Professional Documents
Culture Documents
How To Create and Analyze A Rutile Crystal Structure in Crystalmaker
Uploaded by
api-456947878100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
205 views6 pagesOriginal Title
how to create and analyze a rutile crystal structure in crystalmaker
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
205 views6 pagesHow To Create and Analyze A Rutile Crystal Structure in Crystalmaker
Uploaded by
api-456947878Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 6
How to Create and Analyze a Rutile Crystal Structure
in CrystalMaker
By: Keith Ostrowski
Background and Purpose
Rutile is a naturally occurring mineral that is made primarily of titanium dioxide (TiO2). It is the
most common natural form of titanium dioxide and is often used to produce titanium metal.
Rutile can also be used to manufacture refractory ceramics and to produce pigments. When
Rutile is ground to a fine powder, it can be used as a pigment in paint, plastics, paper, foods, and
other applications to create a bright white color.
The purpose of this guide is to teach the general reader how to create a Rutile crystal structure
using CrystalMaker software. CrystalMaker is a paramount computer program for materials
scientists and engineers that allows the user to create a crystal structure and analyze its
properties. This guide provides a simple procedure for beginners who have a brief background in
crystal structures and have interest in using CrystalMaker. In order to follow along with the
instructions, users must have access to CrystalMaker software.
List of Materials Needed
• A desktop or portable computer
• CrystalMaker software package installed on the computer of use
Procedure
• Setting up the workspace
• Choosing the space group
• Setting the lattice parameters
• Setting the atomic positions
• Adding the bonds
• Analyzing the bond distance
Setting up the Workspace
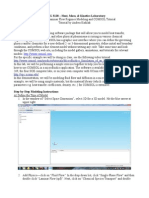
1. Open CrystalMaker
2. Select the “Add” tab in the top left side of
the screen indicated by the black arrow
Selecting the “Add” tab will open
a drop-down menu with options
such as “New Crystal…” and
“New Molecule…”
3. Click on “New Crystal…” indicated by the
green arrow
The “Crystal Editor” window will
then appear.
Choosing the Space Group
The space groups on CrystalMaker are very customizable with many different options to choose
from. For the purpose of this guide, Rutile’s specific space group will be used. Any deviations
from the selections chosen will result in a crystal that is not Rutile.
1. Click “Browse” to the right of the space
group box indicated by the blue arrow
The Space Group Browser will
now appear.
The space group can also be
typed in manually but the Space
Group Browser method is used
to show how the browser works
2. Select “Tetragonal” in the left box
of the browser shown by the red
arrow
3. Select “P” in the center box of the
browser shown by the black arrow
4. Select “P42/mnm” in the right box
of the browser shown by the green
arrow
5. Close the Space Group browser by clicking anywhere off of the browser
This will take you back to the previous window.
Setting the Lattice Parameters
Lattice parameters on CrystalMaker are customizable. In order to obtain a Rutile crystal
structure, Rutile’s specific lattice parameters, which are indicated below, must be used.
1. Type “4.594” in the leftmost box to
the right of “Lattice Parameters”
labeled “a [Å]” indicated by the blue
arrow
2. Type “2.958” in the rightmost box to
the right of “Lattice Parameters”
labeled “c [Å]” indicated by the red
arrow
Setting the Atomic Positions
1. Click on the “+” button once in the
bottom left-hand side of the tab
This will add a second site to the
chart above.
The default labels are Site1 and
Site2. The default occupancy
for both is Silicon and the
default position is 0,0,0.
2. Change the Label and Occupancy of the top site to
“Ti” by clicking on the box and typing “Ti” shown
by black arrows
The position of the atom will remain 0,0,0.
3. Change the Label and Occupancy of the second site
to “O” shown by blue arrows
4. Correct the position of the “O” atom by changing
the “x” position to “0.305” and “y” position to
“0.305” indicated by green and red arrows,
respectively
The “z” position will remain 0.
