Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ibon Resp Alkalosis
Uploaded by
Ako Gle C MarizCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ibon Resp Alkalosis
Uploaded by
Ako Gle C MarizCopyright:
Available Formats
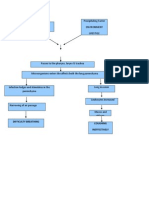
Predisposing Factors Age Sex
Precipitating Factors
pain Anxiety, Psychosis Fever Stroke Meningitis Tumor Anemia High Altitude Salicylate Toxicity Pregnancy, progesterone Pulmonary diseases: pneumonia, pulmonary edema, Pnuemothorax.
Low partial Pressure of the Oxygen in Arterial Blood (Pao2) Peripheral Chemoreceptors Rate of Firing Increases Stimulation of the Respiratory Center in the Medulla Hyperventilation
Hypocapnia
Increase Blood pH
Hypoventilation
Renal buffering
Retention of CO2
H+ Retention
HCO3 Excretion
Blood pH returns to Normal
dizziness, light headedness, agitation, and tingling or numbing around the mouth and in the fingers and hands. Muscle twitching, spasms, and weakness. Seizures, irregular heart beats, and tetany
Nursing diagnosis: Impaired Gas Exchange related to alveolar-capillary membrane changes
1. Monitor respiratory rate, depth, and effort. 2. Auscultate breath sounds. 3. Note character of cough mechanism 4. Assess level of consciuosness. 5. Monitor VS. 6. Evaluate pulse oxymetry. 7. Elevate head of bed. 8. Maintain adequate I/O. 9. Administer meds. 10. Monitor client in therapeutic and adverse reaction of drugs. 11. Encourage frequent position changes.
Nursing diagnosis: Risk for falls related to dizziness 1. Assess factors for fall risk. 2. Assess Mental status changes. 3. Assess Disease-related symptoms. 4. Ensure appropriate room lighting. 5. Encourage to wear shoes /slippers. 6. Provide chair w/ firm seat and arms. 7. Encourage to participate in a regular exercise. 8. Educate about risk factors for fall in home. 9. Place bright, nonskid strips on the edge of stair treads. 10.Ensure rugs are securely fastened to floors. 11.Rearrange furniture. 12.Increase lighting at the top and bottom of stairs.
Nursing diagnosis: Activity Intolerance related to muscle weakness. 1. Determine patient's perception of causes of activity intolerance. 2. Assess level of mobility. 3. Assess nutritional status. 4. Assess potential for physical injury. 5. Assess need for ambulation aids. 6. Monitor sleep pattern. 7. Observe and document response to activity. 8. Assess emotional response. 9. Establish guidelines and goals of activities. 10. Encourage adequate rest periods. 11. Refrain performing nonessential procedures. 12. Anticipate patient's needs. 13. Assist with ADLs. 14. Assist patient to plan activities. 15. Encourage verbalization of feelings regarding limitations. 16. Progress activity gradually. 17. Encourage ROM exercises. 18. Teach appropriate use of environmental aids.
You might also like
- Hole's Human Anatomy and Physiology: Shier W Butler W LewisDocument60 pagesHole's Human Anatomy and Physiology: Shier W Butler W LewisAko Gle C MarizNo ratings yet
- Malaria .....Document3 pagesMalaria .....ulcNo ratings yet
- Simple Resignation Letter Template: Brief, Focused, To The PointDocument1 pageSimple Resignation Letter Template: Brief, Focused, To The PointAko Gle C MarizNo ratings yet
- Death and Dying: We Are Alive, Therefore We Will DieDocument1 pageDeath and Dying: We Are Alive, Therefore We Will DieAko Gle C MarizNo ratings yet
- Death and Dying: We Are Alive, Therefore We Will DieDocument1 pageDeath and Dying: We Are Alive, Therefore We Will DieAko Gle C MarizNo ratings yet
- Death and Dying: We Are Alive, Therefore We Will DieDocument1 pageDeath and Dying: We Are Alive, Therefore We Will DieAko Gle C MarizNo ratings yet
- Gown DesignDocument1 pageGown DesignAko Gle C MarizNo ratings yet
- FACERONDA-Medical Management For Hypo and Hyper KalemiaDocument4 pagesFACERONDA-Medical Management For Hypo and Hyper KalemiaAko Gle C MarizNo ratings yet
- Anthrax 2012 ReportDocument6 pagesAnthrax 2012 ReportAko Gle C MarizNo ratings yet
- Pcap PathophysiologyDocument3 pagesPcap PathophysiologyAko Gle C Mariz80% (10)
