Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Unit 5: Business Finance: WWW - Carol.co - Uk
Uploaded by
punte77Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Unit 5: Business Finance: WWW - Carol.co - Uk
Uploaded by
punte77Copyright:
Available Formats
UNIT 5: Business Finance
Recommended prior knowledge: None but some students may have covered similar material at IGCSE. The unit in context: This unit deals with the need for business finance and the main sources of it. Finance is central to business activity and the ability to raise capital from appropriate sources at different stages of a firms development and growth is one of the key determinants of a successful business. Although the material covered is very different from previous units there is a constant requirement to refer to the other functional areas of business and stress the role that adequate finance plays in successful marketing, operations management and so on. There are clear links between Business Finance and Unit 6, Business Accounting. Outline: This is quite a short unit but the concepts it contains are very important to understanding the importance of finance and the need to raise it from appropriate sources. The significance of liquidity to a firms survival and growth needs to be made clear. The importance difference between profit and cash needs to be emphasized from the outset. The three parts of this unit comprise: The need for business finance, sources of finance and money and capital market institutions.
Learning Outcomes
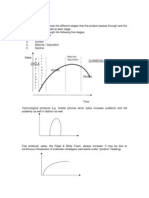
a) The need for business finance Students should be able to: i.) analyse the need for finance during start up and growth stages of a business. ii.) understand the differences between revenue and capital expenditure and that each require different sources of finance. iii.) analyse the meaning and importance of working capital and the factors that determine the amount of working capital required by a business
Suggested Teaching and Student Activities
business finance can be effectively taught through the means of simulated businesses created by the students. The Young Enterprise scheme is excellent. Starting up and operating a simple trading business even just making and selling cakes can drive home the need for both fixed and working capital. This could then be extended into Unit 6 with the keeping of simple accounts for the business. Encourage students to learn by doing in this Unit and the next Unit, in particular.
Resources
Stimpson Chapter 25. Exercises such as Directphone, Dominos and Going exclusive with icecream plus share issue exercises on Easyjet and Fibernet. Revision questions P406. Barratt and Mottershead : Chapter 40 (Case Studies at end of chapter useful but require accounting knowledge not yet covered).
Online Resources
The teaching of this Unit and Unit 6 will be aided greatly by referring to actual company accounts. These will be available from companies own sites. Investigate accounts of two businesses to identify finance sources used particularly a high geared and a low geared company. Try www.carol.co.uk and www.londonstockexchange.com. Use your own Government sites to investigate financial support for businesses.
UCLES 2003
revenue and capital spending discuss by asking for as many examples as possible from students using the school/college as an example. small groups of students creating large posters of the working capital cycle for a business of their choice
Jewell: Chapter 29. Be selective about end of chapter questions some require detailed accounting knowledge. 9707/1 Nov 2001 Q 3 9707/1 June 2003 Q4
iv.) understand the significance of the difference between revenue and capital expenditure v.) analyse and evaluate ways of managing working capital the control of working capital b) Sources of capital Students should be able to: i.) understand the main sources / types of short and long term business finance, both internal and external ii.) analyse the advantages and disadvantages of these .
at A level the significance of the distinction between revenue and capital spending can be made effectively after dealing with profit and loss accounts and balance sheets in Unit 6 these two types of spending have different effects on the final accounts. a well planned visit and talk from a bank manager/official can work effectively especially if linked to case studies or simulations. If Young Enterprise type businesses are set up then ask the bank manager to judge the business plan and decide whether to lend or not to each business large posters of sources of finance, short/long term and internal/external can be kept in class and act as a useful revision source. as above plus 9707/2 June 2001 Q2c; 9707/3 Nov 2002 Qc; try leading banks for details of their interest rates to businesses and financial services to industry. Use bank web sites to discover financial options for industry e.g. www.natwest.co.uk and www.barclays.co.uk. Use own country newspapers for articles on businesses raising finance e.g. www.brecorder.com (Pakistan); www.buenosariesherald.com (Argentina); www.bangkokpost.com (Thailand); www.lexpress-net.com (Mauritius).
