Professional Documents
Culture Documents
NCP
Uploaded by
msinsanoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
NCP
Uploaded by
msinsanoCopyright:
Available Formats
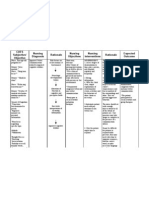
DATE /TIME
CUES
NEEDS
NSG. DIAGNOSIS
OBJECTIVE OF CARE
INTERVENTION
EVALUATION
M A R C H
Subjective cue: Ginagmay lng
S L E E P
Sleep pattern Within 2 days 1. disturbance related span of
Assess
client
and
Goal partially
care, family usual sleep pattern, met, within 2 changes and at that what the have days span of was care, time. patient was the was
akong tulog mam as verbalized by the patient.
to the patient will any
mental illness be able to sleep occurred, secondary to for Bipolar about 6-8 happening if
1 hours per night Identify without disturbances.
there event
a able to sleep
2, Objective cues: 2011 y poor sleep pattern (2-3 hours per night) T y Frequent P A
Disorder Manic Phase.
precipitating
around for about 4-5
onset of sleep problem or if hours per night its chronic. Information from without both client and family disturbances. sleep
clarifies Scientific
specific
disturbance.
Yawning y y y y Restlessness Irritability Lethargy dark circles under eyes y Daytime
T E R N
Basis: Studies indicate abnormal sleep electroencep halograms in many individuals with mood disorders. This has led to the theory that disorder mood many
2.
Instruct patient to
follow as consistent a daily schedule for retiring and arising as possible. This promotes regulation of the circadian rhythm, and reduces the energy required for adaptation to changes. 3. Instruct to avoid large
Sleepiness y y Poor eye contact Decrease attention span y decrease ability to function
fluid intake before bedtime. This helps patients who otherwise may need to void during the night. 4. Increase daytime
physical activities as
reflects abnormal regulation of circadian rhythm Source: Doenges, Moorhuse and Murr. 2011.Davis Nurses Pocket Guide. Edition 12th
indicated. This reduces stress and promotes sleep. 5. Discourage pattern of
daytime naps unless deemed necessary to meet sleep requirements or if part of ones usual pattern. Napping can disrupt normal sleep patterns; however, elderly patients do better with frequent naps during the day to counter their shorter nighttime sleep schedules. 6. Suggest to client that if
he does not feel drowsy after 20 minutes, get up and
engage in quiet activity that is boring- not stimulating. Waiting that will not come can increase anxiety and frustration. Doing something monotonous at bedtime might have the client become drowsy. 7. Develop a sleep
relaxation program with client (e.g., progressive muscle imagery). both physical
relaxation, Employing
and mental relaxation can help minimize anxiety and promote sleep.
8.
Review sleep hygiene with the client.
measures
Determine if the client does any of the ff: refrain from naps, alcohol and caffeine at night; follow a regular retiring and arising schedule;
exercise pattern. Identifying baseline helps target
needed interventions.
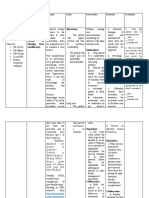
DATE /TIME
CUES
NEEDS
NSG. DIAGNOSIS
PLAN OF CARE
INTERVENTION
EXPECTED OUTCOME
M A R C H
Subjective:
S E L
Objective cues: Somatic Delusion Flight of ideas Circumstantiality Excessive talking Decrease attention span y Poor eye contact
y 2, y y 2011 y y
P E R C
Risk for Impaired Within 1 hour 1. Establish rapport to the social interaction span of care, patient. establishing related to patient will be rapport will promote disturbed able to develop participation and trust. thought process trusting 2. Observe patient while secondary to relationship relating to family. To Bipolar 1 with the note prevalent Disorder Manic student nurse interaction pattern. Phase. within the 3. Determine patients use of reasonable coping skills and defense period of time. mechanism affects Scientific ability to be involved in
Within 1 hour span of care, patient was
able to develop trusting relationship with student within reasonable period of time. the nurse the
E P T I O N
Basis: Impaired social
social situation. 4. Provide positive reinforcement for improvement in social behaviors and interaction. or encourages continuation of desired behaviors and effort s for change. 5. Correct clients
interaction is an insufficient excessive quantity ineffective quality of social exchange. REFERENCE: Doenges, Moorhuse Murr. Davis Pocket and 2011. Nurses Guide. or
description of inaccurate perception, and describe the situation as it exists in reality. Explanation of, and participation in, real situations and real
12th Edition
activities interferes with the ability to respond delusions or hallucinations. 6. Do not argue or deny the belief. Use reasonable doubt as a therapeutic technique. Arguing with the client or denying the belief serves no useful purpose, because delusional ideas are not eliminated by approach and the development of a trusting relationship
may be impeded. 7. Give positive reinforcement when client is able to differentiate between reality- based and non-reality- based thinking. Positive reinforcement enhances self- esteem and encourages repetition of desirable behaviors. 8. Provide supportive group therapy when indicated. Positive feedback from group members will increase self- esteem.
