Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Family and Functionalism
Uploaded by
Ioana OrzeaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Family and Functionalism
Uploaded by
Ioana OrzeaCopyright:
Available Formats
whats what
Aim
Key words:
Variation
Socialisation
Functionalism
Todays critics
Parsons
Murdock
Gough
Lesson title: The universal family viewed
through functionalist perspectives
Module title: Families and Households
I love her
And I love
her
THE FAMILY
The family is a huge topic in sociology and perhaps this is a
reflection of the role it plays within society. Throughout
the world the family is seen as one of the most important
social units, so much so the UN designated 1994 as the Year
of the Family. Today we are going to explore the following
questions:
A lesbian couple are celebrating the first birthday of their quadruplets.
Melanie Snee and Emma Miller have organised a family party for their three boys
and one girl to mark the occasion.
Markus, Lucas, Harrison and Lara were carried by Ms Miller, 30, after fertility
treatment using a sperm donor.
She gave birth to the foursome in just four minutes.
whats what
Aim
Key words:
Variation
Socialisation
Functionalism
Todays critics
Parsons
Murdock
Gough
Lesson title: The universal family viewed
through functionalist perspectives
Module title: Families and Households
How can we evaluate functionalism?
Is the family a hard concept to define?
Is the family universal?
What are functionalist perspectives on the
family?
Has the family lost its functions?
whats what
Aim
Key words:
Variation
Socialisation
Functionalism
Todays critics
Parsons
Murdock
Gough
Lesson title: The universal family viewed
through functionalist perspectives
Module title: Families and Households
In analysing the family, functionalists concern
themselves with two main areas:
The functions that the family provides
The functional relationship between the
family and the other social systems
for example the economic system.
whats what
Aim
Key words:
Variation
Socialisation
Functionalism
Todays critics
Parsons
Murdock
Gough
Lesson title: The universal family viewed
through functionalist perspectives
Module title: Families and Households
Sociologists define the family in a variety of
different ways it is therefore a much disputed
concept. Below is a collection of definitions
sociologists have come up with in order to define
this important institution.
The family is a social group characterised by common
residence, economic co-operation and reproduction. It
includes adults of both sexes, at least two of whom
maintain a socially approved sexual relationship, and
one or more children, own or adopted, of the sexually
cohabiting adults.
George Murdock
What problems are there with this definition?
whats what
Aim
Key words:
Variation
Socialisation
Functionalism
Todays critics
Parsons
Murdock
Gough
Lesson title: The universal family viewed
through functionalist perspectives
Module title: Families and Households
A family is a unit made up of people related to
each other by blood, birth or marriage.
What problems are there with this definition?
A family is a social unit made up of people who
support each other in one of several ways; for
example, socially, economically or
psychologically (in providing care, love,
affection etc) or whose members identify with
each other as a supportive unit.
What problems are there with this definition?
whats what
Aim
Key words:
Variation
Socialisation
Functionalism
Todays critics
Parsons
Murdock
Gough
Lesson title: The universal family viewed
through functionalist perspectives
Module title: Families and Households
In defining the family it brings us to the
thorny question-
IS THE FAMILY UNIVERSAL?
Surely it is? Through a show of hands who
agrees that the family is a universal unit
Certainly the sociologist George Murdock thought so.
Murdock (1949) studied 250 different societies around the
world ranging from small hunter-gatherer societies to large
capitalist ones and concluded that the family is universal and can
be defined as a:
whats what
Aim
Key words:
Variation
Socialisation
Functionalism
Todays critics
Parsons
Murdock
Gough
Lesson title: The universal family viewed
through functionalist perspectives
Module title: Families and Households
Social group characterised by common residence,
economic co-operation and reproduction. Contains
adults of both sexes, at least two whom maintain a
socially approved sexual relationship and one or more
children, own or adopted, of the sexually cohabiting
adults
(Haralambos et al PG 319)
It can be distilled down to
The nuclear family is a universal human social grouping.
