Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Buyer Benefit Booklet
Uploaded by
Nagaraj KumbleOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Buyer Benefit Booklet
Uploaded by
Nagaraj KumbleCopyright:
Available Formats
INDEX 1. 2.
Fundamentals of Documentation and Registration Description of the Documents Title Documents Revenue Documents Survey Documents Endorsements Other Relevant Documents Jurisdiction of the Revenue Officers 3. 4. 5. Registration Procedure Stamp Duty Documents Required for the Purpose of Availing Housing Loan Checklist to purchase Agricultural Property Checklist to Purchase Residential Site in an Approved Layout .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. 2 3 3 7 8 8 9 9 11 13
14 15
6. 7.
16
FUNDAMENTALS OF DOCUMENTATION AND REGISTRATION Compliance of statutes for the purpose of procuring immovable property has always been a matter of concern to the prospective purchaser. In order to facilitate our valuable customer, effort is made to provide a brief of the Legal requirements and the method of documentation. While endeavoring to procure an immovable property, the following documents need to be verified. For the purpose of convenience the documents are sub-divided as under: Title documents Revenue documents Survey documents Endorsements Other Relevant Documents Jurisdiction of the Revenue Officers
Fundamentals of Documentation and Registration
Page 2
DESCRIPTION OF THE DOCUMENTS The following documents are required for legal scrutiny. (A) TITLE DOCUMENTS (a) Parent Deed: The Parent Deed means the documents like Sale deed, Partition Deed, Gift Deed, Will, Release Deed, Acquisition through Court, Grant Certificates and all such conveyance documents which establish the flow of the title for at least 13 years. Sale Deed: This is compulsorily registerable document, to be registered before the jurisdictional office of the Sub-Registrar. Sale is transfer of ownership in exchange for a price paid or promised or part-paid and part-promised. Such transfer, in the case of tangible immovable property of the value of one hundred rupees and upwards, or in the case of a reversion or other intangible thing, can be made only by a registered instrument. In the case of tangible immovable property, of a value less than one hundred rupees, such transfer may be made either by a registered instrument or by delivery of the property. Delivery of tangible immovable property takes place when the seller places the buyer or such person as he directs, in possession of the property. It has details like the vendor, the purchaser, the witnesses, the sale consideration, the measurement and particulars of the property and the schedule of the property, etc. There should be clear mention of transfer of Title and Possession in favour of the purchaser, without any encumbrances. Contract for Sale: A contract for the sale of immovable property is a contract that a sale of such property shall take place on terms settled, between the parties. It does not, of itself, create any interest in or charge on such property. Partition Deed / Panchayath Palupatti: This is compulsorily registerable document, to be registered before the jurisdictional office of the Sub-Registrar. However the Panchayat Palupatti also holds legal evidentiary value. The partition is generally for bifurcation of joint ownership existing within the parties. The partition is subject to the provisions of succession envisaged under relevant Succession Act and Rules for the partitioning parties. The essential points are, share of the parties, any common easement rights, respective schedules, respective bifurcation and boundaries, demarcation, etc.
(b)
(c)
(d)
Fundamentals of Documentation and Registration
Page 3
(e)
Gift Deed: This is compulsorily registerable document, to be registered before the jurisdictional office of the sub-registrar having details about the donor, donee, witnesses, the measurement and particulars of the property and the schedule of the property, etc. Gift is the transfer of certain existing movable or immovable property made voluntarily and without consideration, by one person, called the donor, to another, called the donee, and accepted by or on behalf of the donee. Such acceptance must be made during the lifetime of the donor and while he is still capable of giving. If the donee dies before acceptance, the gift is void. Will: This is non-compulsorily registerable document. The document becomes enforceable upon the demise of the Testator. The document necessarily needs that the testator should be in a sound and understanding state of mind with clear description and averments of bequeath and witnessed by two witnesses as required under Indian Succession Act and Indian Evidence Act. Release Deed: This is compulsorily registerable document, to be registered before the jurisdictional office of the Sub-Registrar. The documents will have details about the releasor, releasee and witnesses with or without consideration. There should be clear mention of release and relinquishment of title and possession in favour of releasee without any encumbrances. Through Court: Certain properties leading to dispute are acquired through a judgment and decree passed by competent judicial forum, which has not been either appealed or challenged before the higher forum. The said judgment and decree should be confirmed for the purpose of proper registration, before jurisdictional Sub-Registrar. Grant Certificate: Land Grant Certificate, is issued by the Government under relevant Act & Rules. In respect of Grants to a member of SC/ST community, the provisions under Karnataka SC/ST (PTCL) Act to be followed. The conditions mentioned in the grant certificate are to be strictly taken into consideration. Lease: A lease of immovable property is a transfer of a right to enjoy such property, made for a certain time, express or implied, or in perpetuity, in consideration of a price paid or promised, or of money, a share of crops, service or any other things of value, to be rendered periodically or on specified occasions to the transferor by the transferee, who accepts the transfer on such terms. The transferor is called the lessor, the transferee is called the lessee,
