Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Planning
Uploaded by
Adeem AshrafiCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Planning
Uploaded by
Adeem AshrafiCopyright:
Available Formats
Module 2
Managerial Planning
MANJUNATH VS
ASSISTANT PROFESSOR
Acharya institute of Technology
2
Learning Objectives
Understand the meaning of the planning
Describe the nature of planning
Learn the steps involved in planning process
Describe the types of plans
Understand meaning of objectives
Describe MBO process
Understand the terms strategies, policies,
and procedures
3
Learning Objectives
Understanding Decision making process
Describe different types of decisions
Understand approaches to decision making
process
4
Planning
Planning is outlining future course of action
in order to achieve an objective.
It is the process of visualizing and
anticipating the future by evaluating the past
and assessing the present.
Planning is the trap laid down to capture the
future.
Planning is looking ahead.
5
The nature of planning
Contribution of plan to purpose and
objectives.
Primacy of planning
The pervasiveness of planning
Efficiency of plans
6
Principles pf planning
Take time to plan
Planning can be top down or bottom up
Involve and communicate all those
concerned
Plans must be flexible and dynamic
Evaluation and revision
7
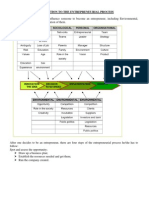
Steps in Planning
Being aware of opportunities
Establish goals
Establish planning premises
Internal premises
External premises
Deciding the planning period
Develop alternatives, evaluate, and select course of
actions
Derivative plans
Review periodically
8
Mission
Statement
Strategic Goals/Plans
Senior Management
(Organization as a whole)
Tactical Goals/Plans
Middle Management
(Major divisions, functions)
Operational Goals/Plans
Lower Management
(Departments, individuals)
Internal Message
Legitimacy,
motivation,
guides,
rationale,
standards
External Message
Legitimacy for
investors, customers,
suppliers, community
Levels of Plans & Their Importance
9
Organizational Mission
Mission = organizations reason for existing
Mission Statement
Broadly states the basic business scope and
operations that distinguishes it from similar types
of organizations
May include the market and customers
Some may describe company values, product
quality, attitudes toward employees
10
Bristol-Myers Squibb
Mission Statement
Our companys mission is to
extend and enhance human life
by providing the highest-quality
pharmaceutical and related
health care products.
11
IBMs Mission as stated by Thomas
Watson (1960)
Respect for the individual
We want to give the best customer service as
of any company in world.
We believe that organization should pursue
all tasks with the idea that they can be
accomplished in a superior fashion.
12
Strategic Goals and Plans
Strategic Goals
Where the organization wants to be in the future
Pertain to the organization as a whole
Strategic Plans
Action Steps used to attain strategic goals
Blueprint that defines the organizational
activities and resource allocations
Tends to be long term
13
Strategic Planning
The four main aspects of strategic planning
that managers can directly influence include:
Vision and Mission
Goals
Strategies
Resource Allocation
14
Strategic Levels and Planning
Corporate-level strategy focuses on the types of
businesses the firm wants to be in, ways to acquire or
divest businesses, allocation of resources among the
businesses, and ways to develop learning and
synergy among those businesses.
Strategic business unit (SBU)
Growth Strategies
15
Strategic Levels and Planning
Business-level strategy refers to the resources
allocated and actions taken to achieve desired goals
in serving a specific market with a highly interrelated
set of goods and/or services.
Three basic questions at the business level are:
1. Who will we be served?
2. What customer needs will be satisfied?
3. How will customer's need be satisfied?
16
Strategic Levels and Planning
Functional-level strategy refers to the actions and
resource commitments established for operations,
marketing, human resources, finance, legal services,
accounting, and the organizations other functional
areas.
Operations strategies
Marketing strategies
Finance strategies
17
Alternative Strategies- TOWS matrix
Internal
External
Internal
Strengths (S)
Internal
weaknesses (W)
External
opportunities (O)
SO Strategy
Maxi-Maxi
WO Strategy
Mini-Maxi
External Threats
(T)
ST Strategy
Maxi-Mini
WT Strategy
Mini-Mini
18
Alternative Strategies- TOWS matrix
WT Strategy- Minimize weaknesses and
threats-Joint ventures, Collaborations,
Liquidate.
