Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Astronomy
Uploaded by
Sujan SinghCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Astronomy
Uploaded by
Sujan SinghCopyright:
Available Formats
ASTRONOMY
Astronomy is that branch of science, which deals with the study of
universe as a whole and of objects, which exist naturally in space, such as
the moon, the sun, stars and Planets, The study of the movement and relative position of the sun, moon,
planets and stars, and the skill of describing the expected effect that
theses are believed to have on the character and behavior of human is called astrology (Jotish Sastra)
Definition and Terms
Celestial sphere: If we assume the space to be a sphere having the earth as its center and all the star lying on its surface, or studded in it. The celestial sphere can be of few kilometers to many thousand kilometer. Zenith and Nadir : These are two points on the celestial sphere opposite to each other and lying above and below the observer. Zenith is the point on the celestial sphere, above the head of the observer and Zenith is the point on the celestial sphere below the observer. Alternatively, these are the points of intersection of the plumb line(drawn through the point of observation) with the celestial sphere.al Sphere. Terrestrial poles and equator: Terrestrial poles are the points of intersection of the axis of rotation of the earth with the earth sphere, and the terrestrial equator is the great circle of the earth which is perpendicular to the axis of rotation of the earth. Celestial poles and Celestial equator: If the earth's axis of rotation is extending on both direction, it will intersect with the celestial sphere at the two points, celestial poles. Similarly Celestial equator is the great circle of the celestial sphere, in which the plane of intersection of the terrestrial equator with the celestial sphere lies.
Definition and Terms
Definition and Terms
Sensible Horizon: In the celestial sphere the point of observation is taken as the center. Sensible
horizon is a great circle of the celestial sphere which passes through the point of observation and is
tangential to the earth surface, or which is perpendicular to the zenith-nadir line. Vertical Circle: The vertical circle of a celestial sphere is a circle passing through the zenith and nadir and therefore all the vertical circles are perpendicular to the horizon.
Observer's meridian: It is a circle which passes through the zenith and nadir of the observation
point as well as through the poles of the celestial sphere. So it is a vertical circle.
Prime meridian: It is a vertical circle which is at right angles to the observer's meridian. Azimuth: It is the angular distance between the observer's meridian and the vertical circle passing
through the observer(Zenith and Nadir) and the heavenly body.
Hour Angle: It is the angular distance between the declination circle and the observer's meridian Latitude: It is the angular distance of the zenith from the equator.
Definition and Terms
Latitude: It is the angular distance of the zenith from the equator.
Co-latitude: It is complementary angle of the latitude, i.e. 90 - latitude. It is also known
as the zenith distance from the poles.
Right Ascension: Right ascension is the angular distance along the equator of the heavenly body from the point of Aries. It is simply written as R.A. and is always measured in the right direction from 0 to 360.
Longitude: the longitude of a place is its distance east or west of the first meridian and is measured by the number of degree in the arc intercepted on the equator between
the meridian of the place and first meridian (Greenwich Meridian)
Definition and Terms
Definition and Terms
Ecliptic: It is the path of the Sun around the earth assuming the earth to
be stationary, traveled in one complete year. Ecliptic intersects the
equator at the point of Aries and the Libra just opposite to Aries. It is the spring season when summer enters into Aries to the northern
hemisphere, and it is the start of winter in the northern hemisphere when
it passes the Libra and enters into the southern hemisphere. There are some important things to discuss to understand the position of
the star, or a heavenly body.
Definition and Terms
JUNE 21
SEPT 21
MARCH 21
DEC 21
Definition and Terms
Definition and Terms
Aphelion: This is the point on the elliptic path of the Sun when it is at its farthest
distance from the earth (Earth is assumed to be stationary, at one of the foci of the
ellipse.)
Perihelion: Perihelion is another point on the ecliptic when the Sun is at the nearest distance from the earth. When the Sun is at its nearest distance to the earth, the apparent motion of the Sun is faster, as compared to other positions.
Note: The Sun is always stationary, but it astronomy we assume the earth to be the center of the universe, so we assume the Sun to be moving. It is called its apparent motion.
