Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Intro Lecture Notes Ch04 Government II
Uploaded by
Katherine SauerOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Intro Lecture Notes Ch04 Government II
Uploaded by
Katherine SauerCopyright:
Available Formats
Economics Dr.
Sauer
Lecture Chapter 4: Government II There are 3 main roles for government: 1. make markets possible 2. deal market failures - externalities - public goods 3. do some wealth redistribution
Keep in mind: There are things the government __________________ to make things better. There are things the government is ________________ under the influence of political incentives and constraints.
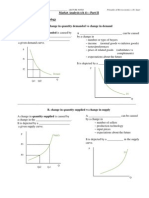
I. Government and Efficiency We do need ___________ government. However, more government isnt necessarily _______________. Explain.
Governments are often described as being ________________. They actually operate exactly as wed expect, given their _______________. -Government has a monopoly in many cases. DMV example
Post Office example
Unless the market is _____________, there is not a compelling reason to have the _____________provide the good. providing the good producing the good itself
When the government is controlling the allocation of resources, it is _____________ and ____________ who are making the decision. - political considerations When the market controls the allocation of resources, they go where theyll earn the _______________. - amoral - supply and demand 1
II. Regulations Some government regulations may be beneficial to some parties, but _______regulations come with a ______________. Why did Milton Friedman argue that more lawyers should be allowed into the practice? Why did many existing lawyers disagree?
Why did the workers in Delhi, India protest the regulation that was imposed in order to clean up pollution?
Some regulations are favored by people who have the _________________ of caring. - DDT example
Not all regulations are _______________________. - striped bass example
Often times a _______________________ pushes for government regulations in their industry to ______________________________. - interior design licenses Sometimes the government acts like a _____________ hand and sometimes like a _________________ hand. Explain.
III. Optimal Size of Government Economics can point out the _______________________, but youll have your own opinion. Framework for thinking about the role of the government in the economy: 1. Government has the potential to enhance the ________________________ of the economy and make us better off as a result. - legal framework - public goods - externalities 2. Some government activity shrinks the size of the pie, but still may be _____________________. - technically inefficient to transfer wealth - many people want some sort of social safety net 3. Some government involvement in the economy is purely ______________________. - good intentions arent enough - some regulations have costs that outweigh the benefits
IV. Taxes Even when the government is engaging in good activities, it must __________________ its spending through taxes. All taxes exert a ___________ on the economy.
The costs of taxes: - fiscal drag - deadweight loss - discourage investment To ___________________ the costs of taxes, economists favor taxes that are: broad simple fair
V. US Government Spending, Deficit, and Debt Bureau of Economic Analysis bea.gov
In 2010, the governments in the US took in $____________trillion. In 2010, households paid $___________ trillion in taxes. producers and importers paid $ __________ trillion in taxes. corporations paid $ ___________ billion in taxes.
In 2010, people and firms paid in $___________billion for social insurance programs.
In 2010, the governments spent $___________trillion on things like national defense, parks, education, and government employees salaries. $___________trillion on things transfer programs like social security. $___________billion on interest on debt. $__________billion on subsidies.
To find out where your income taxes are going: Federal: http://www.whitehouse.gov/taxreceipt Colorado: http://www.colorado.gov/taxtracks/
To find the amount of the yearly deficit, take total receipts minus total expenditures.
When the US government spends more than it collects in taxes, it ________________ to make up the difference. A bond is like an IOU. - People who buy bonds are lending the government money now. -The government promises to pay them back later.