9. Provided feedback to patients negative feelings. To allow the patient experience different views. 10. Encourage to validate perception with others. help patient prioritize those behaviors needing change.
You might also like
- Pharm MnemonicsDocument33 pagesPharm MnemonicsThomson George75% (4)
- New EFT Level 1 ManualDocument64 pagesNew EFT Level 1 Manualemofree100% (6)
- Vocal Health and HygieneDocument50 pagesVocal Health and HygieneclaugmailNo ratings yet
- Treatment Principle BasicsDocument7 pagesTreatment Principle BasicsCarlCordNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Voice PresentationDocument16 pagesPediatric Voice Presentationapi-254429093No ratings yet
- Saudi Prometric Latest Questions AndanswerDocument67 pagesSaudi Prometric Latest Questions AndanswerGloria Jaison100% (4)
- Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Implementio N EvaluationDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan: Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Implementio N EvaluationAndrew James Javier Quidez100% (1)
- Cholera FinalDocument57 pagesCholera FinalBinayaNo ratings yet
- NCP CompilationDocument11 pagesNCP CompilationRene John FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Psych NCPDocument5 pagesPsych NCPJannen Casas100% (3)
- Pregnant Aerobics Instructor Case StudyDocument25 pagesPregnant Aerobics Instructor Case StudyGerly LagutingNo ratings yet
- Group NCPDocument17 pagesGroup NCPNiña Noreen Torres VallegaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan FinalDocument16 pagesNursing Care Plan FinalErickson OcialNo ratings yet
- Farm NoteDocument3 pagesFarm NoteSreya Sanil50% (2)
- NCP PsychosisDocument3 pagesNCP Psychosisinagasi100% (7)
- Diagnostic Test - Pedia With Answer 50 Items Without RatioDocument4 pagesDiagnostic Test - Pedia With Answer 50 Items Without RatioDennis Nabor Muñoz, RN,RMNo ratings yet
- Reading Sub-Test: Answer Key - Part ADocument23 pagesReading Sub-Test: Answer Key - Part AAlwin BrightNo ratings yet
- Bipolar NCPDocument4 pagesBipolar NCPcandy19agustin100% (1)
- IFUGAO ORIGINSDocument3 pagesIFUGAO ORIGINSmsinsano67% (3)
- Asthma Nursing Care Plan NCP Ineffective Airway Clearance CompressDocument2 pagesAsthma Nursing Care Plan NCP Ineffective Airway Clearance CompressMargarette GeresNo ratings yet
- Subjective Cues: Short Term Goal: Short Term GoalDocument3 pagesSubjective Cues: Short Term Goal: Short Term GoalPia Mae BuayaNo ratings yet
- 1 Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument8 pages1 Ineffective Airway ClearanceEsel Mae DinamlingNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Nikolai P. Funcion, FSUU-SNDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan: Nikolai P. Funcion, FSUU-SNNikolai FuncionNo ratings yet
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Outcome Nursingintervention Rationale Evaluation Discharge PlanningDocument5 pagesCues Nursing Diagnosis Outcome Nursingintervention Rationale Evaluation Discharge PlanningBSN 3B-Bulatao,Goergie Ann L. CPUSNNo ratings yet
- Catatan Koas THT 1Document5 pagesCatatan Koas THT 1MEDS easyNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Format Name: - Medical Diagnosis: - DateDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Format Name: - Medical Diagnosis: - DateSheryl Ann Barit PedinesNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For Special ChildrenDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan For Special Childrenharas_dcsaisNo ratings yet
- CASE PRESENTATION PP - Anxiety. Tiffany GordonDocument6 pagesCASE PRESENTATION PP - Anxiety. Tiffany GordonTiffany GordonNo ratings yet
- Knowledge DeficitDocument3 pagesKnowledge DeficitJill DatorNo ratings yet
- Breathing PatternDocument4 pagesBreathing PatternVince John SevillaNo ratings yet
- Date/ Time/ Shift Cues Need Nursing Diagnosis With Rationale Objectives of Care Nursing Interventions With Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesDate/ Time/ Shift Cues Need Nursing Diagnosis With Rationale Objectives of Care Nursing Interventions With Rationale EvaluationPauleen Trisha SamparaniNo ratings yet
