Professional Documents
Culture Documents
29
Uploaded by
sliversniper0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
28 views4 pagesFossil Fuels are formed from the remains of plants and animals which lived millions of years ago. Natural gas and petroleum are produced from the same source. Fractional distillation is used to refine petroleum and it is performed in an oil refinery.
Original Description:
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentFossil Fuels are formed from the remains of plants and animals which lived millions of years ago. Natural gas and petroleum are produced from the same source. Fractional distillation is used to refine petroleum and it is performed in an oil refinery.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
28 views4 pages29
Uploaded by
sliversniperFossil Fuels are formed from the remains of plants and animals which lived millions of years ago. Natural gas and petroleum are produced from the same source. Fractional distillation is used to refine petroleum and it is performed in an oil refinery.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
94 Part 7
Chapter 29 Fossil Fuels
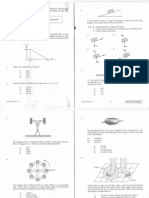
A. Multiple Choice Questions (b) Petroleum is not a good fuel. This is
because it is difficult to burn. When
1. D. 80 % it is burnt, it always undergoes
2. B. C5 C10 incomplete combustion to release a
3. A. petrol. large amount of black smoke and
4. B. Fuel for aeroplanes toxic chemicals. A large quantity of
5. C. 250 350 oC petroleum only releases a small
6. D Heavy Oil amount of energy (i.e. low
7. D. Gas oil efficiency of energy conversion).
8. B. fuel oil, diesel oil, kerosene, naphtha Moreover, petroleum is a very
9. D. Glass viscous and oily liquid. It is very
10. B. True, True difficult to transfer it from one
11. A. True, True container to another one.
(c) Natural gas and petroleum are
B. Fill in the Blanks produced from the same source.
They are formed from the dead
1. fuels remains of small marine plants and
2. Coal, petroleum, natural gas animals millions of years ago.
3. hydrocarbons (d) In industry, fractional distillation is
4. fractional distillation, boiling point ranges used to refine petroleum and it is
5. fractionating tower, trays, bubble caps performed in an oil refinery.
In the process of petroleum refining,
C. Comprehensive Questions petroleum is firstly heated to about
400 oC in a furnace. In the hot
1. Fossil fuels are formed from the remains petroleum, components with low
of plants and animals which lived millions boiling points vaporize while
of years ago. components with high boiling points
2. (a) Millions of years ago, when small remain as liquids. Hence, the
marine plants and animals died, they petroleum becomes a mixture of
sank to the bottom of the seas. Their vapours and liquids.
dead remains were covered by thick This mixture of petroleum is
layers of sand and mud. Heat, pumped into the bottom of a tall
pressure from upper layers and fractionating tower. The tower is
bacteria continued to act on them. divided into several horizontal
These dead remains gradually compartments by trays. There are
changed to petroleum. many bubble caps in each tray. They
ensure that the hot vapour must pass
through the previously condensed
liquid Hence, those components
with high boiling points must
condense. This increases the
Chapter 29 Solutions (EE).doc
Chapter 29 95
efficiency of separation. (c) A: Oil for machines / Making
In addition, the top of tower is at a candles (Any one)
lower temperature than the bottom B: Diesel fuel for buses and
because the top is far apart from the trucks / For cracking to give
furnace (i.e. the heat source). petrol (Any one)
The liquid components fall to the C: Jet fuel / Domestic fuel (Any
bottom while the vapour components one)
rise up the tower. When the vapour D: Raw material for town gas
components rise up from one E: Gaseous fuel
compartment to another, they pass (d) Volatility (ease of evaporation) /
through the bubble caps. The Viscosity / Flammability / Colour
components with high boiling points and sootiness of flame (Any two)
condense in the lower trays and they (e) Any two corresponding to (d)
are heavy fractions. The components Volatility (ease of evaporation):
with low boiling points continue to When the number of carbon atoms
rise up and condense in the higher in the molecules increases, the
trays. They are the light fractions. volatility decreases because the van
(e) der Waals’ forces between the
Fraction Use molecules increase.
Refinery gas Gaseous fuel Viscosity: When the number of
Petrol Fuel for cars carbon atoms in the molecules
Naphtha Raw material for increases, the viscosity increases
town gas because the van der Waals’ forces
Kerosene Jet fuel and between the molecules increase.
domestic fuel Flammability: When the number of
Gas oil / Diesel oil Diesel fuel for carbon atoms in the molecules
buses and trucks, increases, the flammability
for cracking to decreases because the van der
give petrol Waals’ forces between the molecules
Fuel oil Fuel for shops and increases. Thus, they are more
generating difficult to burn.
electricity; for Colour and sootiness of flame:
cracking to give When the number of carbon atoms
petrol in the molecules increases, the
Lubricating oil and Oil for machines; colour of the flame of changes from
waxes making candles yellow with blue edges to orange.
Bitumen For surfacing On the other hand, the flame
roads and roofs becomes more sooty.
3. (a) Fractionating tower (f) In the laboratory, it is difficult to
(b) A: Lubricating oil and waxes obtain the fractions with very high
B: Gas oil boiling points (i.e. >400 oC), but
C: Kerosene these fractions can be obtained in
D: Naphtha industry.
