Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Unit 7: 1. Derive An Expression For Power Spectral Density? Ans
Uploaded by
srinivasOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Unit 7: 1. Derive An Expression For Power Spectral Density? Ans
Uploaded by
srinivasCopyright:
Available Formats
PTSPUNITVII Questions&Answers
GRIETECE 1
UNIT 7
1. Derive an expression for power spectral density?
Ans:
Power Spectral Density
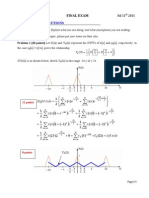
Let us consider a power signal f(t) as shown in the figure 7.1.1 below,
The average power of the signal is given by
P
ug
= lim
1-
1
1
]
2
(t)Jt
1 2
-1 2
.(1)
Let us create a new signal
1
(t) by truncating (t) _
I
2
, .
Thus
1
(t) = (t), |t| <
1
2
= 0, otherwise
The total energy of f(t) is given by
E
1
= ]
1
2
(t) Jt =
1
2n
]
|F
1
()|
2
J
-
.(2)
Where F|
1
(t)] = F
1
()
Also we have ]
2
(t) Jt = ]
1
2
(t) Jt
-
1 2
-1 2
.(3)
Substituting equations (2) and (3) in (1) we get
www.jntuworld.com
www.jntuworld.com
PTSPUNITVII Questions&Answers
GRIETECE 2
P
ug
= lim
1-
1
1
]
1
2
(t) Jt
-
= lim
1-
1
1
.
1
2n
]
|F
1
()|
2
J
-
=
1
2n
] lim
1-
|P
T
(o)|
2
1
J
-
P
avg
=
1
2
] S
I
() u
-
Where S
]
() = lim
1-
|P
T
(o)|
2
1
is referred as power Density Spectrum(PDS) and measured in terms of
voIt
2
Hz
or
wutts
Hz
.
2. An ergodic random process is known to have an auto correlation function
of the from
R
XX
(z) = 1 -|z|, |z| 1
= 0, |z| > 1
Show the spectral density is given by
S
XX
(m) = |
x|n m2
m2
]
2
Ans:
S
XX
() = ] (1 + )c
-]o:
J + ] (1 -)c
-]o:
J
1
0
0
-1
] c
-]o:
J = -
c
-]n
]o
-1
0
=
c
]n
-1
]o
0
-1
] c
-]o:
J = -
c
-]n
]o
0
1
=
1-c
]n
]o
1
0
] c
-]o:
J = ] . J(-
c
-]n
]o
)
0
-1
0
-1
= -.
c
-]n
]o
-1
0
+
1
]o
] c
-]o:
. J
0
-1
www.jntuworld.com
www.jntuworld.com
PTSPUNITVII Questions&Answers
GRIETECE 3
= -
c
]n
]o
+
1
]o
|
c
-]n
]o
]
-1
0
= -
c
]n
]o
+
1
]o
|
c
]n
-1
]o
]
] c
-]o:
J = -.
c
-]n
]o
0
1
+
1
]o
] c
-]o:
J
1
0
1
0
= -
c
-]n
]o
+
1
]o
|
1-c
-]n
]o
]
0
1
= -
c
-]n
]o
+
1
]o
|
1-c
-]n
]o
]
S
XX
() =
c
]n
-1
]o
-
c
]n
]o
+
1
]o
(
c
]n
-1
]o
) +
1-c
-]n
]o
+
c
-]n
]o
-
1
]o
|
1-c
-]n
]o
]
=
2
o
2
-
c
]n
+c
-]n
o
2
=
2
o
2
-
2cos o
o
2
=
4 sn
2
o 2
o
2
= (
2sn o 2
o
)
2
3. Difference between a random variable and a random process. Define auto-
correlation function of a random process?
Ans:
Random Variable Random Process
1. Probabilistic description of the
numerical value of an outcome of
random phenomenon.
2. Time variable is fixed and hence a
number or value.
3. It models a single outcome or result of
a physical phenomenon.
