Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Drug Study-Ceftriaxone Clindamycin
Uploaded by
David VillanuevaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Drug Study-Ceftriaxone Clindamycin
Uploaded by
David VillanuevaCopyright:
Available Formats
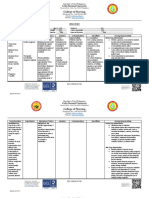
Arellano University Legarda, Manila Submitted by: Trinidad, Czarina May V.
BSN III Section 3 NCM 102-RLE MS Ward Mr. Von Bacuyag July 18-19,25-26, 2011 Name of Patient: Mr. R. A. Age/Sex: 56 year old, male
Name of Drug Generic Name: Ceftriaxone Brand Name: Rocephin
Mechanism of Action -Inhibits bacterial cell wall synthesis, rendering cell wall osmotically unstable, leading to cell death
Adverse Reaction -Leukopenia, serum sickness, anaphylaxis.
Indication -Treatment of LRIT (e.g. bronchitis, pneumonia, bronchopneumonia, emphysema, lung abscess), skin and soft tissue infections. Pre-operative prophylaxis to reduce chance of postoperative surgical infections.
Contraindication -Hypersensitivity to cephalosporins and penicillins, lidocaine or any other local anaesthetic product of the amide type -Use with caution in patients with history of gastrointestinal disease. Nephrotoxicity has been reported following concomitant administration with aminoglycosides.
Side Effects: -Phlebitis, rash, diarrhea, vomiting.
Nursing Responsibilities -Instruct patient to take medication as prescribed for the length of time ordered even if he feels better. -Teach patient to report sore throat, bruising, bleeding and joint pain. -Advise patient to watch out for perineal itching, fever, malaise, redness, pain, swelling, rash diarrhea.
Classification: Antimicrobial and Antiparasitic Availability: Injection and Infusion
Name of drug
Mechanism of Action
Adverse Effects
Indication
Contraindication
Nursing Responsibilities -assess patients infection before and regularly throughout therapy -monitor renal, hepatic, and hematopoetic functions during prolonged therapy. -be alert for adverse reactions and drug interactions -if adverse GI reactions occurs, monitor patients hydration. -tell patient to take entire amount prescribed even after he feels better. -instruct patient to report diarrhea and to avoid selfthreatening psudomembranus colitis -tell patient receiving drug I.V. to report discomfort at infusion site.
Clindamycin ANTIBIOTIC; Anti- infectives
- inhibits bacterial protein synthesis by binding to 50S subunit of ribosome. - hinders or kills susceptible bacteria.
CNS: headache CV: Thrombophlebitis EENT: pharyngitis GI: abdominal pain, Anorexia, bloody or tarry stools, constipation, diarrhea, dysphagia, esophagitis, flatulence, nausea, psuedomembranus colitis, unpleasant or bitter taste, vomiting. GU: UTI HEMATOLOGIC: Eosinophilia, thrombocytopenia, transient leukopenia SKIN: maculopapular rash, urticaria OTHER: anaphylaxis, erythema, pain (I.V. use), induration, pain; sterile abcess (I.M. use)
- infections caused by sensitive staphylococci, streptococci, pneumococci, bacteroides, fusibacterium, clostridium perfringens, and other sensitive aerobic and anaerobic organisms. -endocarditis prophylaxis for dental procedures in patients allergic to penicillin -acne vulgaris -bacterial vaginosis - pneumocystis jiroveci (carinii) pneumonia -toxoplasmosis (cerebral or ocular) immunocompromise d patients
-contraindicated in patients hypersensitive to drug or lincomycin -use cautiously in patients with renal or hepatic disease, asthma, history of GI disease, or significant allergies.
