Professional Documents
Culture Documents
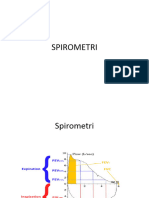
Restriktif Dan Obstruktif
Uploaded by
Syarifah KartikaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Restriktif Dan Obstruktif
Uploaded by
Syarifah KartikaCopyright:
Available Formats
Assessing Obstructive and
Restrictive Patterns
Sudjoko KUSWADJI
Overview
It is often possible to recognize
patterns associated with obstructive or
restrictive lung disease based on the
results of pulmonary function testing.
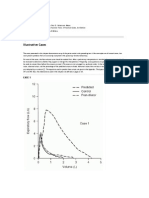
With obstruction:
Patients may have a normal or modestly reduced
vital capacity, but the volume time tracing of the
forced vital capacity will be abnormal.
There is flattening of the slope of the curve at any
given lung volume, reflecting reduced rate of airflow.
The duration of the forced expiratory maneuver is
prolonged; the changes in the rate of expiratory
airflow reduce the FEV1, FEV3, FEV1-to-FVC, FEV3-
to-FVC, and FEF(25-75%).
In small airway disease: FVC is >= 81% of predicted,
but FEF(25-75%) < 65%.
Pasien mungkin memiliki kapasitas vital normal atau sederhana
berkurang, namun volume waktu penelusuran kapasitas vital
paksa akan abnormal.
Ada merata dari kemiringan kurva pada setiap volume paru-
paru yang diberikan, mencerminkan penurunan laju aliran
udara.
Durasi manuver ekspirasi paksa berkepanjangan, perubahan
dalam tingkat aliran udara ekspirasi mengurangi FEV1, FEV3,
FEV1-to-FVC, FEV3-to-FVC, dan FEF (25-75%).
Pada penyakit saluran napas kecil: FVC adalah> = 81% dari
yang diperkirakan, namun FEF (25-75%) <65%.
FEV1 Interpretation
> 80% predicted normal
66-80% predicted mild obstruction
50-65% predicted moderate obstruction
< 50% predicted severe obstruction
FEV1 to FVC ratio Interpretation
>= 70% of predicted normal
61 - 69% of predicted mild obstruction
45 - 60% of predicted moderate obstruction
< 45% of predicted severe obstruction
FEF(25-75%) Interpretation
>= 66% of predicted normal
50 - 65% of predicted mild obstruction
35 - 49% of predicted moderate obstruction
< 35% of predicted severe obstruction
With restriction:
The configuration of the volume-time tracing may
not be abnormal.
The FEV1 and FEV(3) are low because of the reduced
vital capacity.
The FEV1-to-FVC and FEV(3)-to-FVC are normal or
even increased.
The FEF(25-75%) is lower than predicted.
By examining the ratio of measured-to-predicted
lung capacities it is possible to assess the severity
of restrictive lung disease.
Konfigurasi volume-time tracing mungkin tidak
normal.
The FEV1 dan FEV (3) rendah karena kapasitas vital
berkurang.
FEV1-to-FVC dan FEV (3)-to-FVC normal atau bahkan
meningkat.
The FEF (25-75%) lebih rendah dari yang
diperkirakan.
Dengan memeriksa rasio kapasitas paru diukur-ke-
prediksi adalah mungkin untuk menilai keparahan
penyakit paru restriktif.
VC (vital capacity) Interpretation
>= 81% of predicted normal
66 - 80% of predicted mild restriction
51 - 65% of predicted moderate restriction
<= 50% of predicted severe restriction
TLC (total lung
capacity)
Interpretation
>= 81% of predicted normal
66 - 80% of predicted mild restriction
51 - 65% of predicted moderate restriction
<= 50% of predicted severe restriction
where:
The forced vital capacity (FVC) is reported by some to be equivalent to
vital capacity (VC).
di mana:
kapasitas vital paksa (FVC) dilaporkan oleh beberapa orang untuk
menjadi setara dengan kapasitas vital (VC).
References:
Fishman A (editor). Pulmonary
Diseases and Disorders, Second
Edition. McGraw-Hill Book Company.
1988. pages 2483 and 2510
Murray J, Nadel J. Textbook of
Respiratory Medicine, 2nd edition. W.B.
