Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CHEM 181 DL1: Final Report
Uploaded by
Neally WeallyOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
CHEM 181 DL1: Final Report
Uploaded by
Neally WeallyCopyright:
Available Formats
CHEM
181 DL1
St oichiomet ry of a Precipit at ion React ion
Final Report
St ude nt Abdulrazzaq Alnassar
Name
St ude nt ID 45487
Le s s o n Stoichiom etry of a Precipitation Reaction
Ins t it ut io n O cean C ounty C ollege
Se s s io n 2019L1 C HEM 181 DL1
Co ur s e C HEM 181 DL1
Ins t r uc t o r C ynthia Spencer
Exercise 1
1. Give n t hat a t he o r e t ic al yie ld f o r is o lat ing Calc ium Car bo nat e in t his e xpe r ime nt
wo uld be 10 0 % . Fr o m t hat inf o r mat io n and bas e d o n t he r e s ult s yo u o bt aine d in t his
e xpe r ime nt , de s c r ibe yo ur s uc c e s s in t he r e c o ve r y o f c alc ium c ar bo nat e and s ugge s t
t wo po s s ible s o ur c e s o f e r r o r t hat wo uld have c aus e d yo u t o no t o bt ain 10 0 % yie ld.
In m y case the approxim ate 94% yield is obtained which im plies 6% error m ay be due to
incom plete precipitation, drying period less than 24 hours, decim al point accuracy, calibration of
the scale, and possibly due to incom plete filtration of substances.
2. What impac t wo uld adding t wic e as muc h Na 2 CO 3 t han r e quir e d f o r s t o ic hio me t r ic
quant it ie s have o n t he quant it y o f pr o duc t pr o duc e d?
Since the C aC l2 is the lim iting reactant, there is no im pact found by adding twice as m uch
am ount of NaC O 3.
Copyrigh t 2019 - H an ds-On Labs | h t t p://h olscien ce.com 1 / 3
3. De t e r mine t he quant it y (g) o f pur e CaCl 2 in 7.5 g o f CaCl 2 •9H 2 O. Sho w yo ur wo r k.
Molar Mass of C aC l2 • 9H 2 O = 273.07 g/m ol
Molar Mass of C aC l2 = 110.98 g/m ol
(7.5 g C aC l2 • 9H 2 O * 110.98 g C aC l2 ) / 273.07 g C aC l2 •9H 2 O = 3.05 g C aC l2
4. De t e r mine t he quant it y (g) o f pur e MgSO 4 in 2.4 g o f MgSO 4•7H 2 O. Sho w yo ur wo r k.
Molar m ass of MgSO 4 • 7H 2 O = 24.31 + 32.07 + 11(16) + 14(1.01) = 246.45 g/m ol
Molar m ass of MgSO 4 = 24.31 + 32.07 + 4(16) = 120.38 g/m ol
(2.4 g MgSO 4 • 7H 2 O * 120.38 g MgSO 4 ) / 246.45 g MgSO 4 •7H 2 O = 1.17 g MgSO 4
5. Co ns e r vat io n o f mas s was dis c us s e d in t he bac kgr o und. De s c r ibe ho w c o ns e r vat io n o f
mas s (ac t ual, no t t he o r e t ic al) c o uld be c he c ke d in t he e xpe r ime nt pe r f o r me d.
The law of conservation of m ass states that m ass can neither be created nor destroyed. For
conservation of m ass, first, calculate the initial m ass of used C aC l2 . By using this, find the m ass of
C a that was initially used and the m ass of the final product, respectively. By using m ole ratio, find
the m ass of C a in the product and then com pare with initial m ass of used C a. The total m ass (in
gram s) of the reactants equals the total m ass of the products.
