Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Intro Lecture Notes Ch01 Markets
Uploaded by
Katherine SauerOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Intro Lecture Notes Ch01 Markets
Uploaded by
Katherine SauerCopyright:
Available Formats
Economics Dr.
Sauer
Lecture Chapter 1: The Power of Markets The _________________ aligns incentives in a way such that __________________ working in ________________ leads to a ____________ standard of living for ___________ as a whole.
1. The Invisible Hand Adam Smith (1723 1790) is often referred to as the founder of _________________ economics. He was actually a Scottish philosopher of morality who got famous for writing The Theory of Moral Sentiments (1759). - people decide using sympathy, not just selfishness He was an example of the absent minded professor. He studied astronomy. - liked the idea that even though planets moved in their own orbit, there was a natural harmony with the rest of the planets He thought that ___________ could also move in different paths and yet harmonize with one another.
It is not from the benevolence of the butcher, the brewer, or the baker, that we expect our dinner, but from their regard to their own interest. - from An Inquiry into the Nature and Causes of the Wealth of Nations (1776) Smith doesnt say that people are motivated ONLY by ________________. He says that self-interest motivates more powerfully and consistently than things like ___________ or ___________________. The concept of the invisible hand appeared in Moral Sentiments before appearing his now more famous work, The Wealth of Nations. He said that if each person seeks to promote their self-interest, then _______________________. he intends only his own gain, and he is in this, as in many other cases, led by an invisible hand to promote an end which was no part of his intention. Smith never took nor taught an economics course. ECONOMICS DIDNT EXIST!!!! Until the 19th century, academics considered economics a part of ____________________. 1
2. Basic Economic Assumptions A. How Individuals Behave Individuals attempt to make themselves as __________________ as possible, given their individual _______________________. maximize utility This is not the same thing as being selfish. Ex:
Every decision we make involves a ____________________. Examples of a tradeoff involving: - a present activity and future activity
- work vs leisure/family time
- two desirable activities in the present
Whenever we make a decision, we are _____________________ the benefits and costs of the action. - can be things other than money - often include money The higher the _____________associated with an action, the higher the ______________ need to be to get you to take the action.
B. How Firms Behave The goal of a firm is to maximize _________________. Firms have 5 main decisions to make. 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) A market economy will direct resources to their most __________________ use. Prices will ____________ information about the most valuable use.
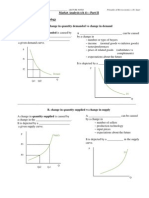
3. The Market and Prices A. Demand The Law of Demand says that there is an _______________ relationship between price and quantity demanded (keeping other things constant income, etc). - as price _________, the quantity demanded __________ - as price _________, the quantity demanded __________ This is why (in general) the demand curve slopes downward. Demand represents consumers _____________________________________ for a good or service. B. Supply The Law of Supply says that there is a __________________ relationship between price and quantity supplied (holding other things constant like the price of raw material inputs). - as price ___________, the quantity supplied ____________ - as price ___________, the quantity supplied ____________ This is why (in general) the supply curve slopes upward. Supply represents producers _____________________. C. Market Equilibrium The Law of Supply & Demand says that the _____________________________ to bring the quantity supplied and quantity demanded into equality.
________________________________________________________________________________ If the price were higher than If the price were lower than equilibrium: P1 equilibrium: P2 Qs Qd Qs Qd __________ ____________ price will _________ price will _________
Surpluses put downward pressure on price. Shortages put upward pressure on price. At P* Qd = Qs no shortage, no surplus price is stable equilibrium price
D. Changes to Equilibrium a. Market For Heroin Example
The Market for Opium:
Favorable weather conditions resulted in a bumper crop of opium. This would shift the supply curve to the _____. The price of Opium _____ and the quantity ______.
The Market for Heroin:
Opium is an input to Heroin. Since the price of Opium fell, the supply of Heroin will ______. The supply curve for Heroin shifts _______. The price of Heroin ______ and the quantity _______.
b. Market for Tuna Example In the past decade Americans have really taken a liking to sashimi tuna, so it is ordered more often at restaurants. When the demand for tuna increases, the demand curve shifts to the _______________. The price _______. The quantity ________.
But how are there magically more fish being caught? Prices _______________ information. When the price of tuna increases, this is a _______________ to fishermen. They will be getting paid more for their catch. - keep boat in water longer - some switch from salmon fishing to tuna fishing The quantity of tuna caught rises.
c. Market for Wheat Example Pakistan is the worlds 9th largest producer of wheat. In 2010, Pakistan experienced widespread flooding that devastated the wheat crop. When the supply of wheat decreases, the supply curve shifts to the _____________. The price __________. The quantity ___________.
d. Market for Oil Example OPEC is well-known as the organization that controls the world supply of oil. From time to time, OPEC will restrict oil production in order to drive up its price. China is currently experiencing major economic growth. The middle class is increasingly able to afford major purchases like automobiles. The consumption of oil in China has dramatically increased in recent years. 5
OPEC restricts production of oil
Chinese consume more oil
________________________________________________________________________________ Markets and competition are good for consumers. Markets are amoral. Economics assumes that people act __________________. - act in a way that makes them better off, not worse off __________________________________________________________________________________ Summary: Adam Smith is the founder of modern economics. Economists Assume - individuals maximize utility - firms maximize profits Demand represents the inverse relationship consumers have with price and quantity demanded. Supply represents the positive relationship with price and quantity supplied. Price will adjust to bring the market into equilibrium. World events will change equilibrium price and quantity in various markets.