Saunders Company. 1994. page 871
You might also like
- Mechanical Ventilation For NursingDocument55 pagesMechanical Ventilation For NursingAmira AttyaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Pulmonary Function TestingDocument58 pagesIntroduction To Pulmonary Function Testingpescao50% (1)
- Clinical Surgery Review 2023: For USMLE Step 2 CK and COMLEX-USA Level 2From EverandClinical Surgery Review 2023: For USMLE Step 2 CK and COMLEX-USA Level 2No ratings yet
- PFT Reveals Lung FunctionDocument35 pagesPFT Reveals Lung FunctionMartha ChaseNo ratings yet
- Interpreting Pulmonary Function TestsDocument10 pagesInterpreting Pulmonary Function TestsSuresh Kumar100% (1)
- Respiratory Function TestDocument7 pagesRespiratory Function TestMarivic DianoNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Function TestsDocument65 pagesPulmonary Function TestsPranathi PrasadNo ratings yet
- Troubleshooting Mechanical VentDocument15 pagesTroubleshooting Mechanical VentIvy Jorene Roman RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Function TestDocument57 pagesPulmonary Function TestDeepika PatelNo ratings yet
- Lung Function Tests: Dr. Partha Pratim DekaDocument80 pagesLung Function Tests: Dr. Partha Pratim DekaDorin PathakNo ratings yet
- SpirometryDocument11 pagesSpirometryTrandafirulNegruNo ratings yet
- BOOK Spirometry in PracticeDocument104 pagesBOOK Spirometry in Practicenadeem khan100% (1)
- Interpreting Pulmonary Function TestsDocument7 pagesInterpreting Pulmonary Function TestsRalucaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Passmedicin 2022Document1,020 pagesRespiratory Passmedicin 2022Faris Firas100% (1)
- SpirometriDocument38 pagesSpirometrivineaprilianitaputriNo ratings yet
- L 3 SpirmetryDocument24 pagesL 3 SpirmetryXajepoxNo ratings yet
- Measurements.: Spirometry Is The Name of The Test, Whilst A Spirometer Is The Device That Is Used To Make TheDocument7 pagesMeasurements.: Spirometry Is The Name of The Test, Whilst A Spirometer Is The Device That Is Used To Make TheDebasis SahooNo ratings yet
- Спирометрия Глава 15Document81 pagesСпирометрия Глава 15Mikhail PisarevNo ratings yet
- Seminar Teste Functionale Studenti-51818Document50 pagesSeminar Teste Functionale Studenti-51818Daniela RobuNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Function HandoutDocument50 pagesPulmonary Function HandoutAbed SabeNo ratings yet
- 1.B.09 Resp TestsDocument2 pages1.B.09 Resp Testsalemante100% (1)
- Pulmonary Function TestsDocument35 pagesPulmonary Function TestsJawad MohammadNo ratings yet
- Spirometric ValuesDocument18 pagesSpirometric ValuesSensing NonsenseNo ratings yet
- SPIROMETRY GUIDE FOR COPD DIAGNOSISDocument2 pagesSPIROMETRY GUIDE FOR COPD DIAGNOSISGiliana P. García AcevedoNo ratings yet
- An Approach To Interpreting Spirometry (Finals) PDFDocument25 pagesAn Approach To Interpreting Spirometry (Finals) PDFVanessa CarinoNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Function TestsDocument28 pagesPulmonary Function TestsHarshit yadavNo ratings yet
- New Spirometry Interpretation Algorithm: Critical AppraisalDocument5 pagesNew Spirometry Interpretation Algorithm: Critical AppraisalLinda AndrianiNo ratings yet
- Lung Function Tests ExplainedDocument35 pagesLung Function Tests ExplainedYazeedNo ratings yet
- GOLD COPD Severity CriteriaDocument6 pagesGOLD COPD Severity CriteriaAjet AsaniNo ratings yet
- Large Lungs in Divers May Be Due to Natural Selection Rather Than TrainingDocument5 pagesLarge Lungs in Divers May Be Due to Natural Selection Rather Than TrainingtwindaNo ratings yet
- InterpretasiHasilSpiroDocument33 pagesInterpretasiHasilSpiroAyahnya RafliNo ratings yet