Data Table 1: Stoichiome try Value s
Copyrigh t 2019 - H an ds-On Labs | h t t p://h olscien ce.com 2 / 3
Initial: CaCl2•2H2O (g) 1.50
Initial: CaCl2•2H2O (mol) 0.0102
Initial: CaCl2 (mol) 0.0102
Initial: Na2CO 3 (mol) 0.0102
Initial: Na2CO 3 (g) 1.08
The ore tical: CaCO 3 (g) 1.02
Mass of Filte r pape r (g) 1.0
Mass of Filte r Pape r + CaCO 3 (g) 1.96
Actual: CaCO 3 (g) 0.96
% Yie ld: 94%
Copyrigh t 2019 - H an ds-On Labs | h t t p://h olscien ce.com 3 / 3
You might also like
- Ross Lab Report - Final DraftDocument6 pagesRoss Lab Report - Final DraftchronosplitzerNo ratings yet
- Chapmann Stoichiometry of A Precipitation ReactionDocument3 pagesChapmann Stoichiometry of A Precipitation ReactionDanyNo ratings yet
- Lab Report Experiment 3 CHM 138Document7 pagesLab Report Experiment 3 CHM 138Muhd Mirza Hizami50% (4)
- A Moisture Swing Sorbent For Direct Air Capture of Carbon Dioxide Thermodynamic and Kinetic AnalysisDocument9 pagesA Moisture Swing Sorbent For Direct Air Capture of Carbon Dioxide Thermodynamic and Kinetic AnalysisY BermainNo ratings yet
- Bioprocess Lab Manual GuideDocument27 pagesBioprocess Lab Manual GuideFatih RushdiNo ratings yet
- Nakasaki1987 A New Composting Model and Assessment of Optimum Operation For Effective Drying of Composting MaterialDocument7 pagesNakasaki1987 A New Composting Model and Assessment of Optimum Operation For Effective Drying of Composting MaterialNeeraj JatNo ratings yet
- GE Text Solutions ManualDocument85 pagesGE Text Solutions ManualElly Yulia ZahrahNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2Document1 pageTutorial 2Porkkodi SugumaranNo ratings yet
- 2013 Bookmatter EnvironmentalEngineeringReview PDFDocument124 pages2013 Bookmatter EnvironmentalEngineeringReview PDFN. PumaNo ratings yet
- Advanced Chemical Reaction EngineeringDocument18 pagesAdvanced Chemical Reaction EngineeringNurul AiniNo ratings yet
- Ch. 7 Worksheet - ThermochemDocument9 pagesCh. 7 Worksheet - Thermochemkjcninja13No ratings yet
- Uguina Et Al 2002 PDFDocument8 pagesUguina Et Al 2002 PDFBrunoNunesCGNo ratings yet
- Experiment: Gravimetric AnalysisDocument9 pagesExperiment: Gravimetric Analysisadda84% (25)
- 3922 03Document115 pages3922 03Vu Hoang VoNo ratings yet
- CHM 420 Lab Report 4Document7 pagesCHM 420 Lab Report 4Adorable PeachyNo ratings yet
- Lab 3-1a, Mass Percent of Carbon in Sodium Bicarbonate (Key)Document7 pagesLab 3-1a, Mass Percent of Carbon in Sodium Bicarbonate (Key)David StainesNo ratings yet
- Che Preboard Exam Day 1 Practice ProblemsDocument4 pagesChe Preboard Exam Day 1 Practice ProblemsAudreyWalangareDimalibot50% (2)
- 78BDocument3 pages78BJamie SchultzNo ratings yet
- Caloric Content of Food Lab ReportDocument6 pagesCaloric Content of Food Lab ReportNeally WeallyNo ratings yet
- Sathyabama University: Register NumberDocument4 pagesSathyabama University: Register NumberAnand UnniNo ratings yet
- (CHM420) Lab Report 4Document8 pages(CHM420) Lab Report 4Nurin Nabila100% (3)
- CHEMICAL PROCESS CALCULATIONS QUESTION BANKDocument7 pagesCHEMICAL PROCESS CALCULATIONS QUESTION BANKArul KamalakumarNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Charateristic and Their Effects On Working Performance of Compartmentalized Anaerobic ReactorDocument6 pagesHydraulic Charateristic and Their Effects On Working Performance of Compartmentalized Anaerobic ReactorThiagoSilvaOliverNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13Document4 pagesChapter 13Poonam CheemaNo ratings yet
