Professional Documents
Culture Documents
OBJECTIVES OF BUSINESS - EE&FA/C - CS&IT - Dr.K.BARANIDHARAN, SRI SAIRAM INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY, CHENNAI-OBJECTIVES OF BUSINESS - EE&FA/C - CS&IT
Uploaded by
Dr.K.Baranidharan0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views15 pagesOBJECTIVES OF BUSINESS - EE&FA/C -CS&IT - Dr.K.BARANIDHARAN, SRI SAIRAM INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY, CHENNAI
Original Title
OBJECTIVES OF BUSINESS - EE&FA/C -CS&IT - Dr.K.BARANIDHARAN, SRI SAIRAM INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY, CHENNAI-OBJECTIVES OF BUSINESS - EE&FA/C -CS&IT
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentOBJECTIVES OF BUSINESS - EE&FA/C -CS&IT - Dr.K.BARANIDHARAN, SRI SAIRAM INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY, CHENNAI
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views15 pagesOBJECTIVES OF BUSINESS - EE&FA/C - CS&IT - Dr.K.BARANIDHARAN, SRI SAIRAM INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY, CHENNAI-OBJECTIVES OF BUSINESS - EE&FA/C - CS&IT
Uploaded by
Dr.K.BaranidharanOBJECTIVES OF BUSINESS - EE&FA/C -CS&IT - Dr.K.BARANIDHARAN, SRI SAIRAM INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY, CHENNAI
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 15
EE&FA/C CS/IT
Dr.K. BARANIDHARAN. MBA
SRI SAIRAM INSTITUTE OF
TECHNOLOGY
CHENNAI
OBJECTIVES OF
BUSINESS
Prepared by :
Dr. K. BARANIDHARAN
OBJECTIVES
(a) Maximization of the sales revenue
(b) Maximization of firms growth rate
(c) Maximization of Managers utility function
(d) Making satisfactory rate of Profit
(e) Long run Survival of the firm
(f) Entry-prevention and risk-avoidance
Objectives of firm
Profit maximisation
Sales maximisation
Revenue maximisation
Satisficing profit
Limit pricing
Objectives
of firm
PROFIT BUSINESS OBJECTIVES
Profit means different things to different people.
To an accountant Profit means the excess of
revenue over all paid out costs including both
manufacturing and overhead expenses.
For all practical purpose, profit or business income
means profit in accounting sense plus non-
allowable expenses.
Economists concept of profit is of Pure Profit
called economic profit or Just profit.
Pure profit is a return over and above opportunity
cost, i. e. the income that a businessman might
expect from the second best alternatives use of his
resources
Profit maximization is the process of identifying
the most efficient manner of obtaining the
highest rate of return from its production model.
Most approaches require that the company look
closely at the costs of production, the current
levels of supply and demand, and the price that
can be obtained for each unit while still
attracting the highest volume of consumers.
For example, the focus may be on finding new
ways to advertise and promote the product line,
especially if those approaches are likely to
generate more revenue and cost less to maintain.
Economic profits = economic revenue
economic costs
SALES REVENUE MAXIMISATION
The reason behind sales revenue maximisation
objectives is the ownership & management in
large business corporations.
Managers an opportunity to set their goal other
than profits maximisation goal, which most-
owner businessman pursue.
Given the opportunity, managers choose to
maximize their own utility function.
The most plausible factor in managers utility
functions is maximisation of the sales revenue.
The factors, which explain the pursuance of
this goal by the managers are following:.
First: Salary and others earnings of managers
are more closely related to sales revenue
than to profits
Second: Banks and financial corporations
look at sales revenue while financing the
corporation.
Third: Trend in sales revenue is a readily
available indicator of the performance of the
firm
MAXIMISATION OF FIRMS GROWTH
RATE
Managers maximize firms balance growth rate
subject to managerial & financial constrains
balance growth rate defined as:
G = GD GC
Where GD = Growth rate of demand of firms
product & GC= growth rate of capital supply of
capital to the firm.
In simple words, A firm growth rate is balanced
when demand for its product & supply of capital
to the firm increase at the same time.