It exists as a distinct and strongly functional group in
every know society
whats what
Aim
Key words:
Variation
Socialisation
Functionalism
Todays critics
Parsons
Murdock
Gough
Lesson title: The universal family viewed
through functionalist perspectives
Module title: Families and Households
However
Some other sociologists, such as Kathleen
Gough has argued that is impossible to
suggest that the family is a universally held
concept. Cultures differ from society to
society and therefore families will also
differ.
She used the Nayar tribe in Southern India as evidence. Girls were ritually
married before puberty but did not have to live with husband or have any
contact with him only obligation was to mourn his death. Once near puberty
girls could take as many visiting husbands (Sandbanham) as she wished. The
men were often away (warriors) so when they returned they would visit one
of their wives after supper have sexual relations with her and then leave
before breakfast
whats what
Aim
Key words:
Variation
Socialisation
Functionalism
Todays critics
Parsons
Murdock
Gough
Lesson title: The universal family viewed
through functionalist perspectives
Module title: Families and Households
Goughs idea that this did not represent a
family were based on the following premises
It did not involve a lifelong union
The husbands had no duty to wives
It was not an economic unit
whats what
Aim
Key words:
Variation
Socialisation
Functionalism
Todays critics
Parsons
Murdock
Gough
Lesson title: The universal family viewed
through functionalist perspectives
Module title: Families and Households
Which point do you feel represents the modern
family unit more?
Come up with your own critically constructed
theory detailing what the family now represents
whats what
Aim
Key words:
Variation
Socialisation
Functionalism
Todays critics
Parsons
Murdock
Gough
Lesson title: The universal family viewed
through functionalist perspectives
Module title: Families and Households
Lets have a brief look at other non-traditional
functional families
THE ISRAELI KIBBUTZIM
In the modern state of Israel there was an
attempt to organize a kibbutz. Collective values
were stressed rather than the selfish ties of
the family. Money and property were owned and
controlled by the community as a whole. After a
short time with their parents children were
taken away and brought up by specially trained
nurses and teachers. They were allowed to see
their parents for only a few hours each day.
Contrary to many expectations the children did
not suffer psychologically as a result of this.
Thus, the functions of the nuclear family may be
replaced by other forms of organisation.
whats what
Aim
Key words:
Variation
Socialisation
Functionalism
Todays critics
Parsons
Murdock
Gough
Lesson title: The universal family viewed
through functionalist perspectives
Module title: Families and Households
The Punk squats of inner cities
New traveller convoys
YouTube - Stonehenge 1984
whats what
Aim
Key words:
Variation
Socialisation
Functionalism
Todays critics
Parsons
Murdock
Gough
Lesson title: The universal family viewed
through functionalist perspectives
Module title: Families and Households
Gough concluded that family is not universal
One solution to this argument suggested by
Scanzoni 89, is to call families primary
relationships. This she argues would solve the
universal argument. However this too is flawed
as it does away with the whole notion of the
family.
whats what
Aim
Key words:
Variation
Socialisation
Functionalism
Todays critics
Parsons
Murdock
Gough
Lesson title: The universal family viewed
through functionalist perspectives
Module title: Families and Households
In analysing the family, functionalists concern themselves with
two main areas:
1.The functions that the family provides
2.The functional relationship between the family and the other
social systems for example the economic system.
a)Murdock (1948) suggested that:
Nuclear family is universal. Family plays four basic functions
that helps society and its individual members
The family does not carry these out exclusively but it does it
most efficiently
Function
Benefit to individual Benefit to society Other Agencies
involved
Sexual
Reproductive
Economic
Educational
Draw and fill out the chart
whats what
Aim
Key words:
Variation
Socialisation
Functionalism
Todays critics
Parsons
Murdock
Gough
Lesson title: The universal family viewed
through functionalist perspectives
Module title: Families and Households
Talcott Parsons (1959)
The family provides two basic functions that no
other institution can provide
Primary Socialisation teaches children the
basic norms and values of society. The child
internalises societies culture and this
ensure value consensus is maintained
Stabilisation of adult personalities family
provides stability and emotional security, a
safe haven away from the stresses of
everyday life. Family works like a warm
bath easing away the worries of the world.
whats what
Aim
Key words:
Variation
Socialisation
Functionalism
Todays critics
Parsons
Murdock
Gough
Lesson title: The universal family viewed
through functionalist perspectives
Module title: Families and Households
Therefore we have to question
HAS THE FAMILY LOST ITS
FUNCTIONS?
