Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ELectric Field and Charge Distribution Notes 2
Uploaded by
plutouecOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
ELectric Field and Charge Distribution Notes 2
Uploaded by
plutouecCopyright:
Available Formats
MAMS ACADEMY FOR CAREER EXCELLENCE
RIYADH, SAUDI ARABIA
ES2
Date: March 15, 2012
PHYSICS NOTES: Electric Field and charge distribution
Electric Field: A region in space where at any point inside that region any charge will experience force. To test there is field at a region by convention we place a positive very small point charge (also known as test charge) at different points. If that test charge experience any force then it means that there exist electric field in that region. It is very similar to gravitational field. If any object experiences force due to its inertia(mass) in a region then it means that there exist gravitation field in that region. All objects are attracted towards Earth because they experience force when they are in region of earths gravitational field. Field is physical quantity when it is represented as a quantity some times we call it electric field intensity or just electric field. It is a vector quantity denoted by E Direction of Electric Field at a point: Its direction is same as that of the force experience by a positive small test charge when placed at that point. Magnitude of Electric Field at a point: It is equal to the force experience by a test charge divided by the F magnitude of test charge. E = . q is the magnitude of test charge, F is the magnitude of force experience q by it. So in vector form field is E = F N . Dimensional Formula is MLT 3 A1 . SI unit is q C Who creates Electric Field: As you know Mass object creates gravitation field around itself. Similarly an Electric charge creates Electric Field around itself. Now we will see different formulas to find field.
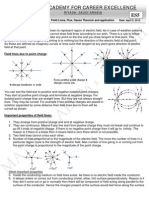
Electric Field due to a Point charge: Consider a point charge q placed in a medium of dielectric constant r . If a test charge qo is placed at a distance r from it. Then it will experience electric force given by qq 1 2o 4 o r r F 1 q q 1 q or E = A 2 B . So, as E = we get E = 2 for vacuum or air it is F= qo q 4 o r r 4 o r r 1 q E= 2. 4 o r 1 Remember to put magnitude of q here. As it varies inversely with distance from point charge. E 2 . The r variation is shown in the plot of E vs r. Field is strongest at close distance and decreases as distance increases becomes zero at infinity. Electric Field due to Many Point Charges: If there exist number of point charges in space then the electric field at a point is the combined effect of the point charges. If charges q1 , q2 ,...qN are located in space then electric field at a point is given by
E = E1 + E2 + ... + EN , where E1, E2, EN are the field due to charges q1,q2,qN at that point . Remember field is a vector quantity so vector laws are used to find resultant field.
Uniform and Non-Uniform Electric Field: If in a region field at all the points is same both in magnitude as well as direction then uniform field exist in that region. If at different points field is different or varies in region such that its magnitude or direction or both varies then non uniform field exist in that region. For example if along a straight line direction of filed is same but magnitude increases. Then field is non uniform. In vector form E = Ex i + E y j + E z k here X, Y and Z components may be a function of time of position will be cleared by solving questions. Electric Charge Distribution: The charge distribution means continuous existence of charge in medium or vacuum. Linear Charge Distribution: Consider a uniform rod of mass M, then mass is uniformly distributed along the length of the rod (linear). Similarly if charges are placed along straight line we call it linear charge distribution. Linear charge density denoted by SI unit C/m. q dq and inst . = avg = dl l Surface Charge Distribution: If along surface charge exists then it is surface charge distribution, surface may be plane, spherical, curved etc. Surface charge density denoted by q dq and inst . = SI unit C/m2. avg = dA A Volume Charge Distribution: For a solid sphere we say mass is distributed throughout the volume(volume mass distribution). Similarly if charge exists throughout the matter body we say volume charge distribution. Volume charge density is q dq denoted by and avg = and inst . = V dV
NOTE: In coming lectures we will find electric Field due and electric potential (discussed later) due to charge distribution. Gauss theorem is also explained using this.
