Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Research study guide
Uploaded by
uwendymae0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views1 pageThis document discusses various aspects of research including defining research, building on past research to discover limitations, operational definitions, theories, establishing quality of research through findings and conclusions, reporting all data and findings, choosing a worthwhile and novel research topic, sampling methods, and reviewing related literature. It provides definitions and examples of different types of research such as descriptive research, case studies, content analysis, longitudinal research, and evaluative research. Key aspects of developing a strong research study such as formulating testable hypotheses, identifying variables, and using appropriate sampling techniques are also outlined.
Original Description:
Review
Original Title
Q3 APP7 Exam Reviewer
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses various aspects of research including defining research, building on past research to discover limitations, operational definitions, theories, establishing quality of research through findings and conclusions, reporting all data and findings, choosing a worthwhile and novel research topic, sampling methods, and reviewing related literature. It provides definitions and examples of different types of research such as descriptive research, case studies, content analysis, longitudinal research, and evaluative research. Key aspects of developing a strong research study such as formulating testable hypotheses, identifying variables, and using appropriate sampling techniques are also outlined.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views1 pageResearch study guide
Uploaded by
uwendymaeThis document discusses various aspects of research including defining research, building on past research to discover limitations, operational definitions, theories, establishing quality of research through findings and conclusions, reporting all data and findings, choosing a worthwhile and novel research topic, sampling methods, and reviewing related literature. It provides definitions and examples of different types of research such as descriptive research, case studies, content analysis, longitudinal research, and evaluative research. Key aspects of developing a strong research study such as formulating testable hypotheses, identifying variables, and using appropriate sampling techniques are also outlined.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
Research is a careful and systematic study and investigation in some field of knowledge.
To be so, it involves defining conditions that need corrective
measures and thorough analysis of its background and its effect.
Research studies can build or change; therefore, challenge of new studies on past researches that were proven true and effective is to discover
limitations and weaknesses of past researches as guide.
Operational definitions of terms used in a research study means how words are connotatively used in a research study.
While concepts are abstraction of meanings from certain realities, propositions are statements about concepts which may be proven true or false.
Theories are set of systematically interrelated concepts, definitions, propositions used to explain a phenomena and these are used as a representation
of relationship between among concepts.
The quality of a research study could be established through: It’s findings and conclusions.
Flaws in procedural design must be well-discussed to shed further light on any gap to other researchers who may want to replicate the study. Flaws
means limitations and weaknesses of the study.
Conclusions of any research must always be supported by relevant data and information.
Data and findings in the research study must all be reported including statistical computations and their interpretations.
The researcher must finally decide that in writing a research paper, the foremost thing to consider is the worth and the novelty of the research topic is
foremost.
Narrowing down a research topic would mean establishing a topic to a more manageable one.
In limiting the topic, you as the researcher must consider three important factors importance, resources and manageability.
Availability of materials and resources on your selected topic calls for more facts and information as support for your study.
In choosing and reading articles about your chosen topic, you need to decide the necessary relevant facts and information.
Adequate data and sufficient analysis of data is important in elaborating findings and conclusions.
A good research topic tests brevity, conciseness and narrowness of a research topic.
The research topic and the statement of the problem are identical because: a) The research topic is expressed in a declarative statement; b) The
research topic guides what to research on; and c) The research problem poses the issue to be tackled in the study.
In a simple descriptive-survey research the variables present the Independent and dependent variables.
The hypothesis are the propositions that must undergo evaluations to its causes and effects.
Three conditions of a good hypothesis include the following standards explainable, testable and with fewer conditions or assumptions.
In a descriptive-survey research, a causal analysis is acceptable where one variable leads to an effect on that other variable.
A trend analysis is a descriptive research that foretells the direction and the future status of certain phenomenon like population size, school enrolment,
business growth, household expenditure, etc.
