Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Eau 052 Alternative Energy Sources For Automobiles L T P
Uploaded by
shubhs5810Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Eau 052 Alternative Energy Sources For Automobiles L T P
Uploaded by
shubhs5810Copyright:
Available Formats
EAU 052 ALTERNATIVE ENERGY SOURCES FOR AUTOMOBILES
LTP 310
UNIT-I Introduction: Need for non conventional energy sources. Energy alternative : solar, photo-voltaic, Hydrogen, Biomass. Electrical - their merits and demerits. UNIT-II Solar photo-voltaic conversion, Collection and storage of solar energy, collection devices, flat plate collectors,concentrating type collectors, principles and working of photo-voltaic Conversion, Applications to automobiles. UNITIII Energy from Bio mass: Photosynthesis, photosynthetic oxygen production, energy plantation. Bio gas production from organic waste, description of Bio gas plant, types of Bio gas plants, problems involved in production and transportation. Application of Bio gas in engines as a single fuel and dual fuel modification -Merits and demerits performance characteristics and their comparison. UNIT-IV Hydrogen Energy: Properties of Hydrogen, sources of Hydrogen, Thermodynamics of water splitting Production of Hydrogen, Electrolysis of water. Thermal decomposition of water. Thermo-chemical production,Biochemical production. UNIT-V Hydrogen fuel, Storage and Transportation methods, Applications to engines modifications necessary, precautions ad safety measures - Performance characteristics in Engine and their comparison. UNIT-VI Electric Automobiles: Design considerations, limitations, opportunities for improvement Batteries, problems,future possibilities , capacities, types , material requirement, Applicability of electric cars, comparative use of fuel and energy. Availability of energy for recharging, impacts on use of fuel and energy .impact on urban air quality, impact on price, material requirement Traction motors and types. UNIT-VII Vegetable Oils: Various vegetable oils for engines-Esterification-Performance in engines-Performance and emission characteristics. UNIT-VIII Use of gas turbines in cars, arrangement, control merits and de- merits. Design of turbochargers for automobiles,their usefulness on the performance.
EAU 063 HYDRALIC & PNEUMATIC SYSTEMS
OBJECTIVE:
LTP 310
The course aims to make student understand the structure and the properties of the fluid. To understand and appreciate the complexities involved in solving the fluid flow problems. To understand the mathematical techniques already in vogue and apply them to the solutions of practical flow problems. To understand the energy exchange process in fluid mechanics handling incompressible fluids. UNIT-I BASIC CONCEPT & PROPERTIES Fluid - definition, distinction between solid and fluid - Units and dimensions - Properties of fluids density, specific weight, specific volume, specific gravity, temperature, viscosity, compressibility, vapour pressure, capillary and surface tension - Fluid statics: concept of fluid static pressure, absolute and gauge pressure measurements by manometers and pressure gauges. UNIT-II: FLUIDKINEMATICS AND FLUID DYNAMICS Fluid Kinematics - Flow visualization - lines of flow - types of flow -velocity field and acceleration continuity equation (one and three dimensional differential forms)- Equation of streamline - stream function - velocity potential function - circulation - flow net. Equations of motion- Euler's equation along a streamline - Bernoulli's equation - applications - venturi meter. Orifice meter, other flow measurement instruments, Pilot Tube. UNIT-III
DIMENSIONAL ANALYSIS
Dimensional numbers, their application. - Buckingham's theorem - applications - similarity laws and
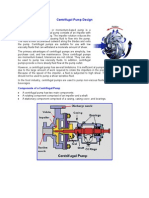
models. UNIT -IV: INCOMPRESSIBLE FLUIDFLOW Viscous flow-Navier- Stroke's equation (Statement only) - Shear stress, pressure gradient relationship laminar flow between parallel plates - Laminar flow through circular tubes (Hagen poiseulle's) Hydraulic and energy gradient - flow through pipes - Darcy - weisback's equation - pipe roughness friction factor - Mody's diagram - minor losses - flow through pipes in series and in parallel - power transmission - Boundary layer flows, boundary layer thickness, boundary layer separation - drag and lift coefficients. UNIT V HYDRAULICTURBINES^HYDRAULICPUMPS, COMPRESSOR & FANS Impact of jet on flat, curved & moving plates -Fluid machines: definition and classification exchange of energy - Euler's equation for turbo machines - Construction of velocity vector diagram's - bead and specific work - component of energy transfer - degree of reaction. Pumps: definition and classifications - Centrifugal pump: classifications, working principles, velocity triangles, specific speed, efficiency and performance curves - reciprocating pump: classification, working principles, indicator diagram., work saved by air vessels and performance curves - cavitations in pumps rotary pumps: working principles of gear and vane pumps. Definition - Classification difference, efficiency,performance curves special application in Auto mobile Industries.