WO Strategies-Minimize weaknesses and
maximize opportunities-Acquire
competencies, take advantage of
opportunities.
19
Alternative Strategies- TOWS matrix
ST Strategy-Maximize strengths and
minimize threats-Build on core competencies
SO Strategy-Maximize strengths and
opportunities-Most desirable position
20
Tactical planning
Tactical planning involves making concrete
decisions regarding what to do, who will do
it, and how to do itwith a normal time
horizon of a year or less.
21
Tactical Goals and Plans
Tactical Goals
- Apply to middle management
- Goals that define the outcomes that major
divisions and departments must achieve
Tactical Plans
-Plans designed to help execute major strategic plans
-Shorter than time frame than strategic plans
22
Operational Goals and Plans
Operational Goals
- Specific, measurable results
- Expected from departments, work groups, and
individuals
Operational Plans
- Organizations lower levels that specify action
steps toward achieving operational goals
- Tool for daily and weekly operations
- Schedules are an important component
23
Goals or Objectives
Objectives are end points of management
action.
Objectives are specific targets to be achieved
by an organization.
24
Characteristics of objectives
Objectives may be tangible or intangible.
Objectives have a hierarchy
Objectives can be short term and long term
Objectives sometimes may be in conflict with
each other.
25
Hierarchy of Goals
Operational
Goals
Tactical
Goals
Strategic
Goals
Mission
Traditional Responsibility
Top
Management
Middle
Management
1st-line
Management
& Workers
Shrinking middle
management
Employee
empowerment
Employees
Today
26
Characteristics of Effective
Goal Setting
Specific and measurable
Specific and measurable
Challenging but realistic
Defined time period
Linked to rewards
27
MBO
MBO is a process where by the superior and
subordinate managers of an organization
jointly identify common goals, define each
individuals major areas of responsibility in
terms of results expected by him and jointly
evaluates and reviews performance and
contributions.
Identify and jointly plan KRAs.
28
Model of the MBO Process
Step 1: Set Goals Step 2: Develop Action Plans
Step 3:
Review Progress
Corporate Strategic Goals
Departmental goals
Individual goals
Step 4: Appraise Overall
Performance
Appraise Performance
Take Corrective Action
Review Progress
Action Plans
29
MBO Benefits and Problems
Benefits of MBO
Manager and employee
efforts are focused on
activities that will lead to
goal attainment
Performance can be
improved at all company
levels
Employees are motivated
Departmental and
individual goals are
aligned with company
goals
Constant change prevents
MBO from taking hold
An environment of poor
employer-employee relations
reduces MBO effectiveness
Mechanistic organizations and
values that discourage
participation can harm the
MBO process
Too much paperwork saps
MBO energy
Problems with MBO
30
Single-Use Plans
For Goals Not Likely To Be Repeated
A program is a complex set of objectives and
plans to achieve an important, one-time
organizational goal
A project is similar to a program, but
generally smaller in scope and complexity
31
Standing Plans
For Tasks Performed Repeatedly
A policy is a general guide to action and
provides direction for people within the
organization
Rules describe how a specific action is to be
performed
Procedures define a precise series of steps
to be used in achieving a specific job
32
Policies
Written
Implied
Appealed
33
Contingency Plans
Specific Situations - unexpected conditions
Identify Uncontrollable Factors
Economic turndowns
Declining markets
Increases in costs of supplies
Technological developments
Safety accidents
Minimize Impact of Uncontrollable Factors
Forecast a range of alternative responses to
most-likely high-impact contingencies
34
Planning for High Performance
Central Planning = Traditional Department
Group of planning specialists who develop plans for
the organization as a whole and its major divisions
and departments and typically report directly to the
president or CEO
Decentralized Planning = High-Performance
Managers work with planning experts to develop their
own goals and plans
35
Planning for High Performance
Planning comes alive when employees are
involved in setting goals and determining the
means to reach them
36
Planning In The New Workplace
Have a strong mission statement and vision
Set stretch goals for excellence
Establish a culture that encourages learning
Embrace event-driven planning
Utilize temporary task forces
Planning still starts and stops at the top
Planning comes alive when employees are involved in
setting goals and determining the means to reach them
37
Decision Making
Decision making includes defining problems,
gathering information,
generating alternatives,
and choosing a course of action.
