Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Industrial Marketing
Uploaded by
muhamad0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
96 views79 pagesindustry
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentindustry
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
96 views79 pagesIndustrial Marketing
Uploaded by
muhamadindustry
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 79
INDUSTRIAL MARKETING
Lecture Notes for Industrial Marketing
By CA Yatish Vernekar
THE MARKETING MIX
The Marketing Mix
The Marketing Mix
The tools available to a business to gain the
reaction it is seeking from its target market
in relation to its marketing objectives
7Ps Price, Product, Promotion, Place,
People, Process, Physical Environment
Traditional 4Ps extended to encompass
growth of service industry
Price
Price
Pricing Strategy
Importance of:
knowing the market
elasticity
keeping an eye
on rivals
Product
Product
Methods used to improve/differentiate
the product and increase sales or target sales more
effectively to gain
a competitive advantage e.g.
Extension strategies
Specialised versions
New editions
Improvements real or otherwise!
Changed packaging
Technology, etc.
Promotion
Promotion
Strategies
to make the consumer aware of the
existence of a product
or service
NOT just advertising
Place
Place
The means by which products and services
get from producer
to consumer and where they can be
accessed by the consumer
The more places to buy the product and the
easier it is made to buy it, the better for the
business (and the consumer?)
People
People
People represent the business
The image they present can be important
First contact often human what is the lasting
image they provide to the customer?
Extent of training and knowledge
of the product/service concerned
Mission statement how relevant?
Do staff represent the desired culture
of the business?
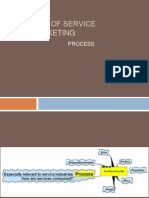
Process
Process
How do people consume services?
What processes do they have to go through to acquire
the services?
Where do they find the availability
of the service?
Contact
Reminders
Registration
Subscription
Form filling
Degree of technology
Physical Environment
Physical Environment
The ambience, mood or physical presentation of
the environment
Smart/shabby?
Trendy/retro/modern/old fashioned?
Light/dark/bright/subdued?
Romantic/chic/loud?
Clean/dirty/unkempt/neat?
Music?
Smell?
The Marketing Mix
Blend of the mix depends upon:
Marketing objectives
Type of product
Target market
Market structure
Rivals behaviour
Global issues culture/religion, etc.
Marketing position
Product portfolio
Product lifecycle
Boston Matrix
SOCIETAL ROLE OF
MARKETING
Societal Concept
Societal concept holds that the
organization's task is to determine the
needs, wants, and interests of target
markets and to deliver in desired
satisfaction more effectively and
efficiently than competitors in a way
that preserves or enhances the
consumer's and society's well being.
Build social & ethical considerations
into marketing practices.
Types of Marketing Channels
Marketing channel: system of marketing
institutions that promotes the physical flow of
goods and services, along with ownership title,
from producers to consumer or business user; also
called a distribution channel
Marketing intermediary: wholesaler or retailer
that operates between producers and consumers or
business users; also called a middleman
Wholesaler: marketing intermediary that takes
title to goods and then distributes these goods
further; also called a jobber or distributor
Direct Selling
Direct channel: marketing channel that moves
goods directly from a producer to ultimate user
Direct selling: strategy designed to establish
direct sales contract between producer and final
user
Channels Using Marketing
Intermediaries
Producer to wholesaler to retailer to consumer
Producer to wholesaler to business user
Producer to agent to wholesaler to retailer to
consumer
Producer to agent to wholesaler to business user
Producer to agent to business user
Dual Distribution: Network that moves
products to a firms target market through
more than one marketing channel
Reverse Channels: Channels designed to
return goods to their producers
Channel Strategy Decisions
Selection of a Marketing Channel
Factors which impact the selection of a
marketing channel include:
Market factors
Product factors
Organizational factors
Competitive factors
DISTRIBUTION
Channel of Distribution - a group of
interrelated organization that directs the
flow of products from producers to ultimate
consumers
Marketing Intermediary - an individual or
organization in marketing channel that
provides a link among producers, other
channel members, and final consumer
Distribution Overages
Intensity Distribution - market coverage in which
all available outlets are used for distributing a
product
Selective Distribution - Market coverage in which
only some of the available outlets are used for
distributing a product
Exclusive Distribution - Market coverage in which
one outlet is used in specific geographic area for
distributing a product
MARKET SEGMENTATION
What is Market?