- Mental Health Case StudyDocument11 pagesMental Health Case Studyapi-453449063No ratings yet
- 6 Nursing Care Plan 1Document2 pages6 Nursing Care Plan 1Denise Louise PoNo ratings yet
- NCP PTBDocument6 pagesNCP PTBJay Dela VegaNo ratings yet
- Nutrition and Metabolic Nursing Diagnosis and InterventionsDocument4 pagesNutrition and Metabolic Nursing Diagnosis and InterventionsKathrina CraveNo ratings yet
- Knowledge DeficitDocument5 pagesKnowledge DeficitteamstrocaNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Coping NCPDocument4 pagesIneffective Coping NCPFrancis Alfred EscaranNo ratings yet
- Cu 4Document3 pagesCu 4Paul SahagunNo ratings yet
- Jake Yvan Dizon Case Study, Chapter 49, Assessment and Management of Patients With Hepatic DisordersDocument8 pagesJake Yvan Dizon Case Study, Chapter 49, Assessment and Management of Patients With Hepatic DisordersJake Yvan DizonNo ratings yet
- Case Report On Bipolar Affective Disorder: Mania With Psychotic SymptomsDocument2 pagesCase Report On Bipolar Affective Disorder: Mania With Psychotic SymptomskslhfwoiebvNo ratings yet
- Com/4-Cholecystitis - Cholelithiasis - Nursing-Care - Plans/2/ 6-OverviewDocument2 pagesCom/4-Cholecystitis - Cholelithiasis - Nursing-Care - Plans/2/ 6-OverviewCharles Belonio Dorado100% (1)
- Subjective: Short Term: Independent: Short TermDocument2 pagesSubjective: Short Term: Independent: Short TermCamille SesaldoNo ratings yet
- Psych NCPDocument1 pagePsych NCPEliza Joy Franco RNNo ratings yet
- A Client With Cushing's Syndrome: Nursing Care PlanDocument1 pageA Client With Cushing's Syndrome: Nursing Care PlanJulius Caesar ColladoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Risk For Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Bleeding From Tonsillectomy Short TermDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan: Risk For Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Bleeding From Tonsillectomy Short TermErika Danalle ArceoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for Alcohol Withdrawal AnxietyDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan for Alcohol Withdrawal Anxietykuro hanabusaNo ratings yet
- Cerebrovascular Accident (CVA) N C P BY BHERU LALDocument1 pageCerebrovascular Accident (CVA) N C P BY BHERU LALBheru LalNo ratings yet
- Rufino, Leslie Kriztel S. BSN 3-2 Group 1Document6 pagesRufino, Leslie Kriztel S. BSN 3-2 Group 1Deinielle Magdangal RomeroNo ratings yet
- NCP PainDocument1 pageNCP PaindwightciderNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for Patient with Delusional DisorderDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan for Patient with Delusional DisorderDan Dan ManaoisNo ratings yet
- NAME: Kristyn Joy D. Atangen: Subjective: DXDocument5 pagesNAME: Kristyn Joy D. Atangen: Subjective: DXTyn TynNo ratings yet
- NCP 2 VertigoDocument2 pagesNCP 2 VertigobananakyuNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for ManiaDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan for ManiaJasmine BaduaNo ratings yet
- Health TeachingDocument4 pagesHealth TeachingChamelli RobinNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument10 pagesNCPNefre Dayap DarrocaNo ratings yet
- Idoc - Pub Nursing Care Plan For Seizure NCPDocument2 pagesIdoc - Pub Nursing Care Plan For Seizure NCPACERET, IVAN LAURENTINE G.No ratings yet
- NCPDocument6 pagesNCPNik Rose ElNo ratings yet
- Drugs (Chino&anna)Document15 pagesDrugs (Chino&anna)Nic JiNo ratings yet
- Therapeutic CommunicationDocument7 pagesTherapeutic CommunicationJoseph Rommel Castro CortezNo ratings yet
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Rationale Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument8 pagesCues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Rationale Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationMa Virginia Nathalia CreerNo ratings yet
- Nursing Diagnosis: Impaired Comfort—pruritisDocument5 pagesNursing Diagnosis: Impaired Comfort—pruritisBondan PalestinNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology: Bipolar DisorderDocument3 pagesPathophysiology: Bipolar DisorderPae EdejerNo ratings yet
- NCP Activity IntoleranceDocument3 pagesNCP Activity IntoleranceJopaii TanakaNo ratings yet
