Professional Documents
Culture Documents
MF0003 Set-2
Uploaded by
Dilipk86Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
MF0003 Set-2
Uploaded by
Dilipk86Copyright:
Available Formats
Sikkim Manipal University 3rd Semester Fall 2010
MBA – III SEM
Taxation Management – MF0003
SET - 2
Q. 1. Mr. Alok is a practicing accountant. He also took 40 lectures in
college at Rs.100 per lecture. His receipt and payment account is given
below;
Receipts Rs. Payments Rs.
To bal b/d 9500 By office expenses 25000
Audit fees 160000 Municipal taxes 600
Remuneration lectures 4000 Personal expenses 5000
Examiner’s fees 1500 Membership fees 500
Interest on securities 1550 LIC Premium 3000
Rent from LOP 3000 Scooter purchased 45000
Royalty on book 6000 Scooter expenses 6000
Balance c/d 185550
270650 270650
i) Office expenses include Rs. 1000 paid as typing charges for preparing
manuscript of his book.
ii) ½ of the scooter expenses relate to personal use.
iii) Scooter being P& M depreciation is allowed at per rate 15 %
iv) Interest of securities includes Rs. 774 being interest on tax free
government securities.
Answer:
Taxation Management SET-2 1
Sikkim Manipal University 3rd Semester Fall 2010
Computation of Income from Profession of Mr. Alok
PARTICULARS Amount Amount
Rs. Ps. Rs. Ps.
Professional Receipts:
1,60,000.0
Audit Fees 0
Remuneration Lectures 4,000.00
Examiner’s Fees 1,500.00
Royalty on Book 6,000.00 1,71,500.00
Less: Professional Payments or Allowable Expenses
Office Expenses 25,000.00
Membership Fees 500.00
Depreciation of Scooter – 45000 / 100 X 15 = 6750 6,750.00
Scooter Expenses – 6000 / 2 = 3000 3,000.00 35,250.00
Income from Professional 1,36,250.00
Q. 2. Enumerate at least 10 items which can be included under the head
‘income from other sources’.
Answer: This is the last and residuary head of income. Any income which is taxable
under the Act but does not find place under any of the first four heads of income (i.e.
Salaries, House Property, Business and Capital Gains) will be assessable under this
residuary head ‘Income from other Sources’.
Incomes chargeable under this head:-
Incomes chargeable under this head of income [Sec. 56(2)]:-
The following incomes shall be chargeable to income tax under the head ‘Income
Other Sources’:
Income from winnings from lotteries, crossword puzzles, races including horse races,
card games and other games of any short or from gambling or betting of any form or
nature whatsoever.
Any sum received by the assessee from his employees as contributions to any
provident fund or superannuating fund or any fund set-up under Employees’ State
Insurance Act, 1948 or any other fund for the welfare of such employees, provided
that it is not chargeable under the head ‘ Profits and Gains of Business or
Profession’.
Taxation Management SET-2 2
Sikkim Manipal University 3rd Semester Fall 2010
Income by way of interest on securities, if the income is not chargeable to income tax
under the head ‘Profits and Gains of Business or Profession’.
Income from machinery, plant or furniture belonging to the assessee and let on hire if
the income is not chargeable to income tax under the head ‘Profits and Gains of
Business or Profession’.
Income of an assessee from letting on hire machinery, plant or furniture belonging to
him and also buildings, and the letting of the buildings is inseparable from the letting
of the said machinery, plant or furniture, if it is not chargeable to income tax under
the head “profits and Gains of Business or Profession’. Income received under a
Keyman insurance policy including bonus on such policy if such income is not
chargeable to income tax under the head ‘Profit and Gains of Business or Profession’
or under the head ‘Salaries’.
Dividend on Shares in Foreign Companies:-
Any fees or commission received by an employee from a person other than his
employer.
All interest including interest on securities.
Income of a tenant from subletting.
Director’s fees. Rent of land not appurtenant to buildings. Agricultural income
from land situated outside India.
Income from markets, ferries, fisheries etc.
Income from leasehold properties.
Remunerations for writing articles in Journals.
Income from undisclosed sources (unexplained investments, unexplained
money, unexplained expenditure etc.).
Interest on employees own contribution to URPF.
Casual income.
Salary of M.P, M.L.A., M.L.C.
