Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Trigonometría: Identidades trigonométricas para el arco triple
Uploaded by
Jhoan Heiner Fabian CristobalOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Trigonometría: Identidades trigonométricas para el arco triple
Uploaded by
Jhoan Heiner Fabian CristobalCopyright:
Available Formats
TRIGONOMETRÍA
IDENTIDADES TRIGONOMÉTRICAS
PARA EL ARCO TRIPLE
DESARROLLO DEL TEMA
I. Sen3x 3Senx – 4Sen3 x
3Tanx – Tan 3x
III. Tan3x
1 – 3Tan2 x
Demostración:
Sen3x = Sen (2x + x) Demostración
Sen3x = Sen2xCosx + Cos2xSenx Sabemos:
TanA TanB TanC – TanATanBTanC
Sabemos por arco doble: Tan A B C
1 – TanATanB TanATanC TanBTanC
Sen2x 2SenxCosx ; Cos2x 1 – 2Sen 2 x
Sea:
Tan3x Tan x x x
Reemplazando:
Tanx Tanx Tanx – TanxTanxTanx
Tan3x
Sen3x = (2Senx Cosx)Cosx + (1 – 2Sen2x) Senx 1 – TanxTanx TanxTanx TanxTanx
Sen3x 2SenxCos 2 x Senx – 2Sen3 x
Efectuando operaciones:
2
Sabemos: Cos x 1 – Sen x 2
3Tanx – Tan 3x
Tan3x
Reemplazando: 1 – 3Tan2 x
2 3
Sen3x = 2Senx (1 – 2Sen x)+ Senx – 2Sen x
En general:
3 3
Sen3x 2Senx – 2Sen x Senx – 2Sen x Sen3x 3Senx – 4Sen3 x
Sen3x 3Senx – 4Sen3x Sen3x Senx 2Cos2x 1
Sen3x 4SenxSen 60 – x Sen 60 x
Análogamente: Cos3x 4Cos 3 x – 3Cosx
Cos3x Cosx 2Cos2x – 1 Cos3x 4 Cos 3 x – 3Cosx
II.
Cos3x Cosx 2Cos2x –1
Demostración: Cos3x 4CosxCos 60 – x Cos 60 x
Sabemos: Cos3x 4Cos 3 x – 3Cosx
Cos3x Cosx 2 x 2Cos 2
x – 3 3Tanx – Tan3 x
Tan3x
1 – 3Tan2 x
2 Tan3x TanxTan 60 – x Tan 60 x
Recordando: 1 Cos2x 2Cos x Doble
Nota:
Cos3x Cosx 2 1 Cos2x – 3
Cot3x CotxCot 60 – x Cot 60 x
Cos3x Cosx 2Cos2x – 1
UNI SEMESTRAL 2013 - III 39 TRIGONOMETRÍA TEMA 11
IDENTIDADES TRIGONOMÉTRICAS PARA EL ARCO TRIPLE
Exigimos más!
problemas resueltos
Problema 1 Problema 2 Nivel difícil
3 3 2007 - II
Simplifique: K Sen x Cos x 1 Calcule E Tan2 x en términos
Sen3x Cos3x 2 4 2 1 1 1
Nivel fácil A) B) C)
de "a", si Secx = a + Tanx. 2 3 4
2005 - I Nivel intermedio 1 1
D) E)
2005 - I 5 6
A) 3Sen2x Cosec6x
1 1 1
A) B) C)
B) –3Sen2x Cosec6x a4 a3 a2 Resolución:
1 4
C)
3
2
Sen2x Cosec6x
D)
a
E)
a Cot x2 4 tan x4 2 csc x
3 Resolución:
D)
2
Sen2x Cosec6x
Tan x Cot x 2 csc x
1 Cos x 2 2
2 x 2
E) –Sen2x Cosec6x E Tg
4 2 1 Cos x Reemplazando:
2
Resolución:
3 3
1 Senx
1 Senx Cosx Cosx
Cot x2 4Tan x4 Tan 2x Cot x2
K 4Sen 4Cos 1 1 Senx 1 Senx
4Sen3x 4Cos3x 2
3Senx Sen3x 3Cosx Cos3x 1
Cosx Cosx
4Tan x Tan x
4 2
4Sen3x 4Cos3x 2
Tan
x
1
3Senx 1 3Cosx 1 1 4 2 ; Tan2 Sec2 1
4Sen3x 4 4Cos3x 4 2 a 1 Tan
x Tan
a a2 4
3 SenxCos3x CosxSen3x 1
Respuesta: C)
4 Sec x 1 Sec x 3
2 x 2Sen3x Cos3x a2
2 2
3Sen x 3x
K Problema 3
2Sen6x
Al resolver la ecuación: Cos x 1
2 3
K 3 Sen2x Cosec6x
2
cot x 4 tan x 2 csc x
2 4
3 1
Respuesta: D) - Sen2x Cosec6x
2 Determine cos x
2 Respuesta: B)
3
UNI SEMESTRAL 2013 - III 40 TRIGONOMETRÍA TEMA 11
You might also like
- 1.2 ExamUNAC2014Idesarro PDFDocument26 pages1.2 ExamUNAC2014Idesarro PDFDavid FerreiraNo ratings yet