(f)
(g)
(h)
(i)
(j)
Fundamentals of Documentation and Registration
Page 4
the price is called the premium, and the money, share, service or other thing to be so rendered is called the rent. (k) Exchange Deed: This is compulsorily registerable document. When two persons mutually transfer the ownership on one thing for the ownership of another, either thing or both things being money only, the transaction is called an exchange. A transfer of property in completion of an exchange can be made only in manner provided for the transfer of such property by sale. Mortgage Deed: (i) Mortgage : A mortgage is the transfer of an interest on specific immovable property for the purpose of securing the payment of money advanced or to be advanced by way of loan, an existing or future debt, or the performance of an engagement which may give rise to a pecuniary liability. The transferor is called a mortgagor, The transferee is called a mortgagee; The principal money and interest for which payment is secured for the time being is called the mortgage-money The instrument (if any) by which the transfer is effected is called a mortgage-deed. Simple Mortgage: Where, without delivering possession of the mortgaged property, the mortgagor binds himself personally to pay the mortgage-money, and agrees, expressly or impliedly, that, in the event of his failure to pay according to his contract, the mortgagee shall have a right to cause the mortgaged property to be sold and the proceeds of sale to be applied, so far as may be necessary, in payment of the mortgagemoney, the transaction is called a simple mortgage and the mortgagee a simple mortgagee. Mortgage by Conditional Sale: Where the mortgagor ostensibly sells the mortgaged property on condition that on default of payment of the mortgage-money on a certain date the sale shall become absolute, or on condition that on such payment being made the sale shall become void, or on condition that on such payment being made the buyer shall transfer the property to the seller, the transaction is called a mortgage by conditional sale. Provided that no such transaction shall be deemed to be a mortgage, unless the condition is embodied in the document which effects or purports to effect the sale.
(l)
(ii)
(iii)
Fundamentals of Documentation and Registration
Page 5
(iv)
Usufructuary Mortgage: Where the mortgagor delivers possession or expressly or by implication and binds himself to deliver possession of the mortgaged property to the mortgagee, and authorizes him to retain such possession until payment of the mortgage-money, and to receive the rents and profits accruing from the property or any part of such rents and profits and to appropriate the same in lieu of interest or in payment of the mortgage money, or partly in lieu of interest or partly in payment of the mortgage-money, the transaction is called an usufructuary mortgage and the mortgage, an usufructuary mortgagee. English Mortgage: Where the mortgagor binds himself to repay the mortgage-money on a certain date, and transfers the mortgaged property absolutely to the mortgagee, but subject to a provision that he will retransfer it to the mortgagor upon payment of the mortgage-money as agreed, the transaction is called an English Mortgage. Mortgage by Deposit of Title-Deeds: Where a person in any of the following towns, namely, the towns of Calcutta, Madras and Bombay, and in any other town which the State Government concerned may, by notification in the official gazette, specify in this behalf, delivers to a creditor or his agent documents of title to immovable property, with intent to create a security thereon, the transaction is called a mortgage by deposit of title-deeds. Anomalous Mortgage: A mortgage which is not a simple mortgage, a mortgage by conditional sale, an usufructuary mortgage, and English Mortgage or a mortgage by deposit of title-deeds within the meaning of this section is called an anomalous mortgage.
(v)
(vi)
(vii)
(m)
Court Auction: Properties which are attached to statutory authorities are sometimes auctioned on the judgment or decree of judicial forum or in compliance to the respective rules. These documents are to be confirmed for the purpose effecting registration before the jurisdiction Sub-Registrar Office. General Power of Attorney (GPA) : This is non-compulsorily registerable document. However, this document required adjudication by either the office of the Sub-Registrar, Public Notary, Judicial Magistrate and the authorities empowered in the office of Indian Embassy. This document when executed, the
(n)
Fundamentals of Documentation and Registration
Page 6
enumerated powers of the executant are delegated in favour of the power of attorney holder. (o) Specific Power of Attorney (SPA) : This is a document similar to GPA except for the situation that, when the power is delegated with respect to a specific or single activity by the executor in favour of the power of attorney holder.