5. Press the “OK” button in the bottom right corner of the window.
This will close the window and a model of spherical atoms in
the crystal structure configuration is left on the screen in
default colors.
Adding the Bonds
1. Select the “Bonds Inspector” button in the top right-
hand part of the screen indicated by a black arrow
2. Click the “Settings” button in the top right of the
“Bonds Inspector” menu indicated by a blue arrow
This will cause a drop-down menu to
appear.
3. Click “Add Bond Specification” from the drop-down
menu indicated by a red arrow
This will add a bond in the “Bonds
Inspector” menu.
4. Press the first “?” button under
“Bond” in the “Bonds Inspector”
menu and select “Ti” shown by a
green arrow
“O” could be chosen as the
first atom as well, just be
sure the second atom is the
opposite atom as the first
one.
5. Press the second “?” button under “Bond” in
the “Bonds Inspector” menu and select “O”
shown by a black arrow
This will add bonds between the Ti
and O atoms in the crystal structure
Congratulations! You have now successfully created a model of the Rutile crystal structure. Now
that this is completed, it is time to use the analyzing tools on CrystalMaker to discover some of
the properties of this crystal structure.
Analyzing Bond Distance
1. Select the “Bond Distance Tool” in the
bottom center of the screen indicated by
the blue arrow
2. Click on an initial atom
In this case the center Ti atom was chosen, but
any atom in the crystal structure can be chosen.
3. Click on a second atom
In this case a neighboring “O” atom
was chosen but any other atom could
be chosen.
Once the second atom is clicked, the
distance between the atoms is shown.
You might also like
- Argus Lab IntroDocument4 pagesArgus Lab IntroIzhaar AliNo ratings yet
- FEA of Composites - Classical Lamination Theory Example 1: Problem DescriptionDocument39 pagesFEA of Composites - Classical Lamination Theory Example 1: Problem DescriptionsagarNo ratings yet
- A Linear Static Analysis of A Steel Plate With A Circular Hole - 2Document17 pagesA Linear Static Analysis of A Steel Plate With A Circular Hole - 2Dev Kumar DevaNo ratings yet
- Elliptical HoleDocument16 pagesElliptical HoleDev Kumar DevaNo ratings yet
- M1_Sciences_et_Génie_des_Matériaux___TP_Modélisation (2) (1)Document10 pagesM1_Sciences_et_Génie_des_Matériaux___TP_Modélisation (2) (1)sandraalimianarNo ratings yet
- Ort Tutorial 01Document21 pagesOrt Tutorial 01Adven TuresNo ratings yet
- Quick Start Guide for CrystalExplorer17Document10 pagesQuick Start Guide for CrystalExplorer17MarjanSplitNo ratings yet
- Material Structure Solid WorksDocument10 pagesMaterial Structure Solid WorksRisira Erantha KannangaraNo ratings yet
- CHEG 3128 - Heat, Mass, & Kinetics LaboratoryDocument8 pagesCHEG 3128 - Heat, Mass, & Kinetics Laboratorydemecheng04No ratings yet
- Stress Analysis Using Deform 3dDocument10 pagesStress Analysis Using Deform 3dramkumar121No ratings yet
- Introduction To FEA With FEMM: Create ModelDocument5 pagesIntroduction To FEA With FEMM: Create ModelWoong KimNo ratings yet
- Planar Truss: Prepare An Analysis ModelDocument12 pagesPlanar Truss: Prepare An Analysis Modelordenador90No ratings yet
