Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Submitted To:-Mr. Nitin Jain Submitted By: - Sushil Kumar PGP 2008-10 Fostiima Business School
Uploaded by
sushil_kumar240 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
282 views14 pagesbond markets in India
Original Title
Bonds Market
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentbond markets in India
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
282 views14 pagesSubmitted To:-Mr. Nitin Jain Submitted By: - Sushil Kumar PGP 2008-10 Fostiima Business School
Uploaded by
sushil_kumar24bond markets in India
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 14
Submitted to :- Mr.
Nitin Jain Submitted By :-
SUSHIL KUMAR
PGP 2008-10
Fostiima business School
WHAT IS A BOND?
A bond is a debt security, similar to an
I.O.U. When you purchase a bond, you are
lending money to a government,
municipality, corporation, federal agency
or other entity known as the issuer.
Bonds issued by corporations or the US
government are usually taxable
Bonds issued by state governments or
municipalities are usually exempt from tax
Components
The issuer, similar to a holder of an option
Principal amount
Specified interest rate; paid to the issuer
yearly (also known as the coupon)
Date of maturity
Basic Bond Concepts
Par Value
Coupon or Interest Rate
Maturity
Redemption Features
Yield
INTEREST RATES
FIXED: Stays same until maturity; i.e: buy a
$1000 bond with 8% fixed interest rate and you
will receive $80 every year until maturity and at
maturity you will receive the $1000 back.
FLOATING: adjustable to prevailing market rates.
PAYABLE AT MATURITY: receive no payments
until maturity and at that time you receive
principal plus the total interest earned
compounded semi-annually at the initial interest
rate.
MATURITY
1.Short-term notes: maturities of up to 4 years;
2.Medium-term notes/bonds: maturities of five
to 12 years;
3.Long-term bonds: maturities of 12 or
more years.
REDEMPTION
Bond with a redemption provision usually
have higher return to compensate for the
risk that the bonds might be called early.
Call Option: provisions that allow or require the
issuer to repay the investors’ principal at a
specified date before maturity.
Put Option: option of requiring the issuer to
repurchase the bonds, at a specified time, prior
to maturity.
YIELD
Yield is the return you actually earn on the
bond--based on the price you
paid and the interest
payment you receive
Two Types of Yields:
Current Yield: annual return on the
dollar amount paid for the bond and is
derived by dividing the bond's interest
payment by its purchase price
Yield To Maturity: total return you will
receive by holding the bond until it
matures or is called.
TYPES OF BONDS
1. Assets Backed Securities
2. Extendible Bonds
3. Foreign Currency Bonds
4. High Yield or Junk Bonds
5. Mortgage-backed Securities
6. Zero Coupon
7. Eurobonds
8. Government Bonds
9. Corporate Bonds
TYPES OF BONDS
Assets Backed Securities :- ABS are bonds or notes
backed by financial assets like receivables.
Extendible Bonds :- An extendible bonds gives its
holder the right to extend the initial maturity to
a longer maturity date.
Foreign Currency Bonds :- A “foreign currency”
bond is bonds that is issued by an issuer in
currency other than its national currency.
High Yield or junk Bonds :- These are usually
purchased for speculative purposes. Junk bonds
typically offer interest rates three to four
percentage points higher than safer government
issues.
TYPES OF BONDS
Mortgage–backed Securities :- Mortgage
securities represent an ownership interest in
mortgage loans made by financial institution
to finance the borrower’s purchase of a home
or other real estate.
Zero coupon Bonds :- Zero coupon bonds are
fixed income securities that are created from
the cash flows that makes up a normal bond.
(Treasury bills)
Eurobonds :- Eurobonds are distinct from
domestic bonds and foreign bonds.
TYPES OF BONDS
Governments Bonds :- Govt. securities are
classified according to the length of time
before maturity
2.Bills- Less than one years
3.Notes- Between one to ten years
4.Bonds- More than 10 years
Corporate Bonds :- Corporate bonds are debt
obligations, or IOUs issued by private and
public corporations.
