Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Case Macro8c1 Ch26
Uploaded by
anon_370978338Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Case Macro8c1 Ch26
Uploaded by
anon_370978338Copyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 11 Money Demand, the Equilibrium Interest Rate, and Monetary Policy Principles of Macroeconomics, Case/Fair, 8e 11.
1 The Demand for Money Multiple Choice
When
you deposit $100 in a bank, the bank A
. pays you B
an interest rate because the deposit is a liability to you.
. charges C
you an interest rate because the deposit is a liability to you.
. pays you D
an interest rate because the deposit is a liability to the bank.
. pays you an interest rate because the deposit is an asset to the bank. Answer
:C
When you
borrow $2,000 from a bank, you ________ an interest rate because the loan is ________. A
. pay; a B
liability to you
. pay; an C
asset to you
. receive; a liability to you D
. pay; a
liability to the bank Answer
:A
Your
money demand is the amount of money you wish to A
. earn. B
. accumulate before you retire. C
. earn per D
hour.
. leave
outside any interest-bearing account. Answer
:D
Sally's $2,000 a month. She deposits $500 in a saving account, buys $200 worth of income government securities, and leaves the rest for daily transactions. Sally's money is demand is A
. $2,000. B
. $1,300. C
. $700. D
. $1,500. Answer
:B
Mary is the 1st of every month and her rent is due on the 15th of every month. This is an paid on example of the A
. cash flow B
problem.
. financial C
float.
. money D
management problem.
nonsynchronization of income and spending. Answer
:D
The balance in Derek's bank account is $750. Derek spends the same amount of money average each day during the month and at the end of the month his account balance is $0. monthly Derek's monthly starting balance is A
. $750. B
. $1500. C
. $1,000. D
. $16.67. Answer
:B
The balance in Bill's bank account is $1,000. Bill spends the same amount of money average each day during the month, and at the end of the month his account balance is $0. monthly Bill's monthly starting balance is A
. $3,000. B
. $1,500. C
. $2,000. D
. $30. Answer
:C
The balance in Derek's bank account is $300. Derek spends the same amount of money average each day during a 30-day month, and at the end of the month his account balance monthly is $0. Derek spends his money at a constant rate of ________ per day. A
. $20 B
. $30 C
. $50 D
. $75 Answer
:A
The balance in Bill's bank account is $900. Bill spends the same amount of money each average day during a 30-day month, and at the end of the month his account balance is $0. monthly Bill spends his money at a constant rate of ________ per day. A
. $75 B
. $100 C
. $30 D
. $90 Answer
:C
Ed's monthly starting balance is $3,000.
Ed spends $100 per day. Initially, Ed keeps all of his income in a non interestbearing checking account. Ed decided to change his strategy and at the beginning of each month he deposits one-third of his income into his checking account and buys two bonds with the remainder of his income. After 10 days he cashes in one bond and after 10 days after that he cashes in the other bond. Which of the following statements is TRUE? A
. If Ed uses B
either strategy, his average monthly balance is $1,500.
. The second involves lower money management costs because Ed now earns interest on strategy the bonds he has purchased. C
. Ed's D
optimal money balance is $100.
. If the paid on bonds decreases, the opportunity cost of Ed's original strategy is interest rate reduced. Answer
:D
An
increase in the interest rate will A
. have no B
impact on the optimal money balance.
. increase C
the optimal money balance.
. lower the D
optimal money balance.
. either decrease the optimal money balance depending on the level of current increase or household wealth. Answer
:C
John's
optimal money balance has increased. This could have been caused by A
. a reduction in the costs paid for switching from bonds to money. B
. a decrease in the price of bonds. C
. a decrease in the amount of transactions spending. D
. a decrease in the interest rate. Answer
:D
Lisa's
optimal monetary balance has decreased. This could have been caused by A
. an increase in the amount of transactions spending. B
. a decrease in the interest rate. C
. a reduction in the costs paid for switching from bonds to money. D
. an increase in the price of bonds. Answer
:C
In terms of the demand for money, the interest rate represents A
. the price of borrowing money. B
. the return on money that is saved for the future. C
. the rate at which current consumption can be exchanged for future consumption. D
. the
opportunity cost of holding money. Answer
:D
The
interest rate paid on bonds increases from 4% to 7%. This will cause A
. no change in the optimal balance because checking deposits don't earn interest. B
. the optimal balance to increase because it raises the opportunity costs of holding money. C
. the optimal balance to decrease because it raises the opportunity cost of holding money. D
. the optimal balance to increase because it reduces the opportunity cost of holding money. Answer
:C
The
price of bonds and the interest rate are A
. positively B
related.
. negatively related. C
. sometimes related and other times negatively related, depending on the bond payments. positively D
. not related. Answer
:B
Jimmy bond a year ago for $16,000. The interest rate has increased to 10%. Jimmy wants bought to sell the bond. To be able to sell the bond Jimmy must charge a price of no more a 5% than A
. $400. B
. $1,000. C
. $8,000. D
. $4,000. Answer
:C
Dirk bond a year ago for $30,000. The interest rate has decreased to 10%. Dirk wants to bought sell the bond. To be able to sell the bond Dirk must charge a price of no more than a 20% A
. $60,000. B
. $45,000. C
. $30,000. D
. $35,000. Answer
:A
Which
of the following is NOT a motive for holding money? A
. The B
transaction motive
. The asset C
motive
. The D
speculative motive
. All of the above Answer
:B
The speculative demand for money is A
. positively B
related to income.
