Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Magnetic Fields Explained
Uploaded by
Krystelle Jade Clerigo0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
80 views10 pagesMagnetic fields are produced by electric currents and affect nearby objects along magnetic field lines. The strength of a magnetic field depends on the material producing it and is measured in Teslas. Magnetic field sources include electric currents in wires which produce concentric circular fields, current loops which concentrate the field in the center, and solenoids which concentrate the field even more. Permanent bar magnets produce closed field lines emerging from the North pole and entering the South pole. The Earth has a similar field to a tilted bar magnet attributed to circulating electric currents in its core.
Original Description:
Original Title
Magnetic Fields
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentMagnetic fields are produced by electric currents and affect nearby objects along magnetic field lines. The strength of a magnetic field depends on the material producing it and is measured in Teslas. Magnetic field sources include electric currents in wires which produce concentric circular fields, current loops which concentrate the field in the center, and solenoids which concentrate the field even more. Permanent bar magnets produce closed field lines emerging from the North pole and entering the South pole. The Earth has a similar field to a tilted bar magnet attributed to circulating electric currents in its core.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
80 views10 pagesMagnetic Fields Explained
Uploaded by
Krystelle Jade ClerigoMagnetic fields are produced by electric currents and affect nearby objects along magnetic field lines. The strength of a magnetic field depends on the material producing it and is measured in Teslas. Magnetic field sources include electric currents in wires which produce concentric circular fields, current loops which concentrate the field in the center, and solenoids which concentrate the field even more. Permanent bar magnets produce closed field lines emerging from the North pole and entering the South pole. The Earth has a similar field to a tilted bar magnet attributed to circulating electric currents in its core.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 10
MAGNETIC FIELDS
RLE 3
WHAT ARE MAGNETIC FIELDS?
Are produced by electric currents, which can be macroscopic currents in wires, or microscopic currents associated with electrons in atomic orbits. Magnetic field sources are essentially dipolar in nature, having a north and south magnetic pole.
Areas where an object exhibits magnetic influence
Idea of magnetic field and magnetic field lines first examined by Michael Faraday & later by James Clerk Maxwell
Affect neighboring objects along things called magnetic field lines
Magnetic strength depends on the material that the object is made of The SI unit for magnetic field is the Tesla
MAGNETIC FIELD SOURCES:
MAGNETIC FIELD OF CURRENT:
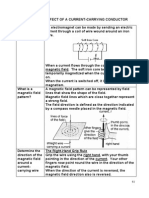
The magnetic field lines around a long wire which carries an electric current form concentric circles around the wire. The direction of the magnetic field is perpendicular to the wire and is in the direction the fingers of your right hand would curl if you wrapped them around the wire with your thumb in the direction of the current.
MAGNETIC FIELD IN CURRENT LOOP
Examining the direction of the magnetic field produced by a current-carrying segment of wire shows that all parts of the loop contribute magnetic field in the same direction inside the loop.
Electric current in a circular loop creates a magnetic field which is more concentrated in the center of the loop than outside the loop. Stacking multiple loops concentrates the field even more into what is called a solenoid.
MAGNETIC FIELD IN SOLENOID
The magnetic field is concentrated in a nearly uniform field in the center of a long selonoid. The field outside is weak and divergent.
MAGNETIC FORCE IN BAR MAGNET
The lines of magnetic field from a bar magnet form closed lines. By convention, the field direction is taken to be outward from the North pole and in to the South pole of the magnet. Permanent magnets can be made from ferromagnetic materials.
MAGNETIC FORCE OF THE EARTH
is similar to that of a bar magnet tilted 11 degrees from the spin axis of the Earth. The Earth's magnetic field is attributed to a dynamo effect of circulating electric current, but it is not constant in direction.
LORENTZ FORCE LAW
Both the electric field and magnetic field can be defined from the Lorentz force law:
The electric force is straightforward, being in the direction of the electric field if the charge q is positive, but the direction of the magnetic part of the force is given by the right hand rule.