- Internal v1 2.3 Gv2 Chemistry Calculations 1 2008Document9 pagesInternal v1 2.3 Gv2 Chemistry Calculations 1 2008Yasaman MohammadiNo ratings yet
- Stack Sampling Results ReportDocument14 pagesStack Sampling Results ReportIsmail SultanNo ratings yet
- Course NotesDocument195 pagesCourse NotesLindi NewmanNo ratings yet
- Lab 1Document4 pagesLab 1Maryam arefNo ratings yet
- chm420 Experiment 4Document11 pageschm420 Experiment 4Afeq NasemeNo ratings yet
- Achapter7 8TextbookSolutionDocument91 pagesAchapter7 8TextbookSolutionjimNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 1Document17 pagesLab Report 1RONALD DECK YAMINo ratings yet
- GATE HELPLINE Bioprocess Engineering MCQ IDocument4 pagesGATE HELPLINE Bioprocess Engineering MCQ ISanthosh Kalash100% (8)
- Environmental Engineering Homework #1 SolutionDocument3 pagesEnvironmental Engineering Homework #1 Solutionjabenne2100% (2)
- Ideal Gas Law DeviationsDocument5 pagesIdeal Gas Law DeviationsJustin Wong0% (1)
- RRRRRR Chido ReactHetExamenOrdinarioJunio2020aDocument4 pagesRRRRRR Chido ReactHetExamenOrdinarioJunio2020aDaniel Moreno CabreraNo ratings yet
- GC Analysis of Alkane MixtureDocument7 pagesGC Analysis of Alkane MixtureoarabileNo ratings yet
- Stoichiometry ChallengeDocument5 pagesStoichiometry ChallengeRochelle TayanNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry Q1 Week 7-8Document15 pagesGeneral Chemistry Q1 Week 7-8ljbenares19No ratings yet
- Gas Chromatography (GC) With Flame-Ionization Detection: PrinciplesDocument7 pagesGas Chromatography (GC) With Flame-Ionization Detection: PrinciplesENGR: MOTIRAMNo ratings yet
- (Received April 1988 Revision 26 Sept. 1988) : Minerals Engineering, Vol. 2, No. 2, Pp. 217-227, 1989Document11 pages(Received April 1988 Revision 26 Sept. 1988) : Minerals Engineering, Vol. 2, No. 2, Pp. 217-227, 1989alinoriNo ratings yet
- Forces between ions and ionic radiiDocument18 pagesForces between ions and ionic radiiRichard RetuyaNo ratings yet
- Biosorption of Mno in Aqueous Solutions Using Pinus InsularisDocument9 pagesBiosorption of Mno in Aqueous Solutions Using Pinus InsularisAYAUWU LOVEDAYNo ratings yet
- Nitrification DenitrificationDocument4 pagesNitrification DenitrificationDon Javier HubbleNo ratings yet
- Con Agua y Carbón ActivadoDocument25 pagesCon Agua y Carbón ActivadoJoha BetancurNo ratings yet
- Gravimetric Analysis of A Chloride SaltDocument9 pagesGravimetric Analysis of A Chloride SaltDorien Villafranco0% (1)
- Tutorial-Manual CH1002Document18 pagesTutorial-Manual CH1002Gift Chulu100% (2)
- Exp't 13: Phase-Transfer-Catalyzed Alkylation of Diethyl MalonateDocument5 pagesExp't 13: Phase-Transfer-Catalyzed Alkylation of Diethyl MalonatelovehopeNo ratings yet
- spr14 Lab ReportDocument7 pagesspr14 Lab Reportapi-253597681No ratings yet
- Adsorption Equilibria ExamplesDocument31 pagesAdsorption Equilibria ExamplesNagwa MansyNo ratings yet
- Energy and Mass Balance of Incinerator PDFDocument11 pagesEnergy and Mass Balance of Incinerator PDFdrop shipNo ratings yet
- Preboard Exam Day1 SET ADocument12 pagesPreboard Exam Day1 SET AJeanne Cortez0% (1)
- UntitledDocument8 pagesUntitledMothish SivakumarNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Winter 2a Exam KeyDocument10 pagesChemistry Winter 2a Exam KeyKaren ZhaoNo ratings yet
- Calorimetry Lab ReportDocument6 pagesCalorimetry Lab ReportFrances Abegail QuezonNo ratings yet