MAXIMISATION OF MANAGERIAL
UTILITY FUNCTION
The manager seek to maximize their own utility function
subject to the minimum level of profit. Managers utility
function is express as:
U= f(S, M, ID)
Where S = additional expenditure of the staff
M= Managerial emoluments
ID = Discretionary Investments
The utility functions which manager seek to maximize
include both quantifiable variables like salary
and slack earnings; non- quantifiable variables
such as prestige, power, status, Job security
professional excellence etc.
LONG RUN SURVIVAL & MARKET
SHARE
According to some economist, the primary goal of the
firm is long run survival.
Some other economists have suggested that attainment &
retention of constant market share is an additional
objective of the firms.
the firm may seek to maximize their profit in the long run
through it is not certain.
Entry-prevention and risk-avoidance, yet another
alternative objectives of the firms suggested by some
economists is to prevent entry-prevention can be:
1. Profit maximisation in the long run
2. Securing a constant market share
3. Avoidance of risk caused by the unpredictable behavior
of the new firms
Micro economist has a vital role to play in running of any
business. Some basic internal issues with which micro-
economist are concerns:
i. Choice of business and nature of product i.e. what to
produce
ii. Choice of size of the firm i. e how much to produce
iii. Choice of technology i.e. choosing the factor-
combination
iv. Choose of price i.e. how to price the commodity
v. How to promote sales
vi. How to face price competition
vii. How to decide on new investments
viii. How to manage profit and capital
ix. How to manage inventory i.e. stock to both finished &
raw material
Economic Goal of the Firm
Short-run vs. Long-run
Nothing to do directly with calendar
time
Short-run: firm can vary amount of
some resources but not others
Long-run: firm can vary amount of
all resources
At times short-run profitability will
be sacrificed for long-run purposes
Goals Other Than Profit
Economic Goals
Market share, Growth rate
Profit margin
Return on investment, Return on
assets
Technological advancement
Customer satisfaction
Shareholder value
Goals Other Than Profit
Non-economic Objectives
Good work environment
Quality products and
services
Corporate citizenship, social
responsibility
You might also like
- Conventional Theory of Firm Assumes Profit Maximization Is The Sole Objective of Business FirmsDocument2 pagesConventional Theory of Firm Assumes Profit Maximization Is The Sole Objective of Business FirmsIyer Deepika100% (1)
- Profit Vs WealthDocument5 pagesProfit Vs Wealthkhareshweta1428No ratings yet
- What Is Finance?Document8 pagesWhat Is Finance?luvpriyaNo ratings yet
- The Firm's Goals and Decision MakingDocument30 pagesThe Firm's Goals and Decision MakingAbdulrahman AlotaibiNo ratings yet
- Firms: Concept & Objectives: By: Akshat.D.YadavDocument11 pagesFirms: Concept & Objectives: By: Akshat.D.YadavyadavakshatNo ratings yet
- Learning Objective of The Chapter: Managing Growth and Transaction Preparing For The Launch of The VentureDocument29 pagesLearning Objective of The Chapter: Managing Growth and Transaction Preparing For The Launch of The VentureWêēdhzæmē ApdyræhmæåñNo ratings yet
- Managerial Eco1Document190 pagesManagerial Eco1ManojNo ratings yet
- Unit I IntroductionDocument11 pagesUnit I IntroductionPRERNA PANDEYNo ratings yet
- Formulation of Financial Strategy: Week #3Document17 pagesFormulation of Financial Strategy: Week #3Waljia BaigNo ratings yet
- Learn Financial Management EssentialsDocument41 pagesLearn Financial Management EssentialsKOSHY N VARGHESENo ratings yet