4. The outcome of a single trial is
represented as X.
5. Collection of all possible numerical
values for one event.
6. Cannot model a random signal.
7. Randomness is associated with the
uncertainty as to which of the possible
outcomes will occur in a given trial.
1. Probabilistic description of the sample
functions of time. It all the possible
outcomes of a random experiments for
all the times.
2. Time variable is not fixed and hence a
waveform.
3. It models the entire physical
phenomenon.
4. The outcome of a single trial
represented as X (t).
5. Collection or ensemble of all possible
sample functions of a process single.
6. Models random signal.
7. Randomness associated with the
uncertainty as which of the possible
waveform will occur in a given trial.
www.jntuworld.com
www.jntuworld.com
PTSPUNITVII Questions&Answers
GRIETECE 4
Autocorrelation Function of a Random Process
The auto correlation function R
XX
(t
1
t
2
) of a random process X (t) is defined as the
expectation of the product of two random variables X(t
1
) and X(t
2
) i.e., the values of the same.
Process X (t) at two different times t
1
and t
2
.
R
XX
(t
1
t
2
) = E|X(t
1
). X(t
2
)]
= ]]x
1
x
2
x
(t
1
- t
2
)(x
1
. x
2
). Jx
1
Jx
2
For stationary random processes, the ACF will depend on the time difference t
2
.t
1
only
rather than on the absolute times t
1
and t
2
.
Thus for stationary processes
R
XX
(t
1
t
2
) = R
XX
(t
2
- t
1
)
= R
XX
(t)
= E|X(t) X(t + )]
= ] x(t) x(t + )
x
(t)X(t + )J
-
Thus the Auto Correlation Function (ACF) is measure similarity for the given samples
of a random process.
www.jntuworld.com
www.jntuworld.com
PTSPUNITVII Questions&Answers
GRIETECE 5
4. Briefly explain the concept of cross power density spectrum?
Ans:
Cross Power Density Spectrum
Consider two jointly wide sense stationary random processes X (t) and Y (t). Let
R
X
() and R
X
() be their cross correlation functions. Then the cross spectral densities are,
S
X
() = ] R
X
(). c
-]o:
. J
-
and S
X
() = ] R
X
(). c
-]o:
. J
-
Consider S
X
(-) = ] R
X
(). c
]o:
. J
-
= ] R
X
(-). c
]o(-:)
J
-
= ] R
X
(). c
-]o:
. J
-
= S
X
()
S
X
() = S
X
(-) = S
X
-
()
Similarly S
X
() = S
X
(-) = S
X
-
()
5. Discuss the properties of cross power density spectrum?
Ans:
Properties of Cross Power Density Spectrum
1. S
X
() = S
X
(-)
= S
X
-
()
We have S
X
() = ] R
X
(). c
-]o:
. J
-
S
X
() = ] R
X
(). c
-]o:
. J
-
Consider S
X
(-) = ] R
X
(). c
]o:
. J
-
= ] R
X
(-). c
]o:
. J
-
= ] R
X
(-). c
-]o(-:)
J
-
=S
X
()
2. Real part of S
X
() is an even function of and imaginary part is an odd function of .
We have S
X
() = ] R
X
(). c
-]o:
. J
-
= ] R
X
(). (cos - ]sin )
-
J
www.jntuworld.com
www.jntuworld.com
PTSPUNITVII Questions&Answers
GRIETECE 6
= ] R
X
(). cos J -] ] R
X
(). sin J
-
|S
X
()]
cuI
= ] R
X
(). cos J
-
Consider |S
X
(-)]
cuI
= ] R
X
(). cos (-) J
-
= ] R
X
(). cos J
-
= |S
X
()]
cuI
Thus, |S
X
()]
cuI
is an even function of frequency.
|S
X
()]
Imugnu
= -] R
X
(). sin J
-
Consider |S
X
(-)]
Imugnu
= -] R
X
(). sin (-) J
-
= ] R
X
(). sin J
-
= -|S
X
()]
Imugnu
Thus, |S
X
()]
Imugnu
is an odd function of frequency.