(B)
REVENUE DOCUMENTS (a) R.R. (Record of Rights) : The document which reflects the details of the property along with the nature of the possession (acquisition of land) and issued by Asst. Tahsildar. M.R. (Mutation Register) : The document which reflects the mode of transfer of the property, name of the present khatedar, other details of the property and nature of the possession (acquisition of land). Extract of MR is issued by the Village Accountant. RTC (Record of Rights, Tenancy and Crop Inspection) : The document which reflects the ownership/measurement of the total land/Karab land/Survey number/name of the occupant/owner/holder/nature of the possession/and about acquisition or encumbrance if any. This document is issued by the Asst. Tahsildar/Village Accountant. P.R.B. (Patta Receipt Book) : The document which reflect the name of the owner/khatedar/Survey number and measurement of the land. This document is issued by the Asst. Tahsildar/Village Accountant. I.D (Voter List/Identity Card/Identity Proof) : The document to prove the identity of the individual. E.C. Encumbrance Certificate : (i) Form No.15 : Existence of any transaction in respect of the property, are recorded in this form, describing the name of the transferor, transferee, date, registration number, volume, page, consideration amount and nature of transaction, etc. Form No.16 : Non-existence of any transaction in respect of the Property during the relevant period, then Certificate indication Nil Encumbrance will be issued in this form.
(b)
(c)
(d)
(e)
(f)
(ii)
Fundamentals of Documentation and Registration
Page 7
(C)
SURVEY DOCUMENTS
(a)
Atlas: The survey document made to scale and indicates the shape and size of the respective survey number (The measurements are generally (in Karnataka) taken in Chains'). This is issued by the ADLR. One Chain = 66 feet One Chain = 100 links One link = 7.92 inches One Acre = 43560 Sq Ft One Acre = 40 guntas
(b)
Tippany: The survey document made to or not to scale and gives the brief description of the respective survey number. This document is issued by ADLR. Podi: It is a process of bifurcation of land along with old and new survey number among the joint owners. This is done by ADLR. Sketch: The document which reflects the survey number/shape of the property and helps to identify the property. This document is issued by ADLR. Akaraband: The document which reflects the area and the rate of assessment, etc in detail of the survey numbers of a village. This document is issues by ADLR. Village Map: The document which reflects the entire village and the shape/location/survey numbers of the Land within the village. This document is issued by ADLR. Zonal regulation Map: The document which reflects the Zone for the purpose of confirming the land usage of the relevant Property (Like Park Zone/Residential etc.)
(c)
(d)
(e)
(f)
(g)
(D)
ENDORSEMENTS: (a) 79 (A) of Land Reform Act: The Karnataka Land Reform Act prohibits certain category of individuals and bodies from purchasing agricultural land in Karnataka. Hence an endorsement issued by Revenue Authorities (AC) indicating that, there are no claims/petition pending before the authorities in respect of such properties, needs to be vetted. The endorsement contains certification with respect to the survey number and extend of land.
Fundamentals of Documentation and Registration
Page 8
(b)
79 (B) of Land Reform Act: Similar to the endorsement under sec 79 (A) of the Land Reforms Act, it is necessary to verify the endorsement under Sec 79 (B) about cases/petitions pending over relevant property. Form 7 & 7(a) Under LR Act: The document which reflects the name of the occupant and further reflects that no tenancy petitions/claims/cases have been filed or pending under this provision. The document is issued by the office of the Tahsildar. PTCL: This certificate is issued by the Asst. Commissioner. The certificate indicates that, there is no claim/petition pending before the revenue tribunal with respect to the particular survey number and the grant lands to the member of SC & ST Communities granted with or without collecting any fees or charges.
(c)
(d)
E)
OTHER RELEVANT DOCUMENTS: (a) Family tree/ Genealogical Tree: Its a document reflecting all the names of the family members, which will be issued by the Village Accountant. Hiduvali Certificate: Its a document reflecting the name of Hiduvalidara (Present owner of the agriculture land) of the Property which will be issued by the Tahsildar Death Certificate: Its a document which reflects the name, date, husband/father's name of the deceased person, which will be issued by the Registrar of Births and Deaths. Tax Paid receipt: Its a document which reflects the Property Number/Survey. No/ date and year for which the owner/holder would have paid the tax. Khatha/Form No.1&12: Its a document which reflects the name of the owner/person in possession of the property.
