Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Modul 3 Introduction To VB Functions: Pusat Pengambangan Bahan Ajar - Umb Nuryasin - Clientserver - VB Function
Uploaded by
yrdianaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Modul 3 Introduction To VB Functions: Pusat Pengambangan Bahan Ajar - Umb Nuryasin - Clientserver - VB Function
Uploaded by
yrdianaCopyright:
Available Formats
Modul 3 Introduction to VB Functions
Functions are similar to normal procedures but the main purpose of the functions is to accept certain inputs and pass them on to the main program to finish the execution. They are two types of function, the built-in functions(or internal functions) and the functions created by the programmers. The general format of a function is functionName(arguments) where arguments are values that are passed on to the functions. In this lesson, we are going to learn two very basic but useful internal functions, i.e. the MsgBox( ) and InputBox ( ) functions.
3.1 MsgBox ( ) Function
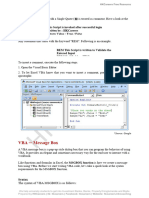
The objective of MsgBox is to produce a pop-up message box and prompt the user to click on a command button before he /she can continues. This message box format is as follows: yourMsg=MsgBox(Prompt, Style Value, Title) The first argument, Prompt, will display the message in the message box. The Style Value will determine what type of command buttons appear on the message box, please refer Table 3.1 for types of command button displayed. The Title argument will display the title of the message board.
PUSAT PENGAMBANGAN BAHAN AJAR UMB
Nuryasin_ClientServer | VB Function
Table 3.1: Style Values Style Value 0 1 2 3 4 5 Named Constant vbOkOnly vbOkCancel vbAbortRetryIgnore vbYesNoCancel vbYesNo vbRetryCancel Buttons Displayed Ok button Ok and Cancel buttons Abort, Retry and Ignore buttons. Yes, No and Cancel buttons Yes and No buttons Retry and Cancel buttons
We can use named constant in place of integers for the second argument to make the programs more readable. In fact, VB6 will automatically shows up a list of names constant where you can select one of them. example: yourMsg=MsgBox( "Click OK to Proceed", 1, "Startup Menu") and yourMsg=Msg("Click OK to Proceed". vbOkCancel,"Startup Menu") are the same. yourMsg is a variable that holds values that are returned by the MsgBox ( ) function. The values are determined by the type of buttons being clicked by the users. It has to be declared as Integer data type in the procedure or in the general declaration section. Table 3.2 shows the values, the corresponding named constant and buttons. Table 3.2 : Return Values and Command Buttons Value 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Named Constant vbOk vbCancel vbAbort vbRetry vbIgnore vbYes vbNo Button Clicked Ok button Cancel button Abort button Retry button Ignore button Yes button No button
Example 3.1 The Interface:
PUSAT PENGAMBANGAN BAHAN AJAR UMB Nuryasin_ClientServer | VB Function
You draw three command buttons and a label as shown in Figure 3.1 Figure 3.1
The procedure for the test button: Private Sub Test_Click() Dim testmsg As Integer testmsg = MsgBox("Click to test", 1, "Test message") If testmsg = 1 Then Display.Caption = "Testing Successful" Else Display.Caption = "Testing fail" End If End Sub When a user click on the test button, the image like the one shown in Figure 3.2 will appear. As the user click on the OK button, the message "Testing successful" will be displayed and when he/she clicks on the Cancel button, the message "Testing fail" will be displayed.
Figure 3.2
PUSAT PENGAMBANGAN BAHAN AJAR UMB
Nuryasin_ClientServer | VB Function
To make the message box looks more sophisticated, you can add an icon besides themessage. There are four types of icons available in VB as shown in Table 3.3 Table 3.3 Value 16 32 48 64 Example 3.2 In this example, the following message box will be displayed: Figure 3.3 Named Constant vbCritical vbQuestion vbExclamation vbInformation Icon
You could draw the same Interface as in example 3.1 but modify the codes as follows: Private Sub test2_Click() Dim testMsg2 As Integer testMsg2 = MsgBox("Click to Test", vbYesNoCancel + vbExclamation, "Test Message") If testMsg2 = 6 Then display2.Caption = "Testing successful" ElseIf testMsg2 = 7 Then display2.Caption = "Are you sure?" Else display2.Caption = "Testing fail" End If End Sub
PUSAT PENGAMBANGAN BAHAN AJAR UMB
Nuryasin_ClientServer | VB Function
3.2 The InputBox( ) Function
An InputBox( ) function will display a message box where the user can enter a value or a message in the form of text. The format is : myMessage=InputBox(Prompt, Title, default_text, x-position, y-position) myMessage is a variant data type but typically it is declared as string, which accept the message input by the users. The arguments are explained as follows: Prompt Title : The message displayed normally as a question asked. : The title of the Input Box.
