Professional Documents
Culture Documents
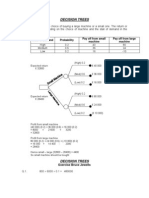
Unit4 A (AS)
Uploaded by
punte77Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Unit4 A (AS)
Uploaded by
punte77Copyright:
Available Formats
OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT (PRODCUTION MANAGEMENT)
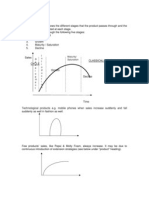
Production takes place when a business takes input, carries out a production process and produces output. In other words it is the conversion of resources such as raw materials or components into goods and services. Production can be done at primary, secondary or tertiary levels. Inputs Land Labour Capital Enterprise Production Process Conversion Outputs Goods Services
Raw Materials Components
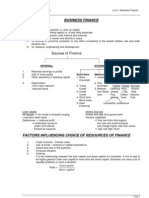
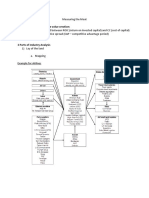
Operations management is a wide range term which indicates the management of production process. It deals with issues like what to produce, what production methods to be used, how to control quality, how to maintain inventory or stock, location and size of the firm and how to make production more efficient. ADDED VALUE OR VALUE ADDED It is the difference between the cost of bought in components and the price charged for the finished product. Value added is not the same as profit. To calculate profit, we need to subtract wages (labour costs) financial costs and overheads. Value added can be calculated by the following formula: Value = Sales External added revenue Expenditure External expenditure does not include the cost of land, labour and capital of the organization. IMPORTANCE OF OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT One major reason for the growing importance of operation management is the need for firms the compete more effectively in the market. To become the leader of the market, most areas of concern revolve around the ask and quality of production. With the help of operations management, firms produce better quality products at reasonable costs and can get a chance of gaining more market share. LOCATION OF THE FIRM Location is the general area selected for a particular business. Its choice is likely to involve a detailed process of analyzing alternatives through investment appraisal and other cost benefit analysis. Industrial location is the geographic positioning of our operation in relation to its customers resources, employers, employees and other markets organizations faces problems in finding out the best location for their business and choice can be critical for success. Location decisions also depend upon the type and size of the business. The best location is one which has comparatively low cost of production and therefore should provide the opportunity to maximize return on investments in terms of sales and profits. FACTORS INFLUENCING THE LOCATION (OF BUSINESS) DECISION Types: Quantitative tax, cost, etc Qualitative availability of labour, legal cultural 1. Population and demand in the market 2. Number and location of competitors 3. Availability and cost of labour 4. Availability and cost of raw materials 5. Degree of government intervention
Rent and cost of land Physical features, weather and quality of land Personal preference and interest of the owners Industrial inertia locating in a congested area where there are already several similar industries 10. External economies of scale 11. Availability of infrastructure, transportation and communication facilities 12. Availability of natural resources and utilities 13. Financial incentives by govt. as regional policy grants profits more, cash surplus, loans are easy ISSUES REGARDING INTERNATIONAL LOCATION A multinational organization has to make key decisions about location as they are dealing with a wide range of local and international markets. Following issues are considered while making this decision: 1. Trade barriers 2. Exchange rates 3. Political stability 4. Legal boundaries 5. Language and cultural barriers 6. Ethical considerations 7. Market opportunities 8. Availability of labour 9. Financial incentives 10. To build a strong corporate image worldwide Multinationals are growing very rapidly and represent a significant source of industrial development in countries throughout the world. Benefits of multinationals to host countries are as follows: 1. increased employment 2. GDP increases 3. economic growth 4. standard of living 5. increased competition 6. improves quality and efficiency 7. controls prices 8. increases variety and choices 9. technology transfer 10. better trained labour 11. revenue to the government 12. foreign investments increase 13. relations between host and guest countries improve politically and economically 14. balance of payment surplus
6. 7. 8. 9.
OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT PRODUCTIVITY
PRODUCTION Production is the measured quantity of output that a firm produces in a given period of time. EFFICIENCY Efficiency is how well resources such as raw material, labour and capital can be used to produce a product or a service. Efficiency can be measured through the following ways 1. labour productivity (output per worker) =
Output per period labour employed in that period
2.
capital productivity (output per unit of capital) =
Output per period quantity / value of capital employed in that period
3.
multi factor productivity =
Output per period cos ts of ( raw material + labour + capital ) employed in that periods
4. capacity utilization =
current output 100 Max. capacity
5.
added value = sales = external expenditure
PRODUCTIVITY It is the means of the ratio of output to any of the firms inputs. Productivity is an efficiency measure. If a firm becomes more productive, it becomes more efficient. Following are the ways in which productivity levels can be increased. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. improve the training of staff to raise skill levels. purchase more technologically advanced equipment to increase the capital productivity improve employee motivation change the layout of work improve working conditions more efficient management
Raising productivity is not always a guarantee for success. It does not crate demand among the customers so it is the quality of management which determines the success of any policy. Discuss and evaluate work study as a method of improving labour efficiency-
You might also like
- Global Production Factors & Marketing Mix for International FirmsDocument15 pagesGlobal Production Factors & Marketing Mix for International FirmsAishwarya SairamNo ratings yet
- Strategic cost management for quality and valueDocument24 pagesStrategic cost management for quality and valuesai500No ratings yet
- HSC Topic: Human Resources ManagementDocument6 pagesHSC Topic: Human Resources ManagementJessica SamNo ratings yet
- HSC Business Studies Syllabus Revision GuideDocument96 pagesHSC Business Studies Syllabus Revision GuideEdward Pym100% (3)
- Definition of ProductivityDocument3 pagesDefinition of Productivityrahulravi4u100% (1)
- MGT 26 Project - Phase 1: Industry - Automobile Organisation - VolkswagonDocument12 pagesMGT 26 Project - Phase 1: Industry - Automobile Organisation - VolkswagonPriyanka GuptaNo ratings yet
- IntRetail Theory11Document31 pagesIntRetail Theory11ellisj152No ratings yet
- Unit 5.1: The Role of Operations ManagementDocument32 pagesUnit 5.1: The Role of Operations ManagementJulius DennisNo ratings yet
- OM processes goods servicesDocument5 pagesOM processes goods servicesImFree OfDebtNo ratings yet
- PomDocument16 pagesPomDhara KanungoNo ratings yet
- Rana Ahmed Raza MCM-F19-406Document6 pagesRana Ahmed Raza MCM-F19-406Arbaz KhanNo ratings yet
- OMBC 204 Unit 1 - 13 Self Assessment MCQsDocument39 pagesOMBC 204 Unit 1 - 13 Self Assessment MCQsPriyanka MahajanNo ratings yet
- Operations and Project ManagementDocument34 pagesOperations and Project ManagementSaadat Ali Mughal100% (1)
- Chapter 3Document9 pagesChapter 3Shakhawat quaderNo ratings yet
- Operations: Role of Operations ManagementDocument14 pagesOperations: Role of Operations ManagementtrollingpersonNo ratings yet
- Operation Management Assignment - 1Document10 pagesOperation Management Assignment - 1defender DhimanNo ratings yet
- Management For Engineers - 3Document33 pagesManagement For Engineers - 3alant k josephNo ratings yet
- Mba HRD Ii Sem 202Document11 pagesMba HRD Ii Sem 202Grace Joy MarcelinoNo ratings yet
- EOS BusinessDocument55 pagesEOS BusinesshamyngocangelNo ratings yet
