Professional Documents
Culture Documents
What is a SWOT Analysis in 40 Characters
Uploaded by
Eslam Taha KhaledOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
What is a SWOT Analysis in 40 Characters
Uploaded by
Eslam Taha KhaledCopyright:
Available Formats
What is a SWOT analysis?
Definition
SWOT is the acronym for Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities and Threats. It is an analytical framework to help summarize in a quick and concise way the risk and opportunities for any company across the value chain. A good SWOT should look into internal and external factors affecting the issue at hand. Factors pertaining to the internal environment of the company. These are usually classified as Strengths (S) or Weaknesses (W) Factors that are external to the company. These are classified as Opportunities (O) or Threats (T). A SWOT analysis helps you match your companys resources and capabilities to threats and opportunities in the competitive environment. SWOT analysis can be very subjective, but adding weighting and criteria to each factor increases the validity of the analysis. Finally, a SWOT (or TOWS)matrix can help pick the best strategy to implement and takes the SWOT analysis to the next step. See our SWOT matrix below .
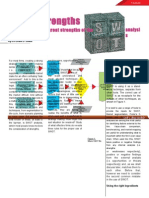
Structure of a SWOT analysis
A SWOT analysis is typically represented by a 4-box model that lists the Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats in the following order: Strengths Opportunities Weaknesses Threats
As you can see the beauty of a SWOT framework lies in its simplicity.
Why use a SWOT analysis?
Methodically and honestly assessing your companys strengths and weaknesses as well as the opportunities and threats it faces gives you a rare opportunity for objective analysis. A SWOT: Is easy to use Combines quantitative and qualitative analysis Encourages interdepartmental collaboration To make sure your analysis is put to good use, include these before and after steps in your analysis process: Set an objective for the analysis
Set aside adequate time for research and information-gathering Evaluate the results of your analysis against your original objective This competitive analysis tool guides you through the SWOT technique and will help you create your own analysis that can help you set a strategic plan or present new ideas to your team.
Conducting a SWOT analysis
There are eight steps required to complete a SWOT analysis and create a SWOT matrix (also known as a TOWS matrix). List external opportunities List external threats List internal strengths List internal weaknesses At this point in the process, youll have a significant list of potential strategies. Youll need to weigh the impact of the various factors in your analysis and select the most feasible strategy to implement. Ideally, youll select a SO strategy, but often youll need to implement one of the other three types of strategies to overcome a weakness or address a threat before being in a position to implement a S-O strategy.
Questions that a SWOT Analysis Should Answer
Here are some questions to help you understand the type of concepts a SWOT should be able to answer. This is list is by no means exhaustive, but will hopefully provide you with some guidance in your endeavors. Strenghts Advantages of proposition? Capabilities? Competitive advantages? USP's (unique selling points)? Resources, Assets, People? Experience, knowledge, data? Financial reserves, likely returns? Marketing - reach, distribution, awareness? Innovative aspects? Location and geographical? Price, value, quality? Accreditations, qualifications, certifications? Processes, systems, IT, communications? Cultural, attitudinal, behavioural?
Management cover, succession? Philosophy and values? Weaknesses Disadvantages of proposition? Gaps in capabilities? Lack of competitive strength? Reputation, presence and reach? Financials? Own known vulnerabilities? Timescales, deadlines and pressures? Cashflow, start-up cash-drain? Continuity, supply chain robustness? Effects on core activities, distraction? Reliability of data, plan predictability? Morale, commitment, leadership? Accreditations, etc? Processes and systems, etc? Management cover, succession? Opportunities Market developments? Competitors' vulnerabilities? Industry or lifestyle trends? Technology development and innovation? Global influences? New markets, vertical, horizontal? Niche target markets? Geographical, export, import? Tactics: eg, surprise, major contracts? Business and product development? Information and research? Partnerships, agencies, distribution? Volumes, production, economies? Seasonal, weather, fashion influences? Threats Political effects? Legislative effects? Environmental effects? IT developments? Competitor intentions - various? Market demand? New technologies, services, ideas? Vital contracts and partners? Sustaining internal capabilities?
Obstacles faced? Insurmountable weaknesses? Loss of key staff? Sustainable financial backing? Economy - home, abroad? Seasonality, weather effects?
The SWOT/TOWS Matrix
To develop strategies that take into account the SWOT profile, a matrix of these factors can be constructed. The SWOT matrix (also known as a TOWS matrix by re-arranging the SWOT letters) is shown below: External Opportunities (O)
List 4-5 external opportunities here 1. 3. 2. 4.
External Threats (T)
List 4-5 external threats here 1. 3. 2. 4.
Internal Strengths (S)
List 4-5 internal threats here 1. 3. 2. 4.