You might also like
- Oral Suspension: 125 mg/5 Powder For Injection: 750 Premixed Containers: 750Document1 pageOral Suspension: 125 mg/5 Powder For Injection: 750 Premixed Containers: 750Diane Grace PadillaNo ratings yet
- CelecoxibDocument2 pagesCelecoxibHazelSteffiNo ratings yet
- Dolan Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDolan Drug StudyLian Robbie BautistaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Nephrotic SyndromeDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Nephrotic SyndromeKristian Karl Bautista Kiw-isNo ratings yet
- DuphalacDocument2 pagesDuphalacianecunarNo ratings yet
- P 398Document1 pageP 398Arup Ratan PaulNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - AmlodipineDocument1 pageDrug Study - AmlodipineDanielle Marie SamblacenoNo ratings yet
- PrednisoloneDocument2 pagesPrednisoloneKatie McPeekNo ratings yet
- Drug study cilostazol intermittent claudicationDocument2 pagesDrug study cilostazol intermittent claudicationart_mutantNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument13 pagesDrug StudyAldrin Ian Oraza AlpeNo ratings yet
- Vitamin KDocument2 pagesVitamin KMuvs RazonNo ratings yet
- Drug Study FDocument3 pagesDrug Study FFatima Love Ariate-ArcasetasNo ratings yet
- Sal But AmolDocument2 pagesSal But AmolKay MirandaNo ratings yet
- LacipilDocument2 pagesLacipilianecunarNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - CefoxitinDocument5 pagesDrug Study - CefoxitinShaniah DawaNo ratings yet
- Aspirin Drug SummDocument2 pagesAspirin Drug SummWarren0% (1)
- Drug Analysis CefoxitinDocument2 pagesDrug Analysis CefoxitinNika LoNo ratings yet
- Ertapenem (Invanz)Document1 pageErtapenem (Invanz)Adrianne BazoNo ratings yet
- CoversylDocument3 pagesCoversylianecunarNo ratings yet
- DrugStudy - CamaristaColeenMaeC (BSN III-G) (Prednisone)Document2 pagesDrugStudy - CamaristaColeenMaeC (BSN III-G) (Prednisone)Coleen Mae CamaristaNo ratings yet
- Medication: Expected Pharmacological Action Therapeutic UseDocument1 pageMedication: Expected Pharmacological Action Therapeutic UseMarina Wasem NetzlaffNo ratings yet
- KetorolacDocument5 pagesKetorolacMichelle Ann P. NacuaNo ratings yet
- Xarelto PDFDocument33 pagesXarelto PDFNovita Dewi LestariNo ratings yet
- Nifedipine and Prednisone Drug StudyDocument5 pagesNifedipine and Prednisone Drug StudyAllyne GavinoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument1 pageDrug StudycliffordbuenoNo ratings yet
- LOSARTANDocument3 pagesLOSARTANReinell GoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug StudyXio PauNo ratings yet
- Rathna Drug Card in (Lovenox)Document1 pageRathna Drug Card in (Lovenox)erdos13No ratings yet
- Tramadol Drug StudyDocument4 pagesTramadol Drug StudyJust A Nsg StudentNo ratings yet
- RituximabDocument2 pagesRituximabBigBoosting100% (2)
- Drug - Htm#description.: Reference: Submitted By: Date Submitted: Submitted ToDocument2 pagesDrug - Htm#description.: Reference: Submitted By: Date Submitted: Submitted ToSHEILA MAE SACLOTNo ratings yet
- Indications:: Brand Name: Classificati OnDocument1 pageIndications:: Brand Name: Classificati OnTel SisonNo ratings yet
- Drug Study EditedDocument5 pagesDrug Study EditedfabtaciousVeelaNo ratings yet
- DRUG-STUDY - BALLON, Karlo CDocument6 pagesDRUG-STUDY - BALLON, Karlo CMelinda Cariño BallonNo ratings yet
- Generic NameDocument2 pagesGeneric NamePerdie Branden ReizNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument21 pagesDrug StudyShyla Garnace JavillonarNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - CefradoxilDocument13 pagesDrug Study - CefradoxilJohara G'naid0% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument20 pagesDrug StudydjanindNo ratings yet
- SpironolactoneDocument2 pagesSpironolactoneNinoska Garcia-Ortiz100% (1)
- Ketorolac: Uses, Dosing, Side EffectsDocument14 pagesKetorolac: Uses, Dosing, Side EffectsVin LandichoNo ratings yet
- Sal But AmolDocument2 pagesSal But AmolCalimlim KimNo ratings yet
- Drug AnalysisDocument3 pagesDrug AnalysisAbby BorabienNo ratings yet
- NCP For Ruptured AppendicitisDocument2 pagesNCP For Ruptured AppendicitisJansen Arquilita RiveraNo ratings yet
- As Pi LetDocument7 pagesAs Pi Letianecunar100% (1)
- Drug Study Domperidone CompressDocument1 pageDrug Study Domperidone CompressAngelica TolledoNo ratings yet
- Cefoxitin Nursing Responsibilities Monitoring ParametersDocument1 pageCefoxitin Nursing Responsibilities Monitoring ParametersDaryl PaglinawanNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug StudyKaloy KamaoNo ratings yet
- Treatment Options for Coronary InsufficiencyDocument7 pagesTreatment Options for Coronary InsufficiencyMae Navidas DigdiganNo ratings yet
- Verapamil HCLDocument3 pagesVerapamil HCLMae Ann Bueno CastillonNo ratings yet