- ENERGY AND MASS BALANCE CALCULATIONS FOR INCINERATORSDocument11 pagesENERGY AND MASS BALANCE CALCULATIONS FOR INCINERATORSnuti_srinivasNo ratings yet
- Dissolved Gas Concentration in Water: Computation as Functions of Temperature, Salinity and PressureFrom EverandDissolved Gas Concentration in Water: Computation as Functions of Temperature, Salinity and PressureNo ratings yet
- Transition Metal-Catalyzed Pyridine Synthesis: Transition Metal-Catalyzed Heterocycle Synthesis SeriesFrom EverandTransition Metal-Catalyzed Pyridine Synthesis: Transition Metal-Catalyzed Heterocycle Synthesis SeriesNo ratings yet
- The Carbon Dioxide Revolution: Challenges and Perspectives for a Global SocietyFrom EverandThe Carbon Dioxide Revolution: Challenges and Perspectives for a Global SocietyNo ratings yet
- Gas Sweetening and Processing Field ManualFrom EverandGas Sweetening and Processing Field ManualRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (7)
- La Canada High School 4-Year Plan: After High School Plans: Career Plans: Eng. 1P Eng. 2P or Eng 2HDocument1 pageLa Canada High School 4-Year Plan: After High School Plans: Career Plans: Eng. 1P Eng. 2P or Eng 2HNeally WeallyNo ratings yet
- SPEA Syllabus Math 265Document4 pagesSPEA Syllabus Math 265Neally WeallyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3-Study Guide: Identify The Terms and Like Terms in The Expression. 1Document3 pagesChapter 3-Study Guide: Identify The Terms and Like Terms in The Expression. 1Neally WeallyNo ratings yet
- CHEM 181 DL1: Final ReportDocument4 pagesCHEM 181 DL1: Final ReportNeally WeallyNo ratings yet
- Observe Chemical & Physical ChangesDocument14 pagesObserve Chemical & Physical ChangesNeally Weally100% (2)
- Unit 6 - Chart of Commonly Misused Words Part 2Document2 pagesUnit 6 - Chart of Commonly Misused Words Part 2Neally WeallyNo ratings yet
- Chart Commonly Misused WordsDocument3 pagesChart Commonly Misused WordsNeally WeallyNo ratings yet
- CHEM 181 DL1: Final ReportDocument16 pagesCHEM 181 DL1: Final ReportNeally WeallyNo ratings yet
- The Question Asks For How Many Moles of Calcium Oxide, Not How Many Grams. Correct Answer Should Be 10 G Ca X (1 Mol/40.07G) X (2 Mol Cao / 2 Mol Ca)Document1 pageThe Question Asks For How Many Moles of Calcium Oxide, Not How Many Grams. Correct Answer Should Be 10 G Ca X (1 Mol/40.07G) X (2 Mol Cao / 2 Mol Ca)Neally WeallyNo ratings yet
- Correct Answer Should Be 19 CM 190 MMDocument1 pageCorrect Answer Should Be 19 CM 190 MMNeally WeallyNo ratings yet
- Caloric Content of Food Lab ReportDocument6 pagesCaloric Content of Food Lab ReportNeally WeallyNo ratings yet
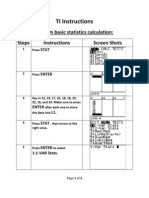
- 7 - Basic Statistics CalculationDocument2 pages7 - Basic Statistics CalculationNeally WeallyNo ratings yet
- Kinematics in One DimensionDocument18 pagesKinematics in One DimensionNeally WeallyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 GasesDocument37 pagesChapter 5 GasesNeally WeallyNo ratings yet
- AP Mechanics Exam Sample 2Document8 pagesAP Mechanics Exam Sample 2Neally WeallyNo ratings yet
- 1 Introduction and MathDocument18 pages1 Introduction and MathNeally WeallyNo ratings yet
- Linear Piston Actuators: by Sekhar Samy, CCI, and Dave Stemler, CCIDocument18 pagesLinear Piston Actuators: by Sekhar Samy, CCI, and Dave Stemler, CCIapi-3854910No ratings yet
- LAU Paleoart Workbook - 2023Document16 pagesLAU Paleoart Workbook - 2023samuelaguilar990No ratings yet