UCLES 2003
iii.) evaluate these sources of finance and make recommendations of suitable finance to meet particular business requirements iv.) analyse and discuss the factors that influence the finance decision
past paper 3 case studies can be used as business scenarios. Students can be asked to suggest the most suitable sources of finance for each business, assuming it is planning to expand
c) Money and Capital market institutions Students should be able to: newspapers can provide useful source material articles on finance i.) understand the functions of and institutions as well as adverts for banks and specialist lending banks and specialist lending institutions. agencies. Students need to question ii.) understand the functions of the why there is such a range of Stock Exchange institutions and their functions.
as above
Try bank sites plus www.londonstockexchange.com and http://www.worldbank.org
iii.) analyse the role of the World Bank and International Monetary Fund as sources of finance especially in developing economies
simple treatment only required no need to go into great detail on structural adjustment programmes etc. Students could do own research on internet.
UCLES 2003
You might also like
- Business Plan Checklist: Plan your way to business successFrom EverandBusiness Plan Checklist: Plan your way to business successRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- UNIT 6: Business Accounting: WWW - Carol.co - UkDocument6 pagesUNIT 6: Business Accounting: WWW - Carol.co - Ukpunte77No ratings yet
- Unit 5: Business Finance: WWW - Carol.co - UkDocument3 pagesUnit 5: Business Finance: WWW - Carol.co - UkSylwia SdiriNo ratings yet
- BF 1118Document14 pagesBF 1118maria vierrasNo ratings yet
- Lecture Note On Feasibility StudyDocument22 pagesLecture Note On Feasibility StudyIwuoha Maxrofuzo Chibueze75% (4)
- FinmanDocument52 pagesFinmanErica RamosNo ratings yet
- Economics (49) : NtroductionDocument25 pagesEconomics (49) : NtroductionAmandeep Singh MankuNo ratings yet
- Instructor-In-Charge: Prof. Niranjan Swain: Niranjanswain@pilani - Bits-Pilani.c.inDocument13 pagesInstructor-In-Charge: Prof. Niranjan Swain: Niranjanswain@pilani - Bits-Pilani.c.inSiddharth MehtaNo ratings yet
- Learning Module in Financial ManagementDocument56 pagesLearning Module in Financial ManagementAlexandra Denise PeraltaNo ratings yet
- BMA 12e IM Ch1Document6 pagesBMA 12e IM Ch1miah haNo ratings yet
- Indian School Al Wadi Al Kabir Department of Commerce Holiday Homework-Xii Project Work in AccountancyDocument15 pagesIndian School Al Wadi Al Kabir Department of Commerce Holiday Homework-Xii Project Work in Accountancyzoom zumNo ratings yet
- Book 8Document8 pagesBook 8gudataaNo ratings yet
- FinMan AE 19 Module 1 Intro To FinManDocument8 pagesFinMan AE 19 Module 1 Intro To FinManMILLARE, Teddy Glo B.No ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Financial ManagementDocument14 pagesLecture 1 Financial ManagementAnabelle Gutierrez JulianoNo ratings yet
- II Semester 2016-17 Course Handout BAV ECON F355Document19 pagesII Semester 2016-17 Course Handout BAV ECON F355Tushit ThakkarNo ratings yet
- N Enterprenuership XII NotesDocument29 pagesN Enterprenuership XII Noteskingsley_psb100% (1)
- MODULE 2: Introduction To Financial ManagementDocument6 pagesMODULE 2: Introduction To Financial ManagementJm JuanillasNo ratings yet