S-O "Max-Max" Strategy Strategies that use strengths to maximize opportunities. W-O "Min-Max" Strategy Strategies that minimize weaknesses by taking advantage of opportunities.
S-T "Max-Min" Strategy Strategies that use strengths to minimize threats. W-T "Min-Min" Strategy Strategies that minimize weaknesses and avoid threats.
Internal Weaknesses (W)
List 4-5 internal weaknesses here 1. 3. 2. 4.
Effectively, you have to match each component with one another. For example, match the internal strengths with external opportunities and list the resulting Strengths/Opportunities strategies in the matrix chart The four strategy types are: S-O strategies pursue opportunities that match the companys strengths. These are the best strategies to employ, but many firms are not in a position to do so. Companies will generally pursue one or several of the other three strategies first to be able to apply StrenghtsOpportunities strategies.
W-O strategies overcome weaknesses to pursue opportunities. Your job is to match internal weaknesses with external opportunities and list the resulting Weaknesses-Opportunities strategies S-T strategies identify ways that the firm can use its strengths to reduce its vulnerability to external threats. Your job is to match internal strengths with external threats and list the resulting Strengths-Threats Strategies W-T strategies establish a defensive plan to prevent the firms weaknesses from making it susceptible to external threats. Your job is to match the internal weaknesses with external threats and record the resulting Weaknesses-Threats Strategies
Examples of SWOT/TOWS Matrix Strategy Types
Here are some examples on the type of things you might find inside a SWOT/TOWS matrix: Strength-Opportunity Strategies Expand globally Increase sales staff Increase advertising Develop new products Diversify Strength-Threat Strategies Diversify Acquire competitor Liquidate Expand locally Re-engineer Weakness-Opportunity Strategies Joint venture Acquire competitor Expand nationally Backward integration Forward integration Weakness-Threat Strategies Divest Increase promotion Retrench Restructure Downsize
You might also like
- SWOT PresentationDocument16 pagesSWOT PresentationDarwin FloresNo ratings yet
- Planning ToolsDocument31 pagesPlanning Toolsmokshagna saitejaNo ratings yet
- Business Organization For BbaDocument101 pagesBusiness Organization For BbaVineet Walia100% (1)
- Chapter 3 Understanding Internal & External EnvironmentsDocument25 pagesChapter 3 Understanding Internal & External Environmentsdaovansang100% (3)
- Organizational Behavior NotesDocument5 pagesOrganizational Behavior Notescyntaff100% (2)
- Individual and GroupDocument14 pagesIndividual and GroupSarita yadavNo ratings yet
- X Chapter 4 The Situation Situational AnalysisDocument13 pagesX Chapter 4 The Situation Situational AnalysisRay100% (1)
- Physical DevelopmentDocument5 pagesPhysical DevelopmentAlexa San pedroNo ratings yet
- 1.4 Entrepreneur's Networking 1.5 Issues: Topic 1: IntroductionDocument13 pages1.4 Entrepreneur's Networking 1.5 Issues: Topic 1: IntroductionHananie NanieNo ratings yet
- #6 Ad AgencyDocument19 pages#6 Ad Agencybabydutt1No ratings yet
- Business DemographyDocument15 pagesBusiness DemographyNeha ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Defining GlobalizationDocument5 pagesDefining Globalizationjim fuentesNo ratings yet
- International Logistics IntroductionDocument29 pagesInternational Logistics IntroductionkarthikNo ratings yet
- SWOT AnalysisDocument10 pagesSWOT AnalysisDipanjan DasNo ratings yet
- Conduct your own SWOT analysis to evaluate strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threatsDocument15 pagesConduct your own SWOT analysis to evaluate strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threatsNitin DavidNo ratings yet
- Swot AnalysisDocument30 pagesSwot AnalysisLos Dee SantosNo ratings yet
- SWOT AnalysisDocument5 pagesSWOT Analysisgyugam100% (1)