3. S
X
() = u if X (t) and Y (t) are orthogonal.
S
X
() = F|R
X
()]
For two orthogonal process X (t) and Y (t), R
X
() = u
Hence, S
X
() = u
4. If X (t) and Y (t) are uncorrelated and of constant means E(X) and E(Y), respectively.
S
X
() = 2nE(X). E(). o()
We have S
X
() = F|R
X
()]
= F|E{X(t). (t +)]]
Since X (t) and Y (t) are uncorrelated
S
X
() = F|E|X(t)]. E|(t +)]]
Since mean of Y (t) is constant, E|(t)] = E|(t +)] = E|]
S
X
() = F|E(X). E()]
= ] E(X). E(). c
-]o:
J
-
= E(X). E() ] c
-]o:
J
-
Since K
P.1
--2nk. o() = 1
P.1
--2no()
S
X
() = 2 n. E(X). E(). o()
www.jntuworld.com
www.jntuworld.com
PTSPUNITVII Questions&Answers
GRIETECE 7
6. Write short notes on
(a) Flicker Noise
(b) Partition Noise
(c) Johnsons Noise
Ans:
(a) Flicker Noise
Due to imperfections in cathode surface of electron tubes and surfaces around
the junctions of semiconductor devices, a noise called flicker noise arises. There will be
random changes in the emission of electrons from the cathode due to these imperfections.
The PSD of this noise is inversely proportional to frequency and is more pronounced at
lower frequencies. This noise can be reduced by processing the cathode surfaces such that
slow varying conditions at the surfaces are avoided.
(b) Partition Noise
In multi-grid tubes like tetrodes and petrodes a noise exists due to fluctuating
division of the electron beam among various grids. This gives rise to another source of
noise in multi grid tubes called partition noise.
(c) Johnsons Noise
This noise is due to the random motion of free electrons in a conducting
medium such as resistor there are conduction electrons in a conductor, which can wonder
randomly through the entire volume of the conductor are in random motion as a result of
receiving thermal energy. Due to this random movement of electrons, there will be
fluctuation in charge distribution, i.e., at one time or the other, the distribution of charge
may not be uniform, i.e., at any given instant of time, an excess of electrons may appear
at one or the other end of the conductor. So, a voltage difference will appear between the
resistor terminals. This random voltage which so appeared is referred to as thermal
resistor noise or thermal noise or Johnsons noise. The thermal noise power is given by
P
n
= KIB wotts
Where,
K = Boltzmann Constant = 1.38 X 10
-23
J/
0
K
B = Bandwidth of noise spectrum
T = Temperature in
0
K
The PSD of thermal noise is
S
n
= KI
wutts
Hz
www.jntuworld.com
www.jntuworld.com
PTSPUNITVII Questions&Answers
GRIETECE 8
7. A random process is defined as Y (t) = X (t)-X (t-a), where X (t) is a WSS
process and a > 0 is a constant. Find the PSD of Y (t) in terms of the
corresponding quantities of X (t).
Ans:
Let R
XX
() and S
XX
() be the auto correlation function and PSD of X(t).
Consider R
(t, t + ) = E|(t). (t +)]
= E|{X(t) - X(t - o)]{X(t +) -X(t + - o)]]
=E|X(t). X(t + ) - X(t). X(t + - o) - X(t - o). X(t +) +
X(t -o). X(t + - o)]
=E|X(t). X(t + )] - E|X(t). X(t + -o)] - E|X(t - o). X(t +
)] + E|X(t - o). X|I + -o)]
= R
XX
() - R
XX
( -o) -R
XX
( + o) + R
XX
()
= 2. R
XX
() - R
XX
( -o) -R
XX
( + o).
