Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Magnetic Forces
Uploaded by
Mark ProchaskaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Magnetic Forces
Uploaded by
Mark ProchaskaCopyright:
Available Formats
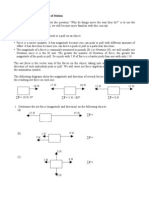
POGIL: Magnetic Forces We have already seen that magnetic fields are ultimately produced by moving charges, which
is what we call an electric current. We will now look at how magnetic fields exert forces on moving charges. The Magnetic Force on a Current-Carrying Wire The diagram below shows a uniform magnetic field B into the page (indicated by the s). A wire carries a conventional current I to the right at a 90 angle to the magnetic field. The length of the wire in the magnetic field is L. FB I B
The magnitude of the force FB that the magnetic field exerts on the wire is described by the equation F B =ILB sin , where is the angle between the wire and the magnetic field vector B. In the diagram above, = 90. The direction of the force exerted by the magnetic field on the wire is found using a right-hand rule. If you point your right hands pointing finger in the direction of conventional current and your middle finger the direction of the magnetic field B, your thumb points in the direction of the force. The righthand rule is illustrated in the picture below, on page 744 of your textbook, and can even be demonstrated by your friendly physics teacher. FB I
1. The unit of measurement of magnetic field strength is the Tesla (abbreviated T). In more basic units, a Tesla is equivalent to a Newton per Ampere-meter (N/A-m). Explain why.
2. The diagram below shows a wire carrying a current of 0.4 A to the left. A length of 0.25 m of the wire is in the presence of a magnetic field of 0.2 T into the page. Find the magnitude and direction of the magnetic force on the wire. B = 0.2 T
0.25 m 0.4 A
3. The diagram below shows a wire carrying a current of 2.5 A toward the top of the page. A length of 2 m of the wire is in the presence of a magnetic field of 0.5 T out of the page (indicated by the dots). Find the magnitude and direction of the magnetic force on the wire. 2m B = 0.5 T
2.5 A
4. The diagram below shows a vertical wire of length 1 m with a current of 3 A flowing upward. The wire is in the presence of a magnetic field of 2 T upward. Find the magnitude and direction of the magnetic force on the wire. B=2T 1m
3A 5. The diagram below shows a wire of length 0.3 m with a current of 3 A flowing at an angle of 30 to the horizontal. The wire is in the presence of a magnetic field of 2 T upward. Find the magnitude and direction of the magnetic force on the wire. B=2T 30 3A
6. What is the angle between the magnetic field and magnetic force on a wire?
7. What is the angle between a wire and the magnetic force on a wire?
8. What conditions are required for a magnetic field to exert a magnetic force on a wire?
9. In the diagram below, a rigid vertical loop of wire is connected to a 20 kg battery. The loop of wire is a square 1.5 m on a side. B=5T battery A magnetic field penetrates through the upper portion of the loop, perpendicularly into to the diagram, so that the entire circuit levitates. (j) Does the current in the circuit run clockwise or counter-clockwise?
1.5 m
(k) What is the current in the circuit?
You might also like
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Time DilationDocument3 pagesTime DilationMark ProchaskaNo ratings yet
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Mass Defect and Binding EnergyDocument3 pagesMass Defect and Binding EnergyMark ProchaskaNo ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- Work and PowerDocument3 pagesWork and PowerMark ProchaskaNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Voltage and ResistanceDocument4 pagesVoltage and ResistanceMark ProchaskaNo ratings yet
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Free Body DiagramsDocument4 pagesFree Body DiagramsMark ProchaskaNo ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- VectorsDocument2 pagesVectorsMark ProchaskaNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Nuclear Fission and FusionDocument4 pagesNuclear Fission and FusionMark ProchaskaNo ratings yet
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Relativistic EnergyDocument4 pagesRelativistic EnergyMark ProchaskaNo ratings yet
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Position, Displacement, VelocityDocument3 pagesPosition, Displacement, VelocityMark Prochaska0% (1)
- Vector ComponentsDocument4 pagesVector ComponentsMark ProchaskaNo ratings yet
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Newton's Second LawDocument3 pagesNewton's Second LawMark ProchaskaNo ratings yet
- EnergyDocument3 pagesEnergyMark ProchaskaNo ratings yet
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Newton's Third LawDocument3 pagesNewton's Third LawMark ProchaskaNo ratings yet
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Newton's First LawDocument3 pagesNewton's First LawMark ProchaskaNo ratings yet
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- Motion in Two Dimensions 2Document3 pagesMotion in Two Dimensions 2Mark ProchaskaNo ratings yet
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Motion in Two Dimensions 1Document4 pagesMotion in Two Dimensions 1Mark ProchaskaNo ratings yet
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Electric CurrentDocument2 pagesElectric CurrentMark ProchaskaNo ratings yet
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- Electromagnetic InductionDocument4 pagesElectromagnetic InductionMark ProchaskaNo ratings yet
- Electric ForcesDocument4 pagesElectric ForcesMark Prochaska100% (1)