38
Managerial Decision Making
Decision making is not easy
It must be done amid
ever-changing factors
unclear information
conflicting points of view
39
Categories of Decisions
Programmed Decisions
Situations occurred often enough to enable
decision rules to be developed and applied in
the future
Made in response to recurring organizational
problems
Non programmed Decisions in response
to unique, poorly defined and largely
unstructured, and have important consequences
to the organization
40
Certainty, Risk, Uncertainty, Ambiguity
Certainty
all the information the decision maker needs is fully available
Risk
decision has clear-cut goals
good information is available
future outcomes associated with each alternative are subject to
chance
Uncertainty
managers know which goals they wish to achieve
information about alternatives and future events is incomplete
managers may have to come up with creative approaches to
alternatives
Ambiguity
by far the most difficult decision situation
goals to be achieved or the problem to be solved is unclear
alternatives are difficult to define
information about outcomes is unavailable
41
Conditions that Affect the Possibility
of Decision Failure
Organizational
Problem
Problem
Solution
Low High Possibility of Failure
Certainty Risk Uncertainty Ambiguity
Programmed
Decisions
Nonprogrammed
Decisions
42
Six Steps in the Managerial
Decision-Making Process
Evaluation
and
Feedback
Diagnosis
and Analysis
of Causes
Recognition of
Decision
Requirement
Development of
Alternatives
Selection of
Desired
Alternative
Implementation
of Chosen
Alternative
Decision-
Making
Process
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
43
Diagnosis and Analysis of Causes
Diagnosis = analyze underlying causal
factors associated with the decision situation
Managers make a mistake if they jump into
generating alternatives without first exploring
the cause of the problem more deeply
44
Underlying Causes - Kepner /Tregoe
What is the state of disequilibrium affecting us?
When did it occur?
Where did it occur?
How did it occur?
To whom did it occur?
What is the urgency of the problem?
What is the interconnectedness of events?
What result came from which activity?
45
Selection of Desired Alternatives
Risk Propensity = willingness to undertake
risk with the opportunity of gaining an
increased payoff
Implementation = using managerial,
administrative, and persuasive abilities to
translate the chosen alternative into action
46
Models of Decision Making
The bounded rationality model contends that
the capacity of the human mind for
formulating and solving complex problems is
small, compared with what is needed for
objectively rational behavior.
47
Bounded Rationality Model
Satisficing
Decision Biases
Inadequate Problem Description
Limited Search for Alternatives
Limited Information
48
Political Model of Decision Making
Political decision
making
Multiple Stakeholders with power such as:
Divergence in problem definition
Divergence in goals
Divergence in solutions
Customers
Investors Employees
Unions
Competitors
Suppliers Regulatory Agencies Legislative Bodies
49
Benefits for the Organization
G Legitimacy
What the organization stands for - reason for being
Symbolizes legitimacy
Employees identify with overall purpose
G Source of Motivation and Commitment
Employees identification with the organization
Motivate by reducing uncertainty
G Guides to Action
Provide a sense of direction; focus attention on specific
targets
Direct efforts toward important outcomes
Provided from Internal and External Messages Goals and Plans Send
50
Benefits for the Organization
G Rationale for Decisions
Learn what organization is trying to accomplish
Make decisions to ensure that internal policies, roles,
performance, structure, products, and expenditures will be
made in accordance with desired outcomes
G Standard of Performance
Serve as performance criteria
Provide a standard of assessment
Provided from Internal and External Messages Goals and Plans Send
51
52
Recap
What is planning?