Interest received on securities of co-operative society. Family pension received by
the widow and heirs of deceased employee (Standard deduction permissible in
respect of family pension is Rs. 15,000 or 1/3 of such pension whichever is less)
Director’s Commission for underwriting shares of a new company, Insurance
Commission not chargeable under the head ‘business or profession’.
Taxation Management SET-2 3
Sikkim Manipal University 3rd Semester Fall 2010
Any sum of money exceeding Rs. 25,000 (Rs. 50,000 on or after
01-04-2006) received without consideration by an individual or a HUF from any
person, the whole of such sum is taxable under this head.
But it does not apply to any sum of money received:
(a) from a relative; or
(b) under a will or by way of inheritance; or
(c) on the occasion of the marriage of the individual; or
(d) in contemplation of death of the payer
For this purpose relative means:
(i) spouse of the individual;
(ii) brother or sister of the individual;
(iii) brother or sister of the spouse of the individual;
(iv) brother or sister of either of the parents of the individual;
(v) any lineal ascendant or descendant of the individual; and of the spouse also
(vi) spouse of the person referred to in (i) to (v)
Interests on Securities:-
The following amounts due to an assessee in the previous year shall be chargeable
to income tax as interest on securities:
(i) Interest on any security of the Central or State Governments;
(ii) Interest on debentures or other securities issued by a local authority;
(iii) Interest on debentures issued by a company (whether Indian or foreign); and
(iv) Interest on debentures or other securities issued by a Statutory Corporation.
Basic of Charge:-
Interest on securities does not accrue from day to day but becomes due on certain
fixed dates only, which are mentioned on the securities. Interest on securities is
chargeable to tax on the basis of accounting method (cash or mercantile) followed by
the assessee. However, where no method of accounting is regularly employed by the
assessee, the income from interest on securities shall be chargeable to tax as the
income of the previous year in which it becomes due though it may be received later.
Taxation Management SET-2 4
Sikkim Manipal University 3rd Semester Fall 2010
Where the assessee adopts cash system of accounting the interest will be taxed on
receipt basis.
Cum interest or Ex-interest Transaction:-
When securities are bought or sold between the two interest dates, the transaction is
either cum-interest or ex-interest. Whatever be the nature of the transaction, the rule
is that interest on securities is regarded as wholly the income of the person who
happens to be the owner at the time when the interest becomes due, irrespective of
whether he was the owner throughout the period of which the interest is paid or not,
and also whether the transaction has been cum-interest or ex-interest.
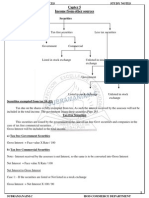
Securities are of four types:-
(i) Tax-free Government Securities: These securities are those, the interest on
which is fully exempt from tax under section 10(15). Interest on such securities is
neither included in total income nor it is taxed.
(ii) Government Securities: Such securities are issued either by the Central
Government or a State Government. These are taxable securities. But no tax is
deducted at source on such securities. Hence, the interest on such securities will not
be grossed up. The amount received or due as the case may be shall be included in
the total income.
(iii) Tax-free Commercial Securities: These are issued by a local authority or
statutory corporation or a company, in the form of debentures or bonds. Really
speaking their interest not tax-free, because tax due on this interest is payable by the
company, or local authority or corporation concerned. These are called tax-free,
because the assessee has not to pay tax on it from his own pocket. The tax paid by
the company (10.2% in case of listed securities, 20.4% in case of unlisted securities)
on this interest is deemed to have been paid on behalf of the assessee, hence the
amount of tax paid on any interest due to an asseessee added to his interest income.
i.e, the interest due to an assessee is grossed up and then this grossed up amount is
included in his total income. The amount of tax paid by the company on this interest
is deducted from the total tax payable by the assessee. For example, if a company
has issued 10% Tax-free Debentures, the debenture-holder will receive the entire
amount of interest calculated at 10% but the amount to be included in the total
income of the debenture holder will be the amount actually received by him as
interest plus income tax thereon paid by the company.
(iv) Less-Tax Commercial Securities: These may be called “Taxable Securities”. In
the case of these securities, income tax is deducted at source on the amount of
interest calculated at the percentage stated on the securities and balance of the
amount of interest left after deduction of the aforesaid income tax is paid to the
security-holder. (The rate of tax deducted at source is 10.2 % in case of listed
securities, 20.4% in case of unlisted securities) If the rate percent of interest is given
it is not grossed up as it is already the gross amount of interest, and income tax is to
be deducted there from. If in the case of these securities, the net amount of interest
received is given, it has got to be grossed up. In any case, it is the gross amount of
interest that is included in the total income of an assessee.