- Standardisation of Lung Function Testing: The Authors' Replies To Readers' CommentsDocument3 pagesStandardisation of Lung Function Testing: The Authors' Replies To Readers' CommentsRESCATEURNo ratings yet
- Spirometry in Primary Care: Global Initiative For Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease (GOLD) 2008Document59 pagesSpirometry in Primary Care: Global Initiative For Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease (GOLD) 2008zulfikar adiNo ratings yet
- Lown-Ganong-Levine Syndrome and Enhanced Atrioventricular Nodal Conduction Author: Section Editor: Deputy EditorDocument12 pagesLown-Ganong-Levine Syndrome and Enhanced Atrioventricular Nodal Conduction Author: Section Editor: Deputy EditorDAT TRANNo ratings yet
- 318 Surgical Correction of ScoliosisDocument7 pages318 Surgical Correction of ScoliosisbangkitayuNo ratings yet
- Spirometry: Lung Function TestDocument7 pagesSpirometry: Lung Function TestJuniar Faiz MNo ratings yet
- ICU Case Study on Guillain-Barre SyndromeDocument9 pagesICU Case Study on Guillain-Barre Syndromesand2123No ratings yet
- 5-Pulmonary Function TestsDocument35 pages5-Pulmonary Function TestsDoha JKNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Function Tests-Nursing MasenoDocument43 pagesPulmonary Function Tests-Nursing Masenoakoeljames8543No ratings yet
- Pulmonary Function Testing Case Questions and Answers: Interpretations and Flow Volume LoopsDocument23 pagesPulmonary Function Testing Case Questions and Answers: Interpretations and Flow Volume LoopswisgeorgekwokNo ratings yet
- Resp Yamashita PulmonaryFunctionTests NotesDocument13 pagesResp Yamashita PulmonaryFunctionTests Notes1233211qwerasdNo ratings yet
- Dr. Rowshne Jahan Spirometry Presentation-1Document40 pagesDr. Rowshne Jahan Spirometry Presentation-1Shahadat Hossain BabuNo ratings yet
- Interpreting Pulmonary Function TestsDocument6 pagesInterpreting Pulmonary Function TestsVittorio Di PaoloNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Respiratory FunctionDocument1 pageAssessment of Respiratory FunctionRoderick AgbuyaNo ratings yet
- BBB 1 - Pulmonary Function Tests InterpretationDocument14 pagesBBB 1 - Pulmonary Function Tests InterpretationArhanNo ratings yet
- Respiratory ICU PDFDocument130 pagesRespiratory ICU PDFAhmed Shihab AhmedNo ratings yet
- 4 2020 Spirometry Quick Glance GuideDocument2 pages4 2020 Spirometry Quick Glance Guidepatrick_raj884545No ratings yet
- Interpretation of Pulmonary Function Tests (PFTS) : Anna Neumeier, MDDocument75 pagesInterpretation of Pulmonary Function Tests (PFTS) : Anna Neumeier, MDryan enotsNo ratings yet
- Ratnawati - Spirometry For Diagnosis OLDDocument61 pagesRatnawati - Spirometry For Diagnosis OLDAndry Wahyudi AgusNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Function Test in Pre Anaesthetic EvaluationDocument10 pagesPulmonary Function Test in Pre Anaesthetic EvaluationSuresh KumarNo ratings yet
- Chest Wall DisordersDocument66 pagesChest Wall DisordersSwathi VivekNo ratings yet
- Lown-Ganong-Levine Syndrome and Enhanced Atrioventricular Nodal ConductionDocument10 pagesLown-Ganong-Levine Syndrome and Enhanced Atrioventricular Nodal ConductionluizplaccoNo ratings yet
- Practical Applications of Pulmonary Function TestsDocument103 pagesPractical Applications of Pulmonary Function TestsKeta PatelNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Function Tests in Clinical PracticeFrom EverandPulmonary Function Tests in Clinical PracticeAli AltalagRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Respiratory Monitoring in Mechanical Ventilation: Techniques and ApplicationsFrom EverandRespiratory Monitoring in Mechanical Ventilation: Techniques and ApplicationsJian-Xin ZhouNo ratings yet
- Essentials in Lung TransplantationFrom EverandEssentials in Lung TransplantationAllan R. GlanvilleNo ratings yet