- Group Presentation on Strategy as a Quest for ValueDocument23 pagesGroup Presentation on Strategy as a Quest for ValueThë FähãdNo ratings yet
- Objectives of A Business FirmDocument9 pagesObjectives of A Business FirmAnand PremNo ratings yet
- Unit-2: Objectives of The FirmDocument21 pagesUnit-2: Objectives of The FirmtjpkNo ratings yet
- Managerial Economics:: Theory, Applications, and CasesDocument50 pagesManagerial Economics:: Theory, Applications, and CasesAbeer ShamiNo ratings yet
- Intro Corporate Finance Course ObjectivesDocument31 pagesIntro Corporate Finance Course ObjectivesSwati OzaNo ratings yet
- PDF FileDocument8 pagesPDF FileAtiqullah sherzadNo ratings yet
- Business Economics: Objectives and Importance of Managerial Economics/TITLEDocument27 pagesBusiness Economics: Objectives and Importance of Managerial Economics/TITLEMaanvi RockzzNo ratings yet
- Goals of FirmsDocument14 pagesGoals of Firmsyugabhore1234No ratings yet
- DocumentDocument6 pagesDocumentKhevnaNo ratings yet
- Financial Management Overview and Key ConceptsDocument16 pagesFinancial Management Overview and Key ConceptsKAUSHIKNo ratings yet
- Maximizing Firm Value Through Ethics & Stakeholder FocusDocument38 pagesMaximizing Firm Value Through Ethics & Stakeholder FocusSULEMAN BUTTNo ratings yet
- SodapdfDocument40 pagesSodapdfcommercewaale1No ratings yet
- Rothaermel Ch. 5 SummaryDocument5 pagesRothaermel Ch. 5 SummaryMichaelNo ratings yet
- Objectives of The Business Firm 1Document8 pagesObjectives of The Business Firm 1rajvinder kaurNo ratings yet
- ABM 503 Objectives of FirmsDocument42 pagesABM 503 Objectives of FirmsHarsh DwivediNo ratings yet
- Course Code:8503 Unit # 03: EntrepreneurshipDocument29 pagesCourse Code:8503 Unit # 03: EntrepreneurshipSalaha AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Business and Profit-FinalDocument21 pagesBusiness and Profit-FinalTrixia SiribanNo ratings yet
- Lecture Two - Goals, Constraints, CostsDocument30 pagesLecture Two - Goals, Constraints, CostsClive NyowanaNo ratings yet
- GRP 3Document4 pagesGRP 3kkv_phani_varma5396No ratings yet
- Finance Notes Business Studies HSCDocument24 pagesFinance Notes Business Studies HSCabonu16No ratings yet
- Responsibility CentresDocument30 pagesResponsibility CentresRafiq TamboliNo ratings yet
- Managerial Economics IntroductionDocument25 pagesManagerial Economics Introductionbnod karkiNo ratings yet
- 103 Me 15Document15 pages103 Me 15Koushik Roy SwtHrtNo ratings yet
- Objectives of Private-Sector BusinessesDocument4 pagesObjectives of Private-Sector BusinessesKhevnaNo ratings yet
- Goals of The Firm - 6Document21 pagesGoals of The Firm - 6Dhruv SoodNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 Strategic Marketing PlanningDocument11 pagesLesson 3 Strategic Marketing PlanningAMOS WASIKENo ratings yet
- MANAGERIAL ECONOMICS NOTES DC Without Market StructuresDocument160 pagesMANAGERIAL ECONOMICS NOTES DC Without Market StructuressanelisofuturemoyoNo ratings yet
- 02-CSFS, ObjectivesDocument12 pages02-CSFS, ObjectivesHastings KapalaNo ratings yet
- BA2-Chapter 9 - Performance MeasurementDocument27 pagesBA2-Chapter 9 - Performance MeasurementAde irma Nur fadhilahNo ratings yet
- Identifying Company's StrategyDocument21 pagesIdentifying Company's StrategyayushiNo ratings yet
- Module VII Profit Mgmt.Document15 pagesModule VII Profit Mgmt.Apoorv BNo ratings yet
- EntrepreneurshipDocument276 pagesEntrepreneurshipLekshmi Chidambaram100% (3)
- Assignment No. 6: Name:-Radha Ghatge Roll No: - 66 Div: - A (MBA)Document16 pagesAssignment No. 6: Name:-Radha Ghatge Roll No: - 66 Div: - A (MBA)RadhikaNo ratings yet
- Objectives of Financial ManagementDocument13 pagesObjectives of Financial ManagementAmandeep KaurNo ratings yet