- Increasing Productivity and Production Management in Wet Processing IndustryDocument7 pagesIncreasing Productivity and Production Management in Wet Processing IndustryJohurul HoqueNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes q4 Week 1 EntrepDocument5 pagesLecture Notes q4 Week 1 EntrepMarishka Aviona AnchingesNo ratings yet
- Assignment of Production and Operations ManagementDocument4 pagesAssignment of Production and Operations ManagementAnkita RajputNo ratings yet
- What is Operations Management? Key Responsibilities and ImportanceDocument17 pagesWhat is Operations Management? Key Responsibilities and Importanceankit_bhasinNo ratings yet
- Haider Ali Mid TermDocument6 pagesHaider Ali Mid TermArbaz KhanNo ratings yet
- Operations Business Studies MAINDocument50 pagesOperations Business Studies MAINAzaz AhmedNo ratings yet
- Quiz 2 AnswersDocument4 pagesQuiz 2 AnswersHana Demi DeeNo ratings yet
- Entrep Group 2Document62 pagesEntrep Group 2Isabel Victoria GarciaNo ratings yet
- The Strategy of Going Global: How International Expansion Boosts ProfitabilityDocument27 pagesThe Strategy of Going Global: How International Expansion Boosts ProfitabilityReeja BaigNo ratings yet
- Operations Strategy: Top 10 Priorities For Operations Managers Product ImprovementsDocument5 pagesOperations Strategy: Top 10 Priorities For Operations Managers Product ImprovementsDuaa WajidNo ratings yet
- MSC MA Lecture 1 OverviewDocument26 pagesMSC MA Lecture 1 OverviewAlwi Al-AidarosNo ratings yet
- MODULE1APPLICATIONDocument6 pagesMODULE1APPLICATIONrica mae sarmientoNo ratings yet
- Managing Operations ProcessesDocument12 pagesManaging Operations ProcessesAzaz AhmedNo ratings yet
- Operation Management QuestionDocument4 pagesOperation Management QuestionAhmedNo ratings yet
- Ritzman O.M Ch-1-EEE - Spring 2023Document20 pagesRitzman O.M Ch-1-EEE - Spring 2023Imran AliNo ratings yet
- First Examination in CBM112Document4 pagesFirst Examination in CBM112Jhoyce LumbaNo ratings yet
- Competitiveness, Strategy, and ProductivityDocument39 pagesCompetitiveness, Strategy, and ProductivityMr. JahirNo ratings yet
- What Is Operation ManagementDocument7 pagesWhat Is Operation Managementheysem100% (1)
- 2013 Business Studies NotesDocument20 pages2013 Business Studies NotesJim Sinclair-AndersonNo ratings yet
- Strategic Management & Competitiveness - 1Document49 pagesStrategic Management & Competitiveness - 1kashifNo ratings yet
- Prouction and Operation ManagementDocument17 pagesProuction and Operation ManagementSmart HackerNo ratings yet
- 1 - Operations and ManagementDocument5 pages1 - Operations and ManagementReno BrownNo ratings yet
- Understanding Business ActivityDocument40 pagesUnderstanding Business ActivityroshanNo ratings yet
- Q1. What New Opportunities You Find Interesting During The Covid 19 For A New Business Venture, Explain With ExamplesDocument6 pagesQ1. What New Opportunities You Find Interesting During The Covid 19 For A New Business Venture, Explain With ExamplesZainab Amin KapadiaNo ratings yet
- Business operations - 4Ms that influence resultsDocument12 pagesBusiness operations - 4Ms that influence resultsFlorenz DacilloNo ratings yet
- Assignment 5 Chapter 5Document5 pagesAssignment 5 Chapter 5Abeba GselassieNo ratings yet
- MOML1Document3 pagesMOML1trustgloballyNo ratings yet
- Notes Unit 1 - CH 1-EnterpriseDocument7 pagesNotes Unit 1 - CH 1-Enterprisekhalid malikNo ratings yet
- Business EnvironmentDocument20 pagesBusiness Environmentojhakamlesh4No ratings yet
- Planning: Prepared By: Louie B. Alejandro Loren Camelo B. AberoniaDocument19 pagesPlanning: Prepared By: Louie B. Alejandro Loren Camelo B. AberoniaLouie AlejandroNo ratings yet
- Operations Management Midterm - Chapter NotesDocument16 pagesOperations Management Midterm - Chapter NotesgNo ratings yet