. positively C
related to interest rate.
. negatively related to interest rate. D
. negatively related to income. Answer
:C
The
transactions demand for money is A
. positively B
related to aggregate income.
. positively C
related to the interest rate.
. negatively related to the price level. D
. All of the above Answer
:A
As the rate falls, people hold ________ money instead of bonds because the opportunity interest cost of holding money has ________. A
. more; B
fallen
. less; fallen C
. less; risen D
. more; risen Answer
:A
If
interest rates are lower than what individuals consider normal, they will A
. increase B
their transaction money demand.
. increase C
their speculative money demand.
. decrease D
their speculative money demand.
. decrease their transaction money demand. Answer
:B
If
interest rates increase to a very high level, people will most likely hold A
. more B
bonds and less cash.
. less bonds and less cash. C
. less bonds and more cash. D
. more
bonds and more cash. Answer
:A
Which
of the following will most likely cause a decrease in the quantity of money demand? A
. An increase in the price level B
. An increase in the interest rate C
. An increase in income D
. All of the above Answer
:B
The
transaction demand for money depends on all of the following EXCEPT A
. income. B
. the price C
level.
. the interest rate. D
. the amount of transactions spending. Answer
:C
The
transaction demand for money depends on A
. aggregate income. B
. the price C
level.
. the dollar D
value of transactions.
. All of the above Answer
:D
The
speculative demand for money A
. increases B
when income increases above normal.
. decreases when interest rates decrease below normal. C
. increases D
when interest rates decrease below normal.
. decreases when the price level decreases below normal. Answer
:C
The
transaction demand for money A
. decreases when interest rates decrease below normal. B
. increases C
when interest rates increase above normal.
. decreases when interest rates increase above normal. D
. None of the above Answer
:D
When
the interest rate rises, bond values A
. rise. B
. fall. C
. are D
unchanged because the interest rate paid on a bond is fixed.
. will either increase or decrease depending on the type of bond. Answer
:B
If the
interest rate is higher than normal, people are more likely to hold A
. bonds instead of
money because as the interest rate starts to rise, the value of the bonds will increase.
. bonds C
instead of money because the opportunity cost of money is high.
. money instead of
bonds because the brokerage fees and other costs of buying bonds are high when the interest rate is low.
. money bonds because there is a speculation motive for holding a larger amount of instead of money. Answer
:B
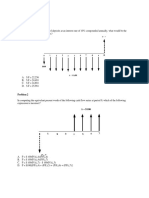
Refer to the information provided in Figure 11.1 below to answer the questions that follow.
Figure 11.1
Refer to Figure 11.1. A movement from Point D to Point A can be caused by A
. a decrease in the interest rate. B
. an increase in income. C
. a decrease in the price level. D
. an increase in the interest rate. Answer
:C
Refer to Figure 11.1. A movement from Point B to Point A can be caused by A
. a decrease in income. B
. an increase in the price level. C
. a decrease in the interest rate. D
. an increase in the interest rate. Answer
:D
Refer to Figure 11.1. A movement from Point B to Point D can be caused by A
. a decrease in income. B
. an increase in the interest rate. C
. a decrease in the interest rate. D
. an increase in income. Answer
:D
Refer to 11.1. All of the following events can cause a movement from Point E to Point A Figure EXCEPT A
. an increase in income. B
. an increase in the price level. C
. a decrease in the interest rate. D
. an increase in transactions. Answer
:C
Refer to Figure The money demand curve will shift from 11.1. A
to
if
. the price B
level increases.
. income C
decreases.
. interest D
rates fall.
. interest
rates rise. Answer
:B
Refer to Figure 11.1. The movement from C to B could be cause by A
. a decrease in the interest rate. B
. an increase in the interest rate. C
. a decrease in income. D
. an increase in the price level. Answer
:A Refer to the information provided in Figure 11.2 below to answer the questions that follow.
Figure 11.2
Refer to 11.2. Suppose money demand is currently at Point A. An increase money demand Figure could be caused by: A
. an increase in the interest rate. B
. an increase in income. C
. a decrease in the interest rate. D
. a decrease in income. Answer
:B
Refer to 11.2. Suppose money demand is currently at Point A. A decrease in the interest Figure rate to 5%, ceteris paribus, will likely A
. decrease B
the quantity of money demanded from $200 million to $100 million.
. increase C
the quantity of money demanded from $100 million to $200 million.
. increase D
the quantity of money demanded from $100 million to $150 million.