PEOPLE
PEOPLE
BUT- Not just ANY people, they have to have
Willingness to buy
Purchasing power [money]
Authority to buy
Types of Markets
Consumer Goods & Services
Industrial Goods & Services
Market Segmentation
With large country
Many different types of people
It is too difficult to create a product that will
satisfy every body, that is why we focus on
the segment of the total market.
Market Segmentation
Definition
Grouping people according to their similarity
related to a particular product category
Market Segmentation
Characteristics
Age
Gender
Geographic
location
Income
Spending pattern
Marital status
Education
Mobility
Demographics
Cultural
background
Market Segmentation
4 commonly used basis for segmentation
Descriptive
Geographic location
Demographic
Behavioral
Psychographic
Benefits
Market Segmentation
Geographic location- based upon where
people live [historically a popular way of
dividing market]
Demographic- based upon age, gender and
income [very often used]
Market Segmentation
Psychographic/ lifestyles- based on peoples
opinions, interests, lifestyles.
Benefits- based on the different expectation
that customer have about what a product/
service can do for them.
PRODUCT DEVELOPMENT
Stages in New- Product
Development
Expensive, time consuming, and risky.
Only one third of the new products
become success stories.
Each step requires a go or no go
decision
Process of Developing New Goods &
Services
Commercialization
Test marketing
Product development
Concept development & business analysis
Screening
Generate new product ideas
PRICING STRATEGY
PRICING
Price - the value that buyer exchange for a
product in the marketing transaction
Pricing Objective:
Market share
Profit
Return on Investment
Status Quo
Pricing Decision and Methods
Factors in Pricing Decisions:
Price and non-price competition
Supply and demand
Consumer perception of price
Pricing Methods:
Cost-Oriented Pricing - Mark-up Pricing
Demand-Oriented Pricing - Break event point
Competition Oriented Pricing
Pricing Strategies
Marketing Concepts
Marketing is the process of planning and executing
the conception, pricing, promotion, and
distribution of idea, goods, and service to create
exchanges that satisfy individual and
organizational objective
Marketing Mix is the combination of products,
price, promotion, and distribution, used to satisfy
the needs of the target market
Product
Variety
Quality
Design
Features
Brand Name
Packaging
Services
Price
List price
Discounts
Allowances
Credit Terms
Promotion
Advertising
Personal Selling
Sales Promotion
Public Relations
Place
Channels
Coverage
Assortments
Locations
Inventory
Transportation
Logistics
Target
Costumers
Intended
Positioning
Marketing Mix
Marketing Activities
Product:
Develop new products
Modify existing
products
Test-market products
Select brand name
Package product
Pricing:
Establish price
objectives
Conduct cost
analysis
Analyze
competitors price
Set actual prices
Marketing Activities
Promotion:
Determine types of
promotion
Design the advertising
massage
Selecting advertising
media
Schedule the
advertisements
Distribution:
Select wholesalers and
retailers
Establish procedures
for handling and
moving products
Find the best locations
for plants, warehouses
and retail outlets
Market
Market is people with the authority, financial
ability, and willingness to purchase a
product
Types of Market:
Consumer market - for personal use
Industrial market - to use in the production
or resell
Target Marketing
Target market - a group of people that has similar
wants and needs which a firm directs its marketing
activities
Undifferentiated approach one marketing mix
for a product to the total market
Market Segmentation approach the division of
the total market into segment with marketing mix
directed to different segment
Market Segmentation
Market segment division of heterogonous market
into homogonous market based on different
characteristics
Segmentation Based:
Geographic bases - city, region
Demographic bases - sex, race, marital
Psychographics - a persons attitude, lifestyle
Product-related - brand loyalty
PRODUCT
Product - a good, service or idea, including all
attributes provided in an exchange between buyer
and seller
Product Classification:
Consumer goods products purchased by
consumers for personal use
Industrial goods product purchased by
companies to produce other products
Classifying Goods