U.S. debt is now equal to economy By Richard Wolf USA Today 1/8/2012 WASHINGTON The soaring national debt has reached a symbolic tipping point: It's now as big as the entire U.S. economy. The amount of money the federal government owes to its creditors, combined with IOUs to government retirement and other programs, now tops $15.23 trillion. That's roughly equal to the value of all goods and services the U.S. economy produces in one year: $15.17 trillion as of September, the latest estimate. Private projections show the economy likely grew to about $15.3 trillion by December a level the debt is likely to surpass this month. "The 100% mark means that your entire debt is as big as everything you're producing in your country," says Steve Bell of the Bipartisan Policy Center, which has proposed cutting nearly $6 trillion in red ink over 10 years. "Clearly, that can't continue." Long-term projections suggest the debt will continue to grow faster than the economy, which would have to expand by at least 6% a year to keep pace. President Obama's 2012 budget shows the debt soaring past $26 trillion a decade from now. Last summer's deficit reduction deal could reduce that to $24 trillion. Many economists, such as the Brookings Institution's William Gale, say a better measure of the nation's debt is how much the government owes creditors, not counting $4.7 trillion owed to future Social Security recipients and other government beneficiaries. By that measure, the debt is roughly a third less: $10.5 trillion, or nearly 70% the size of the economy. That is still high by historic standards. The total national debt topped the size of the economy for three years during and after World War II. It dropped to 32.5% of the economy by 1981, then began a steady climb under President Reagan, doubling over the next 12 years. The combination of recession and stimulus spending caused it to soar again under Obama. Among advanced economies, only Greece, Iceland, Ireland, Italy, Japan and Portugal have debts larger than their economies. Greece, Ireland, Portugal and Italy are at the root of the European debt crisis. The first three needed bailouts from European central banks; Italy's books are monitored by the International Monetary Fund. The White House and Congress agreed in August to cut about $1 trillion from federal agencies over 10 years. An additional $1.2 trillion in automatic spending cuts looms beginning next year if lawmakers can't agree on a better way to do it. Economist Mark Zandi of Moody's Analytics says reaching the 100% mark shows "the grave need to address our long-term fiscal problems."
From the CBO: Projected Outlays and Revenues as % of GDP
Bonus: http://www.federalbudgetchallenge.org/budget_challenge/sim/budget_master.html
__________________________________________________________________________________ Summary Governments are often inefficient, due to incentives. Regulations can be helpful or harmful, they all come with costs, and good intentions are not enough. Economics gives a framework for considering the optimal size of government. Taxes are necessary but also impose costs. The government spends more than it collects.
You might also like
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- CIR v. General Foods Deduction for Media AdvertisingDocument2 pagesCIR v. General Foods Deduction for Media AdvertisingJacob Dalisay100% (3)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- THE HISTORY OF MONEY PART 1Document25 pagesTHE HISTORY OF MONEY PART 1skhicksNo ratings yet
- Sample Partnership AgreementDocument38 pagesSample Partnership AgreementAlex VolkovNo ratings yet
- Withholding Tax Configuration in Sap - Sap Concept HubDocument4 pagesWithholding Tax Configuration in Sap - Sap Concept HubAnanthakumar ANo ratings yet