. increase the quantity of money demanded from $150 million to $300 million. Answer
:C
Refer to 11.2. Suppose the money demand is currently at Point D. A movement to point C Figure could be caused by A
. a decrease in the interest rate. B
. a decrease in the price level. C
. an increase in the interest rate. D
. an increase in the price level. Answer
:B
Refer to 11.2. Suppose that money demand is currently at Point B. A movement to Point D Figure could be caused by A
. an increase in income, ceteris paribus B
. an increase in the price level, ceteris paribus C
. a decrease in the price level, ceteris paribus D
. a decrease in the interest rate, ceteris paribus Answer
:D
Which
of the following causes the quantity demanded of money to increase? A
. An increase in income B
. A decrease in income C
. A decrease in the price level D
. A decrease in the interest rate Answer
:D
The motive shifts the money demand curve, and the ________ motive causes ________ movements along the same money demand curve. A
. B
speculative; transaction
. C
transaction; precautionary
. D
transaction; speculative
precautionary; transaction Answer
:C
Refer to the information provided in Table 11.1 below to answer the questions that follow. Table 11.1
Refer to 11.1. If it costs $11 each time a bond is sold, the optimal average money holdings Table are A
. $600. B
. $400. C
. $300. D
. $200. Answer
:D
Refer to 11.1. If it costs $7 each time a bond is sold, the optimal average money holdings Table are A
. $600. B
. $400. C
. $300. D
. $200. Answer
:B
Refer to 11.1. If the period covered by Table 11.1 is one year, the interest rate paid on Table bonds A
. is 2%. B
. is 3%. C
. is 5%. D
. cannot be determined from this information. Answer
:C True/False 1)
A between the timing of money inflow to the household and the timing of money mismat outflow for household expenses is known as the nonsynchronization of income and ch spending. Answer:
True
F Diff: 2 a
Skill: D
Less hing from bonds to money means less interest switc revenue lost, but higher money management costs. A n s w e r :
True
F a
T
Diff: h nswer: A 2 Skill: C
True
F a
W
Diff: h nswer: A 2 Skill: F
True
F a
I
Diff: f nswer: A 1 Skill: F
True
F Id Diff: 2bond a n Skill: vs A ewhe sn t inter oest rrates sare low m with athe yhope of w selli i ng sthe h m whe tn ointer est h rates oincre l ase. Answer:
True
F a
A
Diff: Answer: 1 Skill: C
True
F A man Diff: 2d for a n Skill: F mon eey xdrive cs einter sest srates dow d n. e Answer:
True
F a
Diff: 1 Skill: F
11.2 The Equilibrium Interest Rate Multiple Choice Refer to the information provided in Figure 11.3 below to answer the questions that follow.
R11 e .3. fAt e an rint ere tst o rat e F of i 6% g , u the rre e a is
. .
shortage of money and the interest rate will rise. C
Figure 11.3
. surplus of money and the interest rate will decline. D
. surplus of money and the interest rate will rise. Answer
:C
Refer to Figure 11.3. At an interest rate of 3%, there is a A
. shortage of money and the interest rate will decline. B
. shortage of money and the interest rate will rise. C
. surplus of money and the interest rate will decline. D
. surplus of money and the interest rate will rise. Answer
:B
Refer to Figure 11.3. An decrease in the GDP, ceteris paribus, will likely A
. increase B
the equilibrium interest rate without changing equilibrium money holdings.
. decrease C
both the equilibrium interest rate and equilibrium money holdings.
. increase D
the equilibrium interest rate and decrease equilibrium money holdings.
. decrease the equilibrium interest rate without changing equilibrium money holdings. Answer
:D
Refer to Figure 11.3. A increase in the price level, ceteris paribus, will likely A
. increase B
both the equilibrium interest rate and equilibrium money holdings.
. decrease C
the equilibrium interest rate without changing equilibrium money holdings.
. increase D
the equilibrium interest rate without changing equilibrium money holdings.
. keep the equilibrium interest constant and increase equilibrium money holdings Answer
:C
Refer to Figure 11.3. An increase in the money supply, ceteris paribus, will likely A
. increase B
the equilibrium interest rate and decrease equilibrium money holdings.
. increase C
the equilibrium interest rate without changing equilibrium money holdings.
. decrease D
the equilibrium interest rate and increase equilibrium money holdings.
. decrease the equilibrium interest rate without changing . equilibrium money holdings. Answer
:C
Refer to 11.3. An decrease in the money supply and an increase in the GDP will, for sure, Figure A
. increase B
the equilibrium interest rate.
. decrease C
the equilibrium interest rate.
. decrease D
the equilibrium interest rate.
. decrease equilibrium money holdings. Answer
:A
Refer to the information provided in Figure 11.4 below to answer the questions that follow.
Figure 11.4
Refer to Figure 11.4. At an interest rate of 6%, there is A
. an excess demand for money of 200. B
. an excess supply of money of 600. C
. an excess supply of money of 200. D
. an excess demand for money of 600. Answer
:C
Refer to Figure 11.4. At an interest rate of 2%, there is A
. an excess supply of money of 300. B
. an excess supply of money of 500. C
. an excess demand for money of 500. D
. an excess demand for money of 300. Answer
:D
Refer to Figure 11.4. The money market will be in equilibrium at an interest rate of A
. 0%. B
. 6%. C
. 4%. D
. 2%. Answer
:C
Refer to Figure 11.4. At an interest rate of 6%, firms and households A
. will B
attempt to increase their holdings of money by selling bonds.
. are C
satisfied with the amount of money they are holding.
. will D
attempt to increase both their holdings of money and their holdings of bonds.
. will
attempt to reduce their holdings of money by buying bonds. Answer
:D
Refer to Figure 11.4. At an interest rate of 2%, firms and households A
. are B
satisfied with the amount of money they are holding.
. will C
attempt to increase their holdings of money by selling bonds.
. will D
attempt to increase both their holdings of money and their holdings of bonds.
. will
attempt to reduce their holdings of money by buying bonds. Answer
:B
Refer to Figure 11.4. At an interest rate of 4%, firms and households A
. are B
satisfied with the amount of money they are holding.
. will C
attempt to reduce their holdings of money by buying bonds.
. will D
attempt to increase their holdings of money by selling bonds.
. will
attempt to increase both their holdings of money and their holdings of bonds. Answer
:A
What will
happen to the equilibrium interest rate when both money supply and GDP decrease? A
. The B
equilibrium interest rate increases.