EOE- 083: PRODUCT DEVELOPMENT
LTP 310
UNIT-1 Concept of Product, definition and scope. Design definitions, old and new design methods, design by evolution, examples such as evolution of sewing M/C, bicycle, safety razor etc., need based developments, technology based developments physical relaibility & economic feasibility of design concepts. UNIT II Murphology of design, divergent, transformation and convergent phases of product design, identification of need, Analysis of need. Design criteria; functional, aesthetics, ergonomics, form, shape, size, colour. Mental blocks, Removal blocs, Ideation techniques, Creativity, Check list. UNIT III Transformations, Brainstorming& Synetics, Morephological techniques. Utility Concept, Utility Valaue, Utility Index, Decision making under Multiple Criteria. Economic aspects, Fixed and variable costs, Break-even analysis. UNIT-IV Reliability considerations, Bath tub curve, Reliability of systems in series and parallel, Failure rate, MTTF and MTBF, Optimum spares from Reliability considerations. Design of display and controls, Man-machine interface, Compatibility of displays and controls. Ergonomic aspects, Anthroprometric data and its importance in design. Application of Computers in Product development & design. UNIT-V Existing techniques, such as work-study, SQC etc. for improving method & quality of product. Innovation versus Invention. Technological Forecasting. Use of Standards for Design.
EAU 801 : Trouble shooting, Servicing & Maintenance of Automobile
LTP 310
UNIT I Automobile maintenance : Importance of maintenance, scheduled and unscheduled maintenance. preparation of
check lists, analysis of breakdown, preventive measures, unit replacement system, maintenance schedule, chassis lubrication schedule, component retrieval, estimating repair cost, maintenance record, warranty period, servicing. Inspection forms. Log books. Trip sheets. Other maintenance record forms. Garage practice : Types of service station/garage, layout of garage. Factors affecting layout, tools & equipments, transport service undertakings, design a layout for different garage. 8 UNIT II Engine Maintenance : Dismantling of engine components, cleaning methods, visual inspection and dimensional check of various engine components, minor and major tune up, reconditioning and repairing methods of engine components. Assembly procedure, special tools used for maintenance, repair and overhauling. 5 Cooling Systems-Anti corrosion and antifreeze solutions, radiator, and thermostat. Lubrication oil topping up, oil change, oil relief valve; fuel feed systems, FIP adjustment and testing, injector testing. 5 UNIT III Chassis and drive line maintenance: Mechanical automotive type gear box- mechanical automatic types. Final reduction, propeller shaft, front and rear suspension systems, brake systems-hydraulic, servo, air. Air bleeding, steering system, axles, wheel alignment-tires. 7 UNIT IV Electric system maintenance : Battery testing method, starter motor, charging system - a DC generator, AC alternator, regulator, ignition system- coil ignition, transistor assisted ignition, capacitor discharge ignition. Electric horn, wiper motor, flasher, electric fuel pump, gauges. Lighting system- head lights focusing. Wiring harness testing. 7 UNIT V Body repair : Minor body panel beating, tinkering, shouldering. Painting : Introduction of automotive paints, types of paints, corrosion and anticorrosion method, rubbing polishing, working of paint booth, door lock mechanism, window glass actuation mechanism. 8