You might also like
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Principles of MIcroeconomics - Lecture - Markets/Supply/Demand - Part 2Document17 pagesPrinciples of MIcroeconomics - Lecture - Markets/Supply/Demand - Part 2Katherine Sauer100% (1)
- Reading Notes Economics - Dr. SauerDocument6 pagesReading Notes Economics - Dr. SauerKatherine SauerNo ratings yet
- Financial Wellness Programming: An Administrative PerspectiveDocument16 pagesFinancial Wellness Programming: An Administrative PerspectiveKatherine SauerNo ratings yet
- Principles of MIcroeconomics - Notes - Markets/Supply/Demand - Part 2Document4 pagesPrinciples of MIcroeconomics - Notes - Markets/Supply/Demand - Part 2Katherine SauerNo ratings yet
- ReadingNotes Chapter06 StatsDocument2 pagesReadingNotes Chapter06 StatsKatherine SauerNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Analyzing Economic Problems 1.1 Why Study Microeconomics?Document4 pagesChapter 1: Analyzing Economic Problems 1.1 Why Study Microeconomics?Katherine SauerNo ratings yet
- Intermediate Microeconomic Theory Katherine M. Sauer, Ph.D. ECO 3010 AD 530-R 303-556-3037 Fall 2012 Ksauer5@msudenver - EduDocument5 pagesIntermediate Microeconomic Theory Katherine M. Sauer, Ph.D. ECO 3010 AD 530-R 303-556-3037 Fall 2012 Ksauer5@msudenver - EduKatherine SauerNo ratings yet
- Principles of MIcroeconomics - Worksheet - IntroductionDocument2 pagesPrinciples of MIcroeconomics - Worksheet - IntroductionKatherine SauerNo ratings yet
- Principles of MIcroeconomics - Reading Outline - IntroductionDocument3 pagesPrinciples of MIcroeconomics - Reading Outline - IntroductionKatherine SauerNo ratings yet
- IntMicro ReadingOutline Ch04 Consumer ChoiceDocument7 pagesIntMicro ReadingOutline Ch04 Consumer ChoiceKatherine SauerNo ratings yet
- IntMicro ReadingOutline Ch03 PreferencesDocument8 pagesIntMicro ReadingOutline Ch03 PreferencesKatherine SauerNo ratings yet
- ReadingNotes Chapter02 StatsDocument2 pagesReadingNotes Chapter02 StatsKatherine SauerNo ratings yet
- Model Summary TemplateDocument1 pageModel Summary TemplateKatherine SauerNo ratings yet
- IntMicro ReadingOutline Ch02 S D and EquilibriumDocument7 pagesIntMicro ReadingOutline Ch02 S D and EquilibriumKatherine SauerNo ratings yet
- ReadingNotes Chapter09 StatsDocument2 pagesReadingNotes Chapter09 StatsKatherine SauerNo ratings yet
- ReadingNotes Chapter08 StatsDocument2 pagesReadingNotes Chapter08 StatsKatherine SauerNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4: Non-Linear Functions 4.1 Quadratic, Cubic and Other Polynomial FunctionsDocument4 pagesChapter 4: Non-Linear Functions 4.1 Quadratic, Cubic and Other Polynomial FunctionsKatherine SauerNo ratings yet
- ReadingNotes Chapter07 StatsDocument3 pagesReadingNotes Chapter07 StatsKatherine SauerNo ratings yet
- PM Iceland Krona QuestionsDocument2 pagesPM Iceland Krona QuestionsKatherine SauerNo ratings yet
- PM Income Tax History QuestionsDocument2 pagesPM Income Tax History QuestionsKatherine SauerNo ratings yet
- ReadingNotes Chapter08 MathDocument2 pagesReadingNotes Chapter08 MathKatherine SauerNo ratings yet
- ReadingNotes Chapter01 StatsDocument5 pagesReadingNotes Chapter01 StatsKatherine Sauer100% (1)
- This Chapter Is Kind of Intense. I Don't Recommend Trying To Read Through The Whole Thing in One SittingDocument5 pagesThis Chapter Is Kind of Intense. I Don't Recommend Trying To Read Through The Whole Thing in One SittingKatherine SauerNo ratings yet
- PM Guilds QuestionsDocument2 pagesPM Guilds QuestionsKatherine SauerNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes - Big Mac IndexDocument2 pagesLecture Notes - Big Mac IndexKatherine SauerNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes - TaxesDocument3 pagesLecture Notes - TaxesKatherine SauerNo ratings yet
- Taxes Individuals Pay: Citizen's Guide To Economics Dr. Katie SauerDocument21 pagesTaxes Individuals Pay: Citizen's Guide To Economics Dr. Katie SauerKatherine SauerNo ratings yet
- Exam 2 Information SheetDocument3 pagesExam 2 Information SheetKatherine SauerNo ratings yet
- Lecture - Big Mac IndexDocument11 pagesLecture - Big Mac IndexKatherine SauerNo ratings yet
- Exam 3 Information SheetDocument1 pageExam 3 Information SheetKatherine SauerNo ratings yet