- Understanding the Definition, Objectives and Role of Profit in BusinessDocument15 pagesUnderstanding the Definition, Objectives and Role of Profit in BusinessIbrahim OjedokunNo ratings yet
- Role of Firms in Society & Their ObjectivesDocument11 pagesRole of Firms in Society & Their ObjectivesMic BaldevaronaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Financial Management FinalDocument24 pagesIntroduction To Financial Management FinalTIBUGWISHA IVANNo ratings yet
- Capsim Management Simulations: What Is A Balanced Scorecard?Document2 pagesCapsim Management Simulations: What Is A Balanced Scorecard?camila lopezNo ratings yet
- Techniques Under Development in Managerial AccountingDocument27 pagesTechniques Under Development in Managerial AccountingMostafa MahmoudNo ratings yet
- Strategic Management NotesDocument54 pagesStrategic Management NotesNilesh MandlikNo ratings yet
- Business Creation and Growth FactorsDocument148 pagesBusiness Creation and Growth FactorsAminu AbdullahiNo ratings yet
- Material 1.3Document18 pagesMaterial 1.3Suryagayathri SNo ratings yet
- Bussines Objectives LecDocument13 pagesBussines Objectives LecAsim Abdelwahab AbdoraboNo ratings yet
- SFM Chapter 2Document29 pagesSFM Chapter 2WilsonNo ratings yet
- Managerial Economics Lecture Notes: Theory of the Firm, Profit TheoriesDocument6 pagesManagerial Economics Lecture Notes: Theory of the Firm, Profit Theoriessherryl caoNo ratings yet
- Objectives of Business Firm-FinalDocument43 pagesObjectives of Business Firm-FinalId Mohammad100% (3)
- ECC101 - Chapter 10 - Part 1Document6 pagesECC101 - Chapter 10 - Part 1AsandeNo ratings yet
- The Firm and Its GoalsDocument24 pagesThe Firm and Its GoalsFadi ChouNo ratings yet
- The Balanced Scorecard: Turn your data into a roadmap to successFrom EverandThe Balanced Scorecard: Turn your data into a roadmap to successRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (4)
- BioDocument2 pagesBioDr.K.BaranidharanNo ratings yet
- Join Zoom Meetinghttps://Sairaminstitutions - Zoom.Us/J/8754501114? PWD Vk5Xwgr6Ntbenkczemzhanv6Nwxmdz09 Meeting Id: 875 450 1114 Passcode: SairamnssDocument1 pageJoin Zoom Meetinghttps://Sairaminstitutions - Zoom.Us/J/8754501114? PWD Vk5Xwgr6Ntbenkczemzhanv6Nwxmdz09 Meeting Id: 875 450 1114 Passcode: SairamnssDr.K.BaranidharanNo ratings yet
- Cash Flow Statement: Dr.K.Baranidharan, SRI SAIRAM INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY, CHENNAI 44Document17 pagesCash Flow Statement: Dr.K.Baranidharan, SRI SAIRAM INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY, CHENNAI 44Dr.K.BaranidharanNo ratings yet
- Temple Ticket PALANI, DR - BARANIDHARAN KULOTHUNGAN, PROF MBA, SRI SAIRAM INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY, CHENNAIDocument2 pagesTemple Ticket PALANI, DR - BARANIDHARAN KULOTHUNGAN, PROF MBA, SRI SAIRAM INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY, CHENNAIDr.K.BaranidharanNo ratings yet
- National Day On Writing:, Oct 2o, 2020Document14 pagesNational Day On Writing:, Oct 2o, 2020Dr.K.BaranidharanNo ratings yet
- Decision Making Skills - DR - BARANIDHARAN KULOTHUNGAN, PROF MBA, SRI SAIRAM INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY, CHENNAIDocument10 pagesDecision Making Skills - DR - BARANIDHARAN KULOTHUNGAN, PROF MBA, SRI SAIRAM INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY, CHENNAIDr.K.BaranidharanNo ratings yet
- Planning Process, DR - Baranidharan Kulothungan, Prof Mba, Sri Sairam Institute of Technology, ChennaiDocument11 pagesPlanning Process, DR - Baranidharan Kulothungan, Prof Mba, Sri Sairam Institute of Technology, ChennaiDr.K.BaranidharanNo ratings yet
- BioDocument2 pagesBioDr.K.BaranidharanNo ratings yet