You might also like
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- IRCTC Retiring Room DarjeelingDocument2 pagesIRCTC Retiring Room DarjeelingplutouecNo ratings yet
- Spicejet MEDA FormDocument2 pagesSpicejet MEDA FormbaggagemattersNo ratings yet
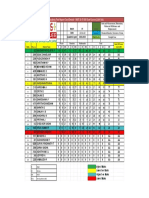
- IIT Results 22 October - Sheet1Document1 pageIIT Results 22 October - Sheet1plutouecNo ratings yet
- 1Document1 page1plutouecNo ratings yet
- IRCTC Retiring Room DarjeelingDocument2 pagesIRCTC Retiring Room DarjeelingplutouecNo ratings yet
- Direct 2728978103937588Document2 pagesDirect 2728978103937588plutouecNo ratings yet
- NEET Results 22 October - Sheet1Document1 pageNEET Results 22 October - Sheet1plutouecNo ratings yet
- ANSWERS 22 OCTOBER - Sheet1Document1 pageANSWERS 22 OCTOBER - Sheet1plutouecNo ratings yet
- Neet Sample PDFDocument18 pagesNeet Sample PDFplutouecNo ratings yet
- 0801 2042Document32 pages0801 2042plutouecNo ratings yet
- Hotel Voucher 1705841104816Document3 pagesHotel Voucher 1705841104816plutouecNo ratings yet
- Mock Test For NEET-2017Document16 pagesMock Test For NEET-2017Nimish Jain90% (10)
- 1518694711NEET Syllabus PhysicsDocument5 pages1518694711NEET Syllabus PhysicsplutouecNo ratings yet
- 1578399358phpD1CAOb PDFDocument9 pages1578399358phpD1CAOb PDFvikas aggarwalNo ratings yet
- Capacitance: 1 - Capacitance of A ConductorDocument1 pageCapacitance: 1 - Capacitance of A ConductorplutouecNo ratings yet
- AtomsDocument24 pagesAtomsVaibhav SinghNo ratings yet
- FacultyAD070919 2Document1 pageFacultyAD070919 2plutouecNo ratings yet
- InvoiceDocument1 pageInvoiceplutouecNo ratings yet
- Electric Potential, Potential Energy, Dipole Notes 3Document2 pagesElectric Potential, Potential Energy, Dipole Notes 3plutouecNo ratings yet
- InvoiceDocument1 pageInvoiceplutouecNo ratings yet
- Properties of Solids and Liquids PDFDocument63 pagesProperties of Solids and Liquids PDFNarendra KumarNo ratings yet
- Forces Assignment 1Document2 pagesForces Assignment 1plutouecNo ratings yet
- Kinematics Type 1Document11 pagesKinematics Type 1Goodmobo 123No ratings yet
- Field and Potential Due To Charge Distribution Notes 4aDocument2 pagesField and Potential Due To Charge Distribution Notes 4aplutouecNo ratings yet
- Field and Potential Due To Charge Distribution Notes 4bDocument3 pagesField and Potential Due To Charge Distribution Notes 4bplutouecNo ratings yet
- ELectric Field Lines and Flux-Gauss Theorem Notes 5Document6 pagesELectric Field Lines and Flux-Gauss Theorem Notes 5plutouecNo ratings yet
- Field, Potential, Torque-Dipole Notes 6Document3 pagesField, Potential, Torque-Dipole Notes 6plutouecNo ratings yet
- ELectric Force Notes 1Document4 pagesELectric Force Notes 1plutouecNo ratings yet
- Error Analysis TutorialDocument8 pagesError Analysis Tutorialthan2147289No ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- History of PhilosophyDocument24 pagesHistory of PhilosophypariciaNo ratings yet
- G8 3rd QuarterDocument22 pagesG8 3rd QuarterJames LucasNo ratings yet
- Saturn in 3rd House - Shani in 3rd Bhava - Saturn in Third HouseDocument3 pagesSaturn in 3rd House - Shani in 3rd Bhava - Saturn in Third HousesrinivasNo ratings yet