Default-text : The default text that appears in the input field where users can use it as his intended input or he may change to the message he wish to key in. x-position and y-position - the position or the coordinate of the input box. Example 3.3 The Interface Figure 3.4
PUSAT PENGAMBANGAN BAHAN AJAR UMB
Nuryasin_ClientServer | VB Function
The procedure for the OK button Private Sub OK_Click() Dim userMsg As String userMsg = InputBox("What is your message?", "Message Entry Form", "Enter your messge here", 500, 700) If userMsg <> "" Then message.Caption = userMsg Else message.Caption = "No Message" End If End Sub When a user click the OK button, the input box as shown in Figure 3.5 will appear. After user entering the message and click OK, the message will be displayed on the caption, if he click Cancel, "No message" will be displayed.
3.3 VB Functions- Part II
3.3.1 Creating Your Own Functions The general format of a function is as follows: Public Function functionName (Arg As dataType,..........) As dataType or Private Function functionName (Arg As dataType,..........) As dataType * Public indicates that the function is applicable to the whole program and Private indicates that the function is only applicable to a certain module or procedure. Example 3.3.1
PUSAT PENGAMBANGAN BAHAN AJAR UMB Nuryasin_ClientServer | VB Function
In this example, a user can calculate future value of a certain amount of money he has today based on the interest rate and the number of years from now supposing he will invest this amount of money somewhere). The calculation is based on the compound interest rate.
Public Function FV(PV As Variant, i As Variant, n As Variant) As Variant 'Formula to calculate Future Value(FV) 'PV denotes Present Value FV = PV * (1 + i / 100) ^ n End Function Private Sub compute_Click() 'This procedure will calculate Future Value Dim FutureVal As Variant Dim PresentVal As Variant Dim interest As Variant Dim period As Variant PresentVal = PV.Text interest = rate.Text period = years.Text
PUSAT PENGAMBANGAN BAHAN AJAR UMB
Nuryasin_ClientServer | VB Function
FutureVal = FV(PresentVal, interest, period) MsgBox ("The Future Value is " & FutureVal) End Sub Example 3.3.2 The following program will automatically compute examination grades based on the marks that a student obtained.
Public Function grade(mark As Variant) As String Select Case mark Case Is >= 80 grade = "A" Case Is >= 70 grade = "B" Case Is >= 60 grade = "C" Case Is >= 50 grade = "D" Case Is >= 40 grade = "E" Case Else grade = "F" End Select End Function
PUSAT PENGAMBANGAN BAHAN AJAR UMB
Nuryasin_ClientServer | VB Function
Private Sub compute_Click() grading.Caption = grade(mark) End Sub Private Sub End_Click() End End Sub
PUSAT PENGAMBANGAN BAHAN AJAR UMB
Nuryasin_ClientServer | VB Function
You might also like
- Consecration of TalismansDocument5 pagesConsecration of Talismansdancinggoat23100% (1)
- ChatGPT & EducationDocument47 pagesChatGPT & EducationAn Lê Trường88% (8)
- Cause Analysis For Spun Pile Crack and BrokenDocument11 pagesCause Analysis For Spun Pile Crack and BrokenRony LesbtNo ratings yet
- Make Your Own GUI in ExcelDocument17 pagesMake Your Own GUI in ExcelLiviu100% (1)
- Visual Basic ConceptsDocument152 pagesVisual Basic ConceptsAnkita MittalNo ratings yet