E: Refinery gas
Chapter 29 Solutions (EE).doc
96 Part 7
4. (a) Fractional distillation. (e) Fraction 1. This is because this
In fractional distillation, petroleum fraction is easy to burn and burn
is separated into different parts with a clear and non-sooty flame.
called fractions according to Thus, this fraction has the highest
different boiling point ranges. demand.
Different hydrocarbons in a fraction
have similar properties. Different 6. HKCEE Question
fractions have different properties to
serve different uses. 7. (a) (i) The glass wool is used to
(b) (i) When the number of carbon enable the petroleum to boil
atoms in the hydrocarbon smoothly.
molecules increases, the Petroleum should not be
viscosity increases. directly heated in the boiling
(ii) When the number of carbon tube; otherwise, the petroleum
atoms in the hydrocarbon boils rapidly and vigorously
molecules increases, their ease (i.e. bumping of petroleum). It
of evaporation decreases. becomes very difficult to
(c) Jet fuel / Domestic fuel (Any one) collect different fractions.
(d) (ii) The cold water is used to
condense the distillate.
(b) 10 360 oC thermometer is
suitable in the set up. This is
because some fractions have a high
boiling point (e.g. about 250 oC.)
(c) The fractions with a small number
of carbon atoms are highly
flammable.
(d) 1. Keep good ventilation in the
laboratory.
5. (a) Different fractions have different 2. Wear protective gloves when
boiling point ranges, so fractional handling petroleum. Avoid
distillation can separate petroleum contact with artificial
into different fractions. petroleum with skin.
(b) Fraction 1: refinery gas 3. Clamp the boiling tube quite
Fraction 2: petrol / naphtha tightly. Avoid applying too
Fraction 3: kerosene strong force when clamping;
Fraction 4: gas oil / diesel oil otherwise, the tube will be
(c) Fraction 4. This is because they broken.
have the largest number of carbon 4. Keep petroleum and its
atoms in the molecules. fractions far away from fire
(d) Fraction 4. This is because the because they are flammable.
molecules in this fraction have a (e) C14 – C25 and above. This is because
high number of carbon atoms, so this fraction has a very high boiling
they burn with sooty and a point. It cannot be obtained by this
non-luminous flame. method in the laboratory.
Chapter 29 Solutions (EE).doc
Chapter 29 97
8. The viscosity increases when the number
of carbon atoms in the molecules
increases. The increasing order of the
number of carbon atom in the molecules
of the fractions is:
petrol < kerosene < diesel oil < fuel oil
Therefore, the increasing order of the
viscosity of the fractions is:
petrol < kerosene < diesel oil < fuel oil
D. Essay-type Question
1. HKCEE Question
Chapter 29 Solutions (EE).doc
You might also like
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- 2005 CBR600RRDocument24 pages2005 CBR600RRanon_904072734No ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Workshop Manual DC09Document52 pagesWorkshop Manual DC09Henry Huayhua75% (8)
- Demolition SpecificationsDocument53 pagesDemolition SpecificationsHamza MamiNo ratings yet
- ESTIMATING COSTSDocument36 pagesESTIMATING COSTSgovindsinghsolankiNo ratings yet
- Roll CoolingDocument14 pagesRoll Coolingzakarii100% (1)
- High VoltageDocument28 pagesHigh VoltageDileep DudiNo ratings yet
- Idm 2018Document433 pagesIdm 2018veevthummuri100% (1)
- Bus Station Design ElementsDocument31 pagesBus Station Design ElementsRapha RachoNo ratings yet
- 2004paper IDocument10 pages2004paper IsliversniperNo ratings yet
- 2006paper 1 MarkingDocument11 pages2006paper 1 MarkingsliversniperNo ratings yet
- 2006 Paper 1Document28 pages2006 Paper 1sliversniperNo ratings yet
- CE Physics 2006 Paper2 (E)Document13 pagesCE Physics 2006 Paper2 (E)08150815whoimNo ratings yet
- 2005paper 2Document13 pages2005paper 2sliversniperNo ratings yet
- 2003 Paper I Marking SchemeDocument10 pages2003 Paper I Marking Schemeapi-3700944No ratings yet
- 2004paper IIDocument13 pages2004paper IIsliversniperNo ratings yet
- 2005paper 1Document16 pages2005paper 1sliversniperNo ratings yet
- 2004 Paper I Marking SchemeDocument12 pages2004 Paper I Marking SchemesliversniperNo ratings yet
- 1999paper IIDocument12 pages1999paper IIsliversniperNo ratings yet
- Physics 2003 Paper IIDocument14 pagesPhysics 2003 Paper IIapi-26423290No ratings yet
