Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Micro K (Potassium Chloride)
Uploaded by
E0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
561 views2 pagesPotassium chloride Peak 1-2 hrs Trade Name Micro-K Classification Dose Route mineral and 40 mEq PO electrolyte replacements / supplements Duration Normal dosage range unknown 40-80 mEq / day Time / frequency daily Onset unknown Nursing Implications (what to focus on) avoid using in patients with known hypersensitivity or intolerance.
Original Description:
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentPotassium chloride Peak 1-2 hrs Trade Name Micro-K Classification Dose Route mineral and 40 mEq PO electrolyte replacements / supplements Duration Normal dosage range unknown 40-80 mEq / day Time / frequency daily Onset unknown Nursing Implications (what to focus on) avoid using in patients with known hypersensitivity or intolerance.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
561 views2 pagesMicro K (Potassium Chloride)
Uploaded by
EPotassium chloride Peak 1-2 hrs Trade Name Micro-K Classification Dose Route mineral and 40 mEq PO electrolyte replacements / supplements Duration Normal dosage range unknown 40-80 mEq / day Time / frequency daily Onset unknown Nursing Implications (what to focus on) avoid using in patients with known hypersensitivity or intolerance.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
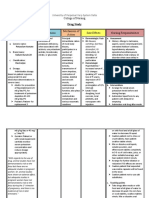
NURS 1566 Clinical Form 3: Clinical Medications Worksheets
(You will need to make additional copies of these forms)
Generic Name Trade Name Classification Dose Route Time/frequency
Potassium Micro-K mineral and 40 mEq PO daily
chloride electrolyte
replacements/
supplements
Peak Onset Duration Normal dosage range
1-2 hrs unknown unknown 40-80 mEq/day
Why is your patient getting this medication For IV meds, compatibility with IV drips and/or
Prevention of potassium depletion; replacement. solutions
N/A
Mechanism of action and indications Nursing Implications (what to focus on)
(Why med ordered) Contraindications/warnings/interactions
Maintain acid-base balance, isotonicity, and Contraindicated in: hyperkalemia, severe renal impairment,
electrophysiologic balance of the cell. Activator in untreated Addison's disease, severe tissue trauma,
many enzymatic reactions; essential to transmission hyperkalemic familial periodic paralysis. Some products
of nerve impulses; contraction of cardiac, skeletal, may contain tartrazine (FDC yellow dye #5) or alcohol;
and smooth muscle; gastric secretion; renal function; avoid using in patients with known hypersensitivity or
tissue synthesis; and carbohydrate metabolism. intolerance. Potassium acetate injection contains
aluminum, which may become toxic with prolonged use to
high risk groups (renal impairment, premature neonates).
Use cautiously in: cardiac disease, renal impairment,
Diabetes mellitus (liquids may contain sugar),
hypomagnesemia (may make correction of hypokalemia
more difficult), GI hypomotility including dysphagia or
esophageal compression from left atrial enlargement
(tablets, capsules). Patients receiving potassium-sparing
drugs.
Common side effects
Abdominal pain, diarrhea, flatulence, nausea, vomiting,
ARRHYTHMIAS
Interactions with other patient drugs, OTC or Lab value alterations caused by medicine
herbal medicines (ask patient specifically) Monitor serum potassium before and periodically during
Use with Avapro (angiotensin II receptor antagonist) therapy. Monitor renal function, serum bicarbonate, and
may lead to hyperkalemia. pH. Determine serum magnesium level if patient has
refractory hypokalemia; hypomagnesemia should be
corrected to facilitate effectiveness of potassium
replacement. Monitor serum chloride because
hypochloremia may occur if replacing potassium without
concurrent chloride
Be sure to teach the patient the following about this
medication
Explain to patient purpose of the medication and the need
to take as directed, especially when concurrent digoxin or
diuretics are taken. A missed dose should be taken as soon
as remembered within 2 hr; if not, return to regular dose
schedule. Do not double dose. Emphasize correct method
of administration. GI irritation or ulceration may result
from chewing enteric-coated tablets or insufficient dilution
of liquid or powder forms. Some extended-release tablets
are contained in a wax matrix that may be expelled in the
stool. This occurrence is not significant. Instruct patient to
avoid salt substitutes or low-salt milk or food unless
approved by health care professional. Patient should be
advised to read all labels to prevent excess potassium
intake. Advise patient regarding sources of dietary
potassium. Encourage compliance with recommended
diet. Instruct patient to report dark, tarry, or bloody stools;
weakness; unusual fatigue; or tingling of extremities.
Notify health care professional if nausea, vomiting,
diarrhea, or stomach discomfort persists. Dosage may
require adjustment. Emphasize the importance of regular
follow-up exams to monitor serum levels and progress.
