Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Indian Contract Act
Uploaded by
Vishal GaurOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Indian Contract Act
Uploaded by
Vishal GaurCopyright:
Available Formats
Social & Legal Issues
Indian Contract Act 1872
Social & Legal Issues
INDIAN CONTRACT ACT 1872
Indian Contract Act consists of the way we enter into a contract, execute a contract, implement provisions of a contract and effects of breach of a contract Provides a framework of rules and regulations which govern formation and performance of contract The Act extends to the whole of India except the State of Jammu and Kashmir and came into effect on 1-9-1872. There are separate Acts which deal with contracts relating to negotiable instruments, transfer of property, sale of goods, etc.
Social & Legal Issues
INDIAN CONTRACT ACT 1872
Contract need not be in writing, unless there is specific provision in law that the contract should be in writing. A verbal contract is equally enforceable, if it can be proved
Social & Legal Issues
FORMATION OF A CONTRACT
an agreement
The agreement should be enforceable by law
WHEN AGREEMENT BECOMES CONTRACT ? WHAT IS AGREEMENT? Every promise and every set of promises forming the consideration for each other. Consensus-ad idem An agreement, the law will enforce is a contract. An agreement is a contract when it is made for some consideration, between parties who are competent, with their free consent and for a lawful object.
Social & Legal Issues
EXAMPLE !!
A agrees to pay Rs 100 to B and B agrees to give him a book which is priced at Rs 100. This is set of promises which form consideration for each other IS A CONTRACT !!
A agrees to pay Rs 100 to B, but B does not promise anything, it is not set of promises forming consideration for each other and hence not an agreement.
NOT A CONTRACT !!
CONSIDERATION : recompense given by the party contracting the other.
ACCEPTANCE : is the consent given to a proposal, and it has the effect of converting the proposal into promise.
PROMISE : A proposal or an offer , when accepted, becomes a promise
Social & Legal Issues
STEPS INVOLVED IN CONTRACT
Offer and its acceptance
Free consent of both parties
Mutual and lawful consideration for agreement
enforceable by law
Parties should be competent to contract Contd.
Object should be lawful
Social & Legal Issues
Certainty and possibility of performance
Contract should not have been declared as void under Contract Act or any other law
VOID CONTRACT : A contract which ceases to be enforceable by law becomes void .Thus, initially a contract cannot be void. The simple reason is that in such a case, it is not a contract at all to begin with. Hence, only a valid contract can become void contract due to some subsequent events. e.g. the person dies or property is destroyed or Government imposes a ban etc. ILLUSTRATION : A agrees to buy a certain horse from B. It turns out that the horse was dead at the time of bargain, though neither party was aware of the fact. The agreement is void.
Social & Legal Issues
Agreement All contracts are agreements, but all agreements are not contract. Salmond The Law of Contracts: is not the whole law of agreement, nor is it the whole law of obligations (commitment). It is the law of those agreements which create obligations and those obligations which have their source in agreements
Social & Legal Issues
Classification of Contract
On the basis of enforceability:
Valid Contract Void Contract Voidable Contract Illegal Contract (Void ab initio) Unenforceable Contracts
On the basis of mode of Creation:
Express Contract Implied Contract Quasi Contract /Constructive contract
Social & Legal Issues
A contract for which there is no legal remedy.
Acceptable alternative ways of describing an unenforceable contract are: An otherwise valid contract, which the courts cannot do anything about if it is breached.
A contract for which the courts cannot help the injured party.
This is an otherwise valid contract but the courts cannot provide a remedy when there is a breach. An example of an unenforceable contract is:
A contract made 10 years ago in which performance of one party was completed 9 years ago but the other party did not pay and no action was taken in the next 9 years. The party that was not paid cannot get paid now because of the Statute of Limitations so the courts can do nothing for the party to whom the money was owed.
Social & Legal Issues
Classification of Contract
On the basis of extent of execution:
Executed Contract Executory Contract Contingent Contract
Social & Legal Issues
Example of Quasi Contract
An example of a quasi-contract is the case of a plumber who accidentally installs a sprinkler system in the lawn of the wrong house. The owner of the house had learned the previous day that his neighbor was getting new sprinklers. That morning, he sees the plumber begin installing them in his own lawn. Pleased at the mistake, he says nothing, and then refuses to pay when the plumber hands him the bill, claiming that he never agreed to pay for the sprinklers. If the plumber can prove that the man knew that the sprinklers were being installed mistakenly on his property and failed to prevent the installation, the court would make him pay under a quasicontract theory. If that knowledge could not be proven, he would not be liable The plumber conferred a benefit on the owner by installing the sprinkler system. The owner accepted the installation of the sprinkler system by not stopping the plumber when he first noticed the mistake. Without payment, the owner will unfairly benefit at the expense of the mistaken plumber.