- Title Page Title: Carbamazepine Versus Levetiracetam in Epilepsy Due To Neurocysticercosis Authors: Akhil P SanthoshDocument16 pagesTitle Page Title: Carbamazepine Versus Levetiracetam in Epilepsy Due To Neurocysticercosis Authors: Akhil P SanthoshPrateek Kumar PandaNo ratings yet
- Predictive Analytics: QM901.1x Prof U Dinesh Kumar, IIMBDocument36 pagesPredictive Analytics: QM901.1x Prof U Dinesh Kumar, IIMBVenkata Nelluri PmpNo ratings yet
- IBM Credit Corp BPR ProcessDocument8 pagesIBM Credit Corp BPR ProcessAnubhav PuriNo ratings yet
- All Types of Switch CommandsDocument11 pagesAll Types of Switch CommandsKunal SahooNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Contemporary Project Management 4th EditionDocument15 pagesSolution Manual For Contemporary Project Management 4th EditionDanaAllendzcfa100% (77)
- TiONA 592 PDS - ENDocument1 pageTiONA 592 PDS - ENQuang VANo ratings yet
- 2021.01.28 - Price Variation of Steel Items - SAIL Ex-Works Prices of Steel - RB-CivilDocument2 pages2021.01.28 - Price Variation of Steel Items - SAIL Ex-Works Prices of Steel - RB-CivilSaugata HalderNo ratings yet
- Applied Physics Mini Launcher Lab ReportDocument12 pagesApplied Physics Mini Launcher Lab ReportTalharashid RamzanNo ratings yet
- Financial Reporting Statement Analysis Project Report: Name of The Company: Tata SteelDocument35 pagesFinancial Reporting Statement Analysis Project Report: Name of The Company: Tata SteelRagava KarthiNo ratings yet
- HIS 101 Home Work 2Document10 pagesHIS 101 Home Work 2Nabil HussainNo ratings yet
- PExam 2020Document126 pagesPExam 2020Omama MaazNo ratings yet
- Motor Electrico Bojin J4103 - B User ManualDocument6 pagesMotor Electrico Bojin J4103 - B User ManualJordan BonnettNo ratings yet
- Hearing God Through Biblical Meditation - 1 PDFDocument20 pagesHearing God Through Biblical Meditation - 1 PDFAlexander PeñaNo ratings yet
- Bhajan Songs PDFDocument36 pagesBhajan Songs PDFsilphansi67% (6)
- Calibration GuideDocument8 pagesCalibration Guideallwin.c4512iNo ratings yet
- 4900 DatasheetDocument2 pages4900 DatasheetMakam Raghu100% (1)
- Cognitive Clusters in SpecificDocument11 pagesCognitive Clusters in SpecificKarel GuevaraNo ratings yet
- Vernacular Architecture: Bhunga Houses, GujaratDocument12 pagesVernacular Architecture: Bhunga Houses, GujaratArjun GuptaNo ratings yet
- FAI - Assignment Sheet (Both Assignments)Document5 pagesFAI - Assignment Sheet (Both Assignments)Wilson WongNo ratings yet
- Ragavendhar Seeks Entry Software JobDocument2 pagesRagavendhar Seeks Entry Software JobfferferfNo ratings yet
- EOD Stanags Overview April 2021Document12 pagesEOD Stanags Overview April 2021den mas paratate leo egoNo ratings yet
- Safety Data Sheet for Instant AdhesiveDocument6 pagesSafety Data Sheet for Instant AdhesiveDiego S. FreitasNo ratings yet
- Broom Manufacture Machine: StartDocument62 pagesBroom Manufacture Machine: StartHaziq PazliNo ratings yet
- Land-Use PlanningDocument15 pagesLand-Use PlanningCiara MaryNo ratings yet
- Penilaian Risiko Kerja Menggunakan Metode Hirarc Di Pt. Sinar Laut Indah Natar Lampung SelatanDocument7 pagesPenilaian Risiko Kerja Menggunakan Metode Hirarc Di Pt. Sinar Laut Indah Natar Lampung SelatanIndun InsiyahNo ratings yet
- Biology GCE 2010 June Paper 1 Mark SchemeDocument10 pagesBiology GCE 2010 June Paper 1 Mark SchemeRicky MartinNo ratings yet
- DownloadDocument11 pagesDownloadAnonymous ffje1rpaNo ratings yet
- Sample ResumeDocument3 pagesSample Resumeapi-380209683% (6)