- MCQ - Decision Making - DR - BARANIDHARAN KULOTHUNGAN, PROF MBA, SRI SAIRAM INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY, CHENNAIDocument1 pageMCQ - Decision Making - DR - BARANIDHARAN KULOTHUNGAN, PROF MBA, SRI SAIRAM INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY, CHENNAIDr.K.BaranidharanNo ratings yet
- RESUME How To Prepared, DR - BARANIDHARAN KULOTHUNGAN, PROF MBA, SRI SAIRAM INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY, CHENNAIDocument2 pagesRESUME How To Prepared, DR - BARANIDHARAN KULOTHUNGAN, PROF MBA, SRI SAIRAM INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY, CHENNAIDr.K.BaranidharanNo ratings yet
- Types of B o - DR - Baranidharan Kulothungan, Prof Mba, Sri Sairam Institute of Technology, ChennaiDocument38 pagesTypes of B o - DR - Baranidharan Kulothungan, Prof Mba, Sri Sairam Institute of Technology, ChennaiDr.K.BaranidharanNo ratings yet
- B.E. / B. Tech. Degree ExaminationDocument2 pagesB.E. / B. Tech. Degree ExaminationDr.K.BaranidharanNo ratings yet
- C V:RES:BIO DATA, How To Prepare, DR - BARANIDHARAN KULOTHUNGAN, PROF MBA, SRI SAIRAM INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY, CHENNAIDocument4 pagesC V:RES:BIO DATA, How To Prepare, DR - BARANIDHARAN KULOTHUNGAN, PROF MBA, SRI SAIRAM INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY, CHENNAIDr.K.BaranidharanNo ratings yet
- Goal Setting - DR - BARANIDHARAN KULOTHUNGAN, PROF MBA, SRI SAIRAM INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY, CHENNAIDocument23 pagesGoal Setting - DR - BARANIDHARAN KULOTHUNGAN, PROF MBA, SRI SAIRAM INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY, CHENNAIDr.K.BaranidharanNo ratings yet
- CV How To Prepareds, DR - BARANIDHARAN KULOTHUNGAN, PROF MBA, SRI SAIRAM INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY, CHENNAIDocument1 pageCV How To Prepareds, DR - BARANIDHARAN KULOTHUNGAN, PROF MBA, SRI SAIRAM INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY, CHENNAIDr.K.BaranidharanNo ratings yet
- BioDocument2 pagesBioDr.K.BaranidharanNo ratings yet
- Example: Total Quality ManagementDocument2 pagesExample: Total Quality ManagementDr.K.BaranidharanNo ratings yet
- BioDocument2 pagesBioDr.K.BaranidharanNo ratings yet
- Nss Camp 2020 - SRI SAIRAM INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYDocument21 pagesNss Camp 2020 - SRI SAIRAM INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYDr.K.BaranidharanNo ratings yet
- Nss Camp 2020 - SRI SAIRAM INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYDocument21 pagesNss Camp 2020 - SRI SAIRAM INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYDr.K.BaranidharanNo ratings yet
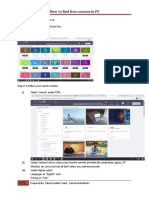
- How To Find The Free Courses in FSDocument2 pagesHow To Find The Free Courses in FSDr.K.BaranidharanNo ratings yet
- How Big Data Analytics Can Transform Businesses in Various IndustriesDocument3 pagesHow Big Data Analytics Can Transform Businesses in Various IndustriesDr.K.BaranidharanNo ratings yet
- 3 Skills PhotoDocument2 pages3 Skills PhotoDr.K.BaranidharanNo ratings yet
- What Is Participative Management StyleDocument2 pagesWhat Is Participative Management StyleDr.K.BaranidharanNo ratings yet
- 1st Sem 2018 MBA RESULTDocument1 page1st Sem 2018 MBA RESULTDr.K.BaranidharanNo ratings yet
- What Are The Four Stages of The Deming CycleDocument2 pagesWhat Are The Four Stages of The Deming CycleDr.K.BaranidharanNo ratings yet
- De LigationDocument1 pageDe LigationDr.K.BaranidharanNo ratings yet
- Merits of Decentralisation. Dr. K.BaranidharanDocument1 pageMerits of Decentralisation. Dr. K.BaranidharanDr.K.BaranidharanNo ratings yet