- Cues Nursing Diagnos Is Backgro Und Knowled Ge Goals and Objectives Nursing Intervention and Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesCues Nursing Diagnos Is Backgro Und Knowled Ge Goals and Objectives Nursing Intervention and Rationale EvaluationSkyla FiestaNo ratings yet
- Everyone Would Be Better Off Without Me" As Verbalized by The PatientDocument4 pagesEveryone Would Be Better Off Without Me" As Verbalized by The PatientDanica Kate GalleonNo ratings yet
- NCP ImmobiltyDocument4 pagesNCP ImmobiltyAlizza Therese Severo AnzanoNo ratings yet
- ER Treatment and Discharge Plan for 23-Year-Old Male with ACL Grade 3 TearTITLE Post-Op Nursing Care and Pain Management for ACL Reconstruction PatientDocument3 pagesER Treatment and Discharge Plan for 23-Year-Old Male with ACL Grade 3 TearTITLE Post-Op Nursing Care and Pain Management for ACL Reconstruction PatientVILLANUEVA ARASELNo ratings yet
- Imbalance Nutrition Lass Than Body Requirements Related To Loss of Appetite Due To Aging.Document1 pageImbalance Nutrition Lass Than Body Requirements Related To Loss of Appetite Due To Aging.Senyorita KHayeNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan 1: Diagnosis Goal Nursing Interventions RationaleDocument8 pagesNursing Care Plan 1: Diagnosis Goal Nursing Interventions RationaleTrysna Ayu SukardiNo ratings yet
- Assessing and Managing Sleep DeprivationDocument2 pagesAssessing and Managing Sleep DeprivationDavid Brillo100% (1)
- College of Nursing and Allied Medical Sciences: WesleyanDocument3 pagesCollege of Nursing and Allied Medical Sciences: WesleyanPrince Juzzel Banag100% (1)
- Gum Bleeding Nursing CareDocument3 pagesGum Bleeding Nursing CareCrystelle MonaresNo ratings yet
- Maintaining Eye Tissue Integrity Through Nursing InterventionsDocument1 pageMaintaining Eye Tissue Integrity Through Nursing Interventionsjanine marie oraizNo ratings yet
- 2Document5 pages2msinsanoNo ratings yet
- Vitamin D Triggers Natural Immune Response Against Tuberculosis, Study FindsDocument4 pagesVitamin D Triggers Natural Immune Response Against Tuberculosis, Study FindsmsinsanoNo ratings yet
- Labor Code of the Philippines overviewDocument1 pageLabor Code of the Philippines overviewmsinsanoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 2012 EditionDocument215 pagesChapter 11 2012 EditionLuis Soriano MitraNo ratings yet
- Klinefelter SyndromeDocument6 pagesKlinefelter Syndromemeeeenon100% (1)
- L1095852 R5 QF-TB Gold Plus BCT IFDocument12 pagesL1095852 R5 QF-TB Gold Plus BCT IFTuấn Minh PhùngNo ratings yet
- SURAT KETERANGAN DOKTERDocument1 pageSURAT KETERANGAN DOKTERalha egaNo ratings yet
- 13497-Texto Del Artículo-48998-1-10-20150925Document7 pages13497-Texto Del Artículo-48998-1-10-20150925Pipe Contecha BernatteNo ratings yet
- NUS Medicine Admission Brochure 2019Document12 pagesNUS Medicine Admission Brochure 2019Glenden KhewNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4intestinal NematodesDocument41 pagesChapter 4intestinal Nematodesdeneke100% (1)
- Mudravig PDFDocument24 pagesMudravig PDFJai KanthNo ratings yet
- Boyd Et Al-2019-Cochrane Database of Systematic ReviewsDocument38 pagesBoyd Et Al-2019-Cochrane Database of Systematic ReviewsomyNo ratings yet
- Fissural CystsDocument17 pagesFissural CystssailalithaNo ratings yet
- 10 BV PDFDocument13 pages10 BV PDFYossy VesriNo ratings yet
- Meier Et Al, 1996Document4 pagesMeier Et Al, 1996boni_sebayangNo ratings yet
- Mouse Dosage CalculatorDocument5 pagesMouse Dosage CalculatorFauzi ChandraNo ratings yet
- 01 M039 43754Document16 pages01 M039 43754DrDeepak PawarNo ratings yet
- A Study of Dissolution Enhancement and Invitro Evaluation of RoxithromycinDocument6 pagesA Study of Dissolution Enhancement and Invitro Evaluation of Roxithromycinanto_pharma7784No ratings yet
- Semen AnalysisDocument2 pagesSemen AnalysisSabir KamalNo ratings yet
- Latest Guideline on Caries-risk Assessment and ManagementDocument8 pagesLatest Guideline on Caries-risk Assessment and ManagementPriscila Belén Chuhuaicura SotoNo ratings yet
- Medical 1 PDFDocument5 pagesMedical 1 PDFsuresh balajiNo ratings yet