- Basic Tutorial 6 - 2D Open Cut TunnelDocument31 pagesBasic Tutorial 6 - 2D Open Cut TunnelDario Manrique GamarraNo ratings yet
- in STAAD - Pro, You May Add Cover Plates To Your Beam Elements As Shown in The Following FigureDocument4 pagesin STAAD - Pro, You May Add Cover Plates To Your Beam Elements As Shown in The Following FigureVince Bagsit PolicarpioNo ratings yet
- Using The Smart IRT Diamond ATR.: To Make Sure That TheDocument5 pagesUsing The Smart IRT Diamond ATR.: To Make Sure That TheKren MGNo ratings yet
- Modify 3D Solids Modify 3D Solids Modify 3D Solids Modify 3D Solids Tutorial Tutorial Tutorial TutorialDocument18 pagesModify 3D Solids Modify 3D Solids Modify 3D Solids Modify 3D Solids Tutorial Tutorial Tutorial TutorialricardoNo ratings yet
- Physium Application: User's GuideDocument20 pagesPhysium Application: User's GuidemksayshiNo ratings yet
- Lab2 Microstrip LPF Fem FDTDDocument24 pagesLab2 Microstrip LPF Fem FDTDTrieu Doan0% (1)
- Catia v5 Sheet Metal Design 1640342388Document85 pagesCatia v5 Sheet Metal Design 1640342388Mesut GodbNo ratings yet
- Catia v5 Sheet Metal Design PDFDocument84 pagesCatia v5 Sheet Metal Design PDFFer AltamiranoNo ratings yet
- CrystalMaker TutorialDocument36 pagesCrystalMaker TutorialVicente GonzálezNo ratings yet
- Catia Sheet Metal Design PDFDocument90 pagesCatia Sheet Metal Design PDFNasos MasourasNo ratings yet
- Tutorial CootDocument17 pagesTutorial CootTanuj ParasteNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Corel RaveDocument13 pagesTutorial Corel RaveFrancisco Alves da Silva Júnior100% (1)
- SAM Design ExampleDocument110 pagesSAM Design Exampleyyanan1118100% (3)
- PCB PrintingDocument12 pagesPCB PrintingNaman AroraNo ratings yet
- Models - Acdc.capacitor DCDocument16 pagesModels - Acdc.capacitor DCFrancisco Rafael CerónNo ratings yet
- Electric Sensor Imaging Inside a Closed BoxDocument5 pagesElectric Sensor Imaging Inside a Closed BoxAlexandraNo ratings yet
- Exercise G: Comparing Element TypesDocument0 pagesExercise G: Comparing Element Typeskishorebondada78No ratings yet
- CIMATRON ToolsDocument18 pagesCIMATRON Toolspepepomez3No ratings yet
- Diptrace TutorialDocument138 pagesDiptrace TutorialJose GutiNo ratings yet
- Workshop 09 - Tablet Coating - Rocky 4.2Document49 pagesWorkshop 09 - Tablet Coating - Rocky 4.2Sai Santhosh Manepally100% (2)
- Tutorial 05 PDFDocument35 pagesTutorial 05 PDFJessie Radaza TutorNo ratings yet
- 2010 08 04 How To Create Mesh Using ICEM CFDDocument16 pages2010 08 04 How To Create Mesh Using ICEM CFDzamriabdlNo ratings yet
- Tut 5. Two-Column Hammerhead Pier PDFDocument35 pagesTut 5. Two-Column Hammerhead Pier PDFOscar Varon BarbosaNo ratings yet
- Toothbrush Holder Exercise 1Document24 pagesToothbrush Holder Exercise 1topjobNo ratings yet
- Computing CapacitanceDocument16 pagesComputing Capacitancepraveeng11100% (1)
- How To Display Lithology Data in StraterDocument7 pagesHow To Display Lithology Data in StraterDede Tedi ArifNo ratings yet
- STDCE TH Editting 01Document43 pagesSTDCE TH Editting 01lavyNo ratings yet