- RevModPhys 75 121Document60 pagesRevModPhys 75 121Furkan OkNo ratings yet
- Gemstones in AstrologyDocument2 pagesGemstones in Astrologyfyou@hotmail.co.nzNo ratings yet
- Time Machine EssayDocument11 pagesTime Machine EssayUday100% (1)
- Introduction To Philosophical Methods PDFDocument17 pagesIntroduction To Philosophical Methods PDFAnand Kumar YadavNo ratings yet
- Science and SuperstitionDocument5 pagesScience and SuperstitionSakshi PukaleNo ratings yet
- Some Basic Properties of English SyntaxDocument12 pagesSome Basic Properties of English SyntaxwawanNo ratings yet
- Andalucia 04Document3 pagesAndalucia 04Mercedes López PortilloNo ratings yet
- Midheaven Extension ProcessDocument11 pagesMidheaven Extension ProcessSharon Wilson86% (7)
- Sosa Judgment and Agency PDFDocument258 pagesSosa Judgment and Agency PDFSimón Palacios BriffaultNo ratings yet
- Griffero, Tonino - Quasi-Things The Paradigm of Atmospheres (2017, State University of New York Press)Document214 pagesGriffero, Tonino - Quasi-Things The Paradigm of Atmospheres (2017, State University of New York Press)Enara Garcia100% (2)
- Maharaja Institute of Technology, Coimbatore: Staff Name: Muniaraj.S Sem: IIDocument3 pagesMaharaja Institute of Technology, Coimbatore: Staff Name: Muniaraj.S Sem: IIM.Saravana Kumar..M.ENo ratings yet
- Gaskin MechanicsDocument47 pagesGaskin MechanicsLia MewwNo ratings yet
- Night Sky Observer's Guide - Willmann-Bell, Inc.Document47 pagesNight Sky Observer's Guide - Willmann-Bell, Inc.parkingbot156No ratings yet
- Abraham, Sylvia - How To Use Tarot SpreadsDocument285 pagesAbraham, Sylvia - How To Use Tarot Spreadschukchev100% (15)
- Pneuma Between Body and Soul - Lloyd PDFDocument12 pagesPneuma Between Body and Soul - Lloyd PDFpreformanNo ratings yet
- Cosmic Sense, Common Sense, and NonsenseDocument93 pagesCosmic Sense, Common Sense, and Nonsensesmeena100% (1)
- What Animals See in The Stars, and What They Stand To LoseDocument3 pagesWhat Animals See in The Stars, and What They Stand To LoseqNo ratings yet
- Sun in VirgoDocument22 pagesSun in VirgoMilica PavlovicNo ratings yet
- Dynamics With MatLabDocument35 pagesDynamics With MatLabDiego Andrew G RNo ratings yet
- Knowledge As The Unity of The Intellect and The Object of Intellection in Islamic PhilosophyDocument15 pagesKnowledge As The Unity of The Intellect and The Object of Intellection in Islamic PhilosophyAmiraNo ratings yet
- DROPS Calculator Metric A4 PDFDocument2 pagesDROPS Calculator Metric A4 PDFfathul syaafNo ratings yet
- Transformasi Dalam MatematikDocument39 pagesTransformasi Dalam MatematikMas Izwatu Solehah MiswanNo ratings yet
- Cosmic RaysDocument92 pagesCosmic RaysJTKirk61No ratings yet
- Determination of The Predominator of A ChartDocument2 pagesDetermination of The Predominator of A ChartMarco SatoriNo ratings yet
- Intro To Vedic AstrologyDocument10 pagesIntro To Vedic AstrologyNikola Durdevic ArteNo ratings yet
- Ikjeifjd: Male Shishir Kantsin 2446115 Moo 2 Y 10 M 19 DDocument1 pageIkjeifjd: Male Shishir Kantsin 2446115 Moo 2 Y 10 M 19 DShishir Kant SinghNo ratings yet
- Haven't Been DownloadedDocument2 pagesHaven't Been DownloadedKaplan YuNo ratings yet