Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Water Quality Analysis
Uploaded by
ksbbs0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
35 views33 pageswater quality analysis
Original Title
water quality analysis
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentwater quality analysis
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
35 views33 pagesWater Quality Analysis
Uploaded by
ksbbswater quality analysis
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 33
CENTRE FOR COAL TECHNOLOGY
UNIVERSITY OF THE PUNJAB
LAHORE
Topic:-
Water Analysis
Presented By:-
KOMAL AROOSH
Session:-
2010-2012
5
/
1
/
2
0
1
1
3
:
3
6
:
1
3
P
M
1
. WATER
. WATER QUALITY
. HARDNESS OF WATER
. SOLIDS IN WATER
. SEPARATION TECHNIQUES
5
/
1
/
2
0
1
1
3
:
3
6
:
1
3
P
M
2
CONTENTS
5
/
1
/
2
0
1
1
3
:
3
6
:
1
3
P
M
3
Water:
Water is undesirable in fuel when it is injected into the
cylinders.
In practice it is impossible to be entirely certain that the
fuel is completely free of water.
Sea water can lead to problems, because the sodium will
get into the cylinder.
Fresh water should not lead to serious problems if it is
evenly distributed in the fuel oil.
5
/
1
/
2
0
1
1
3
:
3
6
:
1
3
P
M
4
WATER QUALITY
Water quality varies with the source.
It may or may not contain
dissolved minerals
dissolved gases
organic matter
microorganisms
combinations of these impurities that cause
deterioration of metalworking fluid performance.
5
/
1
/
2
0
1
1
3
:
3
6
:
1
3
P
M
5
The amount of dissolved minerals, for example, in
lake or river water (surface water) depends on
whether the source is near mineral deposits.
Typically, lake water is of a consistent quality, while
river water varies with weather conditions. Well
water (ground water), since it seeps through
minerals in the earth, tends to contain more
dissolved minerals than either lake or river water.
Surface water, however, is likely to contain a higher
number of microorganisms (bacteria and mold) and
thus need treatment
5
/
1
/
2
0
1
1
3
:
3
6
:
1
3
P
M
6
1.If water is badly polluted-- like raw sewage---
it might be obvious from its appearance or
odor.
2.It might be colored or turbid (cloudy), or have
solids, oil or foam floating on it.
3.It might have a rotten odor, or smell like
industrial chemicals.
5
/
1
/
2
0
1
1
3
:
3
6
:
1
3
P
M
7
Why do we need to analyze water?
THERE ARE TWO ASPECTS OF WATER
ANALYSIS THAT WE NEED TO CONSIDER:
5
/
1
/
2
0
1
1
3
:
3
6
:
1
3
P
M
8
what substances or
organisms are we
interested in testing for-
- and why?
what procedures and
equipment do we use
to make the
measurements, and
how do they work?
TWO ASPECTS OF WATER
5
/
1
/
2
0
1
1
3
:
3
6
:
1
3
P
M
9
HARDNESS OF WATER
What is hardness of water?
Hard water is water that has
high mineral content.
Hardness of water is due to metal
ions(minerals) that are dissolved in the
ground water. These minerals include Ca
2+
,
Mg
2+
, Fe
3+
, SO
4
2-
, and HCO
3
-
. Our hard
water in the southern Indiana area is due to
rain moving through the vast amount of
limestone, CaCO
3.
5
/
1
/
2
0
1
1
3
:
3
6
:
1
3
P
M
10
Hardness of water
5
/
1
/
2
0
1
1
3
:
3
6
:
1
3
P
M
11
WHY BE CONCERNED ABOUT HARD WATER?
The determination of water hardness is a useful test that
provides a measure of quality of water for households and
industrial uses.
Originally, water hardness was defined as the measure of
the capacity of the water to precipitate soap. Hard water is
not a health hazard.