PSD of Y(t) is
S
() = 2. S
XX
() - (c
-]ou
+ c
]ou
)S
XX
()
= 2. S
XX
() - 2. S
XX
(). cos o
=2. S
XX
()|1 -cos o]
=4. S
XX
(). Sin
2
[
ou
2
8. The cross spectral density of two random process X (t) and Y (t) is
S
XY
(m) = 1 +
jm
K
ur -k < < k
= 0 elsewhere
Where k > 0. Find the cross correlation function between the processes?
www.jntuworld.com
www.jntuworld.com
PTSPUNITVII Questions&Answers
GRIETECE 9
Ans:
Cross correlation function
R
X
() =
1
2n
] S
X
(). c
]o:
. J
-
=
1
2n
] [1 +
]o
k
c
]o:
. J
k
-k
=
1
2n
] c
]o:
. J +
1
2n
]
]o
k
. c
]o:
. J
k
-k
k
-k
=
1
2n
j
c
]n
]:
[
-k
k
+
]
2kn
] . c
]o:
. J
k
-k
=
c
]k
-c
-]k
2n]:
+
]
2kn
] . J [
c
]n
]:
k
-k
=
sInk:
n:
+
]
2kn
|j
o.c
]n
]:
[
-k
k
-
1
]:
] c
]o:
. J]
k
-k
=
sInk:
n:
+
1
2kn
j
kc
]k
+kc
-]k
:
[ -
1
2kn:
j
c
]n
]:
[
-k
k
=
sInk:
n:
+
cos k:
n:
-
1
2nk:
j
c
]k
-c
-]k
]:
[
=
1
n:
|sink + cos k] -
1
kn:
2
. sink
9. The auto correlation function of an a periodic random process is R
XX
(z) =
e
-
z
2
2o
2
. Find the PSD and average power of the signal.
Ans:
The power spectral density S
XX
() = ] R
XX
(). c
-]o:
. J
-
= ] c
-
2
2o
2
. c
-]o:
. J
-
= ] c
-_
2
2o
2
+]o:]
. J
-
=] expj-
1
2c
2
{
2
+ 2]o
2
+ (]o
2
)
2
- (]o
2
)
2
][ J
-
www.jntuworld.com
www.jntuworld.com
PTSPUNITVII Questions&Answers
GRIETECE 10
= ] c
-(+]no
2
)
2
2o
2
-
. c
(]no
2
)
2
2o
2
. J
= c
-n
2
o
2
2
] c
-(+]no
2
)
2
2o
2
. J
-
Let
:+]oc
2
2c
= k = J = 2o. Jk
S
XX
() = c
-
n
2
o
2
2
] c
-k
2
. (2o)Jk
-
= 2o. c
-
n
2
o
2
2
] c
-k
2
. Jk
-
= 2o. c
-
n
2
o
2
2
. c. ] c
-k
2
. Jk
0
= 22. o. c
-
n
2
o
2
2
n
2
S
XX
() = 2no
2
. c
-
n
2
o
2
2
Average power is E|X
2
(t)] = R
XX
(u) = 1
10. A stationary random process X(t) has a spectral density S
XX
(m) =
1
m
2
+1
and an independent stationary process Y(t) has the spectral density S
YY
(m) =
m
2
m
2
+1
. Assuming X(t) and Y(t) are of zero mean, find
(a) PSD of U(t) = X(t) + Y(t)
(b) S
XY
(m)and S
XU
(m)
Ans:
(a) PSD of u(t) = S
XX
() + S
()
=
16
o
2
+16
+
o
2
o
2
+16
= 1
www.jntuworld.com
www.jntuworld.com
PTSPUNITVII Questions&Answers
GRIETECE 11
(b) S
X
() = F|R
X
()] = F|E{X(t). (t + )]]
= F||E{X(t)]]. |E{(t + )]]]
= 0
S
X0
() = F|R
X0
()]
= F|E{X(t). u(t + )]]
= F|E|X(t). {X(t + ) +(t +)]|]
= F|E{X(t). X(t + )] +E{X(t). (t +)]]
= F|E{X(t). X(t + )]] + F|E{X(t). (t +)]]
= F|R
XX
()] + F|E|X(t)]. E|(t + )]]
=S
XX
() + u
= S
XX
() =
16
o
2
+16
www.jntuworld.com
www.jntuworld.com
You might also like
- Unit 6: 1. Explain The Classification of Random Process With Neat Sketches. AnsDocument12 pagesUnit 6: 1. Explain The Classification of Random Process With Neat Sketches. Anssrinivas0% (1)
- 02 Discrete Time Signals Systems ReleaseDocument0 pages02 Discrete Time Signals Systems Releasesamu1991tanNo ratings yet
- Solution Mid SemDocument4 pagesSolution Mid SemJyoti ranjan pagodaNo ratings yet
- Response of Bank of Correlators To Noisy Input: A.Raviraja 118W1D8001Document12 pagesResponse of Bank of Correlators To Noisy Input: A.Raviraja 118W1D8001Raviraja AkurathiNo ratings yet