You might also like
- DOWLATH Soln MAGNETISMDocument26 pagesDOWLATH Soln MAGNETISMRuqayya ImranNo ratings yet
- Magnetism NotesDocument51 pagesMagnetism Notesroxiboxi300No ratings yet
- 20.1 Understanding MagnetismDocument30 pages20.1 Understanding MagnetismHasan AlzaghalNo ratings yet
- Magneticeffectofelectriccurrent 1 130509054452 Phpapp02Document29 pagesMagneticeffectofelectriccurrent 1 130509054452 Phpapp02Devika ManiNo ratings yet
- Course: Basic Electrical TechnologyDocument18 pagesCourse: Basic Electrical TechnologyUsman ShahidNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Effects of Ec-Part1Document6 pagesMagnetic Effects of Ec-Part1Prisoner FFNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Effect of Electric Current NotesDocument16 pagesMagnetic Effect of Electric Current NotesNistha GuptaNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Effect of Electric Current NOTESDocument29 pagesMagnetic Effect of Electric Current NOTESRishi Kumar DubeyNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument3 pagesPhysicsMohit TiwariNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Effect of Electric Current PortfolioDocument3 pagesMagnetic Effect of Electric Current PortfolioAshish KumarNo ratings yet
- Science Chapter 13 - 1Document10 pagesScience Chapter 13 - 1Radha SahachariNo ratings yet
- Padhle 10th - Magnetic Effects of Electric CurrentDocument30 pagesPadhle 10th - Magnetic Effects of Electric CurrentBitan DasNo ratings yet
- MagnetisumDocument20 pagesMagnetisumPpppNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Effect of Elctric CurrentDocument47 pagesMagnetic Effect of Elctric Currentrahul.op0001opNo ratings yet
- Class 10 - Chp12 Magnetic Effects of Electric CurrentDocument15 pagesClass 10 - Chp12 Magnetic Effects of Electric Currentankitsingh90No ratings yet
- Magnetic Effect of Electric CurrentDocument6 pagesMagnetic Effect of Electric Currentsandeep vermaNo ratings yet
- Magnetism NotesDocument43 pagesMagnetism Notesassssss manNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Effects of Electric Current - Class Notes - Mind Map - Class 10thDocument27 pagesMagnetic Effects of Electric Current - Class Notes - Mind Map - Class 10thsyedyaseen39375No ratings yet
- Notes of Magnetic Effects of Current Class XDocument14 pagesNotes of Magnetic Effects of Current Class Xskshiarora12No ratings yet
- CBSE Class 10 Science Notes Chapter 13 Magnetic Effects of Electric CurrentDocument13 pagesCBSE Class 10 Science Notes Chapter 13 Magnetic Effects of Electric Currentdrphysics256No ratings yet
- Notes For Magnetic Effects of Electric CurrentDocument9 pagesNotes For Magnetic Effects of Electric Currenttanishq.sonar03No ratings yet
- Physics Document on Magnetism and ElectromagnetismDocument21 pagesPhysics Document on Magnetism and ElectromagnetismPhilip MooreNo ratings yet
- Notes of CH - 13Document10 pagesNotes of CH - 13Shabad SinghNo ratings yet
- 7.magnetic Effect of Electric Current - Doc (VII)Document25 pages7.magnetic Effect of Electric Current - Doc (VII)Haerfing AuwNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 ETT 05112 Magnetic Field, Magnetic Flux and Magnetic Force-2Document60 pagesLecture 5 ETT 05112 Magnetic Field, Magnetic Flux and Magnetic Force-2sebastian hezronNo ratings yet
- Class X Science (Magnetic Effect of Electric Current)Document10 pagesClass X Science (Magnetic Effect of Electric Current)Mohammad RezaullahNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Effects of Electric CurrentDocument27 pagesMagnetic Effects of Electric CurrentMIN. Dr. Tanaji sawant officeNo ratings yet
- Attachment PHPDocument7 pagesAttachment PHPKunal Bagade.No ratings yet
- Faraday's & Lenz LawDocument14 pagesFaraday's & Lenz LawPnDeNo ratings yet
- MAGNETIC EFFECTS OF ELECTRIC CURRENT - Class Notes - Warrior 2023Document51 pagesMAGNETIC EFFECTS OF ELECTRIC CURRENT - Class Notes - Warrior 2023John MathewNo ratings yet
- MagnetismDocument23 pagesMagnetismErrol WaltersNo ratings yet