- Filariasis SPHDocument43 pagesFilariasis SPHAko Gle C MarizNo ratings yet
- Anthrax 2012 ReportDocument6 pagesAnthrax 2012 ReportAko Gle C MarizNo ratings yet
- Neurologic SystemDocument10 pagesNeurologic SystemAko Gle C MarizNo ratings yet
- Theories of Labor OnsetDocument1 pageTheories of Labor OnsetWeng Maesa MontemayorNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Facts About AidsDocument5 pagesThe Facts About AidsTAMBAKI EDMONDNo ratings yet
- Protocolo MMSDocument7 pagesProtocolo MMSrudolfh1309No ratings yet
- Module 5.hiv AidsDocument52 pagesModule 5.hiv AidsAbuu MuzamiluNo ratings yet
- Lars Krantz - English - Assassination As TheatreDocument3 pagesLars Krantz - English - Assassination As TheatreAnonymous Hwc3rtqMNo ratings yet
- Nursing HIVDocument1 pageNursing HIVnovikaneNo ratings yet
- CandidaDocument25 pagesCandidaKenneth Hansen100% (1)
- Bill MaherDocument31 pagesBill MaherKyle HaugstadNo ratings yet
- Balsam Leaflet en PDFDocument8 pagesBalsam Leaflet en PDFEng. Waleed AhmedNo ratings yet
- Nominalization and Passive Voice ExerciseDocument17 pagesNominalization and Passive Voice ExerciseValerijaNo ratings yet
- The Political Model of Louis FarrakhanDocument20 pagesThe Political Model of Louis FarrakhanC KwikNo ratings yet
- Passed Like A ShadowDocument14 pagesPassed Like A ShadowKifaru Micro-electronics100% (4)
- Grade 8Document89 pagesGrade 8Regie Apilado Cayosa100% (1)
- Chronicle Oct 08Document15 pagesChronicle Oct 08chronicleononly100% (1)
- Health, Fitness, and Wellness Issues During AdulthoodDocument30 pagesHealth, Fitness, and Wellness Issues During AdulthoodAflaha KhanNo ratings yet
- Health and Environment: Impacts of HIV/AIDSDocument5 pagesHealth and Environment: Impacts of HIV/AIDSPamela PascoNo ratings yet
- Beneath The Equator Cultures of Desire, Male Homosexuality, and Emerging Gay Communities in Brazil by Richard ParkerDocument273 pagesBeneath The Equator Cultures of Desire, Male Homosexuality, and Emerging Gay Communities in Brazil by Richard ParkerFernanda GomesNo ratings yet
- EBOOK Health Psychology 10Th Edition Ebook PDF Download Full Chapter PDF KindleDocument61 pagesEBOOK Health Psychology 10Th Edition Ebook PDF Download Full Chapter PDF Kindlejennifer.meyer988100% (39)
- Solidarity - Women and ViolenceDocument44 pagesSolidarity - Women and ViolenceSolidarityUSNo ratings yet
- VIH-SIDA Prevension y TratamientoDocument8 pagesVIH-SIDA Prevension y TratamientoDaniel MarquezNo ratings yet
- Infectious Disease Study Guide 2Document32 pagesInfectious Disease Study Guide 2Jim GoetzNo ratings yet
- PSM Epidemiology and Biostatistics ConceptsDocument25 pagesPSM Epidemiology and Biostatistics ConceptsskNo ratings yet
- Mother To Child Transmition of HIVDocument23 pagesMother To Child Transmition of HIVGenoveva Maditias Dwi PertiwiNo ratings yet
- UNDSELF - Prelims ReviDocument11 pagesUNDSELF - Prelims ReviPandora WinterNo ratings yet
- Clinical Manifestation of Oral TuberculosisDocument6 pagesClinical Manifestation of Oral TuberculosisSasa AprilaNo ratings yet
- IHST 2000 Final Exam ReviewDocument71 pagesIHST 2000 Final Exam ReviewPrincess AlexanderNo ratings yet
- Community and Public Health PortfolioDocument90 pagesCommunity and Public Health PortfolioMeevie ToledoNo ratings yet
- WHO HTS Guidelines - Presentation Part 1: Who HTS: HTS Info On The Go: WHO HTS Data DashboardsDocument39 pagesWHO HTS Guidelines - Presentation Part 1: Who HTS: HTS Info On The Go: WHO HTS Data DashboardsBajram OsmaniNo ratings yet
- Human Resource For Health (HRH) Deployment Program 2018Document4 pagesHuman Resource For Health (HRH) Deployment Program 2018John Rey TalayNo ratings yet
- Impaction Bone Grafting in Revision Arthroplasty - C. Delloye, G. Bannister (Eds.) (Marcel Dekker, 2004) WWDocument466 pagesImpaction Bone Grafting in Revision Arthroplasty - C. Delloye, G. Bannister (Eds.) (Marcel Dekker, 2004) WWdt67No ratings yet
- PCHRD Call For Proposals For 2023 Funding - Detailed FINALDocument42 pagesPCHRD Call For Proposals For 2023 Funding - Detailed FINALKiko MunsayacNo ratings yet