Consumer Goods:
Convenience good
inexpensive and
regularly consumed
Shopping goods
moderately expensive
and infrequently
Specialty goods
expensive and rarely
Industrial goods:
Raw material
Components parts
Equipment and
installations
Services
Product Line and Product
Mix
Product Line - a group of related products
that are considered a unit because of
marketing, technical or use similarity
Product Mix - the total group of product
offer sale, or all of the firms product lines
Product Differentiation creation of
product or product image that differs from
existing product to attract consumers
Product Attributes
Brand - a name, sign, symbol, design, or
combination a companys product to
distinguish it product from others
Packaging - the development of a container
and graphic design for a product
Labeling - the display of important
information on a product package
PRICING
Price - the value that buyer exchange for a
product in the marketing transaction
Pricing Objective:
Market share
Profit
Return on Investment
Status Quo
Pricing Decision and Methods
Factors in Pricing Decisions:
Price and non-price competition
Supply and demand
Consumer perception of price
Pricing Methods:
Cost-Oriented Pricing - Mark-up Pricing
Demand-Oriented Pricing - Break event point
Competition Oriented Pricing
Pricing Strategies
Pioneer pricing leadership pricing in the market
Price skimming setting an initial high price to
cover new product cost and generate a profit
Penetration pricing setting an initial low price to
establish a new product in the market
Psychological Pricing setting an initial high
price to respond irrationally consumers
Price Discounting Price reduction offered as an
incentive to purchase
PROMOTION
Promotion - the communication of favorable,
persuasive information about a firm or product in
order to influential buyers
Promotional Objectives:
Informing
Increasing sales
Stabilizing sales
Positioning the product
Building a public image
The Promotion Mix
Promotion Mix - the combination of advertising,
personal selling, sales promotion, publicity used to
promote a specific product
Advertising
Non-personal communication to a target audience
through a mass medium, such as TV, Radio,
newspapers, or magazines, and outdoor display
Types of Advertising:
Primary-Demand Advertising: for all products
Selective Brand Advertising: for specific products
Institutional Advertising: create public image
Advertising Promotion
Advertising Media variety of
communication devices for carrying
massage to potential customers
Direct Mail delivery massage directly to
customer places
Internet Advertising put the massage into
website or mailed directly to customer
Personal Selling
Person-to-person communication with one or
more prospective customers in order to make sale
Telemarketing using telephone to perform the
personal selling process
Types of Salespeople:
Order Getter
Order taker
Support salespeople
Sales Promotion
An activity that offers customers or marketing
intermediaries direct incentives for purchasing a
product
Type of Sales Promotion:
Coupon: reduces the price of a product by stated
amount at the time of purchase
Rebate: an extra discount
Free Sample
Contest: consumer compete for prizes
Trade show
Publicity and Public Relation
Publicity - a non-personal form of
communication transmitted in news story
form and not paid for directly sponsor
Public Relations - a set of communication
activities designed to create and maintain a
favorable public image for firm
Special
Events
Written
Materials
Public
Service
Activities
Speeches
News
Audiovisual
Materials
Corporate
Identity
Materials
Web Site
Major Public Relation Tools
Promotional Strategy:
Push Strategy: promotion of a product to
wholesaler or retailers in the marketing
channel, who in turn promote the product to
consumers
Pull Strategy: promotion of a product
direct to consumers to stimulate strong
consumer demands
DISTRIBUTION
Channel of Distribution - a group of
interrelated organization that directs the
flow of products from producers to ultimate
consumers
Marketing Intermediary - an individual or
organization in marketing channel that
provides a link among producers, other
channel members, and final consumer
Type of Marketing Channels:
Consumer Products:
Producer-consumer: plant and flower, services
Producer-retailer-consumer: automobile, furniture
Producer-wholesaler-retailer-consumer: e.g.