A case study is a descriptive research that aims to have a comprehensive understanding of an individual group. It hopes to capture processes that
explain the characteristics and behavior of a person or groups.
A content analysis is a descriptive research that investigate the social and economic characteristics, opinions, and their knowledge about and behavior
towards a certain phenomenon.
Census is a kind of survey that covers the entire population under investigation.
A sample survey is a kind of survey that covers a portion of the study population.
Correlational is a kind of descriptive research that finds out the extent of relationship between different variables as distinguished by the characteristics
of the study and its system is correlational.
Longitudinal is a kind of study that involves time for investigation to establish some patterns. For example: weight or height patterns, or other change or
growth and development patterns is longitudinal.
Evaluative is a research design that assesses the worthiness of the study. For example: the study aims to evaluate the conduct of an implementation of
a certain program making group of persons who are directly involved in the program as respondents.
Purposive is sampling of respondents is based on the basic requirements of the researcher like choosing only those that meet the criteria of the study.
Quota is a kind of stratified sampling that requires a representation of each stratum, like number of male and female if needed in the study.
Probability is a sampling design that provides the likelihood of selecting as a sample representative.
Non-probability is a sampling design gives no assurance of inclusion as a sample representative.
Random Sampling is a kind of sampling technique where each name in the list is written on a rolled paper, and then drawn to get desired number of
sample respondent.
A kind of sampling technique where each name in the list is written on a rolled paper, and then drawn to get desired number of sample respondent is
Stratified Sampling.
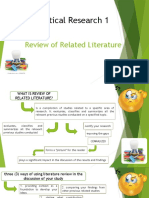
Checklist in Doing the Review of Related Literature YES NO
1. A review of related literature includes all forms of writing.
2. Related literature means those materials that are contributory to the concepts of a specific research study.
3. Previous research studies may be used as reference.
4. Online resources are library resources.
5. Copying the exact words and statements are important in making the review.
6. Reading past researches in general will enrich current research study.
7. Reading relevant past researches will guide one’s investigation of the current study.
8. A researcher must start with what he/she knows and what available materials he/she has to begin his research work.
9. In the chronological approach in presenting the review, the writer starts with themes.
10. Paraphrasing and summarizing related literature to help avoid committing plagiarism (owning other’s work as his/her own.
11. The researcher must look into the statement of the problem and sub problems as reference for his/her review.
12. Abstracts of theses and speeches are inadequate library resources.
13. The review presents some weaknesses and limitations of a specific research.
14. In note-taking, biographical informations are omitted.
15. Direct quotations that are used must be short.
You might also like
- ChatGPT: GUIDE TO WRITE A SCIENTIFIC RESEARCH PAPER FOR ENGINEERS, RESEARCHERS, AND SCIENTISTSFrom EverandChatGPT: GUIDE TO WRITE A SCIENTIFIC RESEARCH PAPER FOR ENGINEERS, RESEARCHERS, AND SCIENTISTSNo ratings yet