Taxation Management SET-2 5
Sikkim Manipal University 3rd Semester Fall 2010
Q. 3. How is tax liability of a company is computed.
Answer:
Computation of Total Income of a Company:-
Particulars Amount Amount
Ascertain the income under the different heads HP + Business XXX
Income + Capital Gain + Other Sources
Add: Income of other persons (if any) u/s 60 & 61 XXX
XXX
Adjustment on account of:
Current losses (if any) XXX
B/forward losses (if any) XXX XXX
(According to section 70 to 80)
Gross Total Income XXX
Less: Deductions under sections (if any)
80G Donations XXX
80GGA Donations to SR & RD XXX
80GGB Contributed to Political parties XXX
80IA Profits from Infrastructure develop XXX
80IAB profits from company engaged in develop of SEZ XXX
80IB Certain industrial undertakings XXX
80IC Certain States XXX
80JJA bio-degradable waste XXX
80JJAA Employment of new workmen XXX
80LA Offshore banking XXX
Net Income XXX
Taxation Management SET-2 6
Sikkim Manipal University 3rd Semester Fall 2010
Computation of Tax Liability of a Company
(A) Under Normal Circumstances/or
Provisions (B) Under MAT
Particulars Amount Particulars Amount
Step I: Find out taxable Income XXX Step I: Find out book profit XXX
Step II: Ascertain 10% of Book
Profit XXX
Step II: Find out tax at 30% on
taxable
income (40% in case of a foreign
company) XXX Add: Surcharge at 10%
(Income Likely to exceed Rs.1
Crore)
Step III: Less: Rebate U/s 88E (if
any) XXX (2.5 % for foreign company) XXX
Tax XXX XXX
Add: Surcharge at 10% Tax + Surcharge XXX
(Income Likely to exceed Rs.1 Crore)
XXX
(2.5 % for foreign company) XXX
Tax + Surcharge
Add: Education Cess on Tax
Surcharge (at 3%) XXX Add: Education Cess at 3% on
Tax + Surcharge (Always Tax
Liability
Less: Tax Rebate or tax credit XXX as per MAT) XXX
Tax Liability XXX
Taxation Management SET-2 7
You might also like
- US Taxation of International Startups and Inbound Individuals: For Founders and Executives, Updated for 2023 rulesFrom EverandUS Taxation of International Startups and Inbound Individuals: For Founders and Executives, Updated for 2023 rulesNo ratings yet
- 21St Century Computer Solutions: A Manual Accounting SimulationFrom Everand21St Century Computer Solutions: A Manual Accounting SimulationNo ratings yet
- Taxation Management DocumentDocument8 pagesTaxation Management DocumentmachhindramNo ratings yet
- Subu Income From Other Sources Final - 2Document5 pagesSubu Income From Other Sources Final - 2Nitesh BhuraNo ratings yet
- Income From Other Sources - NotesDocument4 pagesIncome From Other Sources - NotesAniket AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 v2 RevisedDocument13 pagesChapter 8 v2 RevisedSheilamae Sernadilla GregorioNo ratings yet
- Income From Other Sources Notes and ProblemsDocument6 pagesIncome From Other Sources Notes and Problems20-UCO-517 AJAY KELVIN ANo ratings yet
- 2019 PROBLEM EXERCISES IN INCOME TAXATION and TRAIN LAW (B)Document11 pages2019 PROBLEM EXERCISES IN INCOME TAXATION and TRAIN LAW (B)MGVMonNo ratings yet
- It QuestionsDocument21 pagesIt QuestionssanatnaharNo ratings yet
- Taxation Law & PracticeDocument6 pagesTaxation Law & PracticeJawahar DalalNo ratings yet
- 2nd Term, SY 2019-2020 Quiz On Income Taxation Name: - Section: - Date: - Identification Identify The Following StatementsDocument2 pages2nd Term, SY 2019-2020 Quiz On Income Taxation Name: - Section: - Date: - Identification Identify The Following StatementsVergel MartinezNo ratings yet
- Income Tax Group AssignmentDocument8 pagesIncome Tax Group AssignmentFozle Rabby 182-11-5893No ratings yet