- Transform Analysis of Linear Time-Invariant Systems: P P P P PDocument16 pagesTransform Analysis of Linear Time-Invariant Systems: P P P P PreneeshczNo ratings yet
- RT Solutions-09!10!2011 XIII VXY Paper II Code ADocument18 pagesRT Solutions-09!10!2011 XIII VXY Paper II Code Avishal27042233No ratings yet
- Digital Signal Processing Solution Mannual Chapter Bonus OppenheimDocument14 pagesDigital Signal Processing Solution Mannual Chapter Bonus OppenheimXafran Khan100% (2)
- Random Processes: 3.1 (A) The Mean and Autocorrelation Functions ofDocument21 pagesRandom Processes: 3.1 (A) The Mean and Autocorrelation Functions ofSudipta GhoshNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Stochastic ProcessesDocument6 pagesIntroduction to Stochastic ProcessesJorge MiguelNo ratings yet
- RT Solutions-09!10!2011 XIII VXY Paper II Code BDocument18 pagesRT Solutions-09!10!2011 XIII VXY Paper II Code Bvishal27042233No ratings yet
- Answer Key: Paper-2Document14 pagesAnswer Key: Paper-2vishal110085No ratings yet
- Y_d(Ω) sketch for problem 1Document4 pagesY_d(Ω) sketch for problem 1Le HuyNo ratings yet
- UNIT-3: 1. Explain The Terms Following Terms: (A) Mean (B) Mean Square Value. AnsDocument13 pagesUNIT-3: 1. Explain The Terms Following Terms: (A) Mean (B) Mean Square Value. AnssrinivasNo ratings yet
- Properties of Continuous and Discrete Fourier TransformsDocument10 pagesProperties of Continuous and Discrete Fourier TransformsHandi RizkinugrahaNo ratings yet
- Lec5 6 Ztransform PDFDocument40 pagesLec5 6 Ztransform PDFHussam GujjarNo ratings yet
- FTSheetDocument2 pagesFTSheetdragon_warrior112456804No ratings yet
- Presentation A NuDocument45 pagesPresentation A NuRoopa ShreeNo ratings yet
- Worked Examples Random ProcessesDocument15 pagesWorked Examples Random ProcessesBhagya AmarasekaraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Sampling of Continuous-Time Signals: Biomedical Signal ProcessingDocument19 pagesChapter 4 Sampling of Continuous-Time Signals: Biomedical Signal ProcessingHari2905No ratings yet
- ECE 5650/4650 Tables For Exam I: Sequence Sum FormulasDocument3 pagesECE 5650/4650 Tables For Exam I: Sequence Sum Formulasue06037No ratings yet
- 12 06 2011 Xii Abcd Paper II Code BDocument14 pages12 06 2011 Xii Abcd Paper II Code Bvishal110085No ratings yet
- Ch. 1: Review of ProbabilityDocument19 pagesCh. 1: Review of ProbabilityKyusang ParkNo ratings yet
- Stationary Random ProcessesDocument62 pagesStationary Random ProcessesGramoz CubreliNo ratings yet
- Discrete Signals and SystemsDocument111 pagesDiscrete Signals and SystemsharivarahiNo ratings yet
- Differentiation Formulas GuideDocument1 pageDifferentiation Formulas GuideNeHa SoniNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 3Document20 pagesChapter - 3gebretsadkan abrhaNo ratings yet
- 04MA246EX Ran PDFDocument15 pages04MA246EX Ran PDFznchicago338No ratings yet
- EL-4701 Modelos de Sistemas: FormularioDocument9 pagesEL-4701 Modelos de Sistemas: FormularioEmmanuel AcostaNo ratings yet
- Discrete-Time Signals and SystemsDocument111 pagesDiscrete-Time Signals and Systemsduraivel_anNo ratings yet