As society has become more and more advanced
some sociologists, especially functionalists have
begun to suggest that the family is beginning to
lose some of the important functions that it
once provided. However instead in true
functionalist light rather than claiming that this
is causing the family to disappear, they argue
that it has caused it to become more specialised.
whats what
Aim
Key words:
Variation
Socialisation
Functionalism
Todays critics
Parsons
Murdock
Gough
Lesson title: The universal family viewed
through functionalist perspectives
Module title: Families and Households
What functions have the family lost?
Lost Functions Who has taken over?
Copy and complete
whats what
Aim
Key words:
Variation
Socialisation
Functionalism
Todays critics
Parsons
Murdock
Gough
Lesson title: The universal family viewed
through functionalist perspectives
Module title: Families and Households
Therefore functionalist perspectives on the
family would acknowledge that
Statistics show that the nuclear family is
one of the most popular families in our
society
They stress how well this type of family
fits into modern society.
Very conservative theory, takes for
granted that the nuclear family is normal
and universal. What about family
diversity?
The nuclear family is NOT universal
Ignores conflict within the family. Is the
family such a nice place for some people?
What about the dark side of the family?
Assumes that ALL families useful and
essential functions, married couples are
pictured as living in domestic bliss, being
good in bed and effective socialisers of the
next generation!
whats what
Aim
Key words:
Variation
Socialisation
Functionalism
Todays critics
Parsons
Murdock
Gough
Lesson title: The universal family viewed
through functionalist perspectives
Module title: Families and Households
Parsons (1959) on many levels the
family is now in fact functionless.
It no longer engages in economic
production, it has no political
power and it is not vital to
integrate wider society. Other
institutions such as schools,
business, welfare organisations
etc. have now taken over. This is
a positive thing for the family as
it has allowed the family to focus
on the two functions that it does
best.
whats what
Aim
Key words:
Variation
Socialisation
Functionalism
Todays critics
Parsons
Murdock
Gough
Lesson title: The universal family viewed
through functionalist perspectives
Module title: Families and Households
The loss of function question can
be counterbalanced by a re
assessment of the role of outside
agencies the now dovetail into the
family unit- smaller more holistic
and inclusive schools for example
whats what
Aim
Key words:
Variation
Socialisation
Functionalism
Todays critics
Parsons
Murdock
Gough
Lesson title: The universal family viewed
through functionalist perspectives
Module title: Families and Households
Arguments against the loss of functions
Ronald Fletcher (1966) inst he is also a functionalist but he argues that
the family has not only retained its functions but those functions have
increase in size and importance. Specialised institutions have only
added to and improved the familys functions, not superseded them.
How can Fletchers argument be applied to the following institutions:
Copy and complete
Institution How has this helped family not to lose its
functions in that area?