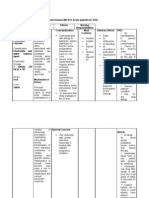
Nursing Process- Assessment Assessment Evaluation
(Pre-administration assessment) Why would you hold or not give this Check after giving
Assess for signs and symptoms of med? Prevention and correction of
hypokalemia (weakness, fatigue, U wave Symptoms of toxicity are those of serum potassium depletion
on ECG, arrhythmias, polyuria, hyperkalemia (slow, irregular
polydipsia) and hyperkalemia. heartbeat; fatigue; muscle weakness;
paresthesia; confusion; dyspnea;
peaked T waves; depressed ST
segments; prolonged QT segments;
widened QRS complexes; loss of P
waves; and cardiac arrhythmias)
You might also like
- Potassium ChlorideDocument2 pagesPotassium ChlorideAdrianne BazoNo ratings yet
- Zaroxolyn MetolazoneDocument1 pageZaroxolyn MetolazoneCassieNo ratings yet
- Drug Potassium ChlorideDocument1 pageDrug Potassium ChlorideSrkocherNo ratings yet
- Drug Potassium Chloride KCLDocument1 pageDrug Potassium Chloride KCLSrkocher100% (3)
- FurosemideDocument1 pageFurosemideCassie100% (1)
- Slow KDocument1 pageSlow KDevon TossellNo ratings yet
- Aldactone SpironlactoneDocument1 pageAldactone SpironlactoneCassie100% (1)
- Dyrenium Triamterene Drug CardDocument1 pageDyrenium Triamterene Drug CardSheri490No ratings yet
- Zocor Drug CardDocument1 pageZocor Drug CardSheri490No ratings yet
- Vitamin DDocument2 pagesVitamin DAdrianne BazoNo ratings yet
- Drug Card LasixDocument2 pagesDrug Card LasixAdrianne Bazo100% (1)
- Glipizide Glucotrol XL Drug CardDocument1 pageGlipizide Glucotrol XL Drug CardSheri490No ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument33 pagesDrug Studyjefwy8No ratings yet
- Furosemide (Lasix)Document1 pageFurosemide (Lasix)E100% (3)
- DS (Calcium + Vit. D)Document6 pagesDS (Calcium + Vit. D)Mary April MendezNo ratings yet
- Brand Name: Generic Name: Stock Dose: Route: Frequency: ClassificationDocument4 pagesBrand Name: Generic Name: Stock Dose: Route: Frequency: ClassificationApril Joy MangsatNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument11 pagesDrug Studyfaula rocamoraNo ratings yet
- TumsDocument2 pagesTumsAdrianne BazoNo ratings yet
- Vasotec EnalaprilDocument1 pageVasotec EnalaprilCassie100% (1)
- Nursing Implication: OB, Lactation, Pedi: GeriDocument29 pagesNursing Implication: OB, Lactation, Pedi: GeriGlyssa CabarrubiasNo ratings yet
- Famotidine (Pepcid)Document1 pageFamotidine (Pepcid)E100% (1)
- NCP DrugDocument13 pagesNCP DrugMhar CamposanoNo ratings yet
- Folic AcidDocument1 pageFolic AcidCassie100% (2)
- MiraLax (Polyethylene Glycol)Document1 pageMiraLax (Polyethylene Glycol)E100% (2)
- Dilantin PhenytoinDocument2 pagesDilantin PhenytoinCassieNo ratings yet
- LasixDocument1 pageLasixKatie McPeek100% (2)
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug StudyOdarp PradzNo ratings yet
- Norvasc Drug CardDocument1 pageNorvasc Drug CardSheri490No ratings yet
- SOAP Pharm D HepaDocument13 pagesSOAP Pharm D HepaFatma HasanNo ratings yet
- Print MeDocument4 pagesPrint MeDoneva Lyn MedinaNo ratings yet
- Protonix (Pantoprazole)Document1 pageProtonix (Pantoprazole)ENo ratings yet
- Protonix IV PantoprazoleDocument1 pageProtonix IV PantoprazoleENo ratings yet
- Vi. Drug Study: Drug Classification Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Reactions Nursing ConsiderationsDocument4 pagesVi. Drug Study: Drug Classification Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Reactions Nursing ConsiderationsMilton CruzNo ratings yet
- Prescribed Fluanxol Depot dosage and administrationDocument4 pagesPrescribed Fluanxol Depot dosage and administrationHavier EsparagueraNo ratings yet