- How To Do A SWOT Analysis For Better Strategic PlanningDocument4 pagesHow To Do A SWOT Analysis For Better Strategic PlanningDatuNo ratings yet
- SWOT AnalysisDocument12 pagesSWOT AnalysisLalit ThakurNo ratings yet
- SWOT Analysis of Amul Dairy CooperativeDocument35 pagesSWOT Analysis of Amul Dairy CooperativeDilshaad ShaikhNo ratings yet
- What Is A SWOT Analysis?: STRENGTHS-make A List of Your Company's Internal Strengths. These Are Any CompetitiveDocument5 pagesWhat Is A SWOT Analysis?: STRENGTHS-make A List of Your Company's Internal Strengths. These Are Any CompetitiveJoice Ann Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- SWOT AnalysisDocument7 pagesSWOT AnalysisNaveen Kishore GattimNo ratings yet
- SWOT Analysis - Docx 2Document11 pagesSWOT Analysis - Docx 2RD OseñaNo ratings yet
- Components of SWOT AnalysisDocument5 pagesComponents of SWOT AnalysisstrtdelossantosNo ratings yet
- SWOT Analysis 1Document8 pagesSWOT Analysis 1Myint FrancoNo ratings yet
- Swot AnalysisDocument16 pagesSwot AnalysisRAVI GIRI GOSWAMINo ratings yet
- De Leon - Dwight - Ce175-1c - E01 - CW2Document3 pagesDe Leon - Dwight - Ce175-1c - E01 - CW2Suzuya JuuzouNo ratings yet
- SWOT Analysis MatrixDocument5 pagesSWOT Analysis MatrixUmar Awan100% (1)
- SWOT and PEST analysis templatesDocument5 pagesSWOT and PEST analysis templatesCoolmaharana MaharanaNo ratings yet
- Definition of 'SWOT Analysis'Document17 pagesDefinition of 'SWOT Analysis'gaffar652No ratings yet
- What Is SWOT AnalysisDocument4 pagesWhat Is SWOT AnalysisParul RanaNo ratings yet
- What Is A SWOT Analysis and Why Should You Use OneDocument15 pagesWhat Is A SWOT Analysis and Why Should You Use Oneuli_siahaanNo ratings yet
- SWOT AnalysisDocument13 pagesSWOT AnalysisAkshat Kaul100% (2)
- To Upload 5Document8 pagesTo Upload 5Nazia PeerooNo ratings yet
- History of Swot AnalysisDocument42 pagesHistory of Swot Analysiscreation toolsNo ratings yet
- Articles Bplans Com How To Perform Swot AnalysisDocument11 pagesArticles Bplans Com How To Perform Swot AnalysisSalomón JiménezNo ratings yet
- SWOT Analysis Shristha BhandariDocument5 pagesSWOT Analysis Shristha Bhandarishristha bhandariNo ratings yet
- Hoe To Download From ScribdDocument42 pagesHoe To Download From ScribdSurya ThakurNo ratings yet
- Swot Report TMDocument5 pagesSwot Report TMTamoomNo ratings yet
- 3 The SWOT and PEST AnalysisDocument69 pages3 The SWOT and PEST AnalysisGileah Ymalay ZuasolaNo ratings yet
- To Upload 1Document8 pagesTo Upload 1Nazia PeerooNo ratings yet
- What Is SWOT AnalysisDocument2 pagesWhat Is SWOT AnalysistdhdhdjNo ratings yet
- SWOT AnalysisDocument16 pagesSWOT Analysisrizwansaeed73No ratings yet
- Lecture SWOT Analysis 265Document7 pagesLecture SWOT Analysis 265Sh Mati Elahi100% (1)
- Swot Analysis ReportDocument3 pagesSwot Analysis Reportleers mcthorn100% (1)
- Infinitea CompanyDocument11 pagesInfinitea CompanyPatricia Barlaan29% (7)
- Hidden Strengths of SWOT AnalysisDocument4 pagesHidden Strengths of SWOT AnalysisDavid SelvaNo ratings yet
- Why Use SWOT AnalysisDocument5 pagesWhy Use SWOT AnalysisᎩᎧᎶᏋᏕᏂ ᏠᎧᏕᏂᎥNo ratings yet
- SWOT Vs TOWSDocument8 pagesSWOT Vs TOWSdhrruv kkNo ratings yet
- On TOWS AnalysisDocument8 pagesOn TOWS Analysisdhrruv kkNo ratings yet
- Generate Strategies with TOWS MatrixDocument8 pagesGenerate Strategies with TOWS Matrixdhrruv kkNo ratings yet
- Analysis - SWOT, Porter, PESTELDocument13 pagesAnalysis - SWOT, Porter, PESTELBayram Cahan100% (1)
- SWOT Analysis - Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and ThreatsDocument6 pagesSWOT Analysis - Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threatscrabrajesh007No ratings yet
- SWOT Analysis: SWOT Analysis (Or SWOT Matrix) Is A Strategic Planning Technique Used To Help A Person orDocument6 pagesSWOT Analysis: SWOT Analysis (Or SWOT Matrix) Is A Strategic Planning Technique Used To Help A Person orАлинаОсадчук-ФердохлебNo ratings yet
- SWOT AnalysisDocument25 pagesSWOT AnalysisChor Chan0% (1)