- Identidades trigonométricas para el arco dobleDocument4 pagesIdentidades trigonométricas para el arco dobleJhoan Heiner Fabian CristobalNo ratings yet
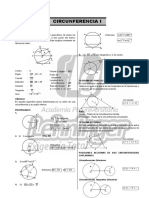
- Circunferencia IDocument4 pagesCircunferencia IKevinEqNo ratings yet
- NCh00146 2 2000 PDFDocument15 pagesNCh00146 2 2000 PDFrenzoesNo ratings yet
- Angulos en Posición NormalDocument2 pagesAngulos en Posición NormalManuel M. ColosNo ratings yet
- Estrella Triangulo PDFDocument14 pagesEstrella Triangulo PDFCk MontillaNo ratings yet
- Introduccion Bioestadistica UCOPressDocument142 pagesIntroduccion Bioestadistica UCOPresslorenzoNo ratings yet
- Práctica 3 Semana 4 (Verano 2020)Document4 pagesPráctica 3 Semana 4 (Verano 2020)Allison PaolaNo ratings yet
- Ángulo Mitad para Quinto Grado de SecundariaDocument2 pagesÁngulo Mitad para Quinto Grado de Secundariaelber527No ratings yet
- Campo ElectricoDocument37 pagesCampo ElectricoChirley LeandraGNo ratings yet
- Identidades trigonométricas fundamentalesDocument7 pagesIdentidades trigonométricas fundamentalesJoelpm22No ratings yet
- Simulacro 2 - Area DDocument15 pagesSimulacro 2 - Area DJEAN ARNOLD HUAYTA FERNANDEZNo ratings yet
- Qui-Semana #8-Ordinario 2020-IiDocument12 pagesQui-Semana #8-Ordinario 2020-IiJorge Cesar Rojas RamosNo ratings yet
- Domiciliaria - Aritmetica Semana 21Document2 pagesDomiciliaria - Aritmetica Semana 21Walter VMNo ratings yet
- 8,1 2023-I - It de Arco TripleDocument62 pages8,1 2023-I - It de Arco Tripleanderson torresNo ratings yet
- Tomoi Geo 5to Cap1Document29 pagesTomoi Geo 5to Cap1Jimena Prsicila Salvador SanchezNo ratings yet
- 6 Fis 4º Cap22 Sol TareaDocument5 pages6 Fis 4º Cap22 Sol TareaJAIRO JHOEL HUAMAN PEÑANo ratings yet
- 13 Sim Ex Adm UNMSM SSMDocument15 pages13 Sim Ex Adm UNMSM SSMPedro Alejandro Mesias Sanchez100% (1)
- Boletin Semana N°15 - Ciclo 2022-IDocument171 pagesBoletin Semana N°15 - Ciclo 2022-IERICK EFRAIN GUERRA ESCOBARNo ratings yet
- Semana 11 - Geometria Plana 2021Document4 pagesSemana 11 - Geometria Plana 2021Elmo Jaime SALAS YAÑEZNo ratings yet
- Semana02 ORD 2013 IDocument109 pagesSemana02 ORD 2013 IEVERNo ratings yet
- Cocientes NotablesDocument2 pagesCocientes NotablesTopografia AyacuchoNo ratings yet
- Tomo 6 Trigonometria PDFDocument58 pagesTomo 6 Trigonometria PDFCésar Alberto Palli Chipana100% (1)
- Area DDocument12 pagesArea DJoshep Martin huallpa laymeNo ratings yet
- Solucionario Semana 2 Cic. Ext. 2012-2013Document87 pagesSolucionario Semana 2 Cic. Ext. 2012-2013Michael Antonio Hurtado CastroNo ratings yet
- Factorización y ecuaciones de segundo y tercer gradoDocument19 pagesFactorización y ecuaciones de segundo y tercer gradoMabel Gay0% (1)
- Trigonometria S2Document6 pagesTrigonometria S2jessica mamaniNo ratings yet
- Aig 2015 A 06Document10 pagesAig 2015 A 06Fredy Poma LimaNo ratings yet
- Práctica N°05 Geometría y Trigonometría 203Document10 pagesPráctica N°05 Geometría y Trigonometría 203Cristhian Mendoza YucraNo ratings yet
- 7proyecto de Vida - ClavesDocument9 pages7proyecto de Vida - ClavesVictor SotoNo ratings yet