- Drug Study LevofloxacinDocument2 pagesDrug Study LevofloxacinDannah BulliandayNo ratings yet
- DioxelDocument1 pageDioxelJosselle Sempio CalientaNo ratings yet
- Clindamycin (Cleocin)Document2 pagesClindamycin (Cleocin)Erickson Caisido GarciaNo ratings yet
- Albuterol Drug StudyDocument7 pagesAlbuterol Drug StudyMaria Charlene OrpillaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrug StudyMaAngelica Tresha RaonNo ratings yet
- Drug Study 2Document4 pagesDrug Study 2roxybabesNo ratings yet
- Ranitidine and Omeprazole Nursing CareDocument3 pagesRanitidine and Omeprazole Nursing CareJose Jr A PerunaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study GabrielaDocument4 pagesDrug Study GabrielaNimrodNo ratings yet
- Ventolin Nebulizer for Bronchospasm ReliefDocument10 pagesVentolin Nebulizer for Bronchospasm ReliefmidskiescreamzNo ratings yet
- Ceftazidime nursing implications for administration and monitoringDocument1 pageCeftazidime nursing implications for administration and monitoringPaulineNo ratings yet
- Cefixime and Azithromycin Drug GuideDocument3 pagesCefixime and Azithromycin Drug GuideArianne Joy SalvadorNo ratings yet
- Philippine Laws Governing Health CareDocument6 pagesPhilippine Laws Governing Health CareAdlair100% (1)
- IntroductionDocument42 pagesIntroductionDavid VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Petty Cash FundDocument14 pagesPetty Cash FundDavid VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Joel Reyes ResumeDocument3 pagesJoel Reyes ResumeDavid VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Neurological basis and theories of emotionDocument5 pagesNeurological basis and theories of emotionDavid VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Hzedtjsfhjwsj Gdysdhg Mechanism of ActionDocument1 pageHzedtjsfhjwsj Gdysdhg Mechanism of ActionDavid VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Do LstenDocument2 pagesDo LstenDavid VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- GND - Arellano University LEGARDADocument13 pagesGND - Arellano University LEGARDADavid VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Dolsten (Mefenamic Acid) : Relief of Pain Including Muscular, Rheumatic, TraumaticDocument2 pagesDolsten (Mefenamic Acid) : Relief of Pain Including Muscular, Rheumatic, TraumaticDavid VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Exposure To Toxic SubstancesDocument21 pagesExposure To Toxic SubstancesDavid VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Wasfjdsfjstjk Mechanism of Action: Mechanism of Action: Mechanism of Action: Mechanism of ActionDocument1 pageWasfjdsfjstjk Mechanism of Action: Mechanism of Action: Mechanism of Action: Mechanism of ActionDavid VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Asia Pacific CollageDocument3 pagesAsia Pacific CollageDavid VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Planning Implementation Scientific Rationale EvaluationDocument1 pageAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Planning Implementation Scientific Rationale EvaluationDavid VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Yhfsjdsjdfj Mechanism of ActionDocument1 pageYhfsjdsjdfj Mechanism of ActionDavid VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Exposure To Toxic SubstancesDocument21 pagesExposure To Toxic SubstancesDavid VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Exposure To Toxic SubstancesDocument21 pagesExposure To Toxic SubstancesDavid VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Social HistoryDocument1 pageSocial HistoryDavid VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Exposure To Toxic SubstancesDocument21 pagesExposure To Toxic SubstancesDavid VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Physical ExaminationDocument2 pagesPhysical ExaminationDavid VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- PDocument3 pagesPDavid VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- JakeDocument1 pageJakeDavid VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Mary Grace Mondia SalaDocument2 pagesMary Grace Mondia SalaDavid VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- AssessmentDocument2 pagesAssessmentDavid VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- AcuteLymphoblasticLeukemia PDFDocument23 pagesAcuteLymphoblasticLeukemia PDFDavid VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Major and Minor Cases ExampleDocument1 pageMajor and Minor Cases ExampleDavid VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Rodel F. (2) 52Document3 pagesRodel F. (2) 52David VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Nervous Tissue Support Cells Brain Medulla Oblongata Central Nervous System Occipital Bone Lumbar Vertebrae Vertebral ColumnDocument3 pagesNervous Tissue Support Cells Brain Medulla Oblongata