. The C
equilibrium interest rate decreases.
. The D
equilibrium interest rate remains constant.
. The impact on the equilibrium interest rate is ambiguous. Answer
:D
If the of money demanded is greater than the quantity of money supplied, then the quantity interest rate will A
. change in B
an uncertain direction.
. rise. C
. remain D
constant.
. fall. Answer
:B
shortage in the money market causes A
. a decrease in the equilibrium interest rate. B
. an increase in the quantity demanded of money. C
. an increase in the equilibrium interest rate. D
. a decrease in the money supply. Answer
:C
surplus in the money market causes A
. a decrease in the equilibrium interest rate. B
. a decrease in the money supply. C
. an increase in the demand for money. D
. a decrease in the quantity demanded of money. Answer
:A Refer to the information provided in Figure 11.5 below to answer the questions that follow.
Figure 11.5
Refer to Figure the interest rate equals 4% and the money supply decreases from 11.5. Assume the interest rate remains at 4% A
to
. If
. money B
demand will increase.
. money C
demand will decrease.
. there will D
be an excess demand for money of 200.
. there will be an excess supply of money of 200. Answer
:C
Refer to Figure
11.5. If the money supply decreases from A
to
. money B
demand must increase for the money market to return to equilibrium.
. the interest rate will fall to 4%. C
. the interest rate will increase to 6%. D
. the money return to equilibrium only if the money supply is decreased to its original level. market will Answer
:C
Refer to Figure
11.5. The money supply curve will shift from A
to
if
. the Fed B
increases the reserve requirement.
. the Fed C
increases the discount rate.
. the D
equilibrium level of output increases.
. the Fed
buys U.S. government securities in the open market. Answer
:D
Refer to Figure
11.5. The money supply curve will shift from A
to
if
. the Fed B
increases the reserve requirement.
. the Fed C
decreases the discount rate.
. the D
equilibrium level of output increases.
. the Fed
buys U.S. government securities in the open market. Answer
:A
Refer to Figure
11.5. If the money supply increases from A
to
. money B
demand must decrease for the money market to return to equilibrium.
. the interest rate will decrease to 4%. C
. the interest rate will increase to 8%. D
. the money return to equilibrium only if the money supply is increased to its original level. market will Answer
:B
Refer to Figure
11.5. The money supply curve will shift from A
to
, if
. the Fed B
increases the reserve requirement.
. the price C
level increases.
. the D
equilibrium level of output decreases.
. the Fed
buys U.S. government securities in the open market. Answer
:D
Refer to Figure
11.5. The money supply curve will shift from A
to
, if
. the Fed B
increases the discount rate.
. the price C
level increases.
. the D
equilibrium level of output decreases.
. the Fed
buys U.S. government securities in the open market. Answer
:A
If there is a surplus in the money market, the Fed can eliminate it by A
. increasing money demand. B
. decreasing money demand. C
. increasing money supply. D
. decreasing money supply. Answer
:D
shortage in the money market can be eliminated through A
. a decrease in the price level. B
. an increase in money supply. C
. a decrease in GDP. D
. all of the above. Answer
:D
When sells government securities, ceteris paribus, the money supply shifts to the ________ the Fed and the equilibrium interest rate ________. A
. left; rises B
. right; rises C
. right; falls D
. left; falls Answer
:A
Decreas required reserve ratio shifts the money supply curve to the ________ and ________ ing the the equilibrium interest rate. A
. left; B
increases
. right; C
increases
. left; D
decreases
. right;
decreases Answer
:D
An e in the level of aggregate output and the sale of government securities by the Fed increas will have what effect on the equilibrium interest rate? A
. No effect B
on the interest rate
. A decrease in the interest rate C
. An increase in the interest rate D
. An
indeterminate effect on the interest rate Answer
:C
Which of the
following pairs of events will definitely lead to an increase in the equilibrium interest rate? A
. The sale of securities by the Federal Reserve and an increase in the price level. government B
. A decrease in the discount rate and an increase in the level of aggregate output. C
. The government securities by the Federal Reserve and a decrease in the price purchase of level. D
. An increase in the required reserve ratio and a decrease in the level of aggregate output. Answer
:A
Which of the
following pairs of events will definitely lead to an decrease in the equilibrium interest rate? A
. The government securities by the Federal Reserve and a increase in the level of purchase of aggregate output. B
. An increase in the discount rate and an increase in the price level. C
. A decrease in the required reserve ratio and a decrease in the level of aggregate output. D
. The sale of securities by the Federal Reserve and a decrease in the price level. government Answer
:C
An e in the discount rate and an decrease in the level of aggregate output will have increas what effect on the equilibrium interest rate? A
. An increase in the interest rate B
. A decrease in the interest rate C
. No effect D
on the interest rate
. An
indeterminate effect on the interest rate Answer
:D Refer to the information provided in Figure 11.6 below to answer the questions that follow.
Figure 11.6
Refer to Figure
11.6. The demand for money curve will shift from A
to
if
. the Fed B
sells government securities on the open market.
. the price C
level decreases.
. the interest rate increases. D
. the
aggregate level of output increases. Answer
:D
Refer to Figure 11.6. If the demand for money curve shifts from will A
to
, the equilibrium interest rate
. increase B
from 5% to 7%.
. increase C
from 5% to 10%.
. decrease D
from 7% to 5%.