- Econ f315 Summer Term 2016-17 IdDocument13 pagesEcon f315 Summer Term 2016-17 IdSrikar RenikindhiNo ratings yet
- AC3059 Financial ManagementDocument4 pagesAC3059 Financial ManagementSaad AtharNo ratings yet
- AC3059 Financial ManagementDocument4 pagesAC3059 Financial ManagementJ TNo ratings yet
- Fstep Manual Investment Banking FinalDocument208 pagesFstep Manual Investment Banking FinalThiện Phong100% (3)
- Tools Assignments 10Document10 pagesTools Assignments 10Hongyi-George SongNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - Financial Management and Policies - SyllabusDocument7 pagesChapter 5 - Financial Management and Policies - SyllabusharithraaNo ratings yet
- Term Paper of Financial ManagementDocument6 pagesTerm Paper of Financial Managementafmzmxkayjyoso100% (1)
- 2 FA Course ENG Final PDFDocument142 pages2 FA Course ENG Final PDFCinar InalNo ratings yet
- Annamalai University: Directorate of Distance EducationDocument4 pagesAnnamalai University: Directorate of Distance EducationAdd K100% (1)
- Corporate Level StrategyDocument49 pagesCorporate Level StrategyHuy PhamNo ratings yet
- FINANCE COURSES - Student Learning Outcomes: FIN 240: Legal Environment of BusinessDocument18 pagesFINANCE COURSES - Student Learning Outcomes: FIN 240: Legal Environment of BusinessGrant GreenNo ratings yet
- Draft Training Manual FOR General Entrepreneurship Courses in UniversitiesDocument45 pagesDraft Training Manual FOR General Entrepreneurship Courses in UniversitiesMuh'd Kabir ZakariyyahNo ratings yet
- Financial ManagementDocument419 pagesFinancial ManagementVishnu SureshNo ratings yet
- Basic Business Finance 07Document8 pagesBasic Business Finance 07knockdwnNo ratings yet
- Project Proposal FinalDocument14 pagesProject Proposal Finalapi-320213112100% (2)
- Entrepreneurship ProcessDocument3 pagesEntrepreneurship ProcessDavs ThorNo ratings yet
- GSM687Document11 pagesGSM687icdawar0% (1)
- Study System Session Topic Study Bank Date Completed 0 SyllabusDocument10 pagesStudy System Session Topic Study Bank Date Completed 0 SyllabusMadalina CiupercaNo ratings yet
- Finance Electives PresentationDocument15 pagesFinance Electives PresentationAbhinaba GhoseNo ratings yet
- Bim 29 V Tri SyllabiDocument26 pagesBim 29 V Tri SyllabishivamusNo ratings yet
- Financial Statement Analasis.: Name of The Student:-SOUMIK DUTTADocument10 pagesFinancial Statement Analasis.: Name of The Student:-SOUMIK DUTTAMD AdnanNo ratings yet
- Executive SummaryDocument65 pagesExecutive SummaryTahir HussainNo ratings yet
- Syllabus B7345-001 Entrepreneurial FinanceDocument7 pagesSyllabus B7345-001 Entrepreneurial FinanceTrang TranNo ratings yet
- ECON F315 - FIN F315 - Financial ManagementDocument14 pagesECON F315 - FIN F315 - Financial ManagementShikhar SahayNo ratings yet
- FPSAA5 - Finance SourcesDocument3 pagesFPSAA5 - Finance SourcesNuriel AguilarNo ratings yet
- Case Studies of Business AdministrationDocument18 pagesCase Studies of Business AdministrationAnamika Sengupta100% (1)
- Business Finance Pre - Test and Lesson 1Document29 pagesBusiness Finance Pre - Test and Lesson 1Iekzkad RealvillaNo ratings yet
- 7 F 93 CB 558 CDocument20 pages7 F 93 CB 558 CPabloCaicedoArellanoNo ratings yet