- Review of Related LiteratureDocument12 pagesReview of Related LiteraturePearl Anne ManilaNo ratings yet
- Selecting Relevant LiteratureDocument22 pagesSelecting Relevant LiteratureXYRA LOU SEDANo ratings yet
- Review of Related LiteratureDocument13 pagesReview of Related LiteratureMaria Josa Tolentino De NievaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 RegineDocument13 pagesChapter 7 RegineRonnie De Vera UnoNo ratings yet
- Practical Research 2Document6 pagesPractical Research 2Joly-Ann Rose BulabonNo ratings yet
- Practical Research 1-Week5-6Document22 pagesPractical Research 1-Week5-6XYRA LOU SEDANo ratings yet
- RDL - RRL Quiz 2Document2 pagesRDL - RRL Quiz 2Jared Darren S. OngNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Chapter 2Document8 pagesLesson 1 Chapter 2Pat HortezanoNo ratings yet
- Week 7 Lesson PR2Document27 pagesWeek 7 Lesson PR2Charles AnicieteNo ratings yet
- PR1 Handout 4Document7 pagesPR1 Handout 4Celina BautistaNo ratings yet
- Practical Research Chapter 2Document15 pagesPractical Research Chapter 2Dexter RimorinNo ratings yet
- Week 008 Module Learning From Others and Reviewing The LiteratureDocument5 pagesWeek 008 Module Learning From Others and Reviewing The LiteraturedsdsdNo ratings yet
- CH - 05 POLIT Reviewing The LiteraturDocument26 pagesCH - 05 POLIT Reviewing The Literaturhadi23001No ratings yet
- RRL and ReferencingDocument35 pagesRRL and ReferencingPatrice Del MundoNo ratings yet
- APP 007 4th ACHIEVEMENT TEST REVIEWERDocument8 pagesAPP 007 4th ACHIEVEMENT TEST REVIEWERMerwin CayadingNo ratings yet
- HANDOUTS-Review of Related LiteratureDocument13 pagesHANDOUTS-Review of Related Literatureshey mahilumNo ratings yet
- RES 1 Module 4 REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE AND Plagiarism APA MLA Citation StyleDocument4 pagesRES 1 Module 4 REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE AND Plagiarism APA MLA Citation StyleJAMES PATRICKNo ratings yet
- PRACTICAL RESEARCH GUIDEDocument22 pagesPRACTICAL RESEARCH GUIDESonny Boy SajoniaNo ratings yet
- Business research literature reviewDocument9 pagesBusiness research literature reviewAnita DhakalNo ratings yet
- IndexDocument16 pagesIndexkyrzenmaruquezNo ratings yet
- Chapter Five - Review of Related Literature and StudiesDocument4 pagesChapter Five - Review of Related Literature and StudiesVELUNTA, Nina GabrielleNo ratings yet
- Five Purpose of Literature ReviewDocument5 pagesFive Purpose of Literature Reviewdrnpguwgf100% (1)
- LITERATUREDocument40 pagesLITERATUREmary.angeles002No ratings yet
- Review of Related LiteratureDocument34 pagesReview of Related LiteratureTrina BolibolNo ratings yet
- Dec - Practical ResearchDocument5 pagesDec - Practical ResearchJaimee Mojica TaligonNo ratings yet
- Review of The Related Literature ObjectivesDocument15 pagesReview of The Related Literature ObjectivesYosef KetemaNo ratings yet
- University Research Writing GuideDocument27 pagesUniversity Research Writing GuideMARY ABIGAIL TAYAGNo ratings yet
- Study Guide Q2Document7 pagesStudy Guide Q2Keanu Reeve CamorroNo ratings yet
- Smith Galgo FebCharabella LAS#11Document7 pagesSmith Galgo FebCharabella LAS#11Feb Charabella Lunasin GalgoNo ratings yet
- ResearchReviewer STE10Document4 pagesResearchReviewer STE10stiler987651234No ratings yet
- Lesson 11 Theoretical Conceptual FrameworkDocument25 pagesLesson 11 Theoretical Conceptual FrameworkFritzee Sofhia BanaganNo ratings yet
- RRL HandoutsDocument6 pagesRRL HandoutsKirt Allen FloridaNo ratings yet
- Types of Quali and RRLDocument11 pagesTypes of Quali and RRLRostanica ViloriaNo ratings yet