. remain at 7%. Answer
:A
Refer to Figure 11.6. If the demand for money curve shifts from at 5%, there will be A
to
and the interest rate remains
. an excess demand for money. B
. an excess supply of money. C
. an D
equilibrium in the money market.
. an
equilibrium in the bond market. Answer
:A
Which
of the following leads to an increase in the interest rate? A
. A decrease in the price level B
. A decrease in aggregate output C
. A sale of D
government securities by the Fed
. A decrease in the discount rate Answer
:C
Which
of the following leads to a decrease in the interest rate? A
. An increase in the price level B
. A sale of C
government securities by the Fed
. An increase in the GDP D
. A decrease in the required reserve ratio Answer
:D
Refer to the information provided in Figure 11.7 below to answer the questions that follow.
Figure 11.7
Refer to Figure
11.7. The demand for money curve will shift from A
to
if
. the Fed B
sells government securities on the open market.
. the price C
level decreases.
. the interest rate increases. D
. the level of aggregate output increases. Answer
:D
Refer to Figure 11.7. If the demand for money curve shifts from will A
to
, the equilibrium interest rate
. decrease B
from 7% to 5%.
. increase C
from 5% to 7%.
. increase D
from 5% to 6%.
. remain at 5%. Answer
:C
Refer to Figure 11.7. If the demand for money curve shifts from at 5%, there will be A
to
and the interest rate remains
. an excess demand for money. B
. an excess supply of money. C
. an D
equilibrium in the money market.
. an
equilibrium in the bond market. Answer
:A
A e in aggregate output, ceteris paribus, will cause the demand for money to ________ decreas and the interest rate to ________. A
. increase; B
increase
. increase; C
decrease
. decrease; decrease D
. decrease; increase Answer
:C
An e in the price level, ceteris paribus, will cause the demand for money to ________ increas and the interest rate to ________. A
. increase; B
increase
. increase; C
decrease
. decrease; decrease D
. decrease; increase Answer
:A
As the
number of transactions in the economy decreases, A
. the supply of money increases. B
. the supply of money decreases. C
. the D
demand for money increases.
. the
demand for money decreases. Answer
:D
Which
of the following events will lead to a decrease in the equilibrium interest rate? A
. An increase in the level of aggregate output B
. A decrease in the required reserve ratio C
. An increase in the price level D
. A sale of government securities by the Federal Reserve Answer
:B
Which
of the following events will lead to an increase in the equilibrium interest rate? A
. A decrease in the level of aggregate output B
. A decrease in the discount rate C
. An increase in the price level D
. A purchase of government securities by the Federal Reserve Answer
:C
True/False 1)
If the
Federal Reserve wants interest rates to decrease, it will buy bonds. Answer:
True
F A ecuri Diff: 1ties a Skill: sby F athe l Fede eral Rese orve f will put g upw oard vpres esure ron n the m equil eibriu n m t inter est srate. Answer:
True
F Ty Diff: 1supp a o Skill: F ly i and n decr cease rinter eest arates s, the eFed coul td h sell egove rnm m ent osecu n rities e. Answer:
True
F a
I
Diff: f nswer: A 1 Skill: A
True
F a
I
Diff: f nswer: A 2 Skill: A
True
F I erve Diff: 2raise a f Skill: C the s t requi h red ereser ve Fratio e, d then ethe rmon aey l supp ly R will erise. s Answer:
True
F a
I .
Diff: n 2 Skill: C
decrease the discount rate. B
11. 3 Loo king Ahe ad Mult iple Cho ice
. tighten C
monetary policy.
. decrease D
the required reserve ratio.
. ease
monetary policy. Answer
:B
In a
period of high unemployment, the Fed would most likely A
. tighten B
monetary policy.
. ease C
monetary policy.
. ease fiscal policy. D
. tighten
fiscal policy. Answer
:B
When ists refer to "tight" monetary policy, they mean that the Federal Reserve is taking econom actions that will A
. increase B
the demand for money.
. decrease C
the demand for money.
. expand the money supply. D
. contract the money supply. Answer
:D
An
example of a tight monetary policy is A
. a decrease in the reserve requirement. B
. the Fed C
selling government securities in the open market.
. a decrease in the discount rate. D
. a decrease in the federal funds rate. Answer
:B
An
example of a tight monetary policy is A
. an increase in the reserve requirement. B
. the Fed C
buying government securities in the open market.
. a decrease in the prime lending rate. D
. a decrease in the discount rate. Answer
:A
When ists refer to "easy" monetary policy, they mean that the Federal Reserve is taking econom actions that will A
. increase B
the demand for money.
. decrease C
the demand for money.
. expand the money supply. D
. contract the money supply. Answer
:C
Which
of the following is an example of an easy monetary policy? A
. An increase in the reserve requirement B
. A decrease in the discount rate C
. An increase in the federal funds rate D
. The Fed selling government securities in the open market Answer
:B True/False 1)
If the
Federal Reserve lowers the discount rate it is easing monetary policy. Answer:
True
F I erve Diff: 1raise a f Skill: F s t reser h ve erequi rem Fents eit is d tight eenin rg amon l etar y R polic ey. s Answer:
True
F Tetar Diff: 1y a i Skill: g F polic h y t stim ulate m the s oecon n omy. Answer:
True
F a
M
Diff: o nswer: A 1 Skill: A
True
F a
W
Diff: h nswer: A 2 Skill: A
True
F Tury Diff: 2bill a h Skill: e A rate is 1 t the 1 rinter . eest 4 arate spaid A p p e n d i x A M u l t i p l e C h o i c e
. on ment securities that mature in less than a year. govern
. on C
government securities that mature in 5 years.