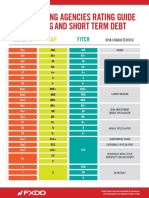
Moody's S&P Fitch
Long Term Short Term Long Term Short Term Long Term Short Term
Aaa AAA AAA Prime
Aa1 AA+ AA+
Aa2 AA AA
Aa3 AA- A-1+ AA- A1+ High grade
A1 A+ A+
A2 P-1 A A-1 A A1
A3 A- A- Upper Medium grade
Baa1 P-2 BBB+ A-2 BBB+ A2
Baa2 BBB BBB
Baa3 P-3 BBB- A-3 BBB- A3 Lower Medium grade
Ba1 BB+ BB+ Non Investmentgrade
Ba2 BB BB speculative
Ba3 BB- BB-
B1 B+ B+
B2 B B
B3 B- B B- B Highly Speculative
Caa CCC+ Substantial risks
Ca CCC Extemely speculative
In default with little
C CCC- C CCC C prospect for discovery
/ DDD
Not Prime D / / In default
You might also like
- Presentation On Money MarketDocument22 pagesPresentation On Money Marketsushil_kumar24No ratings yet
- Buffett's Rules For Your DIY Fund - Eureka ReportDocument4 pagesBuffett's Rules For Your DIY Fund - Eureka ReportPanot JitgaroonNo ratings yet
- Accounting For Business Combinations Final Examination: Name: Date: Professor: Section: ScoreDocument6 pagesAccounting For Business Combinations Final Examination: Name: Date: Professor: Section: ScoreCyrine Miwa Rodriguez100% (2)
- Chapter 6 - Cash Management: Learning ObjectivesDocument5 pagesChapter 6 - Cash Management: Learning Objectives132345usdfghjNo ratings yet
- Order in The Matter of Pancard Clubs LimitedDocument84 pagesOrder in The Matter of Pancard Clubs LimitedShyam SunderNo ratings yet
- Investments in Associates FA AC OverviewDocument85 pagesInvestments in Associates FA AC OverviewHannah Shaira Clemente73% (11)
- Asset-Liability Management in BanksDocument42 pagesAsset-Liability Management in Banksnike_4008a100% (1)
- Bernard W. Dempsey (1903-1960) - Interest and Usury. With An Introduction by Joseph A. Schumpeter (1948)Document242 pagesBernard W. Dempsey (1903-1960) - Interest and Usury. With An Introduction by Joseph A. Schumpeter (1948)Miles Dei100% (1)
- Debt Securities MarketDocument5 pagesDebt Securities MarketXyza Faye RegaladoNo ratings yet
- Surat Peoples Cooperative Bank LTDDocument108 pagesSurat Peoples Cooperative Bank LTDbrmehta06No ratings yet
- Critical Thinking Lecture 05Document8 pagesCritical Thinking Lecture 05Dj TroubleNo ratings yet
- Credit RatingDocument4 pagesCredit RatingNisha ParwaniNo ratings yet
- Credit RatingDocument18 pagesCredit RatingFathima MuhammedNo ratings yet
- FMAI - Ch03 - Bond MarketDocument75 pagesFMAI - Ch03 - Bond Marketngoc duongNo ratings yet
- 986-Article Text-2478-2-10-20190416Document24 pages986-Article Text-2478-2-10-20190416MohitAhujaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 31 Credit+Analysis+-+Credit+Ratings+and+Ratings+AgenciesDocument19 pagesLecture 31 Credit+Analysis+-+Credit+Ratings+and+Ratings+AgenciesTaanNo ratings yet
- Credit Rating ChartsDocument1 pageCredit Rating ChartsSapna KannaidasNo ratings yet
- Bond RatingsDocument2 pagesBond RatingscciesaadNo ratings yet
- Major Rating Agencies Rating Guide For Long and Short Term DebtDocument2 pagesMajor Rating Agencies Rating Guide For Long and Short Term DebtMihaela OanaNo ratings yet
- What Is The Significance of Cost of Capital?Document39 pagesWhat Is The Significance of Cost of Capital?Eric McLaughlinNo ratings yet