School
Hospital
Economic
whats what
Aim
Key words:
Variation
Socialisation
Functionalism
Todays critics
Parsons
Murdock
Gough
Lesson title: The universal family viewed
through functionalist perspectives
Module title: Families and Households
Research task
WIKI Research
# George Murdock
Talcott Parsons
You might also like
- Interpersonal Skills ExercisesDocument25 pagesInterpersonal Skills Exercisesnitin2182295% (19)
- Assertmodule 3Document15 pagesAssertmodule 3Dra Lauramar Santa RiveraNo ratings yet
- Week #2 Lesson Plan: Let's Make Friends and Have Fun TogetherDocument3 pagesWeek #2 Lesson Plan: Let's Make Friends and Have Fun TogetherIoana OrzeaNo ratings yet
- School Captain Speech PDFDocument8 pagesSchool Captain Speech PDFanon_57137216No ratings yet
- Module 4 Understanding AdolescenceDocument28 pagesModule 4 Understanding AdolescenceIoana OrzeaNo ratings yet
- La Colere Du Ciel UkDocument50 pagesLa Colere Du Ciel UkIoana OrzeaNo ratings yet
- Bullying Survey Student PDFDocument3 pagesBullying Survey Student PDFQueenie MaceNo ratings yet
- Bullying GuideDocument6 pagesBullying GuideIoana OrzeaNo ratings yet
- Healthy Relationships Resource Kit - WesternDocument84 pagesHealthy Relationships Resource Kit - WesternJeffrey Peeko100% (1)
- Mountain MeditationDocument4 pagesMountain Meditationkathy100% (1)
- ArticolDocument10 pagesArticolIoana OrzeaNo ratings yet
- Active ListeningDocument7 pagesActive ListeningMastoor F. Al KaboodyNo ratings yet
- Active Listening Guidelines: Ask Open-Ended Questions. Ask For Clarification But Be Polite andDocument1 pageActive Listening Guidelines: Ask Open-Ended Questions. Ask For Clarification But Be Polite andIoana OrzeaNo ratings yet
- Roadmap 2 Success 2017 R 1Document11 pagesRoadmap 2 Success 2017 R 1Ioana OrzeaNo ratings yet
- ActiveListening TrainersGuide ENGDocument13 pagesActiveListening TrainersGuide ENGIoana OrzeaNo ratings yet
- 4 Communication PDFDocument2 pages4 Communication PDFIoana OrzeaNo ratings yet
- Interpreting Children's Human Figure DrawingsDocument5 pagesInterpreting Children's Human Figure DrawingsDi Hidalgo CabanlitNo ratings yet
- "Friends Are Fun!" Bulletin Board: ObjectiveDocument6 pages"Friends Are Fun!" Bulletin Board: ObjectiveIoana OrzeaNo ratings yet
- Stress Monitoring SheetsDocument2 pagesStress Monitoring SheetsIoana OrzeaNo ratings yet
- Identify Feelings WorksheetsDocument1 pageIdentify Feelings WorksheetsIoana OrzeaNo ratings yet
- Conflict Resolution WorksheetsDocument4 pagesConflict Resolution WorksheetsIoana OrzeaNo ratings yet
- Self Esteem Worksheet 1Document3 pagesSelf Esteem Worksheet 1Ioana OrzeaNo ratings yet
- Sentence Completion AdolescentDocument2 pagesSentence Completion AdolescentIoana Orzea100% (1)
- Phobic Obj ExDocument1 pagePhobic Obj ExIoana OrzeaNo ratings yet
- Current Symptoms Self-Report FormDocument1 pageCurrent Symptoms Self-Report FormIoana OrzeaNo ratings yet
- 4 Communication PDFDocument2 pages4 Communication PDFIoana OrzeaNo ratings yet
- Behavior Contract PDFDocument1 pageBehavior Contract PDFIoana OrzeaNo ratings yet
- Marriage, Cohabitation and DivorceDocument4 pagesMarriage, Cohabitation and DivorceIoana OrzeaNo ratings yet
- Therapist Interoceptive PDFDocument1 pageTherapist Interoceptive PDFIoana OrzeaNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Modernity, Postmodernism and International RelationsDocument21 pagesModernity, Postmodernism and International RelationsMuhammad Tabish SarfarazNo ratings yet