- Custom Rail Ring with Bezels: Primary Level SkillsDocument9 pagesCustom Rail Ring with Bezels: Primary Level SkillsMashhoud RajputNo ratings yet
- ENVI Tutorial: Basic Hyperspectral AnalysisDocument10 pagesENVI Tutorial: Basic Hyperspectral AnalysisPartha GhoshNo ratings yet
- 18 TUTNonlinearStaticAnalysisNonlinearMaterial PDFDocument25 pages18 TUTNonlinearStaticAnalysisNonlinearMaterial PDFrishit_aNo ratings yet
- Use COMSOL Multiphysics To Make A 2D Simulation of Poiseuille FlowDocument6 pagesUse COMSOL Multiphysics To Make A 2D Simulation of Poiseuille FlowthatsthisNo ratings yet
- Creating a Geological Model from Data using CMG BuilderDocument25 pagesCreating a Geological Model from Data using CMG BuilderAkib ImtihanNo ratings yet
- Activity 3 - Molecular ModelingDocument6 pagesActivity 3 - Molecular ModelingGraceNo ratings yet
- Pressed Elastoplastic PipeDocument18 pagesPressed Elastoplastic PipeAca DefNo ratings yet
- Optimizing Fluid Flow in Static Mixer PDFDocument15 pagesOptimizing Fluid Flow in Static Mixer PDFabdulfetahNo ratings yet
- Models - Cfd.solar Panel GeomDocument32 pagesModels - Cfd.solar Panel GeomMuhammad Waseem AhmadNo ratings yet
- Two Column Hammerhead Pier Structural Analysis TutorialDocument35 pagesTwo Column Hammerhead Pier Structural Analysis TutorialMohd FaizalNo ratings yet
- SimXpert R3.2 Example ProblemsDocument230 pagesSimXpert R3.2 Example Problemspaulkastle100% (1)
- Create Cylindrical Tank2 Foundation English 2006-07-21Document7 pagesCreate Cylindrical Tank2 Foundation English 2006-07-21Fakhrurozi FaniNo ratings yet
- Analysis of An Adhesively Bonded Joint: 2.1 Creating The GeometryDocument28 pagesAnalysis of An Adhesively Bonded Joint: 2.1 Creating The GeometryGianni BarbaNo ratings yet
- Adsorption LocatortutorialsDocument18 pagesAdsorption LocatortutorialsgueabdelkaderNo ratings yet
- DipTrace TutorialDocument134 pagesDipTrace TutorialMetalloyNo ratings yet
- Lab1 Microstrip Line FEM FDTDDocument32 pagesLab1 Microstrip Line FEM FDTDTrieu DoanNo ratings yet
- Strater 2Document11 pagesStrater 2dhefry0% (1)
- RV 01 PDFDocument9 pagesRV 01 PDFJhoan AmayaNo ratings yet
- Keith Tyler Ostrowski ResumeDocument1 pageKeith Tyler Ostrowski Resumeapi-456947878No ratings yet
- Market Street Bridge Archway AssemblyDocument4 pagesMarket Street Bridge Archway Assemblyapi-456947878No ratings yet
- White Paper-Hernias For Hope 1Document2 pagesWhite Paper-Hernias For Hope 1api-456947878No ratings yet
- Team 6 Full ProposalDocument9 pagesTeam 6 Full Proposalapi-456947878No ratings yet
- Technical Overview AEROSIL Fumed Silica enDocument104 pagesTechnical Overview AEROSIL Fumed Silica enaadd50% (2)
- Enabling 3X NM DRAM: Record Low Leakage 0.4 NM EOT MIM Capacitors With Novel Stack EngineeringDocument3 pagesEnabling 3X NM DRAM: Record Low Leakage 0.4 NM EOT MIM Capacitors With Novel Stack Engineeringedwin7029No ratings yet
- Adv Materials Technologies 2022 Kim Toward Advanced Highk and Electrode Thin Films For DRAM Capacitors Via AtomicDocument23 pagesAdv Materials Technologies 2022 Kim Toward Advanced Highk and Electrode Thin Films For DRAM Capacitors Via Atomic王彥文No ratings yet
- Science Corpus NLPDocument609 pagesScience Corpus NLPRahul SarafNo ratings yet