- SUBA (Detailed) - Gutierrez v. CIRDocument3 pagesSUBA (Detailed) - Gutierrez v. CIRPaul Joshua SubaNo ratings yet
- Financial Model of New RestaurantDocument42 pagesFinancial Model of New RestaurantPrabhdeep Dadyal0% (1)
- KLM 2020Document214 pagesKLM 2020Fendy FendersonNo ratings yet
- Awareness On E-Filing and Tax ReturnsDocument51 pagesAwareness On E-Filing and Tax ReturnsHemanth kumar100% (1)
- Principles of MIcroeconomics - Lecture - Markets/Supply/Demand - Part 2Document17 pagesPrinciples of MIcroeconomics - Lecture - Markets/Supply/Demand - Part 2Katherine Sauer100% (1)
- Reading Notes Economics - Dr. SauerDocument6 pagesReading Notes Economics - Dr. SauerKatherine SauerNo ratings yet
- Financial Wellness Programming: An Administrative PerspectiveDocument16 pagesFinancial Wellness Programming: An Administrative PerspectiveKatherine SauerNo ratings yet
- Principles of MIcroeconomics - Notes - Markets/Supply/Demand - Part 2Document4 pagesPrinciples of MIcroeconomics - Notes - Markets/Supply/Demand - Part 2Katherine SauerNo ratings yet
- ReadingNotes Chapter06 StatsDocument2 pagesReadingNotes Chapter06 StatsKatherine SauerNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Analyzing Economic Problems 1.1 Why Study Microeconomics?Document4 pagesChapter 1: Analyzing Economic Problems 1.1 Why Study Microeconomics?Katherine SauerNo ratings yet
- Intermediate Microeconomic Theory Katherine M. Sauer, Ph.D. ECO 3010 AD 530-R 303-556-3037 Fall 2012 Ksauer5@msudenver - EduDocument5 pagesIntermediate Microeconomic Theory Katherine M. Sauer, Ph.D. ECO 3010 AD 530-R 303-556-3037 Fall 2012 Ksauer5@msudenver - EduKatherine SauerNo ratings yet
- Principles of MIcroeconomics - Worksheet - IntroductionDocument2 pagesPrinciples of MIcroeconomics - Worksheet - IntroductionKatherine SauerNo ratings yet
- Principles of MIcroeconomics - Reading Outline - IntroductionDocument3 pagesPrinciples of MIcroeconomics - Reading Outline - IntroductionKatherine SauerNo ratings yet
- IntMicro ReadingOutline Ch04 Consumer ChoiceDocument7 pagesIntMicro ReadingOutline Ch04 Consumer ChoiceKatherine SauerNo ratings yet
- IntMicro ReadingOutline Ch03 PreferencesDocument8 pagesIntMicro ReadingOutline Ch03 PreferencesKatherine SauerNo ratings yet
- ReadingNotes Chapter02 StatsDocument2 pagesReadingNotes Chapter02 StatsKatherine SauerNo ratings yet
- Model Summary TemplateDocument1 pageModel Summary TemplateKatherine SauerNo ratings yet
- IntMicro ReadingOutline Ch02 S D and EquilibriumDocument7 pagesIntMicro ReadingOutline Ch02 S D and EquilibriumKatherine SauerNo ratings yet
- ReadingNotes Chapter09 StatsDocument2 pagesReadingNotes Chapter09 StatsKatherine SauerNo ratings yet
- ReadingNotes Chapter08 StatsDocument2 pagesReadingNotes Chapter08 StatsKatherine SauerNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4: Non-Linear Functions 4.1 Quadratic, Cubic and Other Polynomial FunctionsDocument4 pagesChapter 4: Non-Linear Functions 4.1 Quadratic, Cubic and Other Polynomial FunctionsKatherine SauerNo ratings yet
- ReadingNotes Chapter07 StatsDocument3 pagesReadingNotes Chapter07 StatsKatherine SauerNo ratings yet
- PM Iceland Krona QuestionsDocument2 pagesPM Iceland Krona QuestionsKatherine SauerNo ratings yet
- PM Income Tax History QuestionsDocument2 pagesPM Income Tax History QuestionsKatherine SauerNo ratings yet
- ReadingNotes Chapter08 MathDocument2 pagesReadingNotes Chapter08 MathKatherine SauerNo ratings yet
- ReadingNotes Chapter01 StatsDocument5 pagesReadingNotes Chapter01 StatsKatherine Sauer100% (1)
- This Chapter Is Kind of Intense. I Don't Recommend Trying To Read Through The Whole Thing in One SittingDocument5 pagesThis Chapter Is Kind of Intense. I Don't Recommend Trying To Read Through The Whole Thing in One SittingKatherine SauerNo ratings yet