- Inferencia en la comprensión lectoraDocument112 pagesInferencia en la comprensión lectoraF SNo ratings yet
- 19bc6d39-d2a9-4c22-a38d-37256cd45292Document106 pages19bc6d39-d2a9-4c22-a38d-37256cd45292LALESHKA TIFANI PANDIA QUISPENo ratings yet
- Semana 18 Certezas, DiaposDocument39 pagesSemana 18 Certezas, Diaposrafael fernando100% (1)
- RAICES COMUNEsDocument2 pagesRAICES COMUNEsLeonel David de LimaNo ratings yet
- Estequiometría IIDocument1 pageEstequiometría IIKenyi Omar Holguino SullaNo ratings yet
- ÁLGEBRA Semana7Document47 pagesÁLGEBRA Semana7carlos rubio garciaNo ratings yet
- Trigonometría S4Document2 pagesTrigonometría S4Kronos SacNo ratings yet
- Mpe-Semana #02-Ciclo Ordinario 2023-I PDFDocument163 pagesMpe-Semana #02-Ciclo Ordinario 2023-I PDFAriana De la Cruz TorresNo ratings yet
- Semana 02 - ÉxitoDocument2 pagesSemana 02 - Éxitojuan carlos lluncor fallaNo ratings yet
- Trigonometría: Áreas de sectores circularesDocument14 pagesTrigonometría: Áreas de sectores circularesGiancarlo100% (1)
- Preguntas PR Opuestas: Asociación Fondo de Investigadores y EditoresDocument7 pagesPreguntas PR Opuestas: Asociación Fondo de Investigadores y EditoresDavid Ccañihua QuispeNo ratings yet
- Solucionario CEPREUNMSM 2011 II Boletin 1 A D EDocument98 pagesSolucionario CEPREUNMSM 2011 II Boletin 1 A D EMilagros HuamanNo ratings yet
- Cttrig5siii SRDocument8 pagesCttrig5siii SRAdrian Sanchez0% (1)
- Ab1 2015 Q 07 PDFDocument10 pagesAb1 2015 Q 07 PDFDanny Chavez ZunigaNo ratings yet
- Química 0.2Document14 pagesQuímica 0.2GiancarloNo ratings yet
- Semana 1Document8 pagesSemana 1FátimaNo ratings yet
- 2do Material de Estudio Geometría PRE 2023-2Document51 pages2do Material de Estudio Geometría PRE 2023-2Manuel ArevaloNo ratings yet
- Circunferencia IIDocument4 pagesCircunferencia IIKevinEq100% (1)
- RV Bloque CS - Sesion 1 - Formato DecoDocument8 pagesRV Bloque CS - Sesion 1 - Formato DecoFernanda Mio Vera100% (1)
- Equivalencias LogicasDocument3 pagesEquivalencias LogicasMariadenisTavaraNo ratings yet
- G Sem05Document7 pagesG Sem05Mate AyudaNo ratings yet
- TR Sem21Document7 pagesTR Sem21Angeln Calsin CariNo ratings yet
- 2 Alg 4º Cap22 Sol TareaDocument7 pages2 Alg 4º Cap22 Sol TareaJAIRO JHOEL HUAMAN PEÑANo ratings yet
- Coconut CrqsDocument5 pagesCoconut CrqsYyyuh0% (1)
- Iii Unidad-5° Fisica-Sem6-Movimiento Armónico SimpleDocument18 pagesIii Unidad-5° Fisica-Sem6-Movimiento Armónico SimpleMariajose Soles GuerreroNo ratings yet
- Conjuntos y subconjuntos en ingenieríaDocument12 pagesConjuntos y subconjuntos en ingenieríadavid dellymin alvarez canoNo ratings yet
- Cidech: Congruencia de TriánguloDocument2 pagesCidech: Congruencia de TriánguloRonald ArdilesNo ratings yet
- Tomoii Arit 4to Cap6Document17 pagesTomoii Arit 4to Cap6Rocio Caballero CaballeroNo ratings yet
- MatematicaDocument43 pagesMatematicajose joseph100% (1)