- Vehicles: Experiments in Synthetic Psychology Valentino BraitenbergDocument18 pagesVehicles: Experiments in Synthetic Psychology Valentino BraitenbergRoxana AronNo ratings yet
- Statistical Measures of DataDocument11 pagesStatistical Measures of DataMary Roxanne AngelesNo ratings yet
- Pure Theory of Law by Hans Kelsen, JurisprudenceDocument24 pagesPure Theory of Law by Hans Kelsen, JurisprudenceNidhi Navneet83% (6)
- Ucsp JoanDocument35 pagesUcsp JoanJodan CayananNo ratings yet
- Dugger Sherman (1997)Document20 pagesDugger Sherman (1997)Bruno PaimNo ratings yet
- What Is Organizational Behavior?: Shamila Nabi KhanDocument21 pagesWhat Is Organizational Behavior?: Shamila Nabi KhanRobert GravesNo ratings yet
- Modern Paganism in World Cultures 2005 PDFDocument392 pagesModern Paganism in World Cultures 2005 PDFLilith Rising100% (1)
- Herbert Spencer & Early Social EvolutionistsDocument6 pagesHerbert Spencer & Early Social EvolutionistsIvan HernandezNo ratings yet
- Slum UpliftmentDocument33 pagesSlum UpliftmentKrishna MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Bi: Notes For A Bissexual Revolution (Shiri Eisner)Document310 pagesBi: Notes For A Bissexual Revolution (Shiri Eisner)Lia Martins100% (3)
- CITATION Sau16 /L 13321Document2 pagesCITATION Sau16 /L 13321Mark Christian AlmazamNo ratings yet
- Introduction To SociologyDocument19 pagesIntroduction To SociologySidra KhanNo ratings yet
- Study Guide Module 1: Introduction To UcspDocument22 pagesStudy Guide Module 1: Introduction To Ucspchewykookie ahNo ratings yet
- Relationship between Loneliness and Juvenile DelinquencyDocument5 pagesRelationship between Loneliness and Juvenile DelinquencyGarvin GoeiNo ratings yet
- Sociology Semester VDocument29 pagesSociology Semester VDevyani JaiswalNo ratings yet
- VSKUB MSWDocument9 pagesVSKUB MSWSreenivasa Reddy DNo ratings yet
- Three Traditions of Network ResearchDocument15 pagesThree Traditions of Network ResearchLonlon VictorioNo ratings yet
- Beyond Binary Views of Spirituality and ReligionDocument21 pagesBeyond Binary Views of Spirituality and ReligionLenore ImnotNo ratings yet
- Conceptios of Health Promotion Held by Preregistration Student NursesDocument6 pagesConceptios of Health Promotion Held by Preregistration Student NursesIliana OlveraNo ratings yet
- Types of Identity Transformation in Drug Addiction and RecoveryDocument13 pagesTypes of Identity Transformation in Drug Addiction and RecoveryFerdy AzzhNo ratings yet
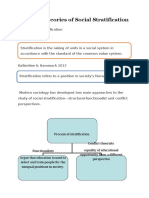
- Notes On Topic 3 Classical Theories of Social StratificationDocument13 pagesNotes On Topic 3 Classical Theories of Social StratificationkathirNo ratings yet
- Uts M1L2Document3 pagesUts M1L2Juan PauloNo ratings yet
- AP Psychology Chapter 1Document2 pagesAP Psychology Chapter 1kyokkokenNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Sociology for Health StudentsDocument60 pagesIntroduction to Sociology for Health Studentsmuhirwa SamuelNo ratings yet
- Culture, Society and Politics PizzaDocument51 pagesCulture, Society and Politics PizzaHarlyn DatoonNo ratings yet
- Metropolis - AgambenDocument3 pagesMetropolis - Agambenbillypilgrim_sfeNo ratings yet
- Tamil Nadu National Law University: Criminology ProjectDocument7 pagesTamil Nadu National Law University: Criminology ProjectMohandas PeriyasamyNo ratings yet
- The Self and The Development of The Social WorldDocument5 pagesThe Self and The Development of The Social Worldhandyoklos50% (2)
- Social Change and Media - Taimoor TKDocument44 pagesSocial Change and Media - Taimoor TKmuhammadtaimoorkhan100% (2)