. on D
government securities that mature in 10 years.
. on
government securities that mature in 30 years. Answer
:A
The rate that commercial banks charge each other for borrowing and lending reserves interest is called A
. the B
commercial rate.
. the price C
interest rate.
. the federal funds rate. D
. the
discount rate. Answer
:C
Which
of the following types of interest rates change daily? A
. The prime rate B
. The federal funds rate C
. The D
discount rate
. The
corporate rate Answer
:B
On an
unsecured loan, your bank will highly likely charge an interest rate A
. below the B
prime rate.
. above the prime rate. C
. below the discount rate. D
. below the federal funds rate. Answer
:B
Assume interest rate on a bond is 5% and the expected one-year rate a year from now is the one- 7%. According to the expectations theory of the term structure of interest rates, the year two-year rate will be A
. 5%. B
. 6%. C
. 7%. D
. 12%. Answer
:B
Assume one-year interest rate on a bond is 7%, and the one-year expected rate a year from the now is 9%. According to the expectations theory of the term structure of interest current rates, the two-year interest rate is A
. 7%. B
. 16%. C
. 9%. D
. 8%. Answer
:D
The
interest rate on a two-year security will continue to adjust until it is equal to A
. half the B
interest rate on a one-year security.
. twice the C
interest rate on a one-year security.
. an average of the current one-year rate and the expected one-year rate for next year. D
. the sum of the current one-year rate and the expected one-year rate for next year. Answer
:C
The Fed can influence long-term interest rates by A
. influencing the current one-year rate. B
. affecting C
people's expectations of future short-term rates.
. influencing the demand for money in the short run. D
. A and B. Answer
:D
Govern ment securities that mature in less than a year are called A
. Federal B
funds bonds.
. C
government bonds.
. Federal D
Reserve bonds.
. Treasury bills. Answer
:D
What is the most widely followed short-term interest rate? A
. The federal funds rate B
. The three- month Treasury bill rate C
. The D
commercial paper rate
. The
government bond rate Answer
:B
Govern ment securities with terms of more than one year are called A
. Treasury B
bills.
. federal C
funds bonds.
. capital D
bills.
government bonds. Answer
:D
The rate that banks are charged when they borrow reserves from other banks is the interest A
. federal B
funds rate.
. AAA C
corporate bond rate.
. commercial paper rate. D
. prime rate. Answer
:A
The
federal funds rate is a A
. one-month rate. B
. one-week C
rate.
. one-day D
rate.
. one-year rate. Answer
:C
Federal funds are A
. interbank B
loans.
. raised by C
taxes.
. loans that banks get from the Fed. D
. bonds
issued by the federal government. Answer
:A
The
rate that the Fed controls most closely through its open-market operations is the A
. prime rate. B
. federal C
funds rate.
. commercial paper rate. D
government bonds rate. Answer
:B
The
rate that the least risky firms pay on bonds that they issue is the A
. prime rate. B
. triple-A C
corporate bond rate.
. commercial paper rate. D
. federal
funds rate. Answer
:B
True/False 1)
Federal funds rate is the tax rate on income. Answer:
True
F a
C
Diff: o nswer: A 1 Skill: F
True
F Test Diff: 1rate a h Skill: e an F is aver t age w of othe expe ycted einter aest rrate each i of n the t two eyear rs. Answer:
True
F T follo Diff: 1wed a h Skill: e A watc hed m short oterm sinter t est rate w is i the d prim ee l rate. y Answer:
True
F a
T
Diff: h nswer: A 2 Skill: F
True
F Diff: 2 a
Skill: F
You might also like
- CFP Exam Calculation Workbook: 400+ Calculations to Prepare for the CFP Exam (2018 Edition)From EverandCFP Exam Calculation Workbook: 400+ Calculations to Prepare for the CFP Exam (2018 Edition)Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Self Study Exercises Chapter 7 With AnswersDocument24 pagesSelf Study Exercises Chapter 7 With Answersabed abedNo ratings yet
- Exam Multiple Choice Questions on Bonds, Interest Rates, and Money DemandDocument21 pagesExam Multiple Choice Questions on Bonds, Interest Rates, and Money DemandErsin TukenmezNo ratings yet
- Discounted cash flow valuationDocument8 pagesDiscounted cash flow valuationKhalil Ben JemiaNo ratings yet
- Practice Questions For Exam III (Time Value of Money and Valuation and Rates of Return)Document25 pagesPractice Questions For Exam III (Time Value of Money and Valuation and Rates of Return)Kim FloresNo ratings yet
- Tute 2 QuestionsDocument8 pagesTute 2 QuestionsPham Thuy HuyenNo ratings yet
- Practice FinalDocument8 pagesPractice FinalGrace CheungNo ratings yet
- Answer: ADocument7 pagesAnswer: AGrace CheungNo ratings yet
