Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Spinal Cord
Uploaded by
Julia IshakOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Spinal Cord
Uploaded by
Julia IshakCopyright:
Available Formats
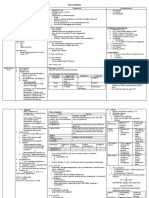
The Spinal Cord (Gross Anatomy)
1. Extent Begins: Below foramen magnum in the skull; upper border of 1st cervical vertebra,
atlas.
Ends: at intervertebral disc btwn L1 and L2
;at birth = (L2-L3)
;3rd month IUL (intrauterine life – in the worm), level of spinal cord = level of
vertebrae
2. Enlargement 2 enlargements:
1) Cervical => brachial plexus
2) Lumbo-Sacral => lumbar & sacral plexus
3. Ending -tapers = to form Conus Medullaris
-continues d/w = as a fibrous thread called filum terminalis (=pia) which ends at the
coccyx
4. Length 45 cm
5. Protection i. Bony protection = Vertebral canal, formed by the bony vertebral column
i.Bony ii.Membranous Protection = Meninges:
ii.Membranous a. Dura mater: (Latin: dura hard)
iii.Fluid Suspension b. Arachnoid mater: (Greek: arakness = spider)
iv. Denticulate c. Pia mater: (Greek: pia = tender)
ligaments # Arachnoid & dura mater normally occupy the vertebral canal well in the sacrum,
down to about vertebral level S2.
iii.Fluid Suspension = Cerebro-spinal Fluid = CSF
# CSF is contained in the subarachnoid space, btwn the pia & arachnoid
Epidural space or extradural space;
Site: outside the dura mater, btwn dura mater & walls of the vertebral canal
Contains connective tissue, fat & internal vertebral plexus
Surface Anatomy;
Vertebral lvl T11 – L1/2 : sacral region of spinal cord
Vertebral lvl L1/2 : end of spinal cord (in adult)
Vertebral lvl S2 : end of dura sac & subarachnoid space
iv. Denticulate ligament
- Lateral extension of the pia mater
- extending from the cord in a coronal plane
- about midway btwn the dorsal & ventral nerve roots
- To meet the internal aspect of the arachnoid in a series of sawtooth-like
projections
- Which helps to tether the spinal cord within the subarachnoid space.
6. Features External features
Anterior aspect: Anterior median fissure (1) & anterior nerve root of spinal nerve.
-external Posterior aspect: Posterior median sulcus (2), postero-lateral sulcus (3)(posterior
-internal root of spinal nerve)& postero-intermediate sulcus (4)(only on cervical and upper
thoracic segments).
*Spinal segments: = part of spinal cord to which a pair of posterior and anterior
spinal roots are attached. 31 spinal segments.
*Dermatomes = area of skin supplied by the somatosensory fibers from a single
spinal nerve
Internal features
=central canal, central gray matter, peripheral white matter, RF
Central Gray Matter;
*H-shape with central canal
*Anterior horn (Motor)
*Posterior horn (Sensory)
*Lateral horn (Autonomic)
-T1 to L2 or L3
*Gray commissure
Peripheral White Matter (P, L, A)
*Myelinated nerve fibers
*Anterior white column
*Lateral white column
*Posterior white column (C&G)
*Anterior white commissure
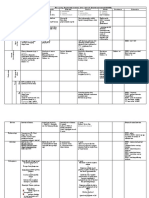
7. Blood supply 1.Spinal artery (2 ant 1 ant & 2 post)
Ant & post spinal arteries are not of
2.Radicular arteries (ant & post) sufficient calibre to maintain throughout
the entire spinal cord. Hencem they rely to
a great extent on the radicular component
Vertebral art ant spinal art (2 spinal artery join) single anterior spinal artery.
This courses along the anterior median fissure of the spinal cord.
Supplies anterior 2/3 of the cord.
Posterior inferior cerebellar artery (PICA) or vertebral art post spinal art (2 in no)
– supply the posterior 1/3 of the cord
Cervical region – radicular artery from deep and ascending branches of cervical art
Thoracic region - radicular artery from posterior intercostals artery
Lumbar region – radicular artery from lumbar artery
Sacral region – radicular artery from lateral sacral artery
Radicular arteries are segmentally represented.
Branches are mainly given to anterior and lateral horns of the cord and tracts of the
anterior and lateral white matters of the cord.
The largest radicular art artery of ADAMKIEMICZ (radicularis magna) - present at
the spinal cord level T12-L2 may provide the entire arterial supply for the caudal
2/3 of the spinal cord. – enters the spinal cord in the lower thoracic or upper lumbar
area.
Clinically, this area of the spinal cord is susceptible to vascular insult should this
radicular art be compromised.