When hard water is heated, CaCO
3
precipitates out, which
then clogs pipes and industrial boilers. This leads to
malfunction or damage and is expensive to remove
5
/
1
/
2
0
1
1
3
:
3
6
:
1
3
P
M
12
TYPES OF HARDNESS
There are two basic types of water hardness:
1. Temporary hardness
2. Permanent hardness
5
/
1
/
2
0
1
1
3
:
3
6
:
1
3
P
M
13
TEMPORARY HARDNESS
5
/
1
/
2
0
1
1
3
:
3
6
:
1
3
P
M
14
Temporary Hardness is due to the bicarbonate
ion, HCO
3
-
, being present in the water. This type of
hardness can be removed by boiling the water to
expel the CO
2
.
Ca(HCO
3
)
2
CaCO
3
+ H
2
O + CO
2
Heating
Mg(HCO
3
)
2
Ma (OH)
2
+ 2CO
2
Heating
Main Mechanism
Permanent hardness
Permanent hardness is due to the presence of the
ions Ca
2+
, Mg
+2
, Fe
3+
and SO
4
-
. This type of
hardness cannot be eliminated by boiling. The
water with this type of hardness is said to
be permanently hard.
5
/
1
/
2
0
1
1
3
:
3
6
:
1
3
P
M
15
SOLIDS IN
WATER
5
/
1
/
2
0
1
1
3
:
3
6
:
1
3
P
M
16
DISSOLVED SOLIDS
The total dissolved solids can have a significant impact on
the quality of water. The amount of dissolved solids affects
the water for almost all of its uses, whether for drinking,
agricultural, or industrial use. The recommended maximum
limit of dissolved solids in drinking water is 500 ppm
5
/
1
/
2
0
1
1
3
:
3
6
:
1
3
P
M
17
PROBLEMS RELATED TO DISSOLVED SOLIDS
The problems caused by dissolved material relate
to taste and odor, hardness, and corrosion and
scaling in the distribution system, among others.
Several different types of dissolved solids could be
toxic if the levels become too high. These include
barium, arsenic, cadmium, chromium, lead,
mercury, selenium, and silver. Each of these are
regulated by the EPA and have maximum
contaminant levels assigned to them.
5
/
1
/
2
0
1
1
3
:
3
6
:
1
3
P
M
18
SUSPENDED SOLIDS
Suspended solids refers to small solid particles which
remain in suspension in water as a colloid or due to the
motion of the water. It is used as one indicator of water
quality.
5
/
1
/
2
0
1
1
3
:
3
6
:
1
3
P
M
19
PROBLEMS RELATED TO SUSPENDED PARTICLES
High concentrations of suspended solids
can cause many problems for stream health
and aquatic life.
5
/
1
/
2
0
1
1
3
:
3
6
:
1
3
P
M
20
5
/
1
/
2
0
1
1
3
:
3
6
:
1
3
P
M
21
SEPARATION
TECHNIQUES
Separation technique include
1. Filtration
2. Distillation
3. Extraction
5
/
1
/
2
0
1
1
3
:
3
6
:
1
3
P
M
22
Filtration:
The water is passed through a fine-pore filter which can
be made of paper, glass fibers, a cellulose acetate
membrane, etc.
Filtration through a filter of some agreed-upon standard
pore size can be used to separate "suspended" from
"dissolved" portions of the analyte. The analyte may be
the suspended matter which is captured on the filter-- or
the filter may be used to clarify the water for analysis of a
dissolved material.
5
/
1
/
2
0
1
1
3
:
3
6
:
1
3
P
M
23
Distillation:
If the analyte can be boiled out of the water, or along
with the water, then the vapors can be cooled and re-
condensed or trapped in a liquid form in a different
container. This way the analyte can be removed from the
interfering substances in the original water sample. Often
the sample is made acidic or alkaline, or treated
chemically in some other way before distillation, to
convert the analyte into a volatile (easily evaporated)
form, and to immobilize or neutralize interfering
substances.