Central Nervous System Occipital Bone Lumbar Vertebrae Vertebral ColumnDavid VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Objectives of The StudyDocument20 pagesObjectives of The StudyDavid VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Specific ObjectiveDocument20 pagesSpecific ObjectiveDavid VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Nationa L Pokéde X English Name Japanese Name Johto Hoe NN Sinnoh Unov A (O LD) Evolution FromDocument143 pagesNationa L Pokéde X English Name Japanese Name Johto Hoe NN Sinnoh Unov A (O LD) Evolution FromDavid VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Surgical Item - Price ListDocument2 pagesSurgical Item - Price ListRamnish MishraNo ratings yet
- A Comparative Study Between Various Models of Eco-Brick and Hollow BlocksDocument9 pagesA Comparative Study Between Various Models of Eco-Brick and Hollow BlocksMykaila Ysa ValdezNo ratings yet
- PatternPro Variable Pitch GunDocument2 pagesPatternPro Variable Pitch GunVõ HòaNo ratings yet
- Comparative Evaluation of The Diametral Tensile Strength of Four Commercially Available Luting Cements An in - Vitro StudyDocument16 pagesComparative Evaluation of The Diametral Tensile Strength of Four Commercially Available Luting Cements An in - Vitro StudyInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Design AI Platform Using Fuzzy Logic Technique To Diagnose Kidney DiseasesDocument9 pagesDesign AI Platform Using Fuzzy Logic Technique To Diagnose Kidney DiseasesTELKOMNIKANo ratings yet
- Caregiving Learning Activity SheetDocument7 pagesCaregiving Learning Activity SheetJuvy Lyn Conda100% (5)
- IEC60947 3 Approved PDFDocument3 pagesIEC60947 3 Approved PDFosmpotNo ratings yet
- Project Report On Biodegradable Plates, Glasses, Food Container, Spoon Etc.Document6 pagesProject Report On Biodegradable Plates, Glasses, Food Container, Spoon Etc.EIRI Board of Consultants and Publishers0% (1)
- A Text Book On Nursing Management AccordDocument790 pagesA Text Book On Nursing Management AccordMohammed AfzalNo ratings yet
- Civil-Engineering-Final-Year-Project-Quarry Dust As A Substitute of River Sand in Concrete Mixes PDFDocument75 pagesCivil-Engineering-Final-Year-Project-Quarry Dust As A Substitute of River Sand in Concrete Mixes PDFVEERKUMAR GNDEC100% (1)
- Dladla Effect 2013Document231 pagesDladla Effect 2013TheDreamMNo ratings yet
- Rendemen Dan Skrining Fitokimia Pada Ekstrak DaunDocument6 pagesRendemen Dan Skrining Fitokimia Pada Ekstrak DaunArdya YusidhaNo ratings yet
- Refrigerant Color Code ChartDocument11 pagesRefrigerant Color Code ChartJeffcaster ComelNo ratings yet
- Questions That Appear On Every NBMEDocument6 pagesQuestions That Appear On Every NBMESanz100% (1)
- 016-5032-002-C - SmarTrax - Case IH STX-Steiger-Quadtrac (AccuGuide-Ready) and New Holland TJ-T90X0-T9XXX (IntelliSteer-Ready) - Installation ManualDocument26 pages016-5032-002-C - SmarTrax - Case IH STX-Steiger-Quadtrac (AccuGuide-Ready) and New Holland TJ-T90X0-T9XXX (IntelliSteer-Ready) - Installation ManualAndreyNo ratings yet
- Archives of Oral Biology 100 (2019) 42-48Document7 pagesArchives of Oral Biology 100 (2019) 42-48pedro cuellar proNo ratings yet
- M96SC05 Oleo StrutDocument6 pagesM96SC05 Oleo Strutchaumont12345No ratings yet
- Personal and Group Trainer Juan Carlos GonzalezDocument2 pagesPersonal and Group Trainer Juan Carlos GonzalezDidier G PeñuelaNo ratings yet
- Coa Polivinilpirrolidona K-90 (PVP K-90) Lote 20221019Document1 pageCoa Polivinilpirrolidona K-90 (PVP K-90) Lote 20221019Ives AlbarracinNo ratings yet
- Urinary System 1. List The Functions of The KidneysDocument6 pagesUrinary System 1. List The Functions of The KidneysheerNo ratings yet
- HZB-15S Service ManualDocument20 pagesHZB-15S Service ManualJason Cravy100% (1)
- Narrative Poetry 6305Document14 pagesNarrative Poetry 6305Siti AisyahNo ratings yet
- 16 Point Msds Format As Per ISO-DIS11014 PDFDocument8 pages16 Point Msds Format As Per ISO-DIS11014 PDFAntony JebarajNo ratings yet
- 5 (Jeremy Stranks) Health and Safety Pocket BookDocument10 pages5 (Jeremy Stranks) Health and Safety Pocket BookTuralNo ratings yet
- F 204 (AutoRecovered)Document27 pagesF 204 (AutoRecovered)safiqulislam100% (1)
- Excipients As StabilizersDocument7 pagesExcipients As StabilizersxdgvsdgNo ratings yet
- SpokenEnglish Section1 TheSoundSystemOfEnglishDocument132 pagesSpokenEnglish Section1 TheSoundSystemOfEnglishRaj Yash100% (1)
- Paper Pet ProjectDocument27 pagesPaper Pet Projectapi-406104878No ratings yet
- Annotated Bibliography Graphic OrganizerDocument4 pagesAnnotated Bibliography Graphic Organizerapi-348035481No ratings yet
- What It Is and The Six Steps Necessary To Achieve ItDocument40 pagesWhat It Is and The Six Steps Necessary To Achieve ItMalory RobayoNo ratings yet