8. Venous drainage This is by 6 irregular, plexiform channels.
There is one along:
1. The anterior and posterior midlines;
2. Along the line of attachment of the dorsal roots of each side;
3. Along the line of attachment of the ventral roots of each side.
These are drained by the radicular veins.
Each, in turn empty into a dense plexus of veins located in the epidural
space epidural venous plexus/ Batson internal vertebral venous plexus.
9. Clinical importance 1.Lumbar puncture (LP);
-Lumbar cistern; subarachnoid space below vertebral level L1/2 occupied with
CSF & cauda equina not by spinal cord.
-Inserting needle into it to get a sample of CSF w/out damaging spinal cord = LP
Adult; best done at vertebral level L3/4
[Highest point of iliac crest = over L4 spine]
Child; LP perform one or two intervertebral spaces lower.
Subarachnoid space; LP, for diagnostis purpose or myelography (X-ray)
Epidural space; epidural anaesthesia
1.will anaesthetize the spinal nerve roots
2.useful for the procedures in the pelvis & perineum (supplied by lumbar &
sacral nerves) where the patient is unfit for general anaesthesia
Subarachnoid spaces; spinal anaesthesia;
(a) Anaesthetics injected into the subarachnoid spaces. The specific gravity
of the agent is greater than the CSF & so by altering the position of the
patient the anaesthetic can be restricted to the lower region of the
subarachnoid space.
(b) It produces more profound anaesthesia & lasts longer than an epidural
anaesthesia.
Spinal cord injury
Cx = fracture or dislocation; Vertebral canal size larger. Spinal cord escape from
injury.
-but if there is displacement of the spinal cord section immediate death
-respiration stop if lesion above origin of phrenic nerve
Th = Vertebral canal size smaller; spinal cord displacement
L= anatomy help the patient spinal cord ends at lower border of L1
↘V foramina enlarged – spinal roots ample, minimal injury
Injury = functional disturbance at or below the lesion level.
You might also like
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- HistamineDocument2 pagesHistamineJulia IshakNo ratings yet
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- MB Rickettsiaceae PassDocument2 pagesMB Rickettsiaceae PassJulia IshakNo ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- Brain StemDocument3 pagesBrain StemJulia IshakNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Aminoglycosides LadscapeDocument2 pagesAminoglycosides LadscapeJulia IshakNo ratings yet
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- MB Rickettsiaceae PassDocument2 pagesMB Rickettsiaceae PassJulia IshakNo ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Antifolate DrugsDocument2 pagesAntifolate DrugsJulia IshakNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- ArthropodsDocument2 pagesArthropodsJulia IshakNo ratings yet
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Venum OrgDocument3 pagesVenum OrgJulia IshakNo ratings yet
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Drug Absorption N Routes of Drug Transmission Systemic NonDocument3 pagesDrug Absorption N Routes of Drug Transmission Systemic NonJulia IshakNo ratings yet
- Herpes VirusesDocument4 pagesHerpes VirusesJulia IshakNo ratings yet
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Anti FungalsDocument4 pagesAnti FungalsJulia IshakNo ratings yet
- MB Mycobacterium PassDocument2 pagesMB Mycobacterium PassJulia IshakNo ratings yet
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- AminoglycosidesDocument2 pagesAminoglycosidesJulia IshakNo ratings yet
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Dna Gyrase InhibitorDocument2 pagesDna Gyrase InhibitorJulia IshakNo ratings yet
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- Except in Viruses - May Be RNADocument6 pagesExcept in Viruses - May Be RNAJulia IshakNo ratings yet
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Aureus C. Diphteriae (Man) : Classification Based On HaemolysisDocument4 pagesAureus C. Diphteriae (Man) : Classification Based On HaemolysisJulia IshakNo ratings yet
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- MB GP 4 CB PassDocument2 pagesMB GP 4 CB PassJulia IshakNo ratings yet
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- MB Gp5 X-Entero PassDocument2 pagesMB Gp5 X-Entero PassJulia IshakNo ratings yet
- MB GP 5 Entero PassDocument4 pagesMB GP 5 Entero PassJulia IshakNo ratings yet