Importance of planning
Principles of planning
Steps in planning
Levels of planning
Types of plans
Mission, objectives
53
Recap
MBO
Standing plans and single use plans
Strategies and operational plans
Decision making
Decision making process
Types of decisions
Bounded rationality concept
Advantages of planning
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Choosing Your Business Organizational StructureDocument3 pagesChoosing Your Business Organizational StructureAdeem Ashrafi100% (1)
- Corn Processing Investment Feasibility PDFDocument4 pagesCorn Processing Investment Feasibility PDFfekremariam Ambaw100% (1)
- Mobile Computer Repair BusinessDocument15 pagesMobile Computer Repair Businessnabeelhasan88100% (1)
- MMDocument2 pagesMMAdeem AshrafiNo ratings yet
- Security and Security Market OperationsDocument303 pagesSecurity and Security Market OperationsAdeem AshrafiNo ratings yet
- Job DesignDocument3 pagesJob DesignAdeem AshrafiNo ratings yet
- Recent Trends in Financial InnovationDocument5 pagesRecent Trends in Financial InnovationAdeem AshrafiNo ratings yet
- Risk and UncertainityDocument2 pagesRisk and UncertainityAdeem AshrafiNo ratings yet
- The Universal BankingDocument5 pagesThe Universal BankingAdeem AshrafiNo ratings yet
- Capital StructureDocument4 pagesCapital StructureAdeem Ashrafi100% (2)
- Meaning of LeverageDocument5 pagesMeaning of LeverageAdeem AshrafiNo ratings yet
- Working CapitalDocument15 pagesWorking CapitalAdeem AshrafiNo ratings yet
- Capital StructureDocument4 pagesCapital StructureAdeem Ashrafi100% (2)
- Financial Policy and Strategic PlanningDocument294 pagesFinancial Policy and Strategic PlanningAdeem AshrafiNo ratings yet
- Meaning of StaffingDocument11 pagesMeaning of StaffingAdeem AshrafiNo ratings yet
- Barriers To EntrepreneurshipDocument2 pagesBarriers To Entrepreneurshipanas_786No ratings yet
- Entrepreneurial ProcessDocument2 pagesEntrepreneurial ProcessAdeem AshrafiNo ratings yet
- Dividend DecisionDocument4 pagesDividend DecisionAdeem AshrafiNo ratings yet
- Types of Business Entities in IndiaDocument5 pagesTypes of Business Entities in IndiaAdeem AshrafiNo ratings yet
- Working CapitalDocument15 pagesWorking CapitalAdeem AshrafiNo ratings yet
- Institutional Support For SSIDocument3 pagesInstitutional Support For SSIAdeem AshrafiNo ratings yet
- Family VentureDocument5 pagesFamily VentureAdeem AshrafiNo ratings yet
- Institutional Support For New VenturesDocument8 pagesInstitutional Support For New VenturesAdeem AshrafiNo ratings yet
- Hawthorne ExperimentDocument4 pagesHawthorne ExperimentAdeem Ashrafi100% (1)
- Operations Managemen1Document1 pageOperations Managemen1Adeem AshrafiNo ratings yet
- Risk and UncertainityDocument7 pagesRisk and UncertainityAdeem AshrafiNo ratings yet
- Meaning of StaffingDocument11 pagesMeaning of StaffingAdeem AshrafiNo ratings yet
- DEPARTMENTATIONDocument1 pageDEPARTMENTATIONAdeem Ashrafi100% (1)
- BusinessesDocument4 pagesBusinessesAdeem AshrafiNo ratings yet
- DEPARTMENTATIONDocument1 pageDEPARTMENTATIONAdeem Ashrafi100% (1)
- TechnicallyDocument5 pagesTechnicallyAdeem AshrafiNo ratings yet
- Contract of BelongingDocument10 pagesContract of Belongingoccupyallst50% (6)
- Department of Labor: 1992 00014Document4 pagesDepartment of Labor: 1992 00014USA_DepartmentOfLaborNo ratings yet
- CHHOUR, Phengse (Hosei University) "Why Do Cambodian Technical Intern Trainees Flee From Their Workplaces in Japan?"Document5 pagesCHHOUR, Phengse (Hosei University) "Why Do Cambodian Technical Intern Trainees Flee From Their Workplaces in Japan?"cẩm túNo ratings yet