- DSP ProblemsDocument10 pagesDSP ProblemsMohammed YounisNo ratings yet
- AIEEE MathsDocument3 pagesAIEEE MathsSk SharukhNo ratings yet
- Do NOT Bring A Copy To The Exam!: ECE355F Final Examination - Fourier Properties Sheet December 11, 2008Document2 pagesDo NOT Bring A Copy To The Exam!: ECE355F Final Examination - Fourier Properties Sheet December 11, 2008Barry FungNo ratings yet
- FourierTransform DTDocument111 pagesFourierTransform DTdoroteja2332No ratings yet
- Laplace Transform Properties and ApplicationsDocument22 pagesLaplace Transform Properties and ApplicationsAnthony KwoNo ratings yet
- Sum and Difference of Inverse of FXDocument3 pagesSum and Difference of Inverse of FXHamza GamingNo ratings yet
- 1T4 Basic MathematicsDocument15 pages1T4 Basic MathematicsSimeonPetrovNo ratings yet
- Jee Main Model Questions: MathematicsDocument2 pagesJee Main Model Questions: MathematicsVijayabhaskarareddy VemireddyNo ratings yet
- RT Solutions-22!01!2012 XIII VXY Paper II Code A SolDocument16 pagesRT Solutions-22!01!2012 XIII VXY Paper II Code A Solvishal110085No ratings yet
- RT Solutions-24!02!2012 XI PQRS J Paper I Code ADocument16 pagesRT Solutions-24!02!2012 XI PQRS J Paper I Code Avishal110085No ratings yet
- PTSPQNAUNITVIIIDocument13 pagesPTSPQNAUNITVIIIsrinivasNo ratings yet
- Chpt05-FEM For 2D SolidsnewDocument56 pagesChpt05-FEM For 2D SolidsnewKrishna MyakalaNo ratings yet
- 351 - 27435 - EE411 - 2015 - 1 - 1 - 1 - 0 7 EE411 Lec12 State Space RepresentationDocument61 pages351 - 27435 - EE411 - 2015 - 1 - 1 - 1 - 0 7 EE411 Lec12 State Space Representationn̷i̷z̷a̷r̷ k̷ıd̷d̷i̷No ratings yet
- Week3 CHAPTER1: Laplace Transform MAT485/565Document7 pagesWeek3 CHAPTER1: Laplace Transform MAT485/565qistinaNo ratings yet
- RT Solutions-09!10!2011 XIII VXY Paper I Code ADocument16 pagesRT Solutions-09!10!2011 XIII VXY Paper I Code Avishal27042233No ratings yet
- δ (n) = u (n) - u (n-3) = 1 ,n=0Document37 pagesδ (n) = u (n) - u (n-3) = 1 ,n=0roberttheivadasNo ratings yet
- Answer Key: Paper-1Document16 pagesAnswer Key: Paper-1vishal110085No ratings yet
- Ps 4 SolDocument23 pagesPs 4 SolEmNo ratings yet
- Digital Signal ProcessingDocument53 pagesDigital Signal ProcessingWilliam VenegasNo ratings yet
- 2 Signals and Systems: Part I: Solutions To Recommended ProblemsDocument9 pages2 Signals and Systems: Part I: Solutions To Recommended ProblemssamibdzNo ratings yet
- FormDocument6 pagesFormBruno AmorosoNo ratings yet
- Random Process in Analog Communication SystemsDocument91 pagesRandom Process in Analog Communication SystemsEkaveera Gouribhatla100% (1)
- CH 1 PDFDocument43 pagesCH 1 PDFVimala ElumalaiNo ratings yet
- Problems on Signals and SystemsDocument6 pagesProblems on Signals and SystemsOral RobertzNo ratings yet
- TABELA: Derivadas, Integrais e Identidades TrigonométricasDocument1 pageTABELA: Derivadas, Integrais e Identidades TrigonométricasCharlesDavidNo ratings yet
- Inverse Trigonometric Functions (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandInverse Trigonometric Functions (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankNo ratings yet
- Analytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageFrom EverandAnalytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageNo ratings yet
- Application of Derivatives Tangents and Normals (Calculus) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandApplication of Derivatives Tangents and Normals (Calculus) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Ac Theory Moqwdule09Document12 pagesAc Theory Moqwdule09Vikas VernekarNo ratings yet
- ECE 2-1 r13Document12 pagesECE 2-1 r13srinivasNo ratings yet
- I Love You in 100 LanguagesDocument2 pagesI Love You in 100 LanguagesMadelapizNo ratings yet
- SQL Server Transaction Log ManagementDocument209 pagesSQL Server Transaction Log ManagementCarlos Eduardo100% (1)
- EdgeDocument27 pagesEdgesrinivasNo ratings yet
- Ac Theory Module07Document8 pagesAc Theory Module07srinivasNo ratings yet
- Ac Theory Module10Document11 pagesAc Theory Module10srinivasNo ratings yet
- TransformatoriDocument21 pagesTransformatoriantoniomkdNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Wireless NetworksDocument22 pagesIntroduction To Wireless NetworkssrinivasNo ratings yet
- Ac Theory Module06Document9 pagesAc Theory Module06srinivasNo ratings yet
- Ac Theory Module05Document12 pagesAc Theory Module05srinivasNo ratings yet
- DC Transients: What Happens When Things ChangeDocument10 pagesDC Transients: What Happens When Things Changethangaraj_icNo ratings yet
- Ac TheoryDocument15 pagesAc TheoryAnonymous vKD3FG6RkNo ratings yet
- AC CircuitDocument10 pagesAC CircuitSandun LakminaNo ratings yet
- Ac Theory Module02Document13 pagesAc Theory Module02bec08busNo ratings yet
- Computer Networks and Information SecurityDocument35 pagesComputer Networks and Information SecuritysrinivasNo ratings yet
- THESISDocument88 pagesTHESISmahwishkamilNo ratings yet
- PTSPQNAUNITVIIIDocument13 pagesPTSPQNAUNITVIIIsrinivasNo ratings yet
- UNIT-3: 1. Explain The Terms Following Terms: (A) Mean (B) Mean Square Value. AnsDocument13 pagesUNIT-3: 1. Explain The Terms Following Terms: (A) Mean (B) Mean Square Value. AnssrinivasNo ratings yet
- Unit 4: PTSP Unit Iv Questions & AnswersDocument10 pagesUnit 4: PTSP Unit Iv Questions & AnswerssrinivasNo ratings yet
- Probability and StatisticsDocument15 pagesProbability and StatisticssrinivasNo ratings yet
- PTSP Q&A Unit 2Document16 pagesPTSP Q&A Unit 2dsrilatharajuNo ratings yet
- Maximise Potential & Reach Customers With MarketingDocument2 pagesMaximise Potential & Reach Customers With MarketingsrinivasNo ratings yet
- Unit - 1: 1. Explain About The Partition of A Sampling Space Theorem? AnsDocument14 pagesUnit - 1: 1. Explain About The Partition of A Sampling Space Theorem? AnssrinivasNo ratings yet
- 54105-Mt-Vlsi Technology and DesignDocument2 pages54105-Mt-Vlsi Technology and DesignSrinivasa Rao G100% (2)
- MT Digital System DesignDocument1 pageMT Digital System Designvasudevareddy100% (1)
- M.tech Advanced Digital Signal ProcessingDocument2 pagesM.tech Advanced Digital Signal ProcessingsrinivasNo ratings yet