- The Credit Rating Agencies of Bangladesh and Around The World and Their FunctionDocument6 pagesThe Credit Rating Agencies of Bangladesh and Around The World and Their FunctionMd. Mustafezur Rahaman BhuiyanNo ratings yet
- Ratings Information For Publicly Traded Debt Issued Through The City of Stockton and Its Related AgenciesDocument2 pagesRatings Information For Publicly Traded Debt Issued Through The City of Stockton and Its Related AgenciesSteve GOopNo ratings yet
- Οι δεικτες Αξιολόγήσης Σε Απλα ελληνικαDocument3 pagesΟι δεικτες Αξιολόγήσης Σε Απλα ελληνικαDalianis ArgyriosNo ratings yet
- Investment GradeDocument3 pagesInvestment GradeMauricio ZvikNo ratings yet
- What Are Credit Rating Agencies?Document11 pagesWhat Are Credit Rating Agencies?Calvin S D'SouzaNo ratings yet
- What Are Credit Rating Agencies?Document11 pagesWhat Are Credit Rating Agencies?Calvin S D'SouzaNo ratings yet
- What Are Credit Rating Agencies?Document11 pagesWhat Are Credit Rating Agencies?Calvin S D'SouzaNo ratings yet
- What Are Credit Rating Agencies?Document11 pagesWhat Are Credit Rating Agencies?Calvin S D'SouzaNo ratings yet
- Bond MarketsDocument27 pagesBond MarketsPhạm Quốc TuấnNo ratings yet
- Credit Rating ScaleDocument1 pageCredit Rating ScaleVaibhav MNo ratings yet
- Credit Ratings PDFDocument1 pageCredit Ratings PDFkirti gNo ratings yet
- Group5 CreditratingmonitoringDocument20 pagesGroup5 CreditratingmonitoringGabriel SolanaNo ratings yet
- Ɂʏɲʄɿɲʆɻʎ Ȱʌɶʑʌɻʎ BSC, MSC Ʌɿʏɿʃɳʌɻʎ ɸʉɷʘʌʉʎbab, BSC, MSC, PH - DcandidateDocument3 pagesɁʏɲʄɿɲʆɻʎ Ȱʌɶʑʌɻʎ BSC, MSC Ʌɿʏɿʃɳʌɻʎ ɸʉɷʘʌʉʎbab, BSC, MSC, PH - DcandidatetpitikarisNo ratings yet
- 5 - Unit III - Managing Credit Risk in Money MarketDocument32 pages5 - Unit III - Managing Credit Risk in Money MarketMichael RosquitaNo ratings yet
- Money Markets: Dr. Pradiptarathi Panda Assistant Professor, NismDocument50 pagesMoney Markets: Dr. Pradiptarathi Panda Assistant Professor, NismMaunil OzaNo ratings yet
- Congress March 2018 Box Eng 5Document4 pagesCongress March 2018 Box Eng 5Lina MurciaNo ratings yet
- Finmark ReportDocument8 pagesFinmark ReportPeachy CamNo ratings yet
- Ch. 6. Slides. (Interest Rate Struc)Document16 pagesCh. 6. Slides. (Interest Rate Struc)rafifhammoud123No ratings yet
- 335 Chap 6x BondsDocument10 pages335 Chap 6x BondsEbenezerMebrateNo ratings yet
- South African Insurer Downgrades: David Laxton Neil Gosrani Trevor BarsdorfDocument8 pagesSouth African Insurer Downgrades: David Laxton Neil Gosrani Trevor BarsdorfPaul RadomskyNo ratings yet
- Principles of Managerial Finance: Fifteenth Edition, Global EditionDocument35 pagesPrinciples of Managerial Finance: Fifteenth Edition, Global Editionpatrecia 1896No ratings yet
- CreditratingDocument20 pagesCreditratingNeethu NairNo ratings yet
- Financial Institutions Management - Chapter 4 Solutions PDFDocument6 pagesFinancial Institutions Management - Chapter 4 Solutions PDFJarrod RodriguesNo ratings yet
- DBRS Rating ScaleDocument1 pageDBRS Rating ScaleJonathan OrdóñezNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 Lecturer 2 Long Term DebtDocument6 pagesUnit 6 Lecturer 2 Long Term DebtSuvash KhanalNo ratings yet