- Management Science Unit - 1: What Is Operations Management?Document27 pagesManagement Science Unit - 1: What Is Operations Management?Sushma ReddyNo ratings yet
- Ops Management Final by MZSDocument57 pagesOps Management Final by MZSzubairsalmanpkNo ratings yet
- Investment Plan Profit & Loss StatementDocument6 pagesInvestment Plan Profit & Loss StatementAyubu SambalaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Business EnvironmentDocument13 pagesIntroduction To Business Environmentjahazi2No ratings yet
- Shortnotes GhgsourcingDocument11 pagesShortnotes GhgsourcingYasith WeerasingheNo ratings yet
- Chapter Outline on Introduction to Operations ManagementDocument24 pagesChapter Outline on Introduction to Operations ManagementMonevaNo ratings yet
- ENTREPRENEURSHIP ReviewerDocument3 pagesENTREPRENEURSHIP ReviewerMonica de DiosNo ratings yet
- How to Enhance Productivity Under Cost Control, Quality Control as Well as Time, in a Private or Public OrganizationFrom EverandHow to Enhance Productivity Under Cost Control, Quality Control as Well as Time, in a Private or Public OrganizationNo ratings yet
- HBR's 10 Must Reads on Strategy (including featured article "What Is Strategy?" by Michael E. Porter)From EverandHBR's 10 Must Reads on Strategy (including featured article "What Is Strategy?" by Michael E. Porter)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (25)
- The Outsourcing Revolution (Review and Analysis of Corbett's Book)From EverandThe Outsourcing Revolution (Review and Analysis of Corbett's Book)No ratings yet
- Unit7 D (A2)Document10 pagesUnit7 D (A2)punte77No ratings yet
- Unit7 e (A2)Document10 pagesUnit7 e (A2)punte77No ratings yet
- Unit6 F (AS)Document6 pagesUnit6 F (AS)punte77No ratings yet
- Unit6 A (AS)Document1 pageUnit6 A (AS)punte77No ratings yet
- UNIT 7: Information For Decision Making: © UCLES 2003Document3 pagesUNIT 7: Information For Decision Making: © UCLES 2003punte77No ratings yet
- Unit7 CompleteDocument3 pagesUnit7 Completepunte77No ratings yet
- Unit6 G (A2)Document2 pagesUnit6 G (A2)punte77No ratings yet
- Unit5 B (A2)Document1 pageUnit5 B (A2)punte77No ratings yet
- UNIT 6: Business Accounting: WWW - Carol.co - UkDocument6 pagesUNIT 6: Business Accounting: WWW - Carol.co - Ukpunte77No ratings yet
- Ratio Analysis: S Liabilitie Current Assets CurrentDocument8 pagesRatio Analysis: S Liabilitie Current Assets Currentpunte77No ratings yet
- Unit5 CompleteDocument4 pagesUnit5 Completepunte77No ratings yet
- Unit5 A (A2)Document3 pagesUnit5 A (A2)punte77No ratings yet
- Unit6 e (AS)Document7 pagesUnit6 e (AS)punte77No ratings yet
- Unit6 A (AS)Document1 pageUnit6 A (AS)punte77No ratings yet
- Unit 5: Business Finance: WWW - Carol.co - UkDocument3 pagesUnit 5: Business Finance: WWW - Carol.co - Ukpunte77No ratings yet
- Unit3 D (AS)Document1 pageUnit3 D (AS)punte77No ratings yet
- Marketing Research: Internal Sources of Data External Sources of DataDocument12 pagesMarketing Research: Internal Sources of Data External Sources of Datapunte77No ratings yet
- Unit4 C (AS)Document3 pagesUnit4 C (AS)punte77No ratings yet
- Operations Management Production PlanningDocument6 pagesOperations Management Production Planningpunte77No ratings yet
- UNIT 3: People in Organisations: © UCLES 2003Document6 pagesUNIT 3: People in Organisations: © UCLES 2003punte77No ratings yet
- Break - Even Analysis Exercises: On Contributi Ts Fixed CosDocument7 pagesBreak - Even Analysis Exercises: On Contributi Ts Fixed Cospunte77No ratings yet
- Unit4 (A2)Document1 pageUnit4 (A2)punte77No ratings yet
- Unit4 e (A2)Document3 pagesUnit4 e (A2)punte77No ratings yet
- Unit4 B (AS)Document27 pagesUnit4 B (AS)punte77No ratings yet