- Atomic NucleiDocument4 pagesAtomic NucleiMark ProchaskaNo ratings yet
- POGIL: Length ContractionDocument3 pagesPOGIL: Length ContractionMark ProchaskaNo ratings yet
- Electric PowerDocument4 pagesElectric PowerMark ProchaskaNo ratings yet
- AccelerationDocument2 pagesAccelerationMark Prochaska0% (1)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Working and PowerDocument4 pagesWorking and PowerMark ProchaskaNo ratings yet
- Work and PowerDocument4 pagesWork and PowerMark Prochaska100% (1)
- WavesDocument4 pagesWavesMark ProchaskaNo ratings yet
- VelocityDocument4 pagesVelocityMark ProchaskaNo ratings yet
- Temperature and HeatingDocument4 pagesTemperature and HeatingMark ProchaskaNo ratings yet
- Universal GravitationDocument3 pagesUniversal GravitationMark ProchaskaNo ratings yet
- End Effector Analysis PDFDocument34 pagesEnd Effector Analysis PDFBas RamuNo ratings yet
- AutoCAD 3D ModuleDocument13 pagesAutoCAD 3D ModuletogentongNo ratings yet
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- 21 Magnetic Forces and FieldsDocument11 pages21 Magnetic Forces and Fieldssoe0303No ratings yet
- CeasarDocument28 pagesCeasarkaruna346No ratings yet
- The Magnetic FieldDocument40 pagesThe Magnetic Fieldyuliantoriski19No ratings yet
- Chapter 5A. TorqueDocument32 pagesChapter 5A. TorqueNeo TarunNo ratings yet
- Muma - Mulenga 1586370412 A PDFDocument8 pagesMuma - Mulenga 1586370412 A PDFBethelNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 - Torsion - 2015Document38 pagesLecture 6 - Torsion - 2015imranjamiNo ratings yet
- Right Hand Thumb RuleDocument1 pageRight Hand Thumb RuleAnonymous SKbL67p9No ratings yet
- OpenSCAD Cookbook OpenSCAD Recipes For Learning 3D ModelingDocument144 pagesOpenSCAD Cookbook OpenSCAD Recipes For Learning 3D Modelingticonzero2010No ratings yet
- Right Hand RuleDocument14 pagesRight Hand RuleTyra Christine Victorio FloresNo ratings yet
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Magnetism: Forces, Theories & Types in 40 CharactersDocument21 pagesMagnetism: Forces, Theories & Types in 40 CharactersEricka ArceNo ratings yet
- Concept Summary: Chapter 21 Magnetic Forces and Magnetic FieldsDocument2 pagesConcept Summary: Chapter 21 Magnetic Forces and Magnetic FieldsMichelle DyNo ratings yet
- Lect 13Document27 pagesLect 13Aswin SivaramanNo ratings yet
- MA Tutorial Creating Fixtures For MA 3DDocument21 pagesMA Tutorial Creating Fixtures For MA 3DSilvana Bidirinis Ramirez100% (1)
- CH 28 PDFDocument44 pagesCH 28 PDFHamza QureshiNo ratings yet
- AI & Neuro Cognitive Systems Forward KinematicsDocument56 pagesAI & Neuro Cognitive Systems Forward Kinematics김덕규No ratings yet
- Multiaxis & Machining: Handbook Volume 3Document56 pagesMultiaxis & Machining: Handbook Volume 3Cristian FuentesNo ratings yet
- DC Motor ProjectDocument18 pagesDC Motor ProjectUnicorn UnicornNo ratings yet
- Ncstudio Programming Manual-R5.08Document74 pagesNcstudio Programming Manual-R5.08kubik369100% (2)
- Magnetism Guided NotesDocument14 pagesMagnetism Guided Notesdericksonj32No ratings yet
- 01-Chapter 01 - Units, Physical Quantities, and VectorsDocument83 pages01-Chapter 01 - Units, Physical Quantities, and VectorsAbdullah AnwarNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Magnetic EffectDocument8 pagesClass 10 Magnetic EffectVirendra BansalNo ratings yet
- Phys Ther 1986 Dostal 351 9Document11 pagesPhys Ther 1986 Dostal 351 9Roar SyltebøNo ratings yet
- Oersted's principle whenever a charge moves through a straight conductor, a circular magnetic field is created around the conductorDocument4 pagesOersted's principle whenever a charge moves through a straight conductor, a circular magnetic field is created around the conductorMaden betoNo ratings yet
- CNC Milling Programing GuideDocument52 pagesCNC Milling Programing Guidercaleta100% (1)
- NC Machine Feed Axis Positions Process Variables Safety MonitoringDocument4 pagesNC Machine Feed Axis Positions Process Variables Safety MonitoringMuthuMuthuNo ratings yet
- Sources of Magnetic FieldsDocument13 pagesSources of Magnetic FieldsAbdalla FarisNo ratings yet
- Describing Baseball Pitch Movement With Right-Hand Rules: A. Terry Bahill, David G. BaldwinDocument8 pagesDescribing Baseball Pitch Movement With Right-Hand Rules: A. Terry Bahill, David G. BaldwinnurudinsatharNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 MagnetismDocument53 pagesChapter 5 MagnetismmunirahNo ratings yet
- Quantum Physics: What Everyone Needs to KnowFrom EverandQuantum Physics: What Everyone Needs to KnowRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (48)
- Quantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessFrom EverandQuantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (6)
- Quantum Physics for Beginners Who Flunked Math And Science: Quantum Mechanics And Physics Made Easy Guide In Plain Simple EnglishFrom EverandQuantum Physics for Beginners Who Flunked Math And Science: Quantum Mechanics And Physics Made Easy Guide In Plain Simple EnglishRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (18)
- Too Big for a Single Mind: How the Greatest Generation of Physicists Uncovered the Quantum WorldFrom EverandToo Big for a Single Mind: How the Greatest Generation of Physicists Uncovered the Quantum WorldRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (8)
- Summary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingFrom EverandSummary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- The Tao of Physics: An Exploration of the Parallels between Modern Physics and Eastern MysticismFrom EverandThe Tao of Physics: An Exploration of the Parallels between Modern Physics and Eastern MysticismRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (500)