- Income Tax Rules for Agricultural Income and Property Tax DeductionsDocument9 pagesIncome Tax Rules for Agricultural Income and Property Tax DeductionsHeraldWilsonNo ratings yet
- HANDOUTS-GROSS-INCOMEDocument7 pagesHANDOUTS-GROSS-INCOMEbernadethsobritoNo ratings yet
- Final MF0003 2nd AssigDocument6 pagesFinal MF0003 2nd Assignigistwold5192No ratings yet
- Income From Other SourcesDocument19 pagesIncome From Other SourcesRam RamNo ratings yet
- Income From Other SourcesDocument9 pagesIncome From Other Sourcesrajsab20061093No ratings yet
- Class Lectures on Income from Business Part 1Document8 pagesClass Lectures on Income from Business Part 1Muhammad RaufNo ratings yet
- Morales Taxation Topic 4 Fringe BenefitsDocument14 pagesMorales Taxation Topic 4 Fringe BenefitsMary Joice Delos santosNo ratings yet
- Tax Deducted at SourceDocument29 pagesTax Deducted at SourceChaitany Joshi0% (2)
- PROFITS AND GAINS FROM BUSINESS OR PROFESSION (Sec.28 to 44DDocument31 pagesPROFITS AND GAINS FROM BUSINESS OR PROFESSION (Sec.28 to 44DUday KumarNo ratings yet
- Income Tax Introduction: Guide to Key ConceptsDocument13 pagesIncome Tax Introduction: Guide to Key ConceptsRhea SharmaNo ratings yet
- Fringe Benefit Tax 2Document20 pagesFringe Benefit Tax 2shpo.porras.uiNo ratings yet
- Income Tax in IndiaDocument19 pagesIncome Tax in IndiaConcepts TreeNo ratings yet
- Closed End Fund CompanyDocument33 pagesClosed End Fund CompanyIvy LiewNo ratings yet
- Income From Other SourcesDocument8 pagesIncome From Other SourcesSonali MuskanNo ratings yet
- 7th Term - Legal Frameworks of ConstructionDocument79 pages7th Term - Legal Frameworks of ConstructionShreedharNo ratings yet
- A Guide To Your Personal Income TaxDocument7 pagesA Guide To Your Personal Income TaxRekha SinghNo ratings yet
- Far Eastern University - Manila Income Taxation TAX1101 Fringe Benefit TaxDocument10 pagesFar Eastern University - Manila Income Taxation TAX1101 Fringe Benefit TaxRyan Christian BalanquitNo ratings yet
- Income From Profits and Gains of Business or ProfessionDocument10 pagesIncome From Profits and Gains of Business or ProfessionPraveen EkkaNo ratings yet
- Deductions From Income From Other SourcesDocument7 pagesDeductions From Income From Other SourcesPADMANABHAN POTTINo ratings yet
- Income From Other Sources-AshimaDocument4 pagesIncome From Other Sources-AshimaAbhinav Kumar GuptaNo ratings yet
- Income From Other SourcesDocument17 pagesIncome From Other Sourcesrakhee dewanNo ratings yet
- INCOME FROM BUSINESSDocument23 pagesINCOME FROM BUSINESSkhushi shahNo ratings yet
- Tax Law AssignDocument10 pagesTax Law AssignZeeshan AliNo ratings yet
- Tax Guide 2011-2012Document0 pagesTax Guide 2011-2012anpuselvi125No ratings yet
- Income Tax: Introduction - An OverviewDocument14 pagesIncome Tax: Introduction - An OverviewAkshitNo ratings yet
- CAPITAL GAINS TAXDocument6 pagesCAPITAL GAINS TAXMuskanDodejaNo ratings yet
- Income From Other SourcesDocument12 pagesIncome From Other Sourcessanjul2008No ratings yet
- Taxation-in-Malaysia 17e8839393Document2 pagesTaxation-in-Malaysia 17e8839393thiru mangaiNo ratings yet
- LIM2019PROBLEMEXERCISESININCOMETAXATIONandTRAINLAW BDocument11 pagesLIM2019PROBLEMEXERCISESININCOMETAXATIONandTRAINLAW BMark MagnoNo ratings yet
- Public CHAPTER 4Document15 pagesPublic CHAPTER 4embiale ayaluNo ratings yet
- Notes7 - Accounting For ReceiptsDocument8 pagesNotes7 - Accounting For ReceiptsRachel GellerNo ratings yet
- Intro - Taxation - 2019Document24 pagesIntro - Taxation - 2019Abdullah FNo ratings yet