- MB GP 4 B& C PassDocument3 pagesMB GP 4 B& C PassJulia IshakNo ratings yet
- MB Spirochaete PassDocument2 pagesMB Spirochaete PassJulia IshakNo ratings yet
- MB Gp2 PassDocument1 pageMB Gp2 PassJulia IshakNo ratings yet
- MB Bacterial Growth, Nutrition & CultureDocument1 pageMB Bacterial Growth, Nutrition & CultureJulia IshakNo ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- MB Bacterial ClassificationDocument1 pageMB Bacterial ClassificationJulia IshakNo ratings yet
- ClostridiumDocument1 pageClostridiumJulia IshakNo ratings yet
- Bacterial Virulence FactorsDocument2 pagesBacterial Virulence FactorsJulia IshakNo ratings yet
- Bacterial MorphologyDocument2 pagesBacterial MorphologyJulia IshakNo ratings yet
- Subcutaneous MycosesDocument1 pageSubcutaneous MycosesJulia IshakNo ratings yet
- Systemic MycosesDocument2 pagesSystemic MycosesJulia IshakNo ratings yet
- Clay Shoveler's FractureDocument26 pagesClay Shoveler's FracturerineeshNo ratings yet
- Spinal Cord InjuryDocument28 pagesSpinal Cord InjuryLouie John AbilaNo ratings yet
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Grow Taller by 3 To 6 Inches After Puberty!!!!! 5 Simple Exercises That Will Increase Your Height Naturally at Any AgeDocument6 pagesGrow Taller by 3 To 6 Inches After Puberty!!!!! 5 Simple Exercises That Will Increase Your Height Naturally at Any Agevampire_459No ratings yet
- PDF Cervical Spine AnatomyDocument71 pagesPDF Cervical Spine AnatomyAqilla Fadia HayaNo ratings yet
- College of Health Sciences: Sultan Kudarat State UniversityDocument8 pagesCollege of Health Sciences: Sultan Kudarat State UniversityGeremie Magno Mana-ayNo ratings yet
- Yoga Secrets-YoungDocument246 pagesYoga Secrets-YoungJack Sellner88% (8)
- Anatomy 5 PDFDocument25 pagesAnatomy 5 PDFMohammad Jamal OwesatNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Spinal CordDocument50 pagesAnatomy of The Spinal CordAlwi Qatsir AlyaNo ratings yet
- Skull PositioningDocument10 pagesSkull PositioningShionna MandyNo ratings yet
- KyphosisDocument22 pagesKyphosisRaiganNo ratings yet
- RAMNATH Sciatica Presentation 0812Document57 pagesRAMNATH Sciatica Presentation 0812Nisa SulistiaNo ratings yet
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Nizam'S Institute of Medical Vs Prasanth S Dhananka Ors On 14 May 2009Document26 pagesNizam'S Institute of Medical Vs Prasanth S Dhananka Ors On 14 May 2009Saket SubhamNo ratings yet
- VSAQS Imp - Biom.Document8 pagesVSAQS Imp - Biom.Meenakshiputraeashwarprasad MacherlaNo ratings yet
- Biomechanics of SpineDocument40 pagesBiomechanics of SpineSreeraj S R100% (1)
- Burial of A Viking Woman PDFDocument40 pagesBurial of A Viking Woman PDFsakupljackostijuNo ratings yet
- VERITAS D1.6.2 Final LastDocument55 pagesVERITAS D1.6.2 Final LastgkoutNo ratings yet
- Axial Skeleton ScriptDocument4 pagesAxial Skeleton ScriptMichaelVincentLimNo ratings yet
- Brachial Plexus InjuriesDocument346 pagesBrachial Plexus InjuriesvinaymanNo ratings yet
- MED BACK of LBPDocument23 pagesMED BACK of LBPleeyan2wenty6No ratings yet
- Teach Yourself NeuroanatomyDocument38 pagesTeach Yourself NeuroanatomySambili Tonny100% (3)
- PHS 3240 2003 The Nervous System Dr. W. Staines Department of Cellular and Molecular Medicine, RGN RM 2231Document24 pagesPHS 3240 2003 The Nervous System Dr. W. Staines Department of Cellular and Molecular Medicine, RGN RM 2231Maria Tarry MiraniNo ratings yet
- Banner Page: IHCP To Cover HCPCS Code B4105Document10 pagesBanner Page: IHCP To Cover HCPCS Code B4105Indiana Family to FamilyNo ratings yet
- Guía de Peces Del Atlantico Vol IIDocument781 pagesGuía de Peces Del Atlantico Vol IIjessica mendez100% (1)
- BPO SyllabusDocument82 pagesBPO SyllabusAman ShandilyaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 To 10Document22 pagesChapter 3 To 10Angelica Ecal Migriño67% (3)
- ANAT 242 Course Outline PingliuDocument67 pagesANAT 242 Course Outline PingliuAnonymous 9oTm71No ratings yet
- Compalab MidtermDocument5 pagesCompalab MidtermraphaelNo ratings yet
- DNS PDFDocument12 pagesDNS PDFMaksim BogdanovNo ratings yet
- Spinal Injury Module Revised 2016Document15 pagesSpinal Injury Module Revised 2016Kuliah CidelNo ratings yet
- CNS: Anatomy, Cases of Trauma, Congenital, Infection, Degeneration & TumorsDocument29 pagesCNS: Anatomy, Cases of Trauma, Congenital, Infection, Degeneration & Tumorsamir hamzahNo ratings yet