- UNIT 4: Operations Management: WWW - Economy.gov - EgDocument6 pagesUNIT 4: Operations Management: WWW - Economy.gov - EgEmran AleeNo ratings yet
- Tecnicas para Cartas de Amor U OdioDocument4 pagesTecnicas para Cartas de Amor U OdioChristian Gabriel Stampacchio100% (16)
- Unit3 A (AS)Document8 pagesUnit3 A (AS)punte77100% (1)
- Unit3 Ce (AS)Document29 pagesUnit3 Ce (AS)punte77No ratings yet
- Pricing StrategyDocument9 pagesPricing StrategyMark Xavier SalazarNo ratings yet
- Economics of the FirmDocument32 pagesEconomics of the FirmAakash GuptaNo ratings yet
- Cost Accounting: Sixteenth EditionDocument29 pagesCost Accounting: Sixteenth EditionHIMANSHU AGRAWALNo ratings yet
- AnnelieAsser FinalThesisDocument68 pagesAnnelieAsser FinalThesisAnnelie AsserNo ratings yet
- Economics IADocument2 pagesEconomics IAAditya Patel67% (3)
- Test Bank For Managerial Economics and Strategy 3rd Edition by PerloffDocument10 pagesTest Bank For Managerial Economics and Strategy 3rd Edition by PerloffDominic Glaze100% (33)
- Business Ethics ANSWERSDocument3 pagesBusiness Ethics ANSWERSMỹ HàNo ratings yet
- Bbqfun Sales Data Worksheet: PerformanceDocument8 pagesBbqfun Sales Data Worksheet: PerformanceJoyce BalagotNo ratings yet
- Construction Contracts ReviewDocument7 pagesConstruction Contracts ReviewRojin TingabngabNo ratings yet
- Small Scale IndustriesDocument88 pagesSmall Scale Industriesashish.bms992% (13)
- Dealing With Competition: Ap Te r4Document25 pagesDealing With Competition: Ap Te r4Md Mozaddedul KarimNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document7 pagesChapter 1Janine LerumNo ratings yet
- BY Rosemary O. OBASI Department of Accounting, Benson Idahosa University, Benin City Edo State, Nigeria +2348053314596Document23 pagesBY Rosemary O. OBASI Department of Accounting, Benson Idahosa University, Benin City Edo State, Nigeria +2348053314596VivienNo ratings yet
- Covid 19 VaccineDocument39 pagesCovid 19 Vaccinehamza AliNo ratings yet
- The Concept of Exchange Leads To The Concept of A MarketDocument163 pagesThe Concept of Exchange Leads To The Concept of A MarketHarsh RajNo ratings yet
- Measuring The Moat - 3Document7 pagesMeasuring The Moat - 3piyushNo ratings yet
- Desirability Profitability Longevity: We'Re Here To HelpDocument1 pageDesirability Profitability Longevity: We'Re Here To Helpdivyansh thakreNo ratings yet
- Japanese EndakaDocument18 pagesJapanese EndakaGunner Anukalpa RoyNo ratings yet
- The Concept of A Company Value Chain: BuyersDocument12 pagesThe Concept of A Company Value Chain: BuyersCarolyn ImaniNo ratings yet
- OB Group Assignment Group 7Document9 pagesOB Group Assignment Group 7Rekik Solomon100% (3)
- Corporate FinanceDocument310 pagesCorporate Financeaditya.c122No ratings yet
- Cement o Cartel No RuegaDocument23 pagesCement o Cartel No RuegaCARLOS ANDRES VASCO CORREANo ratings yet
- Assessment Quiz EconomicsDocument35 pagesAssessment Quiz EconomicsBlack SoyaNo ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument2 pagesCase StudySejal SitaniNo ratings yet
- A Study On Financial Performance Analysis at Magnum Enterprise, BangaloreDocument74 pagesA Study On Financial Performance Analysis at Magnum Enterprise, BangaloredarshanNo ratings yet
- Michigan Ross Casebook Consulting Case Interview Book 2012密西根密歇根大学罗斯商学院咨询案例面试Document180 pagesMichigan Ross Casebook Consulting Case Interview Book 2012密西根密歇根大学罗斯商学院咨询案例面试issac liNo ratings yet
- FM AssignmentDocument30 pagesFM AssignmentANSHUL AGRAWAL MBA 2021-23 (Delhi)No ratings yet
- Price Discrimination ApplicationsDocument22 pagesPrice Discrimination ApplicationsAmine El AzdiNo ratings yet
- Full AssignmentDocument46 pagesFull AssignmentCassandra LimNo ratings yet
- Friends Break-Even Analysis - Group10 - B21Document16 pagesFriends Break-Even Analysis - Group10 - B2120Raka Zain SusetyoNo ratings yet