- Organizational Appraisal Internal AssessmentDocument7 pagesOrganizational Appraisal Internal AssessmentAllen Gevryel Ragged A. GabrielNo ratings yet
- Marketing Management - SWOT AnalysisDocument8 pagesMarketing Management - SWOT AnalysissakhawatNo ratings yet
- SWOT AnalysisDocument53 pagesSWOT Analysisdivjn367% (6)
- Cross SWOT AnalysisDocument2 pagesCross SWOT AnalysisNhocdaica Nguyen100% (1)
- Swot AnalysisDocument13 pagesSwot AnalysisEr Paras ThakurNo ratings yet
- The Internationalization Process of High Fashion CompaniesDocument19 pagesThe Internationalization Process of High Fashion CompaniesLiv AmatoNo ratings yet
- Bajaj Allianz 2017-18Document96 pagesBajaj Allianz 2017-18Akshat JainNo ratings yet
- Project management methods and market analysisDocument3 pagesProject management methods and market analysisMR. DEVASHISH GAUTAMNo ratings yet
- CPAR MAS Preweek May 2005 EditionDocument17 pagesCPAR MAS Preweek May 2005 EditionDarrelNo ratings yet
- F9Chap1 TutorSlidesDocument81 pagesF9Chap1 TutorSlidesSeema Parboo-AliNo ratings yet
- University of The Philippines: Swiss Guard Consulting IncDocument5 pagesUniversity of The Philippines: Swiss Guard Consulting IncLance EstopenNo ratings yet
- Group-4 Case Study On Mcdonald'sDocument20 pagesGroup-4 Case Study On Mcdonald'sDhruv SainiNo ratings yet
- Rising Star - Senco Gold Ltd.Document22 pagesRising Star - Senco Gold Ltd.deepaksinghbishtNo ratings yet
- JKMS Business Loan ApplicationDocument3 pagesJKMS Business Loan Applicationgerhard greylingNo ratings yet
- Management Skills Application 14th Edition Rue Test BankDocument19 pagesManagement Skills Application 14th Edition Rue Test BankJamesGrantwncma100% (13)
- Absolute Cost Advantage TheoryDocument18 pagesAbsolute Cost Advantage Theoryvinaykn53No ratings yet
- MSD Clothing IndustryDocument95 pagesMSD Clothing IndustryDrBollapu Sudarshan0% (1)
- Case Pantene FinalDocument6 pagesCase Pantene Finalapi-241899000100% (1)
- Type of Manufacturing SystemDocument18 pagesType of Manufacturing Systemamit8615100% (5)
- Payback Method - Payback Period Formula - AccountingToolsDocument5 pagesPayback Method - Payback Period Formula - AccountingToolsFriedeagle OilNo ratings yet
- 5f8578c99b75470018830b19 1613016615 ACC223 - WEEK4 5 - ULOaDocument17 pages5f8578c99b75470018830b19 1613016615 ACC223 - WEEK4 5 - ULOaClaudee Veel SociasNo ratings yet
- 9th Chapter 3 - Planning and Implementing Customer Relationship Management ProjectsDocument32 pages9th Chapter 3 - Planning and Implementing Customer Relationship Management ProjectsHarpreetNo ratings yet
- Job Opportunities in The Film IndustryDocument7 pagesJob Opportunities in The Film Industryapi-496240163No ratings yet
- Retail Manager JDDocument4 pagesRetail Manager JDMj PayalNo ratings yet
- Balance of Payments AccountingDocument4 pagesBalance of Payments AccountingDanielleNo ratings yet
- Applied Value Investing (Duggal) FA2016Document3 pagesApplied Value Investing (Duggal) FA2016darwin12No ratings yet
- Auto Cash Rule SetDocument4 pagesAuto Cash Rule SetSingh Anish K.No ratings yet
- Analysis Supply Chain Management Performance Using SCOR Method in Compressor Distributor Company at PT. Pola Petro DevelopmentDocument12 pagesAnalysis Supply Chain Management Performance Using SCOR Method in Compressor Distributor Company at PT. Pola Petro DevelopmentInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- 01.21st Century Supply ChainsDocument16 pages01.21st Century Supply ChainsIkhsan AditamaNo ratings yet
- Quality management system overviewDocument2 pagesQuality management system overviewKarol FernandezNo ratings yet
- Sales Management NotesDocument8 pagesSales Management NotesDisha MathurNo ratings yet
- Pooja KukrejaDocument97 pagesPooja Kukrejachandershekhar0% (1)
- Managerial Applications of StatisticsDocument10 pagesManagerial Applications of StatisticsSai Aditya100% (1)
- Industry Analysis Report FinalDocument24 pagesIndustry Analysis Report FinalJeshwanth SonuNo ratings yet