- PM Guilds QuestionsDocument2 pagesPM Guilds QuestionsKatherine SauerNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes - Big Mac IndexDocument2 pagesLecture Notes - Big Mac IndexKatherine SauerNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes - TaxesDocument3 pagesLecture Notes - TaxesKatherine SauerNo ratings yet
- Taxes Individuals Pay: Citizen's Guide To Economics Dr. Katie SauerDocument21 pagesTaxes Individuals Pay: Citizen's Guide To Economics Dr. Katie SauerKatherine SauerNo ratings yet
- Exam 2 Information SheetDocument3 pagesExam 2 Information SheetKatherine SauerNo ratings yet
- Lecture - Big Mac IndexDocument11 pagesLecture - Big Mac IndexKatherine SauerNo ratings yet
- Exam 3 Information SheetDocument1 pageExam 3 Information SheetKatherine SauerNo ratings yet
- GST Audit Amendment Notes by Pankaj GargDocument12 pagesGST Audit Amendment Notes by Pankaj GargGopal Airan100% (2)
- Market Value Vs Fair MV - 1Document7 pagesMarket Value Vs Fair MV - 1Jigesh MehtaNo ratings yet
- Burgum July QuarterlyDocument767 pagesBurgum July QuarterlyRob PortNo ratings yet
- Module4 AE26 ITDocument7 pagesModule4 AE26 ITJemalyn PiliNo ratings yet
- Robert Nelson, The Philippine Economic MysteryDocument44 pagesRobert Nelson, The Philippine Economic Mysteryjustadorkyyy100% (1)
- Government Without Any Expectation of Direct Return in Benefit ". Ability To Pay. Taxed in The Same Way Without Any DiscriminationDocument42 pagesGovernment Without Any Expectation of Direct Return in Benefit ". Ability To Pay. Taxed in The Same Way Without Any DiscriminationyebegashetNo ratings yet
- Offer Letter for SKOL Breweries SharesDocument16 pagesOffer Letter for SKOL Breweries SharesvmmalviyaNo ratings yet
- Mutual Shoe Company v. Commissioner of Internal Revenue, 238 F.2d 729, 1st Cir. (1956)Document7 pagesMutual Shoe Company v. Commissioner of Internal Revenue, 238 F.2d 729, 1st Cir. (1956)Scribd Government DocsNo ratings yet
- Work Book PDFDocument25 pagesWork Book PDFvinulalNo ratings yet
- Fiscal IzationDocument4 pagesFiscal IzationMilan JankovicNo ratings yet
- Tax Accounting Assignment Solution and ComputationDocument10 pagesTax Accounting Assignment Solution and Computationsamuel debebeNo ratings yet
- 5 Fort Bonifacio Development Corporation Vs Cir Consolidated 2Document45 pages5 Fort Bonifacio Development Corporation Vs Cir Consolidated 2Nikki Diane CadizNo ratings yet
- Avenue E-Commerce Limited: You SavedDocument1 pageAvenue E-Commerce Limited: You SavedRahul KeniNo ratings yet
- Basic math quiz with 21 multiple choice questionsDocument11 pagesBasic math quiz with 21 multiple choice questionsHeliosNo ratings yet
- Modules 4-6 - Comprehensive Problem - Answer SheetDocument26 pagesModules 4-6 - Comprehensive Problem - Answer SheetLeizyl de MesaNo ratings yet
- EITCDocument2 pagesEITCrobertwiblinNo ratings yet
- Billing Address: Tax InvoiceDocument1 pageBilling Address: Tax InvoiceManojkumar DNo ratings yet
- Indian Petroleum and Natural Gas Statistics 2016-17Document222 pagesIndian Petroleum and Natural Gas Statistics 2016-17Sumantrra ChattopadhyayNo ratings yet
- Vikrant Tyres Plant History and MilestonesDocument51 pagesVikrant Tyres Plant History and MilestonesUdayveerSinghNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 General Principles and Concepts of TaxationDocument14 pagesChapter 1 General Principles and Concepts of TaxationDea Lyn Bacula25% (4)
- The Full Truth About FastracksDocument24 pagesThe Full Truth About FastracksIndependence InstituteNo ratings yet
- Commissioner of Customs vs. ReluniaDocument5 pagesCommissioner of Customs vs. Reluniaelna ocampoNo ratings yet