- HP 5973 Quick ReferenceDocument28 pagesHP 5973 Quick ReferenceDavid ruizNo ratings yet
- Donny UfoaksesDocument27 pagesDonny UfoaksesKang Bowo D'wizardNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9-10 (PPE) Reinzo GallegoDocument48 pagesChapter 9-10 (PPE) Reinzo GallegoReinzo GallegoNo ratings yet
- Revised Man As A Biological BeingDocument8 pagesRevised Man As A Biological Beingapi-3832208No ratings yet
- Power Bi ProjectsDocument15 pagesPower Bi ProjectssandeshNo ratings yet
- Choose the Best WordDocument7 pagesChoose the Best WordJohnny JohnnieeNo ratings yet
- Homo Sapiens ActivityDocument8 pagesHomo Sapiens ActivityJhon Leamarch BaliguatNo ratings yet
- Write 10 Lines On My Favourite Subject EnglishDocument1 pageWrite 10 Lines On My Favourite Subject EnglishIrene ThebestNo ratings yet
- Rescue Triangle PDFDocument18 pagesRescue Triangle PDFrabas_No ratings yet
- PGP TutorialDocument21 pagesPGP TutorialSabri AllaniNo ratings yet
- Center of Gravity and Shear Center of Thin-Walled Open-Section Composite BeamsDocument6 pagesCenter of Gravity and Shear Center of Thin-Walled Open-Section Composite Beamsredz00100% (1)
- Aircraft ChecksDocument10 pagesAircraft ChecksAshirbad RathaNo ratings yet
- Types of LogoDocument3 pagesTypes of Logomark anthony ordonioNo ratings yet
- Ch. 7 - Audit Reports CA Study NotesDocument3 pagesCh. 7 - Audit Reports CA Study NotesUnpredictable TalentNo ratings yet
- Consumer Behaviour Towards AppleDocument47 pagesConsumer Behaviour Towards AppleAdnan Yusufzai69% (62)
- Medical filter performance specificationsDocument1 pageMedical filter performance specificationsPT.Intidaya Dinamika SejatiNo ratings yet
- Mythic Magazine 017Document43 pagesMythic Magazine 017William Warren100% (1)
- Philippine College of Northwestern Luzon Bachelor of Science in Business AdministrationDocument7 pagesPhilippine College of Northwestern Luzon Bachelor of Science in Business Administrationzackwayne100% (1)
- Startups Helping - India Go GreenDocument13 pagesStartups Helping - India Go Greensimran kNo ratings yet
- Published Filer List 06072019 Sorted by CodeDocument198 pagesPublished Filer List 06072019 Sorted by Codeherveduprince1No ratings yet
- Biomechanics of Advanced Tennis: January 2003Document7 pagesBiomechanics of Advanced Tennis: January 2003Katrien BalNo ratings yet
- Analysis of VariancesDocument40 pagesAnalysis of VariancesSameer MalhotraNo ratings yet
- ArtigoPublicado ABR 14360Document14 pagesArtigoPublicado ABR 14360Sultonmurod ZokhidovNo ratings yet
- Marksmanship: Subject: III. Definition of TermsDocument16 pagesMarksmanship: Subject: III. Definition of TermsAmber EbayaNo ratings yet
- Electrophoresis and Fractionation of Wheat GlutenDocument14 pagesElectrophoresis and Fractionation of Wheat GlutensecucaNo ratings yet
- ThesisDocument250 pagesThesislax mediaNo ratings yet
- MSC Euribia - 2023-06-01Document2 pagesMSC Euribia - 2023-06-01蔡國懷No ratings yet
- HU675FE ManualDocument44 pagesHU675FE ManualMar VeroNo ratings yet