- 2-4 Steps in Developing Application:: Visual BasicDocument12 pages2-4 Steps in Developing Application:: Visual BasicM MNo ratings yet
- E7d61 139.new Directions in Race Ethnicity and CrimeDocument208 pagesE7d61 139.new Directions in Race Ethnicity and CrimeFlia Rincon Garcia SoyGabyNo ratings yet
- VBA User Form DemonstrationDocument6 pagesVBA User Form Demonstrationcniraj743566No ratings yet
- Waves and Ocean Structures Journal of Marine Science and EngineeringDocument292 pagesWaves and Ocean Structures Journal of Marine Science and Engineeringheinz billNo ratings yet
- A Project Report ON Strategic Purchasing Procedure, Systems and Policies (Hospital Industry)Document20 pagesA Project Report ON Strategic Purchasing Procedure, Systems and Policies (Hospital Industry)amitwin1983No ratings yet
- Save Your Time with VBA!: 5 Quality VBA Books In One Package!From EverandSave Your Time with VBA!: 5 Quality VBA Books In One Package!No ratings yet
- Visual Basic Message BoxDocument11 pagesVisual Basic Message BoxJenny BautistaNo ratings yet
- Msgbox and InputboxDocument5 pagesMsgbox and Inputboxkishi8mempinNo ratings yet
- Functions String ManipulationDocument23 pagesFunctions String Manipulationaseret423100% (1)
- Chapter 4Document2 pagesChapter 4robdmacentNo ratings yet
- Visual Basic Notes 1Document18 pagesVisual Basic Notes 1Vasudev lahotiNo ratings yet
- Syntax of MsgBox Function in VBADocument3 pagesSyntax of MsgBox Function in VBAAguest SukamtoNo ratings yet
- Form LoginDocument8 pagesForm LoginNina Indah LestariNo ratings yet
- 2.2.1 Numeric Data TypesDocument9 pages2.2.1 Numeric Data TypesKashif SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Syntax: Msgbox (Prompt (, Buttons) (, Title) (, Helpfile, Context) )Document8 pagesSyntax: Msgbox (Prompt (, Buttons) (, Title) (, Helpfile, Context) )ArianeNo ratings yet
- Visual Basic Programming KeypointDocument53 pagesVisual Basic Programming Keypointaudibertm260No ratings yet
- Belajar VBA Sangat Simple TerpakaiDocument32 pagesBelajar VBA Sangat Simple TerpakaiKaharuddin JamesNo ratings yet
- Lesson 10: Introduction To VB Built-In Functions: 10.1 Msgbox FunctionDocument17 pagesLesson 10: Introduction To VB Built-In Functions: 10.1 Msgbox Functionalokkumar_9365No ratings yet
- Lecture 4+5Document12 pagesLecture 4+5Karar Haidar AltalibiNo ratings yet
- Visual BasicDocument69 pagesVisual Basicujjwalscorpio22No ratings yet
- ComProg Module - M8 FinalDocument6 pagesComProg Module - M8 FinalLEO JR GREFALDONo ratings yet
- Every Visual Basic Control Consists of Three Important ElementsDocument33 pagesEvery Visual Basic Control Consists of Three Important ElementsnitNo ratings yet
- Fixed Dilogue, Fixed Toolwindow: FormsDocument17 pagesFixed Dilogue, Fixed Toolwindow: Formsyuvi1234No ratings yet
- Formatting Functions: Visual BasicDocument17 pagesFormatting Functions: Visual BasicCrysvenneBisligNo ratings yet
- VB 6.0 TutorialsDocument19 pagesVB 6.0 TutorialsSantoshNo ratings yet
- VB FunctionsDocument3 pagesVB FunctionsbharatNo ratings yet
- Designing The Form and Other Controls (Week Three)Document99 pagesDesigning The Form and Other Controls (Week Three)proflatibedrew6No ratings yet
- VB Program ExamplesDocument65 pagesVB Program ExamplessakthivelNo ratings yet
- Userform ExampleDocument9 pagesUserform Examplejuancar373No ratings yet