Social & Legal Issues
Essential Elements of a Valid Contract
1. Proposal and Acceptance: 1. Proposal=offer 2. Essentials Essentials of a Proposal a) Expression of Willingness to do or abstain from doing something b) Expression must be to another person c) Must be made with the view to obtain the assent of the other person. d) Term of proposal must be definite
Social & Legal Issues
Legal Rules Regarding a valid Proposal
A valid proposal must be in conformity with the following: a) It should be expressed or implied b) Terms should be certain and not loose or vague c) Should be capable of creating legal relation. d) An invitation to proposal is not a proposal e) Communicated to the proposee f) Should not contain a term the non compliance of which would amount to acceptance g) Can be made subject to any terms and conditions h) Two identical cross offers do not make a contract. i) May be specific or general.
Social & Legal Issues
Essentials of Valid Acceptance
1) Acceptance must be absolute and unqualified consensus ad idem 2) Acceptance must be expressed in some usual and reasonable manner 3) Mental acceptance is not sufficient in law. 4) Acceptance must be communicated to the proposer 5) Acceptance must be given within reasonable time 6) Acceptance of the proposal is the acceptance of terms. 7) Acceptance of the proposal need not always be expressed in words 8) Acceptance must be by a certain person 9) If the act is done in ignorance of the proposal, it is no acceptance of the proposal
Social & Legal Issues
b) Intention to create Legal Relation c) Lawful Consideration- No consideration no contract Exceptions to No Consideration No Contract 1. An agreement which is registered in writing and based on natural love and affection is valid and enforceable by law. 2. Past voluntary Service 3. Consideration is not required for the creation of an agency. 4. Promise to pay time bared debt is valid if the promise is in writing and duly signed. 5. Consideration to charity 6. Completed Gift
Social & Legal Issues
Capacity of Parties one who is of the age of majority is of sound mind-lunatics, idiots, drunken or intoxicated persons.
disqualified from contracting by any law to which he is subject. Alien enemies, Foreign Ambassadors, Convict, Company/corporation and insolvents.
Social & Legal Issues
Position of agreements by a Minor
An agreement by a minor is void and inoperative as against him No restitution Beneficial agreements are valid contracts No ratification on attaining the age of majority: Contract void ab- initio Minors liability for necessaries Minor partner Contract by minor and adult jointly Position of Minors parents
Social & Legal Issues
Free Consent
Distinction Between Coercion and Undue Influence Points of Distinction Basis Coercion Undue Influence
Consent is obtained Consent is obtained by the by threat of an dominating will of the offence other Mainly of physical character Its of Violent character Its of moral character Subtle in Character
Nature Character
Social & Legal Issues
Distinction between Fraud and Misrepresentation
Points of Distinction
Intention to deceive False statement
Misrepresentation
There is no intention to deceive
Fraud
There is intention to deceive
A false innocent statement False statement without intention to deceive deliberately made to deceive The person making the statement does not believe it to be true Contract Voidable at the option of the party injured and gives right to an independent action in tort (civil wrong doing). This plea can not be raised in case of fraud , except in cases when silence amounts to fraud
Belief of the person making The person making the the statement statement believes it to be true Effects of Breach Contract Voidable at the option of the party injured
Effect of Discovering truth
The contract cannot be avoided if the party whose consent was so caused, had the means of discovering the truth with ordinary diligence
Social & Legal Issues
Lawful Objects: The object of the agreement is unlawful in following cases: If it is forbidden by law If it is of such a nature that , if permitted it would defeat the provision of any law. If it is fraudulent (deceptive). If it involves or implies injury to a person or property of another. If the Court regards it as immoral or exposed to public policy.
Social & Legal Issues
Contingent Contract
a) b) c) A contingent contract is a contract to do or not to do something , if some event collateral to such contract does or does not happen. Contract of insurance and contracts of indemnity (protection) and Guarantee (assurance) are examples of contingent contract. Essentials of Contingent Contract Dependence on a future event Collateral Event: incidental happening as a chance consequence Uncertain Event unknown
Social & Legal Issues
Quasi Contract A quasi contract is not a contract In a Quasi contract the rights and obligations do not arise as a result of an agreement b/w the parties but the law imposes certain obligations under some special circumstances. It is based upon the principle of equity that a person shall not be allowed to get benefit at the expense of another.