- Properties Of Magnets And Magnetic Fields Under 40 CharactersDocument11 pagesProperties Of Magnets And Magnetic Fields Under 40 CharactersnaeiyuNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Fields: Asst. Prof. Dr. Gülnihal MuratoğluDocument33 pagesMagnetic Fields: Asst. Prof. Dr. Gülnihal MuratoğluKarim SharafNo ratings yet
- Phy - Magnetic Effects of Current WsDocument11 pagesPhy - Magnetic Effects of Current Wsburramokshitha88No ratings yet
- Physics Project: Magnetic Effect of Electric CurrentDocument10 pagesPhysics Project: Magnetic Effect of Electric CurrentananditaNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Effects of Electric Current - Class 10Document6 pagesMagnetic Effects of Electric Current - Class 10rachna chhabraNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Effect of CurrentDocument7 pagesMagnetic Effect of CurrentgoyalnahveNo ratings yet
- Magnets and Electricity: Write-On Grade 5Document13 pagesMagnets and Electricity: Write-On Grade 5tica1118No ratings yet
- CBSE Class 10 Science Magnetic Effects NotesDocument12 pagesCBSE Class 10 Science Magnetic Effects NotesAkshithNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Magnetic EffectDocument8 pagesClass 10 Magnetic EffectVirendra BansalNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetism For Printing ModuleDocument24 pagesElectromagnetism For Printing ModuleBob PhigglebottomNo ratings yet
- Moving Charges and MagnetismDocument32 pagesMoving Charges and MagnetismKrish BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Effect of Current (Prashant Kirad)Document12 pagesMagnetic Effect of Current (Prashant Kirad)kckvali100% (5)
- Physics - Magnetism and ElectromagnetismDocument7 pagesPhysics - Magnetism and ElectromagnetismNaomi JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Effects of Electric CurrentDocument29 pagesMagnetic Effects of Electric CurrentDevika TannaNo ratings yet
- ATPL Inst 2.1 PDFDocument8 pagesATPL Inst 2.1 PDFKoustubh VadalkarNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetism (Autosaved)Document45 pagesElectromagnetism (Autosaved)Melai Rodriguez IbardalozaNo ratings yet
- Magnetism and Electromagnetism: June 17 2012Document30 pagesMagnetism and Electromagnetism: June 17 2012Lava SatNo ratings yet
- Chapter-13 Magnetic Effect of CurrentDocument19 pagesChapter-13 Magnetic Effect of CurrentSuhani GosainNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Force20Document48 pagesElectromagnetic Force20Waqar BashirNo ratings yet
- Chapter 20 MagnetismDocument29 pagesChapter 20 MagnetismRua NarutoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Electromagnetism PDFDocument94 pagesChapter 4 - Electromagnetism PDFnurul nabilaNo ratings yet
- Q1: What Is A Magnet?Document7 pagesQ1: What Is A Magnet?Lulun NeithamNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Induction and Faraday's LawsDocument13 pagesMagnetic Induction and Faraday's LawsShara TayonaNo ratings yet
- 1-Magnetism NotesDocument34 pages1-Magnetism NotesSharon DingNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 1 G9 Term 3Document23 pagesChapter - 1 G9 Term 3Stunt BroNo ratings yet
- Some Basic Principle of MagnetismDocument2 pagesSome Basic Principle of MagnetismAce Matthew100% (1)
- Magnetism AND ElectromagnetismDocument16 pagesMagnetism AND ElectromagnetismRoNo ratings yet
- CLASS-10 Subject: ScienceDocument62 pagesCLASS-10 Subject: ScienceZeonNo ratings yet
- (IELTSMaterial - Com) 100 IELTS Speaking Part 2 Topics in 2016 & 2017 & Sample Answers PDFDocument135 pages(IELTSMaterial - Com) 100 IELTS Speaking Part 2 Topics in 2016 & 2017 & Sample Answers PDFUyenNo ratings yet
- 2nd PageDocument1 page2nd PageKrystelle Jade ClerigoNo ratings yet
- MEDSDocument11 pagesMEDSKrystelle Jade ClerigoNo ratings yet
- 3rd Tri BleedingDocument5 pages3rd Tri BleedingKrystelle Jade ClerigoNo ratings yet
- Principle of Totality and IntegrityDocument3 pagesPrinciple of Totality and IntegrityKrystelle Jade Clerigo75% (4)
- PSYCH - Nursing ProblemsDocument4 pagesPSYCH - Nursing ProblemsKrystelle Jade ClerigoNo ratings yet
- PSYCH - Nursing ProblemsDocument4 pagesPSYCH - Nursing ProblemsKrystelle Jade ClerigoNo ratings yet