- Annexure - 1 Table 2.3 (A) Long-Term Rating Grades Mapping: SBP Rating Grade Fitch Moody's S&PDocument1 pageAnnexure - 1 Table 2.3 (A) Long-Term Rating Grades Mapping: SBP Rating Grade Fitch Moody's S&PSidrah ShaikhNo ratings yet
- The Economics of Money, Banking, and Financial Markets: Twelfth Edition, Global EditionDocument33 pagesThe Economics of Money, Banking, and Financial Markets: Twelfth Edition, Global EditionOtgoo HNo ratings yet
- Citigroup Inc.: Summary of Credit and Financial Strength RatingsDocument1 pageCitigroup Inc.: Summary of Credit and Financial Strength RatingsjoseNo ratings yet
- Chap 2 (2) Structure of IRDocument46 pagesChap 2 (2) Structure of IRHoàng Lâm NguyễnNo ratings yet
- AG 2012-05 - Credit Rating AgenciesDocument3 pagesAG 2012-05 - Credit Rating AgenciesR&S StuffNo ratings yet
- Bonds: Submitted To: Mr. Salman Ahmed Shaikh Submitted By: Khalid Irfan (BM-15047)Document10 pagesBonds: Submitted To: Mr. Salman Ahmed Shaikh Submitted By: Khalid Irfan (BM-15047)exceedorNo ratings yet
- BFC5926 Seminar 5 - Long-Term Debt MarketsDocument58 pagesBFC5926 Seminar 5 - Long-Term Debt MarketsMengdi ZhangNo ratings yet
- Principles of Managerial Finance: Fifteenth Edition, Global EditionDocument15 pagesPrinciples of Managerial Finance: Fifteenth Edition, Global EditionNuu 'No ratings yet
- David Gillmor enDocument47 pagesDavid Gillmor enJerico ConsultoriaNo ratings yet
- Ratings PDFDocument2 pagesRatings PDFMihaela OanaNo ratings yet
- Fixed Income Investor PresentationDocument27 pagesFixed Income Investor PresentationsaxobobNo ratings yet
- Globe Capacitors 14nov2019Document6 pagesGlobe Capacitors 14nov2019Puneet367No ratings yet
- Subject - Financial Services: Credit RatingDocument25 pagesSubject - Financial Services: Credit RatingDileep SinghNo ratings yet
- Annexure-2: Table: 1-ECAI's Credit Rating Categories Mapped With BB Rating GradeDocument1 pageAnnexure-2: Table: 1-ECAI's Credit Rating Categories Mapped With BB Rating GradeovifinNo ratings yet
- From Here To There: A Clear View of Retirement For Women - Webinar, Part 4Document27 pagesFrom Here To There: A Clear View of Retirement For Women - Webinar, Part 4LNP MEDIA GROUP, Inc.No ratings yet
- List of Credit Rating AgenciesDocument2 pagesList of Credit Rating AgenciesArslan KhalidNo ratings yet
- CRISIL Unit Linked Insurance Plan (ULIP) Ranking: As On March 2021Document45 pagesCRISIL Unit Linked Insurance Plan (ULIP) Ranking: As On March 2021chriscolmanNo ratings yet
- Pondy Oxides and Chemicals 22apr2019Document6 pagesPondy Oxides and Chemicals 22apr2019DarshanNo ratings yet
- Credit Rating - FinDocument3 pagesCredit Rating - FinLyanna MormontNo ratings yet
- CDO: Collateralized Debt ObligationDocument15 pagesCDO: Collateralized Debt ObligationAbhijeet PatilNo ratings yet
- Sameen - 1495 - 16124 - 1 - Lecture # 11 - Basel - I II &IIIDocument24 pagesSameen - 1495 - 16124 - 1 - Lecture # 11 - Basel - I II &IIIMasroor Ahmed ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Baroda Home LoanDocument31 pagesBaroda Home LoanRajkot academyNo ratings yet