(b)
(c)
(d)
(e)
F)
JURISDICTION OF THE REVENUE OFFICIERS: (a) (b) (c) D.C (Deputy Commissioner): Grant Certificate and Conversion Certificate A.C (Assistant Commissioner): Endorsement under PTCL ADLR (Assistant Director Land Records): Atlas/Village Map/Sketch/Akaraband/Survey Map. ST/AT (Spl Tahsildar & Asst Tahsildar): Record of Rights, RTC, Endorsement under sec 79 (A) (B) of KLR Act Endorsement under sec 7 and 7(A)
(d)
Fundamentals of Documentation and Registration
Page 9
(e)
V.A (Village Accountant): Mutation Register Extracts /RTC/ Family Tree/ Patta Receipt Pass Book.
(f)
Sub-Registrar: Registration of documents and issuing of certified copies of the Sale Deed/Gift deed/ Partition deed/ Release deed/ Encumbrance Certificates).
(g)
BDA (Bangalore Development Authority): NOC for the formulation of layout/ Nil acquisition certificate/approval of plan for the construction of building having more than 5 floors.
(h)
RI (Revenue Inspector)
(i)
BMRDA (Bangalore Metro Rural Development Authority)
(j)
BIAAPA (Bangalore International Airport Area Planning Authority)
(k)
BMIC (Bangalore Mysore Infrastructure Corridor)
(l)
BBMP (Bruhat Bengaluru Mahanagara Palike)
(m)
TMC (Town Municipal Council)
Fundamentals of Documentation and Registration
Page 10
REGISTRATION PROCEDURE 1. Documents required before Registration of Deed. (a) Title Deed Title deed in the name of vendor in respect of the Property. (If it is a BDA property- allotment letter, procession certificate are required) Original Conveyance deed/ Gift deed /Release deed/ Partition deed/Will/JDA. (b) Khatha Certificate and Extract Latest Khatha Certificate and Khatha extract in the name of the vendor in respect of the property. (c) Tax Paid Receipt Latest tax paid receipt pertaining to the property. (d) Sanctioned Building Plan Sanctioned building plan pertaining to the property (if the building is existing) issued by the competent authority. (e) GPA General Power of Attorney (if the vendor is represented by a GPA holder). Registered /Notarized/Attested by Embassy (if the owner is not within the country). (f) Additional Documents in respect of Agricultural Land Pahani, Extract of Mutation Register, IHR, RR, IL, Patta Receipt Bookconfirming the name of the vendor pertaining to the property (latest and computerized)
2.
The following documents are to be carried at the time of registration:
(a) Sale Deed Should be drafted on a single side of the sheet by an Advocate Licensed document writer. After obtaining the signatures by both the parties i.e. vendor and the purchaser, the said sale deed has to be photocopied. PAN number should be entered in the sale deed (as applicable). Sale consideration cheque/DD particulars, property details, boundaries, etc are to be checked.
Fundamentals of Documentation and Registration
Page 11
(b) Additional Documents Form No.60 (Under IT Act). Form No. 61 (If the value of the property is Rs. 5,00,000/- or more) Form No. 1 Affidavit (2 set):- Stating that registration of the said document does not violate the notification issued under section 22A of the Registration Act. Extract of assessment register of the property. For Agricultural Land: - No objection certificate from Tahsildar. (If the property is a granted land or occupancy rights have been granted under Land Reform Act, 1961, then no object certificate from the concerned Tahsildar to be obtained). 3. The following procedure is to be followed after the completion of the registration process. After registering the conveyance deed the purchaser/ owner should apply for the E.C, to confirm about reflection of transaction of his name. Approach concerned revenue department/authority for transferring the Khatha and other revenue record in his name. Pay up to date tax regularly to the competent authority. To construct building, get the building plan approval from competent authority. (Like BDA/BMP/BBMP/BMRDA/BIAAPA, etc.)