Definition and Terms
Definition and Terms
Converting angular distance into hourly time: If I want to change the angular distance (longitude) into the time, I use the following relationships: 360 degrees = 24 hours. (time) 1 hour(time) = 15 degrees.(angular) 1 degrees = 4 min. (time) 1 min (time)= 15 minutes(angular) 1 min(angular) = 4 seconds(time) 1 seconds(time) = 15 seconds(angular) So a longitude of 82 degrees 30 minutes = 5 hours 30 minutes
You might also like
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (120)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Christianity and Mental Health WEB VERSIONDocument64 pagesChristianity and Mental Health WEB VERSIONWorld Religion NewsNo ratings yet
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- An Etymological Dictionary of The Scottivol 2Document737 pagesAn Etymological Dictionary of The Scottivol 2vstrohmeNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- 1986 Elektric M InfoDocument1 page1986 Elektric M InfoDanielDiasNo ratings yet
- Structure Dhan BDR LasiwaDocument37 pagesStructure Dhan BDR LasiwaSujan Singh100% (1)
- Abramson, Glenda (Ed.) - Oxford Book of Hebrew Short Stories (Oxford, 1996) PDFDocument424 pagesAbramson, Glenda (Ed.) - Oxford Book of Hebrew Short Stories (Oxford, 1996) PDFptalus100% (2)
- Materials System SpecificationDocument14 pagesMaterials System Specificationnadeem shaikhNo ratings yet
- List Of: S.No. ParticularsDocument21 pagesList Of: S.No. ParticularsSujan SinghNo ratings yet
- List Of: S.No. ParticularsDocument21 pagesList Of: S.No. ParticularsSujan SinghNo ratings yet
- Motion and Time: Check Your Progress Factual QuestionsDocument27 pagesMotion and Time: Check Your Progress Factual QuestionsRahul RajNo ratings yet
- AnnulmentDocument9 pagesAnnulmentHumility Mae FrioNo ratings yet
- Grammar For TOEFLDocument23 pagesGrammar For TOEFLClaudia Alejandra B0% (1)
- Ulangan Harian Lesson 4 Kls 6Document3 pagesUlangan Harian Lesson 4 Kls 6Megadevegaalgifari Minozholic Full100% (2)
- Oral Communication in ContextDocument31 pagesOral Communication in ContextPrecious Anne Prudenciano100% (1)
- Syllabus of Lok Sewa Aayog (First Part Exam) For Engineering Buildng and ArchitectDocument4 pagesSyllabus of Lok Sewa Aayog (First Part Exam) For Engineering Buildng and ArchitectKiran Basu100% (2)
- BeamDocument1 pageBeamSujan SinghNo ratings yet
- BOQ NDocument2 pagesBOQ NSujan SinghNo ratings yet
- ND 4may2016 Endoscopy Cad-ModelDocument1 pageND 4may2016 Endoscopy Cad-ModelSujan SinghNo ratings yet
- Candidate Instruction ManualDocument21 pagesCandidate Instruction ManualSujan SinghNo ratings yet
- Basement Wall Design: Check For DepthDocument1 pageBasement Wall Design: Check For DepthSujan SinghNo ratings yet
- FNDDocument3 pagesFNDSujan SinghNo ratings yet
- NBD Eq6Document80 pagesNBD Eq6Sujan SinghNo ratings yet
- Saiwzuzzr 06 V 7Document3 pagesSaiwzuzzr 06 V 7Bibek BasnetNo ratings yet
- Disaster Resilience and Safety:: A) Site ConsiderationDocument9 pagesDisaster Resilience and Safety:: A) Site ConsiderationSujan SinghNo ratings yet
- Slab PDFDocument2 pagesSlab PDFSujan SinghNo ratings yet
- Building and Architecture TheoryDocument3 pagesBuilding and Architecture Theoryशंकर थापाNo ratings yet
- Geometry of Staircase: (Limit State Method As Per IS 456-2000) Design of Stair-CaseDocument2 pagesGeometry of Staircase: (Limit State Method As Per IS 456-2000) Design of Stair-CaseSujan SinghNo ratings yet
- Wall SystemDocument1 pageWall SystemSujan SinghNo ratings yet
- Geometry of Staircase: (Limit State Method As Per IS 456-2000) Design of Stair-CaseDocument2 pagesGeometry of Staircase: (Limit State Method As Per IS 456-2000) Design of Stair-CaseSujan SinghNo ratings yet
- FNDDocument3 pagesFNDSujan SinghNo ratings yet