- VBA Msgbox - A Complete Guide To The VBA Message Box: Paulkelly 0 Com MentsDocument9 pagesVBA Msgbox - A Complete Guide To The VBA Message Box: Paulkelly 0 Com MentsHemalatha S KumarNo ratings yet
- Practical PDFDocument30 pagesPractical PDFRishabh DewanganNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 Working With ControlsDocument4 pagesLesson 5 Working With Controlswilliam nyakeriNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document39 pagesUnit 2deskcode7No ratings yet
- VBA and Excel SolverDocument9 pagesVBA and Excel Solversuperman136No ratings yet
- Hotel Management System Source Code - C#, JAVA, PHP, Programming, Source CodeDocument18 pagesHotel Management System Source Code - C#, JAVA, PHP, Programming, Source CodeBenny BavNo ratings yet
- Lesson1:Introduction: 1.1 A Brief Description of Visual BasicDocument64 pagesLesson1:Introduction: 1.1 A Brief Description of Visual BasicKrisna SharmaNo ratings yet
- Vba Message Box: This Script Is Invoked After Successful Login Written By: Hkcareers Return Value: True / FalseDocument21 pagesVba Message Box: This Script Is Invoked After Successful Login Written By: Hkcareers Return Value: True / FalseHay KwongNo ratings yet
- Programming 2 (Structured Programming) : Worktext in ITC 106Document24 pagesProgramming 2 (Structured Programming) : Worktext in ITC 106Darwin Gapusan RaralioNo ratings yet
- Computer ProgrammingDocument82 pagesComputer ProgrammingTrevor ChadNo ratings yet
- Getting Started Visual BasicDocument20 pagesGetting Started Visual BasicOagilweNo ratings yet
- M A 2019 P E Vba, XML, ASP: Icrosoft Ccess Rogramming BY Xample With ANDDocument1 pageM A 2019 P E Vba, XML, ASP: Icrosoft Ccess Rogramming BY Xample With ANDlkhlmNo ratings yet
- UserformDocument8 pagesUserformPunithan PunithanNo ratings yet
- VB TutorialDocument50 pagesVB Tutorialsb_rameshbabuNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1Document12 pagesTutorial 1alko232No ratings yet
- de#7 #:Ulwlqj#3Urfhgxuhv: 2emhfwlyhvDocument8 pagesde#7 #:Ulwlqj#3Urfhgxuhv: 2emhfwlyhvEdgar RamirezNo ratings yet
- Visual Basic 6Document27 pagesVisual Basic 6Mark Sanchez HipolitoNo ratings yet
- Program ExamplesDocument77 pagesProgram Exampleshahawhohaha1210No ratings yet
- Visual BasicDocument15 pagesVisual BasicnitotalibNo ratings yet
- Notes On VB in ExcelDocument8 pagesNotes On VB in ExcelpasyanteeNo ratings yet
- INTERSCHOOL EXAM OF - VISUAL BASIC - Level: Senior 6 TERM: 1st Academic Year: 2014 Time: 3hoursDocument20 pagesINTERSCHOOL EXAM OF - VISUAL BASIC - Level: Senior 6 TERM: 1st Academic Year: 2014 Time: 3hoursChristian AMANINo ratings yet
- 4 - Graphical User InterfaceDocument53 pages4 - Graphical User InterfaceJyotishalok SaxenaNo ratings yet
- JavaScript Form ValidationDocument16 pagesJavaScript Form ValidationVigneswari ThirumurthyNo ratings yet
- VB1 Revision - Programming With VBDocument10 pagesVB1 Revision - Programming With VBGideon MogeniNo ratings yet
- User Passwords in ExcelDocument2 pagesUser Passwords in ExcelherumamudaNo ratings yet
- User Defined Functions: SyntaxDocument42 pagesUser Defined Functions: SyntaxHajiram BeeviNo ratings yet
- NCC Education International Diploma IN Computer Studies Visual Basic December 2009 - Local ExaminationDocument6 pagesNCC Education International Diploma IN Computer Studies Visual Basic December 2009 - Local ExaminationCedric CedricNo ratings yet