Fundamentals of Documentation and Registration
Page 12
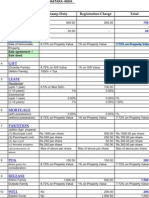
STAMP DUTY
The Karnataka Stamp Act, provides the details about the payment of the stamp duty on various documents being registered before the office of the Sub Registrar. As on 31 Dec 2007, the stamp duties and registration fees is as follows:-
Stamp duty
: 8.4% (for BMP / BBMP / BDA Properties) : 8.5% (for CMC/Village Panchayath Properties)
Registration Miscellaneous Fees
: 1 % fee : Rs 800/- Approx (towards scanning, endorsement, comparing, filing, record of rights & postage fee etc.)
(For the purpose of calculating the stamp duty and registration fees, the latest estimated market value of immovable properties as fixed by the Government of Karnataka, is to be followed).
Fundamentals of Documentation and Registration
Page 13
DOCUMENTS REQUIRED FOR THE PURPOSE OF AVAILING HOUSING LOAN
To avail Housing loan, the following documents are sought by Financial Institutions.
Title deed to trace the origin of the property at least last 13 years. Registered title deed / sale deed / any other document in his name. Khatha Certificate/Extract issued by competent authority. Latest tax paid receipt. E.C. from past 30 years/ 13 years. Betterment charges paid receipt/ Conversion Order issued by competent authority Sanctioned building plan issued by the competent authority if there is existence of building. Legal opinion from an Advocate clearing title in respect of the property. If the owner is represented by GPA holder then appropriate proof/GPA authorizing him/her to mortgage the property is required.
Fundamentals of Documentation and Registration
Page 14
CHECK LIST FOR AGRICULTURAL PROPERTY Documents required while dealing Agricultural property: Title Deed Mother Deed Sale Deed/Partition Deed/Gift Deed Court order etc. NOC from Primary Land Development (PLD) Bank/any Banks Affidavit
Revenue Records R.T.C. from 1974 to till date Mutation Index of Land Record of Rights Patta Pass Book Tax Paid Receipt Hiduvali Certificate
Survey Records Tippany Atlas Sketch Survey Settlement Akaraband
Record form Sub-Registrar Office Certified Copy & E.C. for 30 years Endorsements Endorsement 7 Endorsement 7A Endorsement 79 AB Karnataka SC & ST (Prohibition of Transfer of Certain Land) Act 1978.
Zoning Records Village Map & Zoning Map Other documents Genealogical Tree Identification Document Death Certificate
Fundamentals of Documentation and Registration Page 15
CHECK LIST FOR PURCHASE OF SITES IN AN APPROVED LAYOUT
1. Documents required while purchasing site within jurisdiction of BIAAPA a) b) c) d) e) f) g) h) i) j) k) l) m) n) o) p) q) Valid Conversion order issued by the Deputy Commissioner. Conversion amount paid receipt. RTCs for 30 years issued by the Village Accountant. Tax Paid receipts issued by the Village Accountant. Documents of ownership. Mutation register extracts. Akaraband/Tippani/Podi Extracts. Surveys/Boundary map. Village map Nil Tenancy certificate. Confirmation from the competent authority that there are no acquisition proceedings. Lay-out plan approval by the competent authority. Release of site order. Khatha certificate issued by the revenue authority wherever applicable. Latest tax paid receipts. Encumbrances for the last 30 years. Validity of the Power of Attorney.