- Research Format and Review of Related LiteratureDocument4 pagesResearch Format and Review of Related Literaturelander100% (2)
- Reading Report Citation (QS)Document4 pagesReading Report Citation (QS)MAFFIA IndustriesNo ratings yet
- Literature ReviewDocument81 pagesLiterature Reviewjestoni manipolNo ratings yet
- Assessment Task: A. Write Your Concise Learning About The FollowingDocument5 pagesAssessment Task: A. Write Your Concise Learning About The FollowingYanyan MaputiNo ratings yet
- Ch2-A - ARNEL - CORPUZ SN 2019390031 02192020Document7 pagesCh2-A - ARNEL - CORPUZ SN 2019390031 02192020ArnelCorpuzNo ratings yet
- Review of Related LiteratureDocument19 pagesReview of Related LiteratureRossking GarciaNo ratings yet
- Research FormatDocument10 pagesResearch FormatLea Pearl Imbang Francisco IINo ratings yet
- Literature Review 2017Document19 pagesLiterature Review 2017Abdul RajakNo ratings yet
- Research Methodology PRN 22021921053Document14 pagesResearch Methodology PRN 22021921053Jaisal PanjiyarNo ratings yet
- RM 2combDocument19 pagesRM 2combadiNo ratings yet
- The RRLDocument23 pagesThe RRLEj SabadoNo ratings yet
- Methods of Research: ObjectivesDocument4 pagesMethods of Research: ObjectivesGrace Anne Marie MarasiganNo ratings yet
- WLC RESEARCH FORMAT GUIDEDocument7 pagesWLC RESEARCH FORMAT GUIDEIVORY ACE PALACIONo ratings yet
- Action Research Proposal TemplateDocument3 pagesAction Research Proposal Templateiamsireu floresNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 3 2015Document25 pagesChapter - 3 2015Yona TsegayeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 DiscussionDocument95 pagesChapter 2 DiscussionJay RNo ratings yet
- IN Practical Research 2: Prepared By: Mr. Edgar D. TorresDocument12 pagesIN Practical Research 2: Prepared By: Mr. Edgar D. TorresRayvie Mendeja100% (1)
- Research Proposal Oral RubricsDocument1 pageResearch Proposal Oral RubricsKrizia Mae BrutasNo ratings yet
- Literature ReviewDocument26 pagesLiterature ReviewAlrac Anacta MalaitNo ratings yet
- Review of Related LiteratureDocument15 pagesReview of Related LiteratureJohn Paul LagramaNo ratings yet
- Research Project ProposalDocument5 pagesResearch Project ProposalSujan Raj BonshiNo ratings yet
- Perpertual Succour Academy, Inc.: Teacher-Made Learner's Home TaskDocument4 pagesPerpertual Succour Academy, Inc.: Teacher-Made Learner's Home TaskCry Bero50% (2)
- DEM 401 - Advanced Research Methods in Education: Types of Academic ResearchDocument4 pagesDEM 401 - Advanced Research Methods in Education: Types of Academic ResearchEdlyn NacionalNo ratings yet
- Reading Material W1 2 2Document15 pagesReading Material W1 2 2Mina DahyunNo ratings yet
- App 005 4TH Achievement Test ReviewerDocument5 pagesApp 005 4TH Achievement Test ReviewerPaolo DioquinoNo ratings yet
- Literature Review: Organizing The Persuasive ArgumentsDocument6 pagesLiterature Review: Organizing The Persuasive ArgumentsAnonymous CwJeBCAXpNo ratings yet
- English Verb Tenses ChartDocument2 pagesEnglish Verb Tenses ChartTONY TEMPLOSNo ratings yet
- Reading and Writing Q1 - M1Document14 pagesReading and Writing Q1 - M1ZOSIMO PIZON67% (3)
- Acupuncture Points - Indications II FlashcardsDocument12 pagesAcupuncture Points - Indications II FlashcardsVairamoorthy ArunachalamNo ratings yet
- CMS and CEMC present the 2007 Sun Life Financial Canadian Open Mathematics ChallengeDocument4 pagesCMS and CEMC present the 2007 Sun Life Financial Canadian Open Mathematics ChallengeNicola EvripidouNo ratings yet