- Name: Dilip Kumar. G: Sikkim Manipal University 3 Semester Fall 2010Document11 pagesName: Dilip Kumar. G: Sikkim Manipal University 3 Semester Fall 2010Dilipk86No ratings yet
- ATax - 03Document29 pagesATax - 03Haseeb Ahmed ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Deloitte - A Pocket Guide To Singapore Tax 2014 PDFDocument20 pagesDeloitte - A Pocket Guide To Singapore Tax 2014 PDFAlison YangNo ratings yet
- Project BBA 4th Semister FinanceDocument15 pagesProject BBA 4th Semister FinanceKunal Hire-PatilNo ratings yet
- The Conceptual Basis of Personal Income Tax, Classification of Income, Tax RatesDocument29 pagesThe Conceptual Basis of Personal Income Tax, Classification of Income, Tax RatesgunayNo ratings yet
- Taxation of Residual Income: Cma K.R. RamprakashDocument25 pagesTaxation of Residual Income: Cma K.R. RamprakashShriya JoseincheckalNo ratings yet
- Income Taxation Reviewer: Mariano Marcos State University-College of Law 2011Document59 pagesIncome Taxation Reviewer: Mariano Marcos State University-College of Law 2011Kristelle Quibuyen100% (1)
- Passive IncomeDocument31 pagesPassive IncomeE.D.J100% (1)
- Earnings and Profits Is As FollowsDocument3 pagesEarnings and Profits Is As Followscmau08No ratings yet
- Tax Deduction at SourceDocument62 pagesTax Deduction at SourcePallavisweet100% (1)
- Tax ChangesDocument7 pagesTax ChangesSujan SanjayNo ratings yet
- Taxation Notes 4.1.23 MidtermDocument11 pagesTaxation Notes 4.1.23 MidtermRaissa Anjela Carman-JardenicoNo ratings yet
- 10-Practical Questions of Individuals (78-113)Document38 pages10-Practical Questions of Individuals (78-113)Sajid Saith0% (1)
- Singapore Tax System#published Article# - 1556967521Document17 pagesSingapore Tax System#published Article# - 1556967521Vaibhav ChoudhryNo ratings yet
- All About TAX in Financial Year 2009 - 2010Document40 pagesAll About TAX in Financial Year 2009 - 2010angadjeetNo ratings yet
- Law Students Federation: LL.B. NotesDocument13 pagesLaw Students Federation: LL.B. NotesNagesh ChNo ratings yet
- Mba - Iii Sem Internal Audit & Control - MF0004 Set - 2Document26 pagesMba - Iii Sem Internal Audit & Control - MF0004 Set - 2Dilipk86No ratings yet
- Name: Dilip Kumar. G Roll No.: 520947355Document10 pagesName: Dilip Kumar. G Roll No.: 520947355Dilipk86No ratings yet
- Mba - Iii Sem Mergers & Acquisitions - MF0002 Set - 2Document16 pagesMba - Iii Sem Mergers & Acquisitions - MF0002 Set - 2Dilipk86No ratings yet
- Mba - Iii Sem Security Analysis & Portfolio Management - MF0001 Set - 2Document10 pagesMba - Iii Sem Security Analysis & Portfolio Management - MF0001 Set - 2Dilipk86No ratings yet
- Name: Dilip Kumar. G: Sikkim Manipal University 3 Semester Fall 2010Document11 pagesName: Dilip Kumar. G: Sikkim Manipal University 3 Semester Fall 2010Dilipk86No ratings yet
- Mba - Iii Sem Legal Aspects of Business - MB0035 Set - 2Document15 pagesMba - Iii Sem Legal Aspects of Business - MB0035 Set - 2Dilipk86No ratings yet
- Name: Dilip Kumar. G: Sikkim Manipal University 3 Semester Fall 2010Document9 pagesName: Dilip Kumar. G: Sikkim Manipal University 3 Semester Fall 2010Dilipk86No ratings yet
- Sikkim Manipal University 3 Semester Fall 2010Document14 pagesSikkim Manipal University 3 Semester Fall 2010Dilipk86No ratings yet
- Sikkim Manipal University 3 Semester Fall 2010Document21 pagesSikkim Manipal University 3 Semester Fall 2010Dilipk86No ratings yet
- Mba - Iii Sem Research Methodology - MB0034 Set - 2Document24 pagesMba - Iii Sem Research Methodology - MB0034 Set - 2Dilipk86No ratings yet
