p PDFmanfredm6435No ratings yet
- Relative MotionDocument20 pagesRelative MotionAditya BansalNo ratings yet
- Newton's Second Law of MotionDocument11 pagesNewton's Second Law of MotionKerwin MarasiganNo ratings yet
- Synchronous Machine Pu ModelDocument18 pagesSynchronous Machine Pu ModelDinesh ShettyNo ratings yet
- 1balance and Unbalanced ForcesDocument20 pages1balance and Unbalanced ForcesCabalan O. Charles KevinNo ratings yet
- Physics Assignment 1Document4 pagesPhysics Assignment 1Trí Võ PhạmNo ratings yet
- 12P 25 Nuclear Physics and Radioactivity PDFDocument78 pages12P 25 Nuclear Physics and Radioactivity PDFadimeghaNo ratings yet
- AP Physics I - Newton's Laws and Uniform Circular Motion Study Guide (Chapters 4,5, & 6)Document15 pagesAP Physics I - Newton's Laws and Uniform Circular Motion Study Guide (Chapters 4,5, & 6)Fay SNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 - Kinetics of Particles Energy and Momentum MethodsDocument32 pagesLecture 3 - Kinetics of Particles Energy and Momentum MethodsKeu JiannRong0% (2)
- Lecture DynamicsDocument13 pagesLecture DynamicsmarkosNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry for Schools: Advanced Level and Senior High SchoolFrom EverandOrganic Chemistry for Schools: Advanced Level and Senior High SchoolNo ratings yet
- Periodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincFrom EverandPeriodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (137)
- The Disappearing Spoon: And Other True Tales of Madness, Love, and the History of the World from the Periodic Table of the ElementsFrom EverandThe Disappearing Spoon: And Other True Tales of Madness, Love, and the History of the World from the Periodic Table of the ElementsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (146)
- Is That a Fact?: Frauds, Quacks, and the Real Science of Everyday LifeFrom EverandIs That a Fact?: Frauds, Quacks, and the Real Science of Everyday LifeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- Monkeys, Myths, and Molecules: Separating Fact from Fiction, and the Science of Everyday LifeFrom EverandMonkeys, Myths, and Molecules: Separating Fact from Fiction, and the Science of Everyday LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- The Regenerative Grower's Guide to Garden Amendments: Using Locally Sourced Materials to Make Mineral and Biological Extracts and FermentsFrom EverandThe Regenerative Grower's Guide to Garden Amendments: Using Locally Sourced Materials to Make Mineral and Biological Extracts and FermentsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- The Elements We Live By: How Iron Helps Us Breathe, Potassium Lets Us See, and Other Surprising Superpowers of the Periodic TableFrom EverandThe Elements We Live By: How Iron Helps Us Breathe, Potassium Lets Us See, and Other Surprising Superpowers of the Periodic TableRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (22)
- Science Goes Viral: Captivating Accounts of Science in Everyday LifeFrom EverandScience Goes Viral: Captivating Accounts of Science in Everyday LifeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Nature of Drugs Vol. 1: History, Pharmacology, and Social ImpactFrom EverandThe Nature of Drugs Vol. 1: History, Pharmacology, and Social ImpactRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Chemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeFrom EverandChemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (90)
- Essential Oil Chemistry Formulating Essential Oil Blends that Heal - Aldehyde - Ketone - Lactone: Healing with Essential OilFrom EverandEssential Oil Chemistry Formulating Essential Oil Blends that Heal - Aldehyde - Ketone - Lactone: Healing with Essential OilRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Handbook of Formulating Dermal Applications: A Definitive Practical GuideFrom EverandHandbook of Formulating Dermal Applications: A Definitive Practical GuideNo ratings yet
- Chemistry: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideFrom EverandChemistry: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- A Perfect Red: Empire, Espionage, and the Quest for the Color of DesireFrom EverandA Perfect Red: Empire, Espionage, and the Quest for the Color of DesireRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (129)
- Transformer: The Deep Chemistry of Life and DeathFrom EverandTransformer: The Deep Chemistry of Life and DeathRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (13)
- Bioplastics: A Home Inventors HandbookFrom EverandBioplastics: A Home Inventors HandbookRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Formulating, Packaging, and Marketing of Natural Cosmetic ProductsFrom EverandFormulating, Packaging, and Marketing of Natural Cosmetic ProductsNo ratings yet
- Water-Based Paint Formulations, Vol. 3From EverandWater-Based Paint Formulations, Vol. 3Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (6)
- Formulation and Process Development Strategies for Manufacturing BiopharmaceuticalsFrom EverandFormulation and Process Development Strategies for Manufacturing BiopharmaceuticalsFeroz JameelNo ratings yet
- The Periodic Table of Elements - Post-Transition Metals, Metalloids and Nonmetals | Children's Chemistry BookFrom EverandThe Periodic Table of Elements - Post-Transition Metals, Metalloids and Nonmetals | Children's Chemistry BookNo ratings yet
- Catch Up Chemistry, second edition: For the Life and Medical SciencesFrom EverandCatch Up Chemistry, second edition: For the Life and Medical SciencesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)