- NURS 1566 Clinical Form 3: Clinical Medications WorksheetsDocument1 pageNURS 1566 Clinical Form 3: Clinical Medications WorksheetsAdhaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument12 pagesDrug StudyQueenie Gail Duarte RodrigoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument11 pagesDrug StudyKimberly Ann MendozaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - LactuloseDocument2 pagesDrug Study - LactuloseCath Bril100% (1)
- FUROSEMIDEDocument6 pagesFUROSEMIDEPark JeongyeonNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyKyle Margaret FloresNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument10 pagesDrug StudyHelen ReonalNo ratings yet
- Drug PrilosecDocument1 pageDrug PrilosecSrkocher100% (1)
- Clinical Medication WorksheetDocument1 pageClinical Medication WorksheetSrkocher100% (1)
- RandomDocument2 pagesRandomAllen YnionNo ratings yet
- NURS 1566 Clinical Form 3: Clinical Medications WorksheetsDocument1 pageNURS 1566 Clinical Form 3: Clinical Medications WorksheetsCassie100% (1)
- LantusDocument1 pageLantusCassie100% (4)
- HydrochlorothiazideDocument1 pageHydrochlorothiazideKatie McPeekNo ratings yet
- NCP DS NCM114 RleDocument12 pagesNCP DS NCM114 RleAllysa Kyle AlfonsoNo ratings yet
- Naplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesFrom EverandNaplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Diabetes Ready Reference for Nurse Practitioners: Clear, Concise Guidelines for Effective Patient CareFrom EverandDiabetes Ready Reference for Nurse Practitioners: Clear, Concise Guidelines for Effective Patient CareNo ratings yet
- Constipation: How To Treat Constipation: How To Prevent Constipation: Along With Nutrition, Diet, And Exercise For ConstipationFrom EverandConstipation: How To Treat Constipation: How To Prevent Constipation: Along With Nutrition, Diet, And Exercise For ConstipationNo ratings yet
- Iron Deficiency Anemia PathoDocument6 pagesIron Deficiency Anemia PathoENo ratings yet
- Left-Side CHF PathoDocument5 pagesLeft-Side CHF PathoENo ratings yet
- Influenza B PathoDocument4 pagesInfluenza B PathoENo ratings yet
- Pyelonephritis 1 Running Head: PYELONEPHRITISDocument4 pagesPyelonephritis 1 Running Head: PYELONEPHRITISENo ratings yet
- Hyperparathyroidism PathoDocument2 pagesHyperparathyroidism PathoENo ratings yet
- Chemical Burns PathoDocument2 pagesChemical Burns PathoENo ratings yet
- Congestive Heart FailureDocument4 pagesCongestive Heart FailureENo ratings yet
- Congestive Heart Failure-ABDocument3 pagesCongestive Heart Failure-ABENo ratings yet
- Pneumonia Short PathoDocument2 pagesPneumonia Short PathoENo ratings yet
- Hyponatremic Dehydration PathoDocument4 pagesHyponatremic Dehydration PathoENo ratings yet
- Acute Pancreatitis PathoDocument5 pagesAcute Pancreatitis PathoENo ratings yet
- Bowel Resection PathoDocument7 pagesBowel Resection PathoENo ratings yet
- Autonomic DysreflexiaDocument2 pagesAutonomic DysreflexiaENo ratings yet
- Campral (Acamprosate Calcium)Document1 pageCampral (Acamprosate Calcium)E100% (1)
- Pancreatitis Short PathoDocument2 pagesPancreatitis Short PathoENo ratings yet
- Clinical Medications Worksheets: (Why Med Ordered) Contraindications/warnings/interactionsDocument1 pageClinical Medications Worksheets: (Why Med Ordered) Contraindications/warnings/interactionsENo ratings yet
- Theragran (Multiple Vitamins)Document3 pagesTheragran (Multiple Vitamins)ENo ratings yet
- Subluxation c6c7 Short PathoDocument1 pageSubluxation c6c7 Short PathoENo ratings yet
- Zosyn (Piperacillin/tazobactram)Document2 pagesZosyn (Piperacillin/tazobactram)E67% (3)
- Geodon (Ziprasidone)Document2 pagesGeodon (Ziprasidone)ENo ratings yet
- Buspar (Buspirone)Document1 pageBuspar (Buspirone)ENo ratings yet
- FiberCon (Polycarbophil)Document1 pageFiberCon (Polycarbophil)ENo ratings yet
- ZofranDocument1 pageZofranKatie McPeek0% (1)
- Prozac (Fluoxetine) 40mgDocument1 pageProzac (Fluoxetine) 40mgENo ratings yet