5
/
1
/
2
0
1
1
3
:
3
6
:
1
3
P
M
24
Extraction:
Some analytes may be much more soluble in an organic
solvent than in water. If the solvent does not mix with
water, and the sample is shaken with portions of the
solvent, almost all of the analyte may be transferred from
the water into the solvent, leaving interfering substances
behind. This is known as a "liquid-liquid" extraction. The
analysis may be completed using the organic portion.
There are also continuous versions of this process for
use with liquid or with dry samples.
5
/
1
/
2
0
1
1
3
:
3
6
:
1
3
P
M
25
REFERENCES
Map from Morton Salt at
http://www.mortonsalt.com/soft/sofisoft.htm
^
a
b
c
World Health Organization Hardness in
Drinking-Water, 2003
^
a
b
Hermann Weingrtner, "Water" in Ullmann's
Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry,
2006[december], WileyVCH,
Weinheim.doi:10.1002/14356007.a28_001
http://www.glendalewaterandpower.com/residents/
water_hardnes
http://www.mrwa.com/OPWater%20and%20Impuriti
es.pdf
5
/
1
/
2
0
1
1
3
:
3
6
:
1
3
P
M
26
PARTICULATE
MATTERS
PM2.5 AND PM10 ISSUES
PM EFFECTS
UNDERSTATEMENT OF PM BY HAZCO
HAZCO did not account for fugitive emissions from
the sulphur piles assuming that:
0.02% of all particles will be less than 2 mm
Dr. James Hyne indicates that:
1.0 % of all particles will be less than 0.3 mm
This constitutes a gross understatement of dust
composition by HAZCO
PM DISPERSION MODELING
UNDERSTATEMENTS
Indicates that 24 hr PM 2.5 including HAZCO
and background levels at the property line will
be 2.5 ug/m3
Stated in the air modeling report that ambient
levels are 7.9 ug/m3
5
/
1
/
2
0
1
1
3
:
3
6
:
1
3
P
M
32
IMPACTS TO ADJACENT INDUSTRY
Canexus and ERCO Worldwide produce
sodium chlorate, which is incompatible with
sulphur
Both industries employ open cooling towers,
as will many future developing industries
A Canexus review of the particulates
estimates concludes that, HAZCOs
conclusion that fugitive dust emissions
associated with the storage, handling and
transportation activities will be negligible, is
neither credible nor valid.
You might also like
- Thesis Water Treatment PDFDocument34 pagesThesis Water Treatment PDFAzlyn SyafikahNo ratings yet
- Moosaviraad, 2016Document9 pagesMoosaviraad, 2016Muhammad Ramadhan SaputraNo ratings yet
- 1 Water Quality ParametersDocument48 pages1 Water Quality ParametersNurSyuhada A50% (2)
- Water Quality Parameters ChapterDocument39 pagesWater Quality Parameters ChapterSakinah EnglimanNo ratings yet
- Water Pollution: Prof. A. K. Majumder Department of Mining EngineeringDocument47 pagesWater Pollution: Prof. A. K. Majumder Department of Mining EngineeringAniruddhaDasNo ratings yet
- Water Quality: Criteria Factors Influencing QualityDocument26 pagesWater Quality: Criteria Factors Influencing QualityncisisthebestNo ratings yet
- SEV455 Assignment 1A-BusikuDocument7 pagesSEV455 Assignment 1A-BusikuBusiku SilengaNo ratings yet
- Report 2Document7 pagesReport 2Ahmad AmrNo ratings yet
- Water Treatment and Plant Design PDFDocument87 pagesWater Treatment and Plant Design PDFFatih100% (4)
- G1 - Mohamad Taslin Shah - 1001748107 - Exp 1 - 2Document11 pagesG1 - Mohamad Taslin Shah - 1001748107 - Exp 1 - 2TaslinNo ratings yet