The information given in this booklet is only indicative
Fundamentals of Documentation and Registration
Page 16
You might also like
- Rangappa Vs Sri Mohan On 7 May, 2010Document8 pagesRangappa Vs Sri Mohan On 7 May, 2010Nagaraj KumbleNo ratings yet
- Regularisation of Unauthorised ConstructionDocument29 pagesRegularisation of Unauthorised ConstructionNagaraj KumbleNo ratings yet
- Hindu Intestate Property Inheritance Mitakshara Class I II HeirsDocument2 pagesHindu Intestate Property Inheritance Mitakshara Class I II HeirsNagaraj KumbleNo ratings yet
- Model Sale AgreementDocument4 pagesModel Sale AgreementNagaraj KumbleNo ratings yet
- Notary FeesDocument1 pageNotary FeesNagaraj KumbleNo ratings yet
- CRPC ProcedureDocument357 pagesCRPC ProcedureNagaraj Kumble92% (13)
- NIA - JudgementsDocument45 pagesNIA - JudgementsNagaraj KumbleNo ratings yet
- PTCL Act AbuseDocument2 pagesPTCL Act AbuseNagaraj Kumble100% (4)
- Stamp DutyDocument1 pageStamp DutyNagaraj KumbleNo ratings yet
- Know Your Client (KYC) Application Form (For Individuals Only)Document2 pagesKnow Your Client (KYC) Application Form (For Individuals Only)Amey ShelkeNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5783)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (72)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Moselle Property Sale ContractDocument9 pagesMoselle Property Sale ContractBailey Wright100% (1)
- Aws D1.4-2018Document98 pagesAws D1.4-2018udomNo ratings yet
- Deed of PartitionDocument2 pagesDeed of Partitionroxanne bangasan100% (2)
- Haystack Navarro Vs Pineda PropertyDocument2 pagesHaystack Navarro Vs Pineda PropertyG-shockNo ratings yet
- Equity and Trust ExamDocument4 pagesEquity and Trust ExamXYZNo ratings yet
- Research Question 10Document5 pagesResearch Question 10Pragya NawandarNo ratings yet
- Doas Condo - PerilloDocument3 pagesDoas Condo - PerilloVanessa Mallari100% (1)
- Memorandum of Law: History, Force & Effect of The Land PatentDocument29 pagesMemorandum of Law: History, Force & Effect of The Land Patentjunkmonkey69292100% (1)
- Hybrid Cultures Strategies For Entering and Leaving Modernity (1) INTRODocument11 pagesHybrid Cultures Strategies For Entering and Leaving Modernity (1) INTROdanovaotrNo ratings yet
- Deed of Absolute Sale - BlankDocument2 pagesDeed of Absolute Sale - BlankDarwinCulaNo ratings yet
- Cloud 9 Explanation of RestrictionsDocument11 pagesCloud 9 Explanation of RestrictionsCloud 9 Ranch ClubNo ratings yet
- Succession Cases 1Document29 pagesSuccession Cases 1Gericah RodriguezNo ratings yet
- NOTES ON IPC (RA No. 8293) - LAW On PATENTSDocument21 pagesNOTES ON IPC (RA No. 8293) - LAW On PATENTSela kikayNo ratings yet
- Baguio Lease ContractDocument3 pagesBaguio Lease ContractPilacan KarylNo ratings yet
- Deed of Donation-AcceptanceDocument2 pagesDeed of Donation-Acceptancemamcapiral25No ratings yet
- Deed of Partition - CabuhayDocument3 pagesDeed of Partition - CabuhayrjpogikaayoNo ratings yet
- Deed of Assignment of Shares VHA-JTualDocument3 pagesDeed of Assignment of Shares VHA-JTualJerome MoradaNo ratings yet
- Room Rental AgreementDocument7 pagesRoom Rental AgreementJeannina RadfordNo ratings yet
- SEC. 44 Statutory Liens Affecting TitleDocument55 pagesSEC. 44 Statutory Liens Affecting TitleJarvin David ResusNo ratings yet
- Intellectual Property Right: Patent LawDocument4 pagesIntellectual Property Right: Patent LawIshita AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Commercial Lease Agreement: State of - Rev. 1343D17Document19 pagesCommercial Lease Agreement: State of - Rev. 1343D17Jisselle Marie CustodioNo ratings yet
- Does Article 774 Also Apply To Juridical Persons To TheDocument6 pagesDoes Article 774 Also Apply To Juridical Persons To TheSintas Ng SapatosNo ratings yet
- Property I OutlineDocument52 pagesProperty I OutlineKatie KilbrideNo ratings yet
- Deed of Absolute Sale - Pro FormaDocument4 pagesDeed of Absolute Sale - Pro FormaOgie FermoNo ratings yet
- December 4, 2023 Jordan Property Title SearchDocument81 pagesDecember 4, 2023 Jordan Property Title SearchZyreen CataquisNo ratings yet
- Good Kid - G Major - MN0190054Document10 pagesGood Kid - G Major - MN0190054Deb Mitchelmore100% (3)
- Property I Outline Key ConceptsDocument26 pagesProperty I Outline Key ConceptsACDCNo ratings yet
- Sale Deeds (Drafting & Registration)Document6 pagesSale Deeds (Drafting & Registration)pallavi mohtaNo ratings yet
- Tenancy Agreement DraftDocument8 pagesTenancy Agreement DraftyokekeannNo ratings yet
- Digest LTD 1-3Document3 pagesDigest LTD 1-3John Lester LantinNo ratings yet