- Inductive Grammar Chart (Unit 5, Page 52) : Renzo Bladeck Estrada Mena 30-09-2021Document2 pagesInductive Grammar Chart (Unit 5, Page 52) : Renzo Bladeck Estrada Mena 30-09-2021Bladeck BlacckdeNo ratings yet
- 101 2014 3 eDocument11 pages101 2014 3 eSimbarashe MarisaNo ratings yet
- Math Problem Solving in Action - Getting Students To Love Word Problems, Grades 3-5 PDFDocument188 pagesMath Problem Solving in Action - Getting Students To Love Word Problems, Grades 3-5 PDFOliveen100% (5)
- Aggreko Info GuideDocument19 pagesAggreko Info GuideJeongSikYooNo ratings yet
- Adjectives, movie predictions, and a story about a boy buying a runt rabbitDocument3 pagesAdjectives, movie predictions, and a story about a boy buying a runt rabbitzandiNo ratings yet
- Beg U11 Revision PDFDocument2 pagesBeg U11 Revision PDFBonny IvoNo ratings yet
- San Jose Community College: College of Arts and SciencesDocument5 pagesSan Jose Community College: College of Arts and SciencesSH ENNo ratings yet
- FR QB Vol 1 J23Document473 pagesFR QB Vol 1 J23gopal adhikariNo ratings yet
- IT1 ReportDocument1 pageIT1 ReportFranz Allen RanasNo ratings yet
- Chem237LabManual Fall2012 RDocument94 pagesChem237LabManual Fall2012 RKyle Tosh0% (1)
- Results of 2011 SMOPS (For Webpage)Document14 pagesResults of 2011 SMOPS (For Webpage)Thích Toán HọcNo ratings yet
- G10 - Portfolio Assessment 1 - 2022-2023Document2 pagesG10 - Portfolio Assessment 1 - 2022-2023ayush rajeshNo ratings yet
- Faculty Screening J.ODocument2 pagesFaculty Screening J.OIvy CalladaNo ratings yet
- Pepsi ScreeningDocument13 pagesPepsi Screeningapi-459936554No ratings yet
- Guideline, Research WritingDocument70 pagesGuideline, Research WritingBilal Kemal89% (18)
- Fasil Andargie Fenta: LecturerDocument2 pagesFasil Andargie Fenta: Lecturerfasil AndargieNo ratings yet
- Goal Setting - FinalDocument2 pagesGoal Setting - Finalapi-301796386No ratings yet
- Grade 7 - 10 Class Program Sy 2022 2023Document4 pagesGrade 7 - 10 Class Program Sy 2022 2023Niel Marc TomasNo ratings yet
- BA 301 Syllabus (Summer 2018) Chuck Nobles Portland State University Research & Analysis of Business ProblemsDocument11 pagesBA 301 Syllabus (Summer 2018) Chuck Nobles Portland State University Research & Analysis of Business ProblemsHardlyNo ratings yet
- Carl Dahlhaus, "What Is A Fact of Music History "Document10 pagesCarl Dahlhaus, "What Is A Fact of Music History "sashaNo ratings yet
- Memoir Reflection PaperDocument4 pagesMemoir Reflection Paperapi-301417439No ratings yet
- Top 10 IAS Coaching in Mumbai For UPSC Exam Preparation, Words-3277Document9 pagesTop 10 IAS Coaching in Mumbai For UPSC Exam Preparation, Words-3277Sonali DalaiNo ratings yet
- Core Beliefs Worksheet PDFDocument3 pagesCore Beliefs Worksheet PDFMarieSmithNo ratings yet
- Lullabies: Back Cover Front CoverDocument16 pagesLullabies: Back Cover Front CovermaynarahsNo ratings yet
- Semisupervised Neural Networks For Efficient Hyperspectral Image ClassificationDocument12 pagesSemisupervised Neural Networks For Efficient Hyperspectral Image ClassificationVishal PoonachaNo ratings yet
- Consensus Statements and Clinical Recommendations For Implant Loading ProtocolsDocument4 pagesConsensus Statements and Clinical Recommendations For Implant Loading ProtocolsLarissa RodovalhoNo ratings yet
- Make It Stick by Peter C. Brown, Henry L. Roediger III, Mark A. McDaniel - Book Summary: The Science of Successful LearningFrom EverandMake It Stick by Peter C. Brown, Henry L. Roediger III, Mark A. McDaniel - Book Summary: The Science of Successful LearningRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (55)