- SubcultureDocument3 pagesSubcultureKrystelle Jade ClerigoNo ratings yet
- PSYCH - Nursing ProblemsDocument4 pagesPSYCH - Nursing ProblemsKrystelle Jade ClerigoNo ratings yet
- Socio - Assignment (Finals)Document1 pageSocio - Assignment (Finals)Krystelle Jade ClerigoNo ratings yet
- AngiographyDocument9 pagesAngiographyKrystelle Jade ClerigoNo ratings yet
- Pedia RespiDocument2 pagesPedia RespiKrystelle Jade ClerigoNo ratings yet
- 3rd Tri BleedingDocument5 pages3rd Tri BleedingKrystelle Jade ClerigoNo ratings yet
- Universal Declaration of Human RightsDocument8 pagesUniversal Declaration of Human RightselectedwessNo ratings yet
- Bag Technique (CHN)Document3 pagesBag Technique (CHN)Krystelle Jade Clerigo100% (1)
- Introduction To Community Health Nursing: Lily L. Hsu School of Nursing Shanghai Jiao Tong UniversityDocument28 pagesIntroduction To Community Health Nursing: Lily L. Hsu School of Nursing Shanghai Jiao Tong UniversityKrystelle Jade ClerigoNo ratings yet
- Mobrey: Boiler Water Level ControlsDocument12 pagesMobrey: Boiler Water Level ControlsSrinuNo ratings yet
- DF301Document4 pagesDF301Reikort László67% (3)
- Test BookDocument112 pagesTest BookJamel CharefNo ratings yet
- DS 0330 Data Sheet Solenoide ValveDocument5 pagesDS 0330 Data Sheet Solenoide ValvetueresuecoNo ratings yet
- AGS and GS7 Shift SystemsDocument124 pagesAGS and GS7 Shift Systemsrenat93% (43)
- Solenoid Valve CatalogueDocument24 pagesSolenoid Valve CatalogueAllanNo ratings yet
- Solved Problems-Ch30 - Sources of Magnetic Field - NewDocument9 pagesSolved Problems-Ch30 - Sources of Magnetic Field - Newshihabsultan75% (4)
- Hydraulically Controlled SectionalizerDocument12 pagesHydraulically Controlled SectionalizertonyoduNo ratings yet
- Force On Conductor LabDocument3 pagesForce On Conductor LabRezanoor KabirNo ratings yet
- E47 Repair Manual PDFDocument56 pagesE47 Repair Manual PDFcamohunter71100% (1)
- Electro Magnetic InductionDocument10 pagesElectro Magnetic InductionBashoriie SAng MusafierNo ratings yet
- Nota Padat Fizik F5 ElectromagnetDocument36 pagesNota Padat Fizik F5 Electromagnetslokkro100% (40)
- Case MX - TG Fault CodesDocument7 pagesCase MX - TG Fault CodesPatrik GubinaNo ratings yet
- PDT 80-3200F - Manual Do UsuárioDocument46 pagesPDT 80-3200F - Manual Do UsuárioEdimilson RodriguesNo ratings yet
- Asco Optional Features Complete CatalogDocument12 pagesAsco Optional Features Complete CatalogWalter SilvaNo ratings yet
- Pick - Place PDFDocument44 pagesPick - Place PDFABDOPORSNo ratings yet
- Diagrama Electrico (320B) PDFDocument2 pagesDiagrama Electrico (320B) PDFjulianmata100% (1)
- Catalogue CFL00897 (1) SolenoidesDocument148 pagesCatalogue CFL00897 (1) SolenoidesGERMAN1979No ratings yet
- Control Valve SelectionDocument31 pagesControl Valve SelectionJitendra Sharma100% (1)
- Build efficient Lenzless transformer using resonant LC circuitsDocument8 pagesBuild efficient Lenzless transformer using resonant LC circuitsGindac Ralea100% (1)
- EAOM19Document43 pagesEAOM19nanocycleNo ratings yet
- Diesel Engine Starting Systems ExplainedDocument25 pagesDiesel Engine Starting Systems ExplainedAnderson ToribiioNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetics Experiments Using MATLABDocument99 pagesElectromagnetics Experiments Using MATLABBewnet GetachewNo ratings yet
- 10 Science TP 13 1Document7 pages10 Science TP 13 1KSP Classes GondiaNo ratings yet
- Service Manual Compact Optimum After May 2004 PDFDocument65 pagesService Manual Compact Optimum After May 2004 PDFAndreas BuccioniNo ratings yet
- Electrical Symbols and Line DiagramsDocument38 pagesElectrical Symbols and Line DiagramsantonyamnrNo ratings yet
- Emc GettrdocDocument113 pagesEmc GettrdocfilzovocNo ratings yet
- Intl SCComplCatalog 2009 PDFDocument201 pagesIntl SCComplCatalog 2009 PDFRoberto GerhardtNo ratings yet
- Advanced Electrical Workshop Contents and Electrical Technology FundamentalsDocument205 pagesAdvanced Electrical Workshop Contents and Electrical Technology FundamentalsLucian IftemieNo ratings yet