- Hillsborough County Fire Rescue Employee SurveyDocument57 pagesHillsborough County Fire Rescue Employee SurveyAnonymous YhHeJs100% (1)
- Chapter 3 Payaroll - Wubex-2Document8 pagesChapter 3 Payaroll - Wubex-2Birhanu FelekeNo ratings yet
- Avoiding Set-Ups by Inmates PDFDocument14 pagesAvoiding Set-Ups by Inmates PDFArnieTNo ratings yet
- (Sample) Factors-That-Influence-Job-Satisfaction-Among-Senior-High-Teachers-Final-DraftDocument32 pages(Sample) Factors-That-Influence-Job-Satisfaction-Among-Senior-High-Teachers-Final-DraftAndrea Albester GarinoNo ratings yet
- The Future of Diversity in The NewsDocument56 pagesThe Future of Diversity in The NewsASNENo ratings yet
- The Post-Industrial SocietyDocument132 pagesThe Post-Industrial SocietyIoana Stanciu100% (1)
- 2019 Maxicare Plus Standard - SMALL - WithVAT - 50kDocument16 pages2019 Maxicare Plus Standard - SMALL - WithVAT - 50kLew WallaceNo ratings yet
- Mastering BIR Year-End Compliance Requirements.: AIT Webinar, January 22, 2022 By: Dante R. TorresDocument66 pagesMastering BIR Year-End Compliance Requirements.: AIT Webinar, January 22, 2022 By: Dante R. TorresClarine Kyla Bautista100% (1)
- Comparison of Road Construction by Foreign and Local ContracDocument79 pagesComparison of Road Construction by Foreign and Local ContracGemechu100% (2)
- Burke-Litwin: Organisational Change and Performance Model: by Kedar Gokhale 10-06-04Document12 pagesBurke-Litwin: Organisational Change and Performance Model: by Kedar Gokhale 10-06-04KEDAR GOKHALENo ratings yet
- Agreement For Provision of Services: International Human Resources Development Corporation (Ihrdc)Document3 pagesAgreement For Provision of Services: International Human Resources Development Corporation (Ihrdc)Wael_Barakat_3179No ratings yet
- India's Urbanization & Growth-Poverty LinkagesDocument3 pagesIndia's Urbanization & Growth-Poverty LinkagesRitik GuptaNo ratings yet
- Jsom Undergraduate Resume Katherine PrineDocument1 pageJsom Undergraduate Resume Katherine PrineKatherine PrineNo ratings yet
- Impacts and Restoration Strategy of The Tourism Industry Post Covid-19 PandemicDocument13 pagesImpacts and Restoration Strategy of The Tourism Industry Post Covid-19 PandemicMuhammad Haroon Ul HasnainNo ratings yet
- Wr214 Unit 1 Quiz UploadDocument8 pagesWr214 Unit 1 Quiz UploadFelix ChanNo ratings yet
- Research Proposal: The Impact of Job Satisfaction ON Job PerformanceDocument15 pagesResearch Proposal: The Impact of Job Satisfaction ON Job PerformanceSamia AtiqueNo ratings yet
- Rights and Privileges of TeacherDocument104 pagesRights and Privileges of TeacherFrancis Rico TobesNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 - NotesDocument12 pagesTopic 2 - NotesMichelle RobinsonNo ratings yet
- Cases On Corpo Letter FDocument449 pagesCases On Corpo Letter FShayne RamirezNo ratings yet
- Philippine Village Hotel vs. NLRC FactsDocument4 pagesPhilippine Village Hotel vs. NLRC FactsRaymarc Elizer AsuncionNo ratings yet
- Foreign WorkersDocument1 pageForeign WorkersPUSPADEVI A/P KUPPUSAMY (MOHR)No ratings yet
- An Introduction To HRM ManagementDocument16 pagesAn Introduction To HRM ManagementjoyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 The Strategic Role of Human Resources ManagementDocument18 pagesChapter 1 The Strategic Role of Human Resources ManagementRavnoor KaurNo ratings yet
- ILO-ADB report: Covid-19 impact on youth employment in India and Asia-PacificDocument2 pagesILO-ADB report: Covid-19 impact on youth employment in India and Asia-PacificsurajsinghbhadauriaNo ratings yet
- Nagaland Housing Board Act, 1990Document22 pagesNagaland Housing Board Act, 1990Latest Laws TeamNo ratings yet