- The Everything Guide to Study Skills: Strategies, tips, and tools you need to succeed in school!From EverandThe Everything Guide to Study Skills: Strategies, tips, and tools you need to succeed in school!Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (6)
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- IELTS Speaking Vocabulary Builder (Band 5-6): Master Phrases and Expressions for the IELTS Speaking ExamFrom EverandIELTS Speaking Vocabulary Builder (Band 5-6): Master Phrases and Expressions for the IELTS Speaking ExamRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- TEF Canada Expression Écrite : 150 Topics To SucceedFrom EverandTEF Canada Expression Écrite : 150 Topics To SucceedRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (17)
- Math Olympiad Contests Preparation For Grades 4-8: Competition Level Math for Middle School Students to Win MathCON, AMC-8, MATHCOUNTS, and Math LeaguesFrom EverandMath Olympiad Contests Preparation For Grades 4-8: Competition Level Math for Middle School Students to Win MathCON, AMC-8, MATHCOUNTS, and Math LeaguesNo ratings yet
- ATI TEAS Study Guide: The Most Comprehensive and Up-to-Date Manual to Ace the Nursing Exam on Your First Try with Key Practice Questions, In-Depth Reviews, and Effective Test-Taking StrategiesFrom EverandATI TEAS Study Guide: The Most Comprehensive and Up-to-Date Manual to Ace the Nursing Exam on Your First Try with Key Practice Questions, In-Depth Reviews, and Effective Test-Taking StrategiesNo ratings yet
- 1,001 Questions & Answers for the CWI Exam: Welding Metallurgy and Visual Inspection Study GuideFrom Everand1,001 Questions & Answers for the CWI Exam: Welding Metallurgy and Visual Inspection Study GuideRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (7)
- BCBA Exam Prep A Study Guide to Practice Test Questions With Answers and Master the Board Certified Behavior Analyst ExaminationFrom EverandBCBA Exam Prep A Study Guide to Practice Test Questions With Answers and Master the Board Certified Behavior Analyst ExaminationNo ratings yet
- TEST TAKING STRATEGIES FOR EVERYONE: A Comprehensive Guide to Mastering Test Taking (2023 Beginner Crash Course)From EverandTEST TAKING STRATEGIES FOR EVERYONE: A Comprehensive Guide to Mastering Test Taking (2023 Beginner Crash Course)No ratings yet
- Learning from Lectures: Learning from lectures, listening & notetaking skillsFrom EverandLearning from Lectures: Learning from lectures, listening & notetaking skillsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (6)
- Real Stories: The All-Inclusive Textbook for Developmental Writing and ReadingFrom EverandReal Stories: The All-Inclusive Textbook for Developmental Writing and ReadingNo ratings yet
- 700 Driving Theory Test Questions & Answers: Updated Study Guide With Over 700 Official Style Practise Questions For Cars - Based Off the Highway CodeFrom Everand700 Driving Theory Test Questions & Answers: Updated Study Guide With Over 700 Official Style Practise Questions For Cars - Based Off the Highway CodeNo ratings yet
- Straight-A Study Skills: More Than 200 Essential Strategies to Ace Your Exams, Boost Your Grades, and Achieve Lasting Academic SuccessFrom EverandStraight-A Study Skills: More Than 200 Essential Strategies to Ace Your Exams, Boost Your Grades, and Achieve Lasting Academic SuccessRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (6)
- Master the Public Safety Dispatcher/911 Operator ExamFrom EverandMaster the Public Safety Dispatcher/911 Operator ExamRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)