- 2003paper IDocument8 pages2003paper IsliversniperNo ratings yet
- 2002 Paper I Marking SchemeDocument9 pages2002 Paper I Marking Schemeapi-3700944No ratings yet
- Physics 2002 Paper IIDocument25 pagesPhysics 2002 Paper IIapi-26423290No ratings yet
- Physics 2000 PaperIIDocument14 pagesPhysics 2000 PaperIIapi-26423290No ratings yet
- Physics 2002 Paper 1Document20 pagesPhysics 2002 Paper 1api-3739499100% (2)
- Physics 2000 PaperIDocument19 pagesPhysics 2000 PaperIapi-26423290No ratings yet
- 1995paper IIDocument11 pages1995paper IIsliversniperNo ratings yet
- 1999paper IDocument8 pages1999paper IsliversniperNo ratings yet
- 1997paper IIDocument11 pages1997paper IIsliversniperNo ratings yet
- Physics 1998 PaperIDocument6 pagesPhysics 1998 PaperIapi-26423290No ratings yet
- Physics 1998 PaperIIDocument13 pagesPhysics 1998 PaperIIapi-26423290No ratings yet
- 1996paper IDocument8 pages1996paper IsliversniperNo ratings yet
- 1997paper IDocument8 pages1997paper IsliversniperNo ratings yet
- 1995paper I MarkingDocument10 pages1995paper I MarkingsliversniperNo ratings yet
- 1995paper IDocument8 pages1995paper IsliversniperNo ratings yet
- 1996paper IIDocument11 pages1996paper IIsliversniperNo ratings yet
- 1994paper I MarkingDocument9 pages1994paper I MarkingsliversniperNo ratings yet
- 1994paper IDocument8 pages1994paper IsliversniperNo ratings yet
- 1994paper IIDocument11 pages1994paper IIsliversniperNo ratings yet
- Welding Rod SelectionDocument1 pageWelding Rod Selectionbikas_sahaNo ratings yet
- Designing a 13 kW Pelton Water TurbineDocument10 pagesDesigning a 13 kW Pelton Water TurbineFanie-XNo ratings yet
- Analysis and Economical Design of Water TanksDocument6 pagesAnalysis and Economical Design of Water TanksBTENo ratings yet
- Split Type Air Conditioner Specifications and Installation ManualDocument34 pagesSplit Type Air Conditioner Specifications and Installation ManualMihaela CaciumarciucNo ratings yet
- Atomizer Study For Processing PGMDocument6 pagesAtomizer Study For Processing PGMAFLAC ............No ratings yet
- Design Theory of C FB BoilersDocument15 pagesDesign Theory of C FB Boilersanon_797717906No ratings yet
- Amplifier Owner'S Manual: Power AmplifiersDocument19 pagesAmplifier Owner'S Manual: Power AmplifiersJose Antonio Montiel QuirosNo ratings yet
- VIDA Phase 2 Brochure For WebDocument15 pagesVIDA Phase 2 Brochure For WebJaved Abdul JaleelNo ratings yet
- Ben Saturno Avenue, Barangay Sibut, San Jose City, Nueva Ecija Engr. Enrico G. Divina Gregorio, Mark Erwin P. Villaroman, Ronaldo BDocument3 pagesBen Saturno Avenue, Barangay Sibut, San Jose City, Nueva Ecija Engr. Enrico G. Divina Gregorio, Mark Erwin P. Villaroman, Ronaldo BRomeo VictorNo ratings yet
- The Embedded Design Life Cycle: - Product Specification - Hardware/software Partitioning - Hardware/software IntegrationDocument18 pagesThe Embedded Design Life Cycle: - Product Specification - Hardware/software Partitioning - Hardware/software IntegrationTejinder Singh SagarNo ratings yet
- 000 N EE 0020003 Rev1 Acoustic Insulation SpecificationDocument18 pages000 N EE 0020003 Rev1 Acoustic Insulation Specificationonur gunesNo ratings yet
- Emi Catalog LRDocument40 pagesEmi Catalog LRJon HimesNo ratings yet
- ABC Tile AdhesiveDocument1 pageABC Tile AdhesiveJyrus Jyles CadienteNo ratings yet
- Dust Collector ValvesDocument8 pagesDust Collector ValvesAnonymous lswzqloNo ratings yet
- Continuous Regenerative (Moving Bed) CCR PlatformingDocument4 pagesContinuous Regenerative (Moving Bed) CCR PlatformingAnnissa Nur HidayatiNo ratings yet
- Holiday TestDocument4 pagesHoliday TestSaptarshi MandalNo ratings yet
- Structured Cataalists and Reactors Ceramic CatalistDocument55 pagesStructured Cataalists and Reactors Ceramic CatalistBoby Royan Naira AzdlilNo ratings yet
- Agamograph Template BABBLE DABBLE DODocument3 pagesAgamograph Template BABBLE DABBLE DOMaria Ximena PolancoNo ratings yet
- CU-22L Tissue Culture Chamber: Lighting SystemDocument2 pagesCU-22L Tissue Culture Chamber: Lighting SystemAjay KumarNo ratings yet
- Makan Construction Real Estate New Home New York Buyer Harriman MonroeDocument22 pagesMakan Construction Real Estate New Home New York Buyer Harriman Monroekumar1023No ratings yet
- MGD2004D FL Ybs PDFDocument10 pagesMGD2004D FL Ybs PDFEverton DoradoNo ratings yet
- Perkins Manual BBDocument46 pagesPerkins Manual BBpawar_kinjal110No ratings yet