You might also like
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Lectures On Computational Fluid DynamicsDocument205 pagesLectures On Computational Fluid DynamicsAbhiyan PaudelNo ratings yet
- Flow in Open Channel Lab Report AnalysisDocument24 pagesFlow in Open Channel Lab Report AnalysisIkhwan Z.60% (10)
- Applied Supersonic Aerodynamics TrainingDocument33 pagesApplied Supersonic Aerodynamics TrainingnathanNo ratings yet
- HydromechanicsDocument183 pagesHydromechanicsReza GoldaranNo ratings yet
- Zeta PotentialDocument16 pagesZeta PotentialAbdelrhman AboodaNo ratings yet
- A-Pdf Merger DemoDocument36 pagesA-Pdf Merger DemoAvulsedBRNo ratings yet
- Notes Lecture 2 Fluid StaticsDocument42 pagesNotes Lecture 2 Fluid StaticsPranavMehtaNo ratings yet
- CMOS Biotechnology - H. Lee, D. Ham, R. Westervelt (Springer, 2007) WW PDFDocument394 pagesCMOS Biotechnology - H. Lee, D. Ham, R. Westervelt (Springer, 2007) WW PDFMaria StancuNo ratings yet
- Corrugated Plate Separator (CPS) enDocument2 pagesCorrugated Plate Separator (CPS) enzubair19500% (1)
- Pressure Drop Compressible FlowDocument14 pagesPressure Drop Compressible Flowdilip matalNo ratings yet
- Centrifugal Pump DesignDocument2 pagesCentrifugal Pump Designaby jacobNo ratings yet
- Eeuo Part3 Part3Document2 pagesEeuo Part3 Part3Kelli FloresNo ratings yet
- Tib 10 Pump InducersDocument5 pagesTib 10 Pump InducersscubazNo ratings yet
- Hydro HomeworkDocument5 pagesHydro HomeworkChristian Cannon0% (1)
- SCALE EFFECTS in OWTDocument35 pagesSCALE EFFECTS in OWTJUNIOR JAVIER OLIVO FARRERANo ratings yet
- 300+ (UPDATED) Thermal Engineer Interview Questions 2023Document8 pages300+ (UPDATED) Thermal Engineer Interview Questions 2023Shahameer KooushikNo ratings yet
- Osborne Reynolds ExperimentDocument9 pagesOsborne Reynolds ExperimentchamalNo ratings yet
- Flow of Fluids through Fluidised BedDocument27 pagesFlow of Fluids through Fluidised BedAndersen YunanNo ratings yet
- CFD Course Plan Introduction Modules ApplicationsDocument2 pagesCFD Course Plan Introduction Modules ApplicationsArun MahalingamNo ratings yet
- Bab 4 OkeDocument16 pagesBab 4 OkeDwi amandaNo ratings yet
- Series N55B-M1 and LFN55B-M1 Installation InstructionsDocument2 pagesSeries N55B-M1 and LFN55B-M1 Installation InstructionsWattsNo ratings yet
- 3 - Hydrostatic Force - Tutorial SolutionDocument27 pages3 - Hydrostatic Force - Tutorial Solutionbakrichod100% (1)
- Honors Fluid Dynamics Worksheet (Includes BernoulliDocument1 pageHonors Fluid Dynamics Worksheet (Includes BernoulliAdiyat MakrufiNo ratings yet
- Etiquetas BelcorpDocument1 pageEtiquetas Belcorpesteban sarmientoNo ratings yet
- Coping With Low NPSHA (LinkedIn Article by Behnaz Motamed)Document4 pagesCoping With Low NPSHA (LinkedIn Article by Behnaz Motamed)Behnaz MotamedNo ratings yet
- EPT07t06A Centrifugal PumpsDocument45 pagesEPT07t06A Centrifugal Pumpsapa apaapaNo ratings yet
- Ansys FluidsDocument232 pagesAnsys Fluidscapitan55No ratings yet
- Johnson / Evinrude: Kits Reparacion Bombas Agua - Water Pump KitsDocument9 pagesJohnson / Evinrude: Kits Reparacion Bombas Agua - Water Pump KitsCristianNo ratings yet
- FLUID MECHANICS Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument8 pagesFLUID MECHANICS Multiple Choice QuestionsleGionNo ratings yet
- Lab Report Food Chem Exp 1 FullDocument8 pagesLab Report Food Chem Exp 1 FullNur AsiahNo ratings yet