- Business Finance: Basic Education Department Senior High School ABM SY 2023-2024Document28 pagesBusiness Finance: Basic Education Department Senior High School ABM SY 2023-2024LuWiz DiazNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Business ActivityDocument4 pagesUnit 1 Business ActivityMarisa VetterNo ratings yet
- Business Research MethodDocument25 pagesBusiness Research MethodGimhani LiyanageNo ratings yet
- Dlsu EntrepreneurshipDocument3 pagesDlsu EntrepreneurshipJohaira PanumpangNo ratings yet
- FIN 400 Course SylDocument4 pagesFIN 400 Course SylShebelle ColoradoNo ratings yet
- Advanced Corporate Finance (Moon) SP2016Document7 pagesAdvanced Corporate Finance (Moon) SP2016darwin12100% (1)
- 1.4 An Overview of The Capital Allocation Process: Self-TestDocument1 page1.4 An Overview of The Capital Allocation Process: Self-Testadrien_ducaillouNo ratings yet
- Cash Flow AdministrationDocument5 pagesCash Flow AdministrationGabriela RiveraNo ratings yet
- Business in Action 8th Edition Bovee Solutions ManualDocument15 pagesBusiness in Action 8th Edition Bovee Solutions Manualnhatmaiqfanmk100% (32)
- An Introduction to Stocks, Trading Markets and Corporate Behavior: Student EditionFrom EverandAn Introduction to Stocks, Trading Markets and Corporate Behavior: Student EditionRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Unit7 e (A2)Document10 pagesUnit7 e (A2)punte77No ratings yet
- Unit7 D (A2)Document10 pagesUnit7 D (A2)punte77No ratings yet
- Unit6 A (AS)Document1 pageUnit6 A (AS)punte77No ratings yet
- Unit7 CompleteDocument3 pagesUnit7 Completepunte77No ratings yet
- Unit5 A (A2)Document3 pagesUnit5 A (A2)punte77No ratings yet
- Ratio Analysis: S Liabilitie Current Assets CurrentDocument8 pagesRatio Analysis: S Liabilitie Current Assets Currentpunte77No ratings yet
- Operations Management Production PlanningDocument6 pagesOperations Management Production Planningpunte77No ratings yet
- Unit4 C (AS)Document3 pagesUnit4 C (AS)punte77No ratings yet
- Unit4 A (AS)Document3 pagesUnit4 A (AS)punte77No ratings yet
- Break - Even Analysis Exercises: On Contributi Ts Fixed CosDocument7 pagesBreak - Even Analysis Exercises: On Contributi Ts Fixed Cospunte77No ratings yet
- A2 Option Module 8 Behaviour and Populations: Specification TableDocument18 pagesA2 Option Module 8 Behaviour and Populations: Specification Tablepunte77No ratings yet
- UNIT 3: People in Organisations: © UCLES 2003Document6 pagesUNIT 3: People in Organisations: © UCLES 2003punte77No ratings yet
- Unit3 D (AS)Document1 pageUnit3 D (AS)punte77No ratings yet
- Unit4 (A2)Document1 pageUnit4 (A2)punte77No ratings yet
- Unit3 Ce (AS)Document29 pagesUnit3 Ce (AS)punte77No ratings yet
- Marketing Research: Internal Sources of Data External Sources of DataDocument12 pagesMarketing Research: Internal Sources of Data External Sources of Datapunte77No ratings yet
- Unit2 D (A2)Document2 pagesUnit2 D (A2)punte77No ratings yet
- Unit2 B (A2)Document1 pageUnit2 B (A2)punte77No ratings yet
- Module 4Document69 pagesModule 4punte77No ratings yet
- Module 2Document40 pagesModule 2San SiddzNo ratings yet
- Prepare The Following Based On This Topic: Inflation and Juan Dela Cruz. Statement of The ProblemDocument4 pagesPrepare The Following Based On This Topic: Inflation and Juan Dela Cruz. Statement of The ProblemFrencis A. EsquierdoNo ratings yet