- Slide (Day 1 and 2)Document100 pagesSlide (Day 1 and 2)dinisyafiqoriNo ratings yet
- Alert, Prompt and Confirm MehodsDocument4 pagesAlert, Prompt and Confirm MehodsRevati MenghaniNo ratings yet
- 28 TerminalsDocument42 pages28 TerminalsAlin FazacasNo ratings yet
- Jinivefsiti: Sultan LorisDocument13 pagesJinivefsiti: Sultan LorisSITI HAJAR BINTI MOHD LATEPINo ratings yet
- Keeping Track of Your Time: Keep Track Challenge Welcome GuideDocument1 pageKeeping Track of Your Time: Keep Track Challenge Welcome GuideRizky NurdiansyahNo ratings yet
- DTR Testastretta Valve Adjustment ProcedureDocument10 pagesDTR Testastretta Valve Adjustment ProcedureTony LamprechtNo ratings yet
- Vetoset CA541: Thickbed Cementitious Tile AdhesiveDocument2 pagesVetoset CA541: Thickbed Cementitious Tile Adhesivemus3b1985No ratings yet
- Polysep... Sized For Every Application: Psg-7 Psg-15 Psg-30 Psg-60 Psg-90Document1 pagePolysep... Sized For Every Application: Psg-7 Psg-15 Psg-30 Psg-60 Psg-90Carlos JiménezNo ratings yet
- KRAS QC12K-4X2500 Hydraulic Shearing Machine With E21S ControllerDocument3 pagesKRAS QC12K-4X2500 Hydraulic Shearing Machine With E21S ControllerJohan Sneider100% (1)
- MLX90614Document44 pagesMLX90614ehsan1985No ratings yet
- Types of Chemical Reactions: Synthesis and DecompositionDocument3 pagesTypes of Chemical Reactions: Synthesis and DecompositionAlan MartínNo ratings yet
- Section 1 Company Overview StandardsDocument34 pagesSection 1 Company Overview StandardsChris MedeirosNo ratings yet
- Michael Clapis Cylinder BlocksDocument5 pagesMichael Clapis Cylinder Blocksapi-734979884No ratings yet
- Importance of Porosity - Permeability Relationship in Sandstone Petrophysical PropertiesDocument61 pagesImportance of Porosity - Permeability Relationship in Sandstone Petrophysical PropertiesjrtnNo ratings yet
- Log and Antilog TableDocument3 pagesLog and Antilog TableDeboshri BhattacharjeeNo ratings yet
- 2014 - Intelligence As A Predictor of Outcome in Short-And Long-Term PsychotherapyDocument9 pages2014 - Intelligence As A Predictor of Outcome in Short-And Long-Term PsychotherapyZayne CarrickNo ratings yet
- Names of Planner(s) : Style of Experience: (Whole Class, Small Group, Etc.) Lab: KindergartenDocument4 pagesNames of Planner(s) : Style of Experience: (Whole Class, Small Group, Etc.) Lab: Kindergartenapi-428128701No ratings yet
- FS-1040 FS-1060DN: Parts ListDocument23 pagesFS-1040 FS-1060DN: Parts List1980cvvrNo ratings yet
- EPW, Vol.58, Issue No.44, 04 Nov 2023Document66 pagesEPW, Vol.58, Issue No.44, 04 Nov 2023akashupscmadeeaseNo ratings yet
- Pitch DeckDocument21 pagesPitch DeckIANo ratings yet
- Misc 8DNL 8MPL 8MPN B PDFDocument41 pagesMisc 8DNL 8MPL 8MPN B PDFVesica PiscesNo ratings yet
- 23 Ray Optics Formula Sheets Getmarks AppDocument10 pages23 Ray Optics Formula Sheets Getmarks AppSiddhant KaushikNo ratings yet
- "Organized Crime" and "Organized Crime": Indeterminate Problems of Definition. Hagan Frank E.Document12 pages"Organized Crime" and "Organized Crime": Indeterminate Problems of Definition. Hagan Frank E.Gaston AvilaNo ratings yet
- Poster-Shading PaperDocument1 pagePoster-Shading PaperOsama AljenabiNo ratings yet
- Problem Solving No. 123Document5 pagesProblem Solving No. 123Christy Joy BarboNo ratings yet