- Investment Analysis and Portfolio Management: Lecture 6 Part 1Document70 pagesInvestment Analysis and Portfolio Management: Lecture 6 Part 1jovvy24No ratings yet
- Make Money With Dividends Investing, With Less Risk And Higher ReturnsFrom EverandMake Money With Dividends Investing, With Less Risk And Higher ReturnsNo ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument2 pagesAssignmentsushil_kumar24No ratings yet
- Assignment Micro FinanceDocument19 pagesAssignment Micro Financesushil_kumar24No ratings yet
- Stock MarketDocument28 pagesStock Marketsushil_kumar24100% (1)
- Bonous StrippingDocument3 pagesBonous StrippingKeshavLahotiNo ratings yet
- Banks in Växjö and KalmarDocument2 pagesBanks in Växjö and KalmarsatlohaniNo ratings yet
- Acquisition of Tetley by TataDocument3 pagesAcquisition of Tetley by TataANUSHRI MAYEKARNo ratings yet
- Meaning Wala Pa: Your AnswerDocument3 pagesMeaning Wala Pa: Your AnswerJose Louis Mari S. VelascoNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship - Slides - Getting Funding or Financing - Lesson 7Document42 pagesEntrepreneurship - Slides - Getting Funding or Financing - Lesson 7Hsk KogilanNo ratings yet
- Signature of Depositor Signature of DepositorDocument1 pageSignature of Depositor Signature of DepositorSai Swetha KVNo ratings yet
- Microfinance Management Solution On Tally - ERP9 - MpowerDocument28 pagesMicrofinance Management Solution On Tally - ERP9 - MpowerMilansolutionsNo ratings yet
- Payment Methods - Birbeck CollegeDocument5 pagesPayment Methods - Birbeck CollegeUniDaveNo ratings yet
- Annual Report 2012 3Document263 pagesAnnual Report 2012 3Ali Asghar0% (1)
- Exchange Rate Policy and Modelling in IndiaDocument117 pagesExchange Rate Policy and Modelling in IndiaArjun SriHariNo ratings yet
- The Financial Advisors Investment CaseDocument1 pageThe Financial Advisors Investment CaseAmit PandeyNo ratings yet
- 62 - 71 Lecture Notes SOCF (1-10)Document5 pages62 - 71 Lecture Notes SOCF (1-10)manadish nawazNo ratings yet
- FM Skill Based Questions - 2Document2 pagesFM Skill Based Questions - 2rohitcshettyNo ratings yet
- CPAR Deductions (Batch 92) - HandoutDocument30 pagesCPAR Deductions (Batch 92) - HandoutaudreyNo ratings yet
- Practice Problems For Comprehensive Exam 1573294973795Document8 pagesPractice Problems For Comprehensive Exam 1573294973795Christeena MichaelNo ratings yet
- Credit Card I PdsDocument11 pagesCredit Card I PdsIskandar ZulqarnainNo ratings yet
- MBA Finance1YearDocument10 pagesMBA Finance1Yearshahmonali6940% (1)
- Care RatingsDocument32 pagesCare Ratingskrishna_buntyNo ratings yet
- UPSC Prelims 2022 Answer Key With ExplanationDocument80 pagesUPSC Prelims 2022 Answer Key With ExplanationRiya JesinNo ratings yet
- Perpetual Non Cumulative Preference ShareDocument11 pagesPerpetual Non Cumulative Preference ShareSiddhartha YadavNo ratings yet
- أهمية تحليل الهيكل المالي في تقييم الأداء المالي لمؤسسة باتيميتال بولاية عين دفلى لفترة 2015 2017Document20 pagesأهمية تحليل الهيكل المالي في تقييم الأداء المالي لمؤسسة باتيميتال بولاية عين دفلى لفترة 2015 2017d5tjb9gvpmNo ratings yet
- Liquidation of PartnershipDocument10 pagesLiquidation of PartnershipCrislyn DacdacNo ratings yet