- Vision of Microfinance in IndiaDocument28 pagesVision of Microfinance in Indiashiva1720No ratings yet
- Project Report On Birla Sunlife Mutual FundDocument46 pagesProject Report On Birla Sunlife Mutual FundSandeepSingh83% (6)
- Additional Practice Questions and AnswersDocument32 pagesAdditional Practice Questions and AnswersMonty Bansal100% (1)
- Uucms - Karnataka.gov - in ExamGeneral PrintExamApplicationDocument1 pageUucms - Karnataka.gov - in ExamGeneral PrintExamApplicationmdirfaniffu5No ratings yet
- 3) From - SF - To - VaRDocument48 pages3) From - SF - To - VaRDunsScotoNo ratings yet
- Marketing MathematicsDocument97 pagesMarketing MathematicspsoonekNo ratings yet
- English Q1W1-G5Document221 pagesEnglish Q1W1-G5JONALYN EVANGELISTANo ratings yet
- F7 Workbook Q & A PDFDocument247 pagesF7 Workbook Q & A PDFREGIS Izere100% (1)
- Breakdown ShortDocument1 pageBreakdown ShortJulie Anthonette RistonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Capital MarketsDocument9 pagesChapter 2 Capital MarketsFarah Nader Gooda100% (1)
- C1 - Guaranty Trust Bank PLC Nigeria (A)Document15 pagesC1 - Guaranty Trust Bank PLC Nigeria (A)Anisha RaiNo ratings yet
- 04 2013-2014 Financial AgreementDocument2 pages04 2013-2014 Financial Agreementapi-234678525No ratings yet
- Merchant BankingDocument49 pagesMerchant BankingChandrika DasNo ratings yet
- Company Valuation MethodsDocument20 pagesCompany Valuation MethodsKlaus LaurNo ratings yet
- University of Lagos: School of Postgraduate StudiesDocument17 pagesUniversity of Lagos: School of Postgraduate StudiesAguda Henry OluwasegunNo ratings yet
- Treasury Circular No. 05-2014Document3 pagesTreasury Circular No. 05-2014Jean Monique Oabel-TolentinoNo ratings yet
- SHARES - EXERCISES - KopiaDocument6 pagesSHARES - EXERCISES - KopiaOla KrupaNo ratings yet
- The Fall of The House of Credit PDFDocument382 pagesThe Fall of The House of Credit PDFRichard JohnNo ratings yet
- Foreign Exchange ManagementDocument21 pagesForeign Exchange ManagementSreekanth GhilliNo ratings yet
- FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT Full ModuleDocument72 pagesFINANCIAL MANAGEMENT Full Modulenegamedhane58No ratings yet
- Account Statement As of 21-03-2020 11:43:46 GMT +0530Document2 pagesAccount Statement As of 21-03-2020 11:43:46 GMT +0530Sourabh MeenaNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Survey of Accounting 8th Edition Carl S Warren DownloadDocument21 pagesTest Bank For Survey of Accounting 8th Edition Carl S Warren DownloadCrystalDavisibng100% (18)
- Investment Undertakings PDFDocument64 pagesInvestment Undertakings PDFDianneNo ratings yet
- Demonetisation in India: A Study of Its' Impact On Various Key SectorsDocument8 pagesDemonetisation in India: A Study of Its' Impact On Various Key SectorsHimanshuNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Pay Order and Demand DraftDocument3 pagesDifference Between Pay Order and Demand DraftAman DegraNo ratings yet
- National CPI: (April 2015 = 100) (یرو)Document25 pagesNational CPI: (April 2015 = 100) (یرو)Sakhi AhmadyarNo ratings yet
- 4th Accounts Dec 2021Document2 pages4th Accounts Dec 2021KillingNo ratings yet
- IJCRT2203243Document10 pagesIJCRT2203243Tushar MusaleNo ratings yet
- FMT 14Document8 pagesFMT 14Armel AbarracosoNo ratings yet