convenience goods
Producer-Agent/broker-wholesaler-retailer-
consumer: e.g. consumer products
Type of Marketing Channels
Industrial Products:
producer-industrial user: heavy
equipment and machinery
producer-wholesaler-industrial
user: tools and automotive parts
Distribution Overages
Intensity Distribution - market coverage in which
all available outlets are used for distributing a
product
Selective Distribution - Market coverage in which
only some of the available outlets are used for
distributing a product
Exclusive Distribution - Market coverage in which
one outlet is used in specific geographic area for
distributing a product
Wholesaling
The marketing activities of intermediates who sell to retailer,
industrial users, and other wholesalers.
Types of Wholesalers:
Merchant Wholesaler: takes ownership of goods and the
risks associated with ownership
Sales Branch: a manufacture-owned wholesaler that take
title to products, risks, and provides service
Agent: a wholesaler hired by a buyer or seller on a
permanent basis and paid commissions
Broker: a wholesaler who bring together buyers and seller
on temporary basis
Retailing
The marketing activities involved in selling products
to final consumers for personal or household use
Department Store: a large retailer organized into
separate departments and offering a full line of
services and wide product mix
Supermarket: a large self-service retailer that stock
a wide variety of groceries and a limited
assortment of nonfood products
Retailing
Catalog Showroom: a form of warehouse show-
room where customers select products from
catalogs sent to customers homes or available in
the store
Direct Marketing: non-store retailing that uses
non-personal media to introduce products to
consumers who then purchase the product by mail,
telephone, computer, or TV
Physical Distribution
Those activities that involve the movement of
products through marketing channels from
manufacturer to customer, including:
Transportation: shipping goods to customers by rail, air,
truck, water, and pipeline
Warehousing: the receiving, storing, and shipping
activities involved in the physical distribution of goods
Order Processing: the receipt and preparation of an order
for shipment
Material Handling: the physical handling of products
during transportation and warehousing
Basic Channels of Distribution
Manufacturers/products
Agents/brokers
Wholesalers/distributors
Retailers
Retailers
Consumers and organizational end users
Typical Distribution of Drugs
Manufacturers
Marketing Agents
Retailers/Wholesalers/Distributors
Private
GPs/specialists
Group
Procurement
Office
Retail
Pharmacy
Public Hospitals / Institutions
You might also like
- Product Strategies SampleDocument35 pagesProduct Strategies SampleRashmi SinghNo ratings yet
- Campuran PasaranDocument36 pagesCampuran PasaranmuhamadNo ratings yet
- Benefits of Achieving Customer Service ExcellenceDocument19 pagesBenefits of Achieving Customer Service ExcellencemuhamadNo ratings yet
- The Ethics of Charismatic LeadershipDocument4 pagesThe Ethics of Charismatic LeadershipmuhamadNo ratings yet
- Process of MarketingDocument32 pagesProcess of MarketingmuhamadNo ratings yet
- How To Be A Good Master of CeremoniesDocument17 pagesHow To Be A Good Master of CeremoniesmuhamadNo ratings yet
- Tadzkirah Ramadhaan: Lesson FromDocument47 pagesTadzkirah Ramadhaan: Lesson FrommuhamadNo ratings yet
- How To Be A Good Master of CeremoniesDocument17 pagesHow To Be A Good Master of CeremoniesmuhamadNo ratings yet
- Color PsychologyDocument8 pagesColor PsychologymuhamadNo ratings yet
- Muka Serupa Jackie ChanDocument1 pageMuka Serupa Jackie ChanmuhamadNo ratings yet
- RI Secrets RevealedDocument37 pagesRI Secrets Revealedmuhamad100% (3)
- Color PsychologyDocument8 pagesColor PsychologymuhamadNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Impact of Green Marketing On Customer Satisfaction An Empirical StudyDocument7 pagesImpact of Green Marketing On Customer Satisfaction An Empirical StudyarcherselevatorsNo ratings yet
- Marketing PlanDocument75 pagesMarketing PlanFonzy RoneNo ratings yet
- Marketing Mix - MCQsDocument26 pagesMarketing Mix - MCQsMaxwell;100% (1)
- Internship Report On Marketing Activitie PDFDocument59 pagesInternship Report On Marketing Activitie PDFNafiz FahimNo ratings yet
- Marketing Strategy Implementation at Contractor CompanyDocument53 pagesMarketing Strategy Implementation at Contractor Companyferry firmannaNo ratings yet
- Ebook PDF Customer Service For Hospitality and Tourism 2nd Edition PDFDocument41 pagesEbook PDF Customer Service For Hospitality and Tourism 2nd Edition PDFcecil.slocum194100% (34)
- RESEARCHDocument28 pagesRESEARCHMj MalacaNo ratings yet
- Digital Marketing Plan To Revive Tourism in Romania During COVID19Document14 pagesDigital Marketing Plan To Revive Tourism in Romania During COVID19Diana CraescuNo ratings yet
- Jnu Supply Chain ManagementDocument89 pagesJnu Supply Chain ManagementamaldhasapolloNo ratings yet
- Review of Literature: Chapter - IIDocument45 pagesReview of Literature: Chapter - IIGaurish ApradhNo ratings yet
- Global Business - Unit 4Document86 pagesGlobal Business - Unit 4GauravTiwariNo ratings yet
- Wel Come To My Presentation ON Banana JuiceDocument25 pagesWel Come To My Presentation ON Banana Juicezaber chowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Advertg HBL Module v2Document73 pagesAdvertg HBL Module v2Benjamin Joseph RoqueNo ratings yet
- Internship Project RanjanDocument20 pagesInternship Project RanjanRanjan MandalNo ratings yet
- Marketing Mix PandaDocument11 pagesMarketing Mix Pandamuhdfuad21No ratings yet
- Destination Marketing PlanningDocument8 pagesDestination Marketing PlanningErza MutaqinNo ratings yet
- Marketing mix analysis of LG Butterfly microwave ovenDocument24 pagesMarketing mix analysis of LG Butterfly microwave ovenNishat Tabassum ProvaNo ratings yet
- Marketing Mix Insurance SectorDocument4 pagesMarketing Mix Insurance SectorSantosh Pradhan100% (1)
- Nguyen Thi Thu Hang - Graduation ThesisDocument59 pagesNguyen Thi Thu Hang - Graduation Thesislonelybabi100% (1)
- CBM2 - Module 1Document26 pagesCBM2 - Module 1KAYE MARIE CANIANo ratings yet
- Marketing Notes - Chapter 1Document30 pagesMarketing Notes - Chapter 1Mohadissa Hussain ZadaNo ratings yet
- SWOT Analysis and Marketing Mix Chapter SummaryDocument14 pagesSWOT Analysis and Marketing Mix Chapter SummaryImran DostNo ratings yet
- Essential Marketing Models PDFDocument61 pagesEssential Marketing Models PDFMike Archie Ondieki100% (3)
- A Study of Consumer Behaviour Towards Purchase of Royal Enfield in LucknowDocument97 pagesA Study of Consumer Behaviour Towards Purchase of Royal Enfield in LucknowHarshit Kashyap50% (2)
- Business Plan OverviewDocument41 pagesBusiness Plan OverviewMary De JesusNo ratings yet
- Marketing 4ADocument24 pagesMarketing 4AЭуженио МигелNo ratings yet
- Polytechnic University of The Philippines: Sari Heartland - The Local VillageDocument40 pagesPolytechnic University of The Philippines: Sari Heartland - The Local VillageEmmanuel SidaNo ratings yet
- Marketing MixDocument5 pagesMarketing MixArvish DoongoorNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Hospitality and Tourism ManagementDocument210 pagesFundamentals of Hospitality and Tourism ManagementSumit Pratap85% (13)
- Services Marketing: Presented By: Muskan Jaiswal BBA-3 Sem Doon Business SchoolDocument33 pagesServices Marketing: Presented By: Muskan Jaiswal BBA-3 Sem Doon Business SchoolMuskanNo ratings yet