- Semestral Amantes Del Conocimiento - Algebra - Semana 02 - PolinomiosDocument5 pagesSemestral Amantes Del Conocimiento - Algebra - Semana 02 - PolinomiosOliver SanchezNo ratings yet
- Evaluación Diagnostica 2023 - Matemática 5 SecDocument5 pagesEvaluación Diagnostica 2023 - Matemática 5 SecJohnnyDeLaCruzCamacoNo ratings yet
- T - S5 - Ángulo TripleDocument2 pagesT - S5 - Ángulo TripleAngel Valverde Reyes100% (1)
- Trigonometria-Identidades de Variable TripleDocument7 pagesTrigonometria-Identidades de Variable Triplealejandro arenasNo ratings yet
- Tema 22 - Funciones Trigonométricas Inversas III - PropiedadesDocument4 pagesTema 22 - Funciones Trigonométricas Inversas III - PropiedadesJhoan Heiner Fabian CristobalNo ratings yet
- Tema 18 - Funciones Trigonométricas II - PeriodosDocument4 pagesTema 18 - Funciones Trigonométricas II - PeriodosJhoan Heiner Fabian CristobalNo ratings yet
- Tema 19 - Funciones Trigonométricas III - Trazado de GráficasDocument2 pagesTema 19 - Funciones Trigonométricas III - Trazado de GráficasJhoan Heiner Fabian Cristobal100% (1)
- Tema 15 - Resolución de Triángulos Oblicuángulos I - TeoremasDocument4 pagesTema 15 - Resolución de Triángulos Oblicuángulos I - TeoremasJhoan Heiner Fabian CristobalNo ratings yet
- Tema 08 - Identidades Trigonométricas para El Arco Compuesto II - Tres ArcosDocument2 pagesTema 08 - Identidades Trigonométricas para El Arco Compuesto II - Tres ArcosJhoan Heiner Fabian CristobalNo ratings yet
- Tema 14 - Sumatorias y Productoras TrigonométricasDocument4 pagesTema 14 - Sumatorias y Productoras TrigonométricasJhoan Heiner Fabian Cristobal100% (1)
- Tema 12 - Transformación de Una Suma o Diferencia A ProductoDocument2 pagesTema 12 - Transformación de Una Suma o Diferencia A ProductoJhoan Heiner Fabian CristobalNo ratings yet
- Tema 23 - Ecuaciones Trigonométricas - Elementales y No Elementales PDFDocument4 pagesTema 23 - Ecuaciones Trigonométricas - Elementales y No Elementales PDFJhoan Heiner Fabian Cristobal50% (2)
- Tema 13 - Transformación de Un Producto A Suma o DiferenciaDocument2 pagesTema 13 - Transformación de Un Producto A Suma o DiferenciaJhoan Heiner Fabian Cristobal100% (1)
- Tema 10 - Identidades Trigonométricas para El Arco MitadDocument4 pagesTema 10 - Identidades Trigonométricas para El Arco MitadJhoan Heiner Fabian CristobalNo ratings yet
- Tema 26 - Estudio de La Circunferencia PDFDocument4 pagesTema 26 - Estudio de La Circunferencia PDFJhoan Heiner Fabian CristobalNo ratings yet
- Resolución de inecuaciones trigonométricasDocument2 pagesResolución de inecuaciones trigonométricasJhoan Heiner Fabian Cristobal50% (2)
- 07 Vesalius S.M.a. R.T.angulos Agudos CopiaxDocument6 pages07 Vesalius S.M.a. R.T.angulos Agudos CopiaxJhoan Heiner Fabian CristobalNo ratings yet
- 07 Vesalius S.M.a. R.T.angulos Agudos CopiaxDocument6 pages07 Vesalius S.M.a. R.T.angulos Agudos CopiaxJhoan Heiner Fabian CristobalNo ratings yet
- Relaciones métricas y semejanza en geometríaDocument9 pagesRelaciones métricas y semejanza en geometríaJhoan Heiner Fabian CristobalNo ratings yet