Kinds of Quasi Contracts Claim for necessaries supplied to a person incapable of contacting Reimbursement of person paying money due by another, in payment of which he is interested Obligation of person enjoying benefits of non-gratuitous acts Responsibility of finder of goods Liability of a person to whom money is paid, or thing delivered by mistake or under coercion.
Social & Legal Issues
Contract Vs Quasi Contract Pts. of Distinction Contract Quasi Contract
Purpose Contact results from It is an obligation the will of the parties resembling that expressed with a view created by a contract to create an obligation Contract is an agreement The contract has certain essential elements There is no agreement at all Essentials for formation of a contract are absent
Agreement Essential Elements
Nature
Its a full- fledged It only resembles a contract and is binding contract. Its an implied contract , but its results resemble those created by a contract.
Social & Legal Issues
Discharge Of A Contract
A contract coming to an end by: 1. Discharge by Performance: Actual and Attempted 2. Discharge by Mutual Consent: Novation : substitution Rescission :cancellation Alteration Remission: lesser acceptance of sum Waiver :intentional relinquishment 3. Discharge by supervening (unexpected )impossibility Destruction of subject matter Death of he promissor or personal incapacity Outbreak of war Change of law Non existence of a particular state of things
Social & Legal Issues
Cases not covered by supervening impossibility Difficulty of performance Strikes , lockouts and civil disturbance Commercial Impossibility Default of a third person 4) Discharge by lapse of time 5) Discharge by operation of Law Death of the promissor By insolvency By merger 6)Discharge by breach of contract Anticipatory It occurs when party declares his intention of not performing the contact before the performance Actual: It can occur either on due date of performance or during the course of performance
Social & Legal Issues
Contract of Indemnity
A contract by which one party promises to save the other from the loss caused to him by the conduct of the promisor himself , or by the conduct of any other person is called a contract of indemnity
Example: A and B go into a shop. B says to the shopkeeper" let A have the goods, I will see that you are paid The contract is of indemnity (protection) Indemnifier: Person who promises to make good the loss. Indemnified or Indemnity: Person whose loss is to be made good.
Social & Legal Issues
Contract of Guarantee (Security)
A contract of Guarantee is a contract to perform the promise or discharge the liability of a third person in case of his default.
Ex: A and B go into a shop. A says to the shopkeeper C, Let B have the goods, and if he does not pay, I will?
Social & Legal Issues
Distinction: Contract of Indemnity vs Contract of Guarantee
Pt of Distinction Number of Parties Contract of Indemnity Two. The indemnifier and indemnity holder Contract of Guarantee Three. The creditor, the principal debtor and the surety
Object of Purpose
Reimbursement of loss For the surety of the debt or good conduct of an employer One between indemnifier and the indemnified Three. Principal debtor and creditor, between creditor and surety and the third between the surety and the principal debtor The liability of the surety is secondary
Number of Contracts
Nature of Liability
The liability of the indemnifier is primary in nature.
Social & Legal Issues
Distinction: Contract of Indemnity vs Contract of Guarantee
Pt of Distinction Request by the debtor Contract of Indemnity The indemnifier acts independently without any request of the indemnity holder or the third party Contract of Guarantee It is necessary that the surety should give the guarantee at the request of the debtor
Existing Debt or Duty
In most cases ,there is no existing debt or duty
There is existing debt or duty, the performance of which is guaranteed by the surety The surety, after he discharges the debt owing to the creditor, can proceed against the principal debtor in his own right
Right to Sue
The indemnifier cannot sue the third party for loss in his own name. He can only do so if there is an assignment in his favour
Social & Legal Issues
Bailment and Pledge
Bailment : A bailment is the delivery of goods by one person to another for some purpose, upon a contract that they shall , when the purpose is accomplished , be returned to otherwise disposed of according to the direction of the person delivering them.. Bailor : The person delivering the goods. Bailee: The person to whom the goods are delivered .
Pledge: The bailment of goods as security for payment of a debt or performance of a promise is called pledge. The bailor in this case is called a pawner and the bailee is called the pawnee Pledge is therefore a kind of bailment.