- Decentralisation. Dr.K.BaranidharanDocument1 pageDecentralisation. Dr.K.BaranidharanDr.K.BaranidharanNo ratings yet
- Principles of Delegation. Dr.K.BaranidharanDocument1 pagePrinciples of Delegation. Dr.K.BaranidharanDr.K.BaranidharanNo ratings yet
- The Following Is River Tours Limited S Unadjusted Trial Balance atDocument2 pagesThe Following Is River Tours Limited S Unadjusted Trial Balance atMiroslav GegoskiNo ratings yet
- People of The Philippines Vs Sandiganbayan and Bienvenido TanDocument2 pagesPeople of The Philippines Vs Sandiganbayan and Bienvenido TanRobyAnneLimbitcoAlbarracin100% (2)
- KPMG Nppa New Payments Platform Minimising Payments FraudDocument16 pagesKPMG Nppa New Payments Platform Minimising Payments FrauddavemacbrainNo ratings yet
- New Jeevan Anand (915) : Mr. YesDocument5 pagesNew Jeevan Anand (915) : Mr. YesPankaj YadavNo ratings yet
- TaxSaleResearch OkDocument44 pagesTaxSaleResearch OkMarlon Ferraro100% (1)
- Project Finance in Developing Countries ExplainedDocument8 pagesProject Finance in Developing Countries Explained'Daniel So-fly OramaliNo ratings yet
- SECP Form 6Document4 pagesSECP Form 6mirza faisalNo ratings yet
- Influence of Microfinance On Small Business Development in Namakkal District, TamilnaduDocument5 pagesInfluence of Microfinance On Small Business Development in Namakkal District, Tamilnaduarcherselevators100% (1)
- Negotiable Instruments Act, 1881 PDFDocument61 pagesNegotiable Instruments Act, 1881 PDFmackjbl100% (3)
- Open Banking: A Perspective For Financial InstitutionsDocument22 pagesOpen Banking: A Perspective For Financial InstitutionsAyon BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- Microequities Deep Value Microcap Fund IMDocument28 pagesMicroequities Deep Value Microcap Fund IMMicroequities Pty LtdNo ratings yet
- 2015 Accountancy Question PaperDocument4 pages2015 Accountancy Question PaperJoginder SinghNo ratings yet
- Types of CapitalDocument24 pagesTypes of CapitalAnkita N VyasNo ratings yet
- 4Document1 page4Victoria MrrNo ratings yet
- BankingDocument15 pagesBankingAnchu Theresa JacobNo ratings yet
- 22BSPHH01C1222 - Subham Deb - IrDocument22 pages22BSPHH01C1222 - Subham Deb - Irnilesh.das22hNo ratings yet
- SBI Focused Equity Fund (1) 09162022Document4 pagesSBI Focused Equity Fund (1) 09162022chandana kumarNo ratings yet
- SyllabusDocument45 pagesSyllabusPrachi PNo ratings yet
- Heineken 2004Document50 pagesHeineken 2004k0yujinNo ratings yet
- Securities and Exchange Board of India: Master CircularDocument236 pagesSecurities and Exchange Board of India: Master CircularViral_v2inNo ratings yet
- Audit Module 3 - Financial Statements TemplateDocument11 pagesAudit Module 3 - Financial Statements TemplateSiddhant AggarwalNo ratings yet
- A Critically Compassionate ApproaDocument16 pagesA Critically Compassionate ApproaAna MariaNo ratings yet
- IFC Promotes Private Sector Growth in Developing NationsDocument7 pagesIFC Promotes Private Sector Growth in Developing NationsJawad Ali RaiNo ratings yet
- DMGT104 Financial Accounting PDFDocument317 pagesDMGT104 Financial Accounting PDFNani100% (1)
- Bank Reconciliation NotesDocument3 pagesBank Reconciliation Notesjudel ArielNo ratings yet
- Comparative Analysis of Home Loan in UTI BankDocument95 pagesComparative Analysis of Home Loan in UTI BankMitesh SonegaraNo ratings yet
- Case Digest - OPT and DSTDocument30 pagesCase Digest - OPT and DSTGlargo GlargoNo ratings yet
- EquityDocument29 pagesEquityThuy Linh DoNo ratings yet
- StatementOfAccount 3092378518 Jul17 141113.csvDocument49 pagesStatementOfAccount 3092378518 Jul17 141113.csvOur educational ServiceNo ratings yet
- COMPARISON OF TAKAFUL AND INSURANCEDocument9 pagesCOMPARISON OF TAKAFUL AND INSURANCEHusna FadzilNo ratings yet