- 2014 - Econ - 110A - Blanchard 6e CH 4 HomeworkQuestionsDocument4 pages2014 - Econ - 110A - Blanchard 6e CH 4 HomeworkQuestionsjennye313No ratings yet
- Financial Accounting A Critical Approach CANADIAN Canadian 4th Edition John Friedlan Test Bank DownloadDocument71 pagesFinancial Accounting A Critical Approach CANADIAN Canadian 4th Edition John Friedlan Test Bank DownloadSandra Joyce100% (28)
- Tute 2 QuestionsDocument7 pagesTute 2 QuestionsChi QuỳnhNo ratings yet
- M and B 3 3Rd Edition Dean Croushore Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument36 pagesM and B 3 3Rd Edition Dean Croushore Test Bank Full Chapter PDFmary.rivera849100% (9)
- Theory Questions For Time Value of MoneyDocument2 pagesTheory Questions For Time Value of MoneyKim DavilloNo ratings yet
- Practice Qs 2Document24 pagesPractice Qs 2SANCHITA PATINo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2 QuestionsDocument5 pagesTutorial 2 QuestionsSik WooNo ratings yet
- Hull OFOD10e MultipleChoice Questions and Answers Ch05Document6 pagesHull OFOD10e MultipleChoice Questions and Answers Ch05Kevin Molly KamrathNo ratings yet
- MIDTERM _BONDS(1)Document5 pagesMIDTERM _BONDS(1)danthanh0971No ratings yet
- In Class Problem Solving - 3 - With AnswersDocument13 pagesIn Class Problem Solving - 3 - With AnswersAmeya Talanki100% (1)
- AP Macro Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument6 pagesAP Macro Multiple Choice QuestionsErika Mae MedenillaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document22 pagesChapter 4Minh NguyệtNo ratings yet
- AsdDocument18 pagesAsdJenever Leo SerranoNo ratings yet
- Set 1 Problem Solving with Compound Interest CalculationsDocument37 pagesSet 1 Problem Solving with Compound Interest CalculationsSummer Wynn DacwagNo ratings yet
- Time Value of Money Test BanksDocument34 pagesTime Value of Money Test BanksNor levineNo ratings yet
- Fin302 MCQs PDFDocument13 pagesFin302 MCQs PDFkhushi mishaNo ratings yet
- FINS2624 Quiz BankDocument368 pagesFINS2624 Quiz BankRaymond WingNo ratings yet
- Comparing Investment Rates and Calculating Present ValuesDocument36 pagesComparing Investment Rates and Calculating Present ValuesMark Smith100% (1)
- Finman2 Quiz # 1 Summer Ay 10-11Document2 pagesFinman2 Quiz # 1 Summer Ay 10-11Pierre Capati100% (1)
- Weekly Quiz 2Document30 pagesWeekly Quiz 2Emmmanuel ArthurNo ratings yet
- Finance Applications and Theory 3rd Edition Cornett Test Bank 1Document120 pagesFinance Applications and Theory 3rd Edition Cornett Test Bank 1kyle100% (40)
- Principles of Macroeconomics 11th Edition Case Test BankDocument39 pagesPrinciples of Macroeconomics 11th Edition Case Test Bankpatricksenaxp0dw100% (22)
- Principles of Macroeconomics 11Th Edition Case Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument60 pagesPrinciples of Macroeconomics 11Th Edition Case Test Bank Full Chapter PDFmarthalouisaq6x100% (7)
- Tutorial 2 QuestionsDocument5 pagesTutorial 2 QuestionsNguyễn Thùy Linh 1TC-20ACNNo ratings yet
- Principles of Macroeconomics Version 3 0 3rd Edition Rittenberg Test BankDocument44 pagesPrinciples of Macroeconomics Version 3 0 3rd Edition Rittenberg Test Bankhelenglendacduf100% (28)
- Test Bank - TVM1Document29 pagesTest Bank - TVM1appleNo ratings yet
- Midterm 1 Practice With SolutionsDocument28 pagesMidterm 1 Practice With Solutionszaid nazalNo ratings yet
- Time Value of Money Gitman PDFDocument34 pagesTime Value of Money Gitman PDFEmma Mariz GarciaNo ratings yet
- Time Value of Money (Gitman) PDFDocument34 pagesTime Value of Money (Gitman) PDFMangoStarr Aibelle Vegas0% (1)
- Time Value of Money Test BanksDocument34 pagesTime Value of Money Test BanksJorgeComintanAndanarNo ratings yet
- TVM Chapter 04 Introduction to ValuationDocument6 pagesTVM Chapter 04 Introduction to ValuationLana LoaiNo ratings yet
- Midterm 3 AnswersDocument7 pagesMidterm 3 AnswersDuc TranNo ratings yet
- Bond Valuation and Yield CalculationsDocument12 pagesBond Valuation and Yield CalculationsSeri DiyanaNo ratings yet
- 2 Time Value MoneyDocument39 pages2 Time Value MoneyJomar PorterosNo ratings yet
- Fin 3403 Review 2 (ch5,6,7)Document20 pagesFin 3403 Review 2 (ch5,6,7)MichaelFraserNo ratings yet
- Corporate Finance Exam GuideDocument8 pagesCorporate Finance Exam Guideneilpatrel31No ratings yet
- M Finance 3Rd Edition Cornett Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument27 pagesM Finance 3Rd Edition Cornett Test Bank Full Chapter PDFcordie.borda532100% (11)
- Intermediate Finance - Chapter 6Document23 pagesIntermediate Finance - Chapter 6Gene'sNo ratings yet
- FINC 302, Selected Questions For PracticeDocument30 pagesFINC 302, Selected Questions For PracticethomasNo ratings yet