Social & Legal Issues
Distinction between Pledge and Bailment Pts of Distinction
Purpose
Pledge
Its a bailment for a specific purpose, i.e security for a loan
Bailment
Goods may be bailed for any purpose. Eg. Repair, sale custody etc
Right of Sale
The pledge has a right No such right of sale of sale, on default after to the bailee giving notice to the pledger.
The pledge has no right of using the goods pledged No such restriction exists for the bailee if the nature of such transition so required.
Right of using the goods
You might also like
- Linear Algebra - Exercise 1Document2 pagesLinear Algebra - Exercise 1Vishal GaurNo ratings yet
- Linear Algebra - Exercise 2Document2 pagesLinear Algebra - Exercise 2Vishal GaurNo ratings yet
- VLSI Technology and Applications 10B11EC612 Syllabus-1Document2 pagesVLSI Technology and Applications 10B11EC612 Syllabus-1Vishal GaurNo ratings yet
- Linear Algebra - Exercise 3Document2 pagesLinear Algebra - Exercise 3Vishal GaurNo ratings yet
- Negotiable Instruments ActDocument22 pagesNegotiable Instruments Actshivam007No ratings yet
- Indian Companies Act1956Document52 pagesIndian Companies Act1956Vishal GaurNo ratings yet
- Worksheet NewDocument17 pagesWorksheet NewVishal GaurNo ratings yet
- Consumer Protection ActDocument22 pagesConsumer Protection ActVishal GaurNo ratings yet
- Case Studies - Contract ActDocument1 pageCase Studies - Contract ActVishal GaurNo ratings yet
- Part - 2 Indian Companies ActDocument22 pagesPart - 2 Indian Companies ActVishal GaurNo ratings yet
- 10BNEC732 Mobile CommunicationsDocument2 pages10BNEC732 Mobile CommunicationsVishal GaurNo ratings yet
- Wireless StandardsDocument34 pagesWireless StandardsVishal GaurNo ratings yet
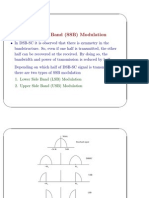
- Digital Modulation: - Continuous-Wave (CW) Modulation (Recap)Document28 pagesDigital Modulation: - Continuous-Wave (CW) Modulation (Recap)HarshaNo ratings yet
- Lecture21-22 SSB VSBDocument16 pagesLecture21-22 SSB VSBVishal GaurNo ratings yet
- Lecture23-24 AngleModulationDocument15 pagesLecture23-24 AngleModulationOsman TolhildanNo ratings yet
- Lecture19 20 Am DSB SCDocument12 pagesLecture19 20 Am DSB SCVishal GaurNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1 (Transformers)Document5 pagesTutorial 1 (Transformers)Vishal GaurNo ratings yet
- Noise in AM FMDocument14 pagesNoise in AM FMHarsha100% (1)
- FTP Roper TiesDocument10 pagesFTP Roper TiesdeepanjankoulNo ratings yet
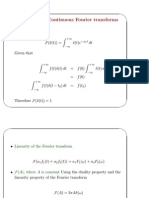
- Continuous Fourier Transforms of Periodic FunctionsDocument5 pagesContinuous Fourier Transforms of Periodic FunctionsanildhasmanaNo ratings yet
- Nyquist Rate and Sampling Theorem PDFDocument9 pagesNyquist Rate and Sampling Theorem PDFAbdul Basit MughalNo ratings yet
- Digital Signal ProcessorsDocument6 pagesDigital Signal ProcessorsVenkatesh SubramanyaNo ratings yet
- TransformersDocument105 pagesTransformersVishal GaurNo ratings yet
- Some Example Continuous Fourier TransformsDocument9 pagesSome Example Continuous Fourier TransformsSrinath SibiNo ratings yet
- Lecture04 FourierSeriesDocument7 pagesLecture04 FourierSeriesVishal GaurNo ratings yet
- Appendix: Some Defintions: The Energy of A Signal X (T) Is Defined AsDocument17 pagesAppendix: Some Defintions: The Energy of A Signal X (T) Is Defined AsVishal GaurNo ratings yet
- Princples of CommunicationDocument9 pagesPrincples of CommunicationHarshaNo ratings yet
- Introduction EMIDocument14 pagesIntroduction EMIVishal GaurNo ratings yet
- Time Complexities of Sorting AlgorithmsDocument1 pageTime Complexities of Sorting AlgorithmsVishal GaurNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Recalpg PDFDocument129 pagesRecalpg PDFDanny FabricioNo ratings yet