- Silvadene (Silver Sulfadiazine)Document1 pageSilvadene (Silver Sulfadiazine)ENo ratings yet
- Lexapro (Escitalopram Oxalate)Document2 pagesLexapro (Escitalopram Oxalate)ENo ratings yet
- Darvocet (Propoxyphene Napsylate/Acetaminophen)Document1 pageDarvocet (Propoxyphene Napsylate/Acetaminophen)ENo ratings yet
- Florinef (Fludrocortisone)Document3 pagesFlorinef (Fludrocortisone)E100% (1)
- Reglan (Metoclopramide)Document3 pagesReglan (Metoclopramide)E100% (1)
- Keppra (Levetiracetam)Document2 pagesKeppra (Levetiracetam)E100% (1)
- MS Nursing ReviewerDocument16 pagesMS Nursing ReviewerSunshine SiopaoNo ratings yet
- Adult Grip Strength Norms For The Baseline Digital DynamometerDocument25 pagesAdult Grip Strength Norms For The Baseline Digital DynamometerOmar Escalante DíazNo ratings yet
- NCP NSDDocument3 pagesNCP NSDshigemasamayumi60% (5)
- Surgery NotesDocument200 pagesSurgery NotesJasneet SinghNo ratings yet
- 03chapter4 PDFDocument72 pages03chapter4 PDFAnonymous bT8Fs8daY2No ratings yet
- NCP Step 2: Nutrition DiagnosisDocument2 pagesNCP Step 2: Nutrition Diagnosisaida putriNo ratings yet
- CC.14.01 Pre and Post Operative CareDocument3 pagesCC.14.01 Pre and Post Operative CareKrupaNo ratings yet
- Abstract Book 2004Document250 pagesAbstract Book 2004kindoicciNo ratings yet
- PNF PatternsDocument19 pagesPNF PatternsDany VirgilNo ratings yet
- Coley 2019Document8 pagesColey 2019KaniNo ratings yet
- CPR GuidelinesDocument30 pagesCPR GuidelineswvhvetNo ratings yet
- AlakalinePhos ARC CHEMDocument8 pagesAlakalinePhos ARC CHEMTanveerNo ratings yet
- Case Report Consent Form TemplateDocument2 pagesCase Report Consent Form TemplateDaniel Antonio Valderrama Merejildo100% (1)
- Baby Gap: The Surprising Truth About America's Infant-Mortality RateDocument2 pagesBaby Gap: The Surprising Truth About America's Infant-Mortality RateJoseph AltmannNo ratings yet
- Doctor Patient CommunicationDocument16 pagesDoctor Patient CommunicationRobby100% (1)
- Avi Kremer Case AnalysisDocument2 pagesAvi Kremer Case AnalysisSurya BakshiNo ratings yet
- Bio Equivalence Study of Tizanidine HCL Tablets 4 MG of DR - Reddys Under Fasting Conditions - Full Text View - Clinical TrialsDocument4 pagesBio Equivalence Study of Tizanidine HCL Tablets 4 MG of DR - Reddys Under Fasting Conditions - Full Text View - Clinical TrialsMuhammad Hafeez ArainNo ratings yet
- General Surgery BlueprintDocument2 pagesGeneral Surgery BlueprintMohammed FaragNo ratings yet
- Close Fracture Radius Ulna Distal Sinistra: Case ReportDocument30 pagesClose Fracture Radius Ulna Distal Sinistra: Case ReportyoyokNo ratings yet
- Er LFD 11Document1 pageEr LFD 11EldwinCauilanNo ratings yet
- NeuVision 900 Operation+ManualDocument169 pagesNeuVision 900 Operation+ManualRafael Salazar100% (1)
- Cases Study in Plasma Cell DyscrasiaDocument87 pagesCases Study in Plasma Cell Dyscrasiadrafq2000No ratings yet
- Cleft Lip or Cleft Palate / Pharyngoplasty Clinical Pathway: Personal DetailsDocument8 pagesCleft Lip or Cleft Palate / Pharyngoplasty Clinical Pathway: Personal DetailsRegine LacosteNo ratings yet
- Paraphrasing: How, Tips, ExamplesDocument9 pagesParaphrasing: How, Tips, ExamplesMahesh RamesNo ratings yet
- Acoustic NeuromaDocument6 pagesAcoustic NeuromayoghaNo ratings yet
- Stages of Gross Motor Development from Infancy to Age 12Document17 pagesStages of Gross Motor Development from Infancy to Age 12Gul RockzzNo ratings yet
- ParkinsonDocument54 pagesParkinsonAngel YapNo ratings yet
- Digital Universe Healthcare Vertical Report ArDocument16 pagesDigital Universe Healthcare Vertical Report ArAmrNo ratings yet
- HEALTH 10 MULTIPLE CHOICEDocument2 pagesHEALTH 10 MULTIPLE CHOICERJLifeOfPedz100% (7)
- Short Sightedness Vs Long SightDocument1 pageShort Sightedness Vs Long SightDevill DavajNo ratings yet