- Hull: Options, Futures and Other Derivatives Chapter 4 Multiple Choice Test BankDocument6 pagesHull: Options, Futures and Other Derivatives Chapter 4 Multiple Choice Test BankKevin Molly KamrathNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4-FinanceDocument14 pagesChapter 4-Financesjenkins66No ratings yet
- Sample Midterm1Document58 pagesSample Midterm1mc080400185No ratings yet
- Test Bank - TVM1Document34 pagesTest Bank - TVM1Evan HochmanNo ratings yet
- Time Value of MechanicsDocument6 pagesTime Value of MechanicsFyaj RohanNo ratings yet
- ch.14 TB 331Document10 pagesch.14 TB 331nickvandervNo ratings yet
- Prior Exam 3Document9 pagesPrior Exam 3Brian WangNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Valuation: The Time Value of MoneyDocument25 pagesIntroduction to Valuation: The Time Value of MoneymehdiNo ratings yet
- CFP Certification Exam Practice Question Workbook: 1,000 Comprehensive Practice Questions (2018 Edition)From EverandCFP Certification Exam Practice Question Workbook: 1,000 Comprehensive Practice Questions (2018 Edition)Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Greek TragedyDocument6 pagesThe Greek TragedyGRK MurtyNo ratings yet
- Mozambique's Strong Economic Growth and Development PotentialDocument10 pagesMozambique's Strong Economic Growth and Development PotentialJoão Assis CatelaNo ratings yet
- Sample Negotiation PlanDocument3 pagesSample Negotiation PlanNikhil Srivastava100% (1)
- UK 200 Annual Report 2010 - The Cost of Cutting (The Lawyer Aug11)Document108 pagesUK 200 Annual Report 2010 - The Cost of Cutting (The Lawyer Aug11)jwh231No ratings yet
- Foundation Unit 11 Topic TestDocument18 pagesFoundation Unit 11 Topic TestLouis SharrockNo ratings yet
- Cash Transfer Agreement for €200M Euro TransactionDocument13 pagesCash Transfer Agreement for €200M Euro TransactionPink AppleNo ratings yet
- SeeNews Top100-2023 - DigitalDocument72 pagesSeeNews Top100-2023 - DigitalMilleni TrachevaNo ratings yet
- 2014 2015 Student Prospectus PDFDocument42 pages2014 2015 Student Prospectus PDFFlorentina EcaterinaNo ratings yet
- Burberry Annual Report 2015-16Document188 pagesBurberry Annual Report 2015-16Siddharth Shekhar100% (1)
- MCQ Set 2Document8 pagesMCQ Set 2judysaysNo ratings yet
- Blackrock Sample Financial ReportingDocument497 pagesBlackrock Sample Financial Reportingduc anhNo ratings yet
- FIS Assignment 1 Group 1Document16 pagesFIS Assignment 1 Group 1Souvik BoseNo ratings yet
- Fianna Fail Pre Budget Submission Final DraftDocument40 pagesFianna Fail Pre Budget Submission Final DraftFFRenewalNo ratings yet
- Be Healthy Be Happy at Georgia and MaltaDocument9 pagesBe Healthy Be Happy at Georgia and MaltaProutist Universal MaltaNo ratings yet
- 3 6int 2006 Dec QDocument9 pages3 6int 2006 Dec QHannan SalimNo ratings yet
- JLL Industrial Capital Markets Outlook (2015 March)Document17 pagesJLL Industrial Capital Markets Outlook (2015 March)vdmaraNo ratings yet
- Regional Economic Integration: Chapter OutlineDocument15 pagesRegional Economic Integration: Chapter Outlinemacmac29No ratings yet
- Report of the Working Group on 'Boosting India's Manufacturing ExportsDocument294 pagesReport of the Working Group on 'Boosting India's Manufacturing ExportsVishanth SundararajanNo ratings yet
- Foreign Exchange Exposure and Risk Management Practices in InfosysDocument14 pagesForeign Exchange Exposure and Risk Management Practices in InfosysGaurish Natekar0% (1)
- 1 Euro To Usd Chart - Google SearchDocument1 page1 Euro To Usd Chart - Google Searchkojlr2020No ratings yet
- Fina CC Case London Youth SymphonyDocument10 pagesFina CC Case London Youth SymphonyFrancisco MarvinNo ratings yet
- OBrien Foreign Exch Chap OneDocument28 pagesOBrien Foreign Exch Chap OneSheri DeanNo ratings yet
- Solnik Chapter 3 Solutions To Questions & Problems (6th Edition)Document6 pagesSolnik Chapter 3 Solutions To Questions & Problems (6th Edition)gilli1trNo ratings yet
- Mohamad Hafiz Bin Ahmad RadziDocument9 pagesMohamad Hafiz Bin Ahmad RadziMohd HafizNo ratings yet
- Background of Foreign Exchange MarketDocument9 pagesBackground of Foreign Exchange MarketLiya Jahan100% (2)
- Dundee Securities - Focus On The Juniors - PDAC2011Document140 pagesDundee Securities - Focus On The Juniors - PDAC2011sirgalNo ratings yet
- D & G Case StudyDocument10 pagesD & G Case StudyVrusti RaoNo ratings yet
- Projected Year-End Financial Results - Third QuarterDocument7 pagesProjected Year-End Financial Results - Third QuarterpkGlobalNo ratings yet
- Tasev v. North MacedoniaDocument23 pagesTasev v. North MacedoniaAnaGeoNo ratings yet
- 2005 Unilever Annual Review and Summary Financial StatementDocument41 pages2005 Unilever Annual Review and Summary Financial StatementAditya ArfanNo ratings yet