- The Punjab Private Housing Schemes and Land Sub-Division Rules, 2010Document52 pagesThe Punjab Private Housing Schemes and Land Sub-Division Rules, 2010Mohammad Raza Mohammad Raza0% (1)
- Tender Document of Tender2813 PDFDocument147 pagesTender Document of Tender2813 PDFbasu_soumen2011No ratings yet
- Participation of Joint Venture Firms in Railway Works TendersDocument6 pagesParticipation of Joint Venture Firms in Railway Works TendersconcretetechgroupNo ratings yet
- Welcome To Presentation On Discharge of SuretyDocument18 pagesWelcome To Presentation On Discharge of SuretyAmit Gurav94% (16)
- BA LLB Hons. 5 YearsDocument122 pagesBA LLB Hons. 5 Yearsvinay jhajhraNo ratings yet
- Kship Bidding Document Vol-I - Final - 11.03Document75 pagesKship Bidding Document Vol-I - Final - 11.03Pradeep KonapoorNo ratings yet
- Building Technology 4Document24 pagesBuilding Technology 4Melaine A. FranciscoNo ratings yet
- ProblemDocument48 pagesProblemArsenio RojoNo ratings yet
- Lamco Docket 7578Document176 pagesLamco Docket 7578Troy UhlmanNo ratings yet
- Dokumen - Tips Commodatum Vs Mutuum Vs DepositDocument8 pagesDokumen - Tips Commodatum Vs Mutuum Vs DepositShazna SendicoNo ratings yet
- Indian Highways Vol.41 3 Mar 13Document82 pagesIndian Highways Vol.41 3 Mar 13Anonymous HJ7hmihh100% (1)
- Corrigendum V 61027 Fab-Strl BarmerDocument3 pagesCorrigendum V 61027 Fab-Strl BarmerPratik GuptaNo ratings yet
- Terp Corp V Banco FilipinoDocument5 pagesTerp Corp V Banco FilipinoJBM De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Education LoanDocument9 pagesEducation LoanPriya Tiku KoulNo ratings yet
- Effects of Guaranty - Mira Hermanos Vs Manila TobacconistsDocument3 pagesEffects of Guaranty - Mira Hermanos Vs Manila TobacconistsPamela ParceNo ratings yet
- Bitanga Vs Pyramid ConstructionDocument10 pagesBitanga Vs Pyramid Constructionlen_dy010487No ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Interpretation of Contracts - Obligations and ContractsDocument44 pagesChapter 5 Interpretation of Contracts - Obligations and ContractsALFREDO PUTAN JRNo ratings yet
- Gur Corporation V Trust Bank of Africa LTD (1987) QB 599: FactsDocument2 pagesGur Corporation V Trust Bank of Africa LTD (1987) QB 599: FactsMUHAMMAD SAQIB GURGAIJNo ratings yet
- Cargill v. Intra Strata AssruanceDocument3 pagesCargill v. Intra Strata AssruancePatrick CarbonellNo ratings yet
- Request For Proposal (RFP) For Enlistment of Valuator PDFDocument25 pagesRequest For Proposal (RFP) For Enlistment of Valuator PDFinnovationNo ratings yet
- Section4 - Particular Conditions of ContractDocument7 pagesSection4 - Particular Conditions of ContractEngr. HayathNo ratings yet
- CP CasesDocument21 pagesCP CasesRochelle GablinesNo ratings yet
- Renovation/Upgradation of MP's Bungalows/Flats TenderDocument157 pagesRenovation/Upgradation of MP's Bungalows/Flats TendernipunNo ratings yet
- Rajasthan State Public Procurement PortalDocument35 pagesRajasthan State Public Procurement PortalRawlot BhatiNo ratings yet
- Second Semester - RemovedDocument26 pagesSecond Semester - RemovedSurekha KulkarniNo ratings yet
- SBI Tender 2 For AO Secunderabad Housekeeping-2021Document45 pagesSBI Tender 2 For AO Secunderabad Housekeeping-2021vuyyuru bhargavNo ratings yet
- Proposed Construction of New Kutulo Airstrip - RetenderDocument112 pagesProposed Construction of New Kutulo Airstrip - RetenderKenyaAirportsNo ratings yet
- Appendix B Specimen Pest Control AgreementDocument25 pagesAppendix B Specimen Pest Control AgreementRaymond Romano100% (1)
- Colortran Price List 1995-1996Document36 pagesColortran Price List 1995-1996Alan MastersNo ratings yet