- Sikkim Manipal University 3 Semester Fall 2010Document22 pagesSikkim Manipal University 3 Semester Fall 2010Dilipk86No ratings yet
- Tyre Factories in IndiaDocument47 pagesTyre Factories in IndiaKedar Kulkarni0% (1)
- SM EntertainmentDocument14 pagesSM EntertainmentSaeful AzisNo ratings yet
- Water Infrastructure Indonesia 2012Document6 pagesWater Infrastructure Indonesia 2012iqsgNo ratings yet
- Hyperinflation and Current Cost Accounting ProblemsDocument4 pagesHyperinflation and Current Cost Accounting ProblemsMaan CabolesNo ratings yet
- Trade War Between US and ChinaDocument1 pageTrade War Between US and ChinaRajarshi MaityNo ratings yet
- 8 McKinsey On Social Impact BondsDocument6 pages8 McKinsey On Social Impact Bondsar15t0tleNo ratings yet
- 313 Practice Exam III 2015 Solution 2Document9 pages313 Practice Exam III 2015 Solution 2Johan JanssonNo ratings yet
- Micro Shots 2010Document158 pagesMicro Shots 2010arif7000No ratings yet
- National Roads Authority: Project Appraisal GuidelinesDocument44 pagesNational Roads Authority: Project Appraisal GuidelinesPratish BalaNo ratings yet
- ECH OutlookDocument9 pagesECH OutlookNasser EbrahimNo ratings yet
- A Big (Double) Deal - Anadarko's Acquisition of Kerr-McGee and Western Gas Resources - 610020-PDF-ENGDocument29 pagesA Big (Double) Deal - Anadarko's Acquisition of Kerr-McGee and Western Gas Resources - 610020-PDF-ENGNishant BiswalNo ratings yet
- Prefinal Review AcfarDocument8 pagesPrefinal Review AcfarBugoy CabasanNo ratings yet
- The World 07232014Document36 pagesThe World 07232014The WorldNo ratings yet
- Absa Personal Share Portfolio One PDFDocument2 pagesAbsa Personal Share Portfolio One PDFmarko joosteNo ratings yet
- Term Loan AppraisalDocument31 pagesTerm Loan AppraisalNeha Sharma100% (2)
- DRR-CCA Integration in Local Development PlanningDocument10 pagesDRR-CCA Integration in Local Development PlanningJEnny RojoNo ratings yet
- Indian Commodity Market: Derivatives and Risk ManagementDocument6 pagesIndian Commodity Market: Derivatives and Risk ManagementVasantha NaikNo ratings yet
- Sum of Digits DepreciationDocument7 pagesSum of Digits DepreciationChikwason Sarcozy MwanzaNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 9 - Earnings Management SummaryDocument3 pagesCHAPTER 9 - Earnings Management SummaryVanadisa SamuelNo ratings yet
- 5.1 Role of Commercial BanksDocument5 pages5.1 Role of Commercial Banksbabunaidu2006No ratings yet
- T.L.e - maRCH 2013 (Major) With AnswersDocument13 pagesT.L.e - maRCH 2013 (Major) With AnswersYaj Cruzada50% (2)
- iFOREX TutorialDocument20 pagesiFOREX TutorialAmjath ShariefNo ratings yet
- Brand Portfolio at LOrealDocument17 pagesBrand Portfolio at LOrealFaheemNo ratings yet
- Richard Branson's Adversity Led to Virgin Business OpportunitiesDocument25 pagesRichard Branson's Adversity Led to Virgin Business OpportunitiesjayannaparkNo ratings yet
- World Bank Briefing BookDocument4 pagesWorld Bank Briefing Bookapi-554844732No ratings yet
- Macro Tutorial 1 (Jan 10, 2018)Document4 pagesMacro Tutorial 1 (Jan 10, 2018)shashankNo ratings yet
- Types of Banks in Nepal: Yogesh BaniyaDocument7 pagesTypes of Banks in Nepal: Yogesh Baniyaanon_665535262No ratings yet
- Summer Training PPT!!Document17 pagesSummer Training PPT!!aayushivamNo ratings yet
- OFTC Lesson 18 - Integrating Order Flow With Traditional Technical AnalysisDocument34 pagesOFTC Lesson 18 - Integrating Order Flow With Traditional Technical AnalysisThanhdat VoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 10 (Reward Management)Document26 pagesLecture 10 (Reward Management)Shoaib HasanNo ratings yet