- JOSHI Bar ScheduleDocument40 pagesJOSHI Bar ScheduleSujan SinghNo ratings yet
- Disaster Resilience and Safety:: A) Site ConsiderationDocument9 pagesDisaster Resilience and Safety:: A) Site ConsiderationSujan SinghNo ratings yet
- Staircasedesigncalculation: I I Material Properties DimensionsDocument3 pagesStaircasedesigncalculation: I I Material Properties DimensionsSujan SinghNo ratings yet
- Pilla System PDFDocument1 pagePilla System PDFSujan SinghNo ratings yet
- Staircasedesigncalculation: I I Material Properties DimensionsDocument3 pagesStaircasedesigncalculation: I I Material Properties DimensionsSujan SinghNo ratings yet
- Geometry of Staircase: (Limit State Method As Per IS 456-2000) Design of Stair-CaseDocument2 pagesGeometry of Staircase: (Limit State Method As Per IS 456-2000) Design of Stair-CaseSujan SinghNo ratings yet
- Structural Design OF: The Proposed Residential BuildingDocument2 pagesStructural Design OF: The Proposed Residential BuildingSujan SinghNo ratings yet
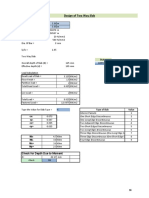
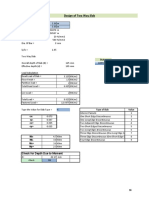
- Design of Two Way Slab: StatusDocument2 pagesDesign of Two Way Slab: StatusSujan SinghNo ratings yet
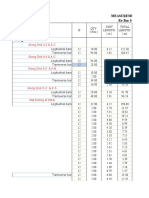
- Final RepDocument32 pagesFinal RepSujan SinghNo ratings yet
- Outline - Criminal Law - RamirezDocument28 pagesOutline - Criminal Law - RamirezgiannaNo ratings yet
- Monastery in Buddhist ArchitectureDocument8 pagesMonastery in Buddhist ArchitectureabdulNo ratings yet
- Test 1Document9 pagesTest 1thu trầnNo ratings yet
- People Vs Felipe Santiago - FCDocument2 pagesPeople Vs Felipe Santiago - FCBryle DrioNo ratings yet
- De Luyen Thi Vao Lop 10 Mon Tieng Anh Nam Hoc 2019Document106 pagesDe Luyen Thi Vao Lop 10 Mon Tieng Anh Nam Hoc 2019Mai PhanNo ratings yet
- Session Guide - Ramil BellenDocument6 pagesSession Guide - Ramil BellenRamilNo ratings yet
- Adverbs Before AdjectivesDocument2 pagesAdverbs Before AdjectivesJuan Sanchez PrietoNo ratings yet
- Trần Phương Mai - Literature - Irony in "Letter to a Funeral Parlor" by Lydia DavisDocument2 pagesTrần Phương Mai - Literature - Irony in "Letter to a Funeral Parlor" by Lydia DavisTrần Phương MaiNo ratings yet
- Formal Letter Format Sample To Whom It May ConcernDocument6 pagesFormal Letter Format Sample To Whom It May Concernoyutlormd100% (1)
- Psychology and Your Life With Power Learning 3Rd Edition Feldman Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument56 pagesPsychology and Your Life With Power Learning 3Rd Edition Feldman Test Bank Full Chapter PDFdiemdac39kgkw100% (9)
- Reflection On Sumilao CaseDocument3 pagesReflection On Sumilao CaseGyrsyl Jaisa GuerreroNo ratings yet
- Bootstrap DatepickerDocument31 pagesBootstrap DatepickerdandczdczNo ratings yet
- Karnu: Gbaya People's Secondary Resistance InspirerDocument5 pagesKarnu: Gbaya People's Secondary Resistance InspirerInayet HadiNo ratings yet
- Undertaking:-: Prime Membership Application Form (Fill With All Capital Letters)Document3 pagesUndertaking:-: Prime Membership Application Form (Fill With All Capital Letters)Anuj ManglaNo ratings yet
- Mooting ExampleDocument35 pagesMooting Exampleluziro tenNo ratings yet
- GemDocument135 pagesGemZelia GregoriouNo ratings yet
- RESO NO. 4 - LANYARD FinalDocument1 pageRESO NO. 4 - LANYARD FinalsharonleefulloNo ratings yet
- Entrep Bazaar Rating SheetDocument7 pagesEntrep Bazaar Rating SheetJupiter WhitesideNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE Business Studies 4th Edition © Hodder & Stoughton LTD 2013Document1 pageCambridge IGCSE Business Studies 4th Edition © Hodder & Stoughton LTD 2013RedrioxNo ratings yet
- HTTP Parameter PollutionDocument45 pagesHTTP Parameter PollutionSpyDr ByTeNo ratings yet