- 7 Termodinamica Celda Electroq P SDocument9 pages7 Termodinamica Celda Electroq P SHania Martinez ValleNo ratings yet
- Anexo 1 Ejercicios y Formato Pre TareaDocument8 pagesAnexo 1 Ejercicios y Formato Pre TareaMayerly Yiceth SiachoqueNo ratings yet
- Guía práctica de vectores en física aplicadaDocument45 pagesGuía práctica de vectores en física aplicadaDiego Liza Garcia0% (2)
- Alginato Modelos ImpresionesDocument14 pagesAlginato Modelos ImpresionesMaria SanchezNo ratings yet
- LógicaDocument12 pagesLógicafreedownloads1No ratings yet
- SintesisDocument4 pagesSintesisStephy AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Adc y TacometroDocument7 pagesAdc y TacometroluizNo ratings yet
- PPT Unidad 01 Tema 01 2020 02 Fund Visuales I (2318)Document66 pagesPPT Unidad 01 Tema 01 2020 02 Fund Visuales I (2318)vangheluxNo ratings yet
- G05 Motores DC 2021-2Document11 pagesG05 Motores DC 2021-2edison barrionuevoNo ratings yet
- Ing Economica Uni1 - Act 1 - Victor RANGELDocument3 pagesIng Economica Uni1 - Act 1 - Victor RANGELVICTOR MANUEL RANGEL HERNANDEZNo ratings yet
- GUÍADocument22 pagesGUÍAJesua RaudalesNo ratings yet
- T6 Tests 3Document33 pagesT6 Tests 3Pilar de la CruzNo ratings yet
- Periodicidad y PropiedadesDocument4 pagesPeriodicidad y PropiedadesIvonne De la RosaNo ratings yet
- Sistemas Digitales Clase #1Document11 pagesSistemas Digitales Clase #1jesusNo ratings yet
- Lenguaje - Guibourg - y - Otros (1) Falta PDFDocument17 pagesLenguaje - Guibourg - y - Otros (1) Falta PDFsantiagoNo ratings yet
- Jason Tobar R (20191020118) 4.88 (D) 1 2 Mendenhall Beaver & BeaverDocument5 pagesJason Tobar R (20191020118) 4.88 (D) 1 2 Mendenhall Beaver & BeaverJASON DAMIAN TOBAR RODRIGUEZNo ratings yet
- Guia Tecnica Valery Julio 2001Document11 pagesGuia Tecnica Valery Julio 2001Youkkat SamiNo ratings yet
- Diseño de Teoria de ColasDocument5 pagesDiseño de Teoria de ColasJessica Mendez SalcedoNo ratings yet
- 0156000501-PEN-CCA-FTM-G-005 - Contrastación Topográfico de Estación Total v.0Document1 page0156000501-PEN-CCA-FTM-G-005 - Contrastación Topográfico de Estación Total v.0jorge vasquezNo ratings yet
- Teun A Van Dijk - Las Estructuras y Funciones Del Discurso-Conf 5Document28 pagesTeun A Van Dijk - Las Estructuras y Funciones Del Discurso-Conf 5Astrid PadillaNo ratings yet
- A35f A40f PDFDocument24 pagesA35f A40f PDFJDelmer VasquezNo ratings yet
- Gui AaaaaaDocument226 pagesGui AaaaaaAroldo Cacildo Vicente VásquezNo ratings yet
- Asp PDFDocument182 pagesAsp PDFA-k AmandaNo ratings yet
- Equilibrio QumiicoDocument7 pagesEquilibrio QumiicoLAURANo ratings yet
- GUIA 3 C.B. Codigo 641Document14 pagesGUIA 3 C.B. Codigo 641Vanessa Maria Bonett SimmondsNo ratings yet
- Trabajo Mecancio 8Document3 pagesTrabajo Mecancio 8Diego Simão Rojas ArrietNo ratings yet
- Movimiento Circular UniformeDocument3 pagesMovimiento Circular UniformeSoloAventurasNadaMazNo ratings yet