- Doctoral ThesisDocument150 pagesDoctoral ThesisMbulanga CrispinNo ratings yet
- Slow Charge Recombination in Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells (DSSC) Using Al2O3 Coated Nanoporous Tio2 FilmsDocument3 pagesSlow Charge Recombination in Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells (DSSC) Using Al2O3 Coated Nanoporous Tio2 Filmscenni laingNo ratings yet
- Build A Forest! With Every Building!: Reynobond - Reynolux With Ecoclean™Document8 pagesBuild A Forest! With Every Building!: Reynobond - Reynolux With Ecoclean™Phạm TháiNo ratings yet
- 1.11 Ceramic MembranesDocument28 pages1.11 Ceramic Membranesfzl123007No ratings yet
- TCC-EH70M Technical Product InfoDocument1 pageTCC-EH70M Technical Product InfosidsaleemNo ratings yet
- TDS Disperbyk-107 enDocument2 pagesTDS Disperbyk-107 enkim verdanaNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0032591020310718 MainDocument13 pages1 s2.0 S0032591020310718 MainBISWAJEET BEHERANo ratings yet
- Casadio Et Al-2012-Journal of Raman SpectrosDocument11 pagesCasadio Et Al-2012-Journal of Raman SpectrosJoão Henrique Ribeiro BarbosaNo ratings yet
- Modulus of Elasticity of PVB-2Document2 pagesModulus of Elasticity of PVB-2songyanxinNo ratings yet
- Superplastic Forming of TitaniumDocument50 pagesSuperplastic Forming of Titaniuminfo7595No ratings yet
- Ajith KMMLDocument24 pagesAjith KMMLGaurav ChandNo ratings yet
- INAO2018 QuestionDocument4 pagesINAO2018 QuestionFahimRajitHossainNo ratings yet
- 2.A Study On Nanomaterials For Water PurificationDocument7 pages2.A Study On Nanomaterials For Water PurificationMihaiNo ratings yet
- Book - Nanotechnology in CoatingsDocument20 pagesBook - Nanotechnology in CoatingsmitrasatapathyNo ratings yet
- Centeno, CRE PDFDocument10 pagesCenteno, CRE PDFrj centenoNo ratings yet
- Glaze ChemistryDocument9 pagesGlaze ChemistrydtkraeutNo ratings yet
- UK Equity ResearchDocument20 pagesUK Equity Researchapi-25923204No ratings yet
- Manufacturing Fine TiO2 Particles by Chloride ProcessDocument2 pagesManufacturing Fine TiO2 Particles by Chloride ProcessDiahAyuSafitriNo ratings yet
- April 2020 FormularyDocument142 pagesApril 2020 FormularyCab Orange100% (3)
- Kobo Surface Treated Pigments and Powders Combined June2015Document9 pagesKobo Surface Treated Pigments and Powders Combined June2015anuyasane9776No ratings yet
- Mirela - Alexandra ENACHE, Norbert KAZAMER, Radu Stepanescu University "Politehnica" of Timișoara, Timișoara, RomaniaDocument9 pagesMirela - Alexandra ENACHE, Norbert KAZAMER, Radu Stepanescu University "Politehnica" of Timișoara, Timișoara, RomaniaStephanie BergNo ratings yet
- Formulation of Toilet, Combo, and Synthetic Cleansing Bars: Edmund D. GeorgeDocument18 pagesFormulation of Toilet, Combo, and Synthetic Cleansing Bars: Edmund D. GeorgeSandra Costa BrasNo ratings yet
- C 146Document12 pagesC 146donaldoguerrero67% (3)
- VASP Study of VO On Rutile TiO2 For Cracking MethanolDocument15 pagesVASP Study of VO On Rutile TiO2 For Cracking MethanoldallonjpNo ratings yet
- US6794333Document12 pagesUS6794333Amir RahbariNo ratings yet
- TiO2 DeterminationDocument9 pagesTiO2 Determinationdoctuer_pdh100% (1)