- Coagulation and Flocculation in Water and Wastewater Treatment - IWA Publishing PDFDocument27 pagesCoagulation and Flocculation in Water and Wastewater Treatment - IWA Publishing PDFНурбек КасимовNo ratings yet
- Langelier Index Corrosion MineralizationDocument17 pagesLangelier Index Corrosion MineralizationdeyprasenNo ratings yet
- UNIT I WaterDocument25 pagesUNIT I WaterYERIPINA SATEESH CHANDRA DEV 19-206100% (1)
- Hard WaterDocument30 pagesHard Waterpriyanshu dhawanNo ratings yet
- NCSC Writeup ChemistryDocument9 pagesNCSC Writeup Chemistryreadingchallenge jnvsklmNo ratings yet
- Exp1 IntroductionDocument6 pagesExp1 IntroductionPoison PinkNo ratings yet
- IE208-L4-Water TreatmentDocument57 pagesIE208-L4-Water TreatmentKristine Mae CabreraNo ratings yet
- Final Chemistry Project WaterDocument22 pagesFinal Chemistry Project WaterSaurabh Suman50% (2)
- Water Purification Focus On DistillationDocument20 pagesWater Purification Focus On DistillationKiran KumarNo ratings yet
- America’s Authority in Membrane Treatment and DesaltingDocument3 pagesAmerica’s Authority in Membrane Treatment and DesaltingRajesh MukkavilliNo ratings yet
- Classification of Water PollutantsDocument4 pagesClassification of Water PollutantsAaliyah boydNo ratings yet
- Challenges with US Drinking Water and the Safe Drinking Water ActDocument9 pagesChallenges with US Drinking Water and the Safe Drinking Water ActFahad AreebNo ratings yet
- Lead Techincal Fs EPADocument4 pagesLead Techincal Fs EPAEric CheahNo ratings yet
- PPTDocument45 pagesPPTThirumal ThirandasNo ratings yet
- OP-Water and ImpuritiesDocument6 pagesOP-Water and ImpuritiesNataraja ManisandeepNo ratings yet
- Manual MT 25T SRH EngDocument174 pagesManual MT 25T SRH EngSiemNo ratings yet
- Methods of Water PurificationDocument15 pagesMethods of Water PurificationParbat Jung KunwarNo ratings yet
- Course Content: Cooling Water - Problems and Solutions'Document31 pagesCourse Content: Cooling Water - Problems and Solutions'Rakesh RanjanNo ratings yet
- Coagulation and Flocculation in Water and Wastewater Treatment PDFDocument19 pagesCoagulation and Flocculation in Water and Wastewater Treatment PDFSayan KirinathanNo ratings yet
- Water Purification Focus On Distillation MAY18Document20 pagesWater Purification Focus On Distillation MAY18Mariangélica DominiNo ratings yet
- Water Quality - Estimations of Physical ParametersDocument6 pagesWater Quality - Estimations of Physical Parameterswakanda foreverNo ratings yet
- Boiler Feed Water ConditioningDocument88 pagesBoiler Feed Water ConditioningGNo ratings yet
- Different Processes in Purifying Laguna de Bay: Selected Parameters Oxygen Saturation and Oxygen DemandDocument12 pagesDifferent Processes in Purifying Laguna de Bay: Selected Parameters Oxygen Saturation and Oxygen DemandiirnitedNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Extended Essay: Çağatay OkmanDocument21 pagesChemistry Extended Essay: Çağatay OkmanMonika GuliaNo ratings yet
- SSS 2 E-Note 3rd Term ChemistryDocument61 pagesSSS 2 E-Note 3rd Term ChemistryDave Blessed100% (3)
- HSC Chemistry Lesson Plan 27Document10 pagesHSC Chemistry Lesson Plan 27Ali HaidarNo ratings yet
- Water TreatmentDocument7 pagesWater TreatmentTamunosaki AwolayeoforiNo ratings yet
- 1-Water ProblemsDocument6 pages1-Water ProblemsshokryNo ratings yet
- Water and Wastewater Engineering Assignment 01Document7 pagesWater and Wastewater Engineering Assignment 01manarajNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2, Water in Chemical IndustryDocument65 pagesChapter 2, Water in Chemical IndustrysineNo ratings yet
- Water Treatment I Kurang KomplitDocument89 pagesWater Treatment I Kurang KomplitEndarAdeCandraNo ratings yet
- Landfill Leachate Treatment by CoagulatiDocument4 pagesLandfill Leachate Treatment by CoagulatiConstantinTudoseNo ratings yet
- Name: Muhamad Aiman Bin Mohd Azman Matrix ID: 2019717423 Class: AS229 3A Date of Submission: 5 April 2020Document12 pagesName: Muhamad Aiman Bin Mohd Azman Matrix ID: 2019717423 Class: AS229 3A Date of Submission: 5 April 2020Muhamad Aiman Mohd AzmanNo ratings yet
- Water Technology Understanding, Interpreting and UTILIZING WATER ANALYSIS DATADocument12 pagesWater Technology Understanding, Interpreting and UTILIZING WATER ANALYSIS DATAMohamed HaboNo ratings yet
- Use of Recycled Water in Concrete Production: Cement Concrete & Aggregates AustraliaDocument27 pagesUse of Recycled Water in Concrete Production: Cement Concrete & Aggregates AustraliaankysurfsNo ratings yet
- Classification and Parameters of Water QualityDocument5 pagesClassification and Parameters of Water QualityPawan Kumar PalNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document14 pagesUnit 1Pawan Kumar PalNo ratings yet
- Drinking Water SolutionsDocument16 pagesDrinking Water SolutionsLiviu SomesanNo ratings yet
- CHE 262 Chemical Processes and SustainabilityDocument24 pagesCHE 262 Chemical Processes and SustainabilityMohd Shahrul Nizam SallehNo ratings yet
- Awareness About The RO Water PurifierDocument7 pagesAwareness About The RO Water PurifiervikaskamaljnuNo ratings yet
- Water Quality Parameters Water Quality: o o o oDocument10 pagesWater Quality Parameters Water Quality: o o o ojammy_titansNo ratings yet
- Water Quality: Dissolved, Nonionic and Undissolved and GasesDocument19 pagesWater Quality: Dissolved, Nonionic and Undissolved and GasesRoxanne Mae RuizNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 SummaryDocument22 pagesUnit 2 SummaryPutu HermayaniNo ratings yet
- Water TreatmentDocument19 pagesWater TreatmentAnonymous 8ooQmMoNs1No ratings yet
- Water Treatment Techniques for Food ProductionDocument8 pagesWater Treatment Techniques for Food ProductionHisExcellencyNo ratings yet
- CEFC 513 Water Quality AnalysisDocument8 pagesCEFC 513 Water Quality AnalysisAmihan De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- ULO3 BDocument3 pagesULO3 BKaris DemetriaNo ratings yet
- Water Treatment Processes: Coagulation and Removal of Suspended SolidsDocument20 pagesWater Treatment Processes: Coagulation and Removal of Suspended SolidsAhmed AbdullatifNo ratings yet
- Microbiological Aspects of Pollution Control: Fundamental Aspects of Pollution Control and Environmental ScienceFrom EverandMicrobiological Aspects of Pollution Control: Fundamental Aspects of Pollution Control and Environmental ScienceNo ratings yet
- Different Types of Audit: Corporate Office: Fl-4, 323A Motilal Gupta Road, Kolkata-700 008, INDIA, Tel: 7999099410Document1 pageDifferent Types of Audit: Corporate Office: Fl-4, 323A Motilal Gupta Road, Kolkata-700 008, INDIA, Tel: 7999099410ksbbsNo ratings yet
- Different Types of Audit: Corporate Office: Fl-4, 323A Motilal Gupta Road, Kolkata-700 008, INDIA, Tel: 7999099410Document1 pageDifferent Types of Audit: Corporate Office: Fl-4, 323A Motilal Gupta Road, Kolkata-700 008, INDIA, Tel: 7999099410ksbbsNo ratings yet
- Design of Logo For MoEF&CC For World Environment Day, 2018Document3 pagesDesign of Logo For MoEF&CC For World Environment Day, 2018ksbbsNo ratings yet
- Characterizing Source EmissionsDocument42 pagesCharacterizing Source EmissionsksbbsNo ratings yet
- So2 & No2 Manual Calculated Data SheetDocument3 pagesSo2 & No2 Manual Calculated Data SheetksbbsNo ratings yet
- ESP Design ParametersDocument34 pagesESP Design ParametersssirupaNo ratings yet
- Hourly Monitoring Report - Air PollutantDocument2 pagesHourly Monitoring Report - Air PollutantksbbsNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Ecology 3EDocument1 pageFundamentals of Ecology 3EksbbsNo ratings yet
- OSPCB RT - DAS ONLINE Data Transmission SystemDocument1 pageOSPCB RT - DAS ONLINE Data Transmission SystemksbbsNo ratings yet
- OSPCB RT - DAS ONLINE Data Transmission SystemDocument1 pageOSPCB RT - DAS ONLINE Data Transmission SystemksbbsNo ratings yet
- Water Treatment Manual DesignDocument78 pagesWater Treatment Manual DesignDavid Lambert100% (2)
- Stack SamplingDocument29 pagesStack SamplingksbbsNo ratings yet
- BOD ProcedureDocument14 pagesBOD ProcedureSajith Ranatunga100% (1)
- Pellet Plant Weather SheetDocument2 pagesPellet Plant Weather SheetksbbsNo ratings yet
- Noise Monitoring DataDocument56 pagesNoise Monitoring DataksbbsNo ratings yet
- R.O.water Analysis Parameter With STDDocument2 pagesR.O.water Analysis Parameter With STDksbbsNo ratings yet
- Major Project - Ramu Naidu Kolli - M. Tech PDFDocument2 pagesMajor Project - Ramu Naidu Kolli - M. Tech PDFksbbsNo ratings yet
- Attendance Sheet Template for Company EmployeesDocument2 pagesAttendance Sheet Template for Company EmployeesksbbsNo ratings yet
- Land Application and Composting of BiosolidsDocument6 pagesLand Application and Composting of BiosolidsksbbsNo ratings yet
- Environmentalpollution 120921165803 Phpapp01Document29 pagesEnvironmentalpollution 120921165803 Phpapp01RommelKilljoyNo ratings yet
- Lucknow Esi Hospital DetailsDocument1 pageLucknow Esi Hospital DetailsksbbsNo ratings yet
- Envirotech ManualDocument2 pagesEnvirotech Manualksbbs100% (1)
- PM2.5 Particulate Monitoring in Ambient AirDocument59 pagesPM2.5 Particulate Monitoring in Ambient AirksbbsNo ratings yet
- H.R. Documentation Format .xlsx1Document2 pagesH.R. Documentation Format .xlsx1ksbbsNo ratings yet
- Environment AuditDocument16 pagesEnvironment AuditksbbsNo ratings yet
- Weather Solve Dust Control SolutionDocument7 pagesWeather Solve Dust Control SolutionksbbsNo ratings yet
- Procedure For Updating Language Resource File For WinCollectDocument1 pageProcedure For Updating Language Resource File For WinCollectksbbsNo ratings yet
- Plain Water Dust Scrubber SystemDocument1 pagePlain Water Dust Scrubber SystemksbbsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16 - Anaerobic Wastewater Treatment PDFDocument42 pagesChapter 16 - Anaerobic Wastewater Treatment PDFmjvsimoes12345No ratings yet
- Resume RahulDocument4 pagesResume RahulksbbsNo ratings yet
- TSC List of Correspondents 201711 PDFDocument180 pagesTSC List of Correspondents 201711 PDFbaroon1234No ratings yet
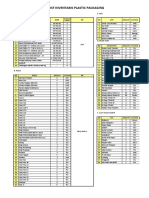
- List Inventaris PPPDocument7 pagesList Inventaris PPPasep nathanNo ratings yet
- Itu-T G.664Document20 pagesItu-T G.664moneyminderNo ratings yet
- 14EEMME00 - Darshna RamawatDocument31 pages14EEMME00 - Darshna Ramawatdatshna ramawatNo ratings yet
- CE8395 QB - by WWW - Easyengineering.net 1Document18 pagesCE8395 QB - by WWW - Easyengineering.net 1sureshkumarNo ratings yet
- Course Outline June 2020Document3 pagesCourse Outline June 2020nurul syafiqah12No ratings yet
- Vlsi DesignDocument2 pagesVlsi DesignXXXNo ratings yet
- Non-powered Fiberglass Whips and MountsDocument2 pagesNon-powered Fiberglass Whips and MountsKateNo ratings yet
- DC-Lec-03 & 04 (Physical Structure of Network)Document44 pagesDC-Lec-03 & 04 (Physical Structure of Network)tabby919100% (4)
- The Future of De-Icing: Safeaero 220Document8 pagesThe Future of De-Icing: Safeaero 220焦中华No ratings yet
- Doosan Solar 470LC-V Excavator Service Manual PDFDocument668 pagesDoosan Solar 470LC-V Excavator Service Manual PDFW Morales100% (1)
- Pump KnowledgeDocument17 pagesPump Knowledgesmupy_122No ratings yet
- 18 F 1320Document308 pages18 F 1320Manolis DespotakisNo ratings yet
- Soft Box System Product Presentation 1Document26 pagesSoft Box System Product Presentation 1jmiller9842No ratings yet
- EDI MessageDocument3 pagesEDI Messagerameshkola1434No ratings yet
- F-E-25 AFX 5 Gallon 50-1 Industrial Grease Pump and PackagesDocument2 pagesF-E-25 AFX 5 Gallon 50-1 Industrial Grease Pump and PackageskenriNo ratings yet
- Homework 5Document3 pagesHomework 5Engr Ghulam MustafaNo ratings yet
- Easy and Accurate Distribution Transformer TestingDocument8 pagesEasy and Accurate Distribution Transformer TestingBash MatNo ratings yet
- FS120-FS200-FS300-FS350-FS400-FS450-FR350-FR450 Service ManualDocument63 pagesFS120-FS200-FS300-FS350-FS400-FS450-FR350-FR450 Service Manualnik_nicholson_189% (18)
- ADX 260 Test One ContentDocument20 pagesADX 260 Test One ContentrainewithaneNo ratings yet
- Bamboo as a Building Material Seminar Report SummaryDocument21 pagesBamboo as a Building Material Seminar Report SummaryRaja ShankarNo ratings yet
- BTW69 1200Document5 pagesBTW69 1200GiraldoCarpioRamosNo ratings yet
- Schem SPI Administration ModuleDocument491 pagesSchem SPI Administration Modulejeeva438475% (4)
- Blasting and Painting ProcedureDocument9 pagesBlasting and Painting Procedureisukuru67% (12)
- Microstructure of a lead-tin eutectic alloyDocument55 pagesMicrostructure of a lead-tin eutectic alloyThaya GanapathyNo ratings yet
- GeForce RTX 3090 GA102 GF PG136-A03 Rev BDocument67 pagesGeForce RTX 3090 GA102 GF PG136-A03 Rev BSe SavNo ratings yet
- Math4220 PDFDocument10 pagesMath4220 PDFjhonmt7No ratings yet
- Batchflux 5015 C: Electromagnetic Flowmeter For Volumetric Filling and BatchingDocument8 pagesBatchflux 5015 C: Electromagnetic Flowmeter For Volumetric Filling and BatchingavikbhaiNo ratings yet
- Astm B344-01Document3 pagesAstm B344-01Srinivasan KrishnamoorthyNo ratings yet
- Expanbar PVC: Centrally and Externally Placed PVC Waterstops. UsesDocument5 pagesExpanbar PVC: Centrally